NCLEX REVIEW QUESTIONS MATERNITY
Document Content and Description Below
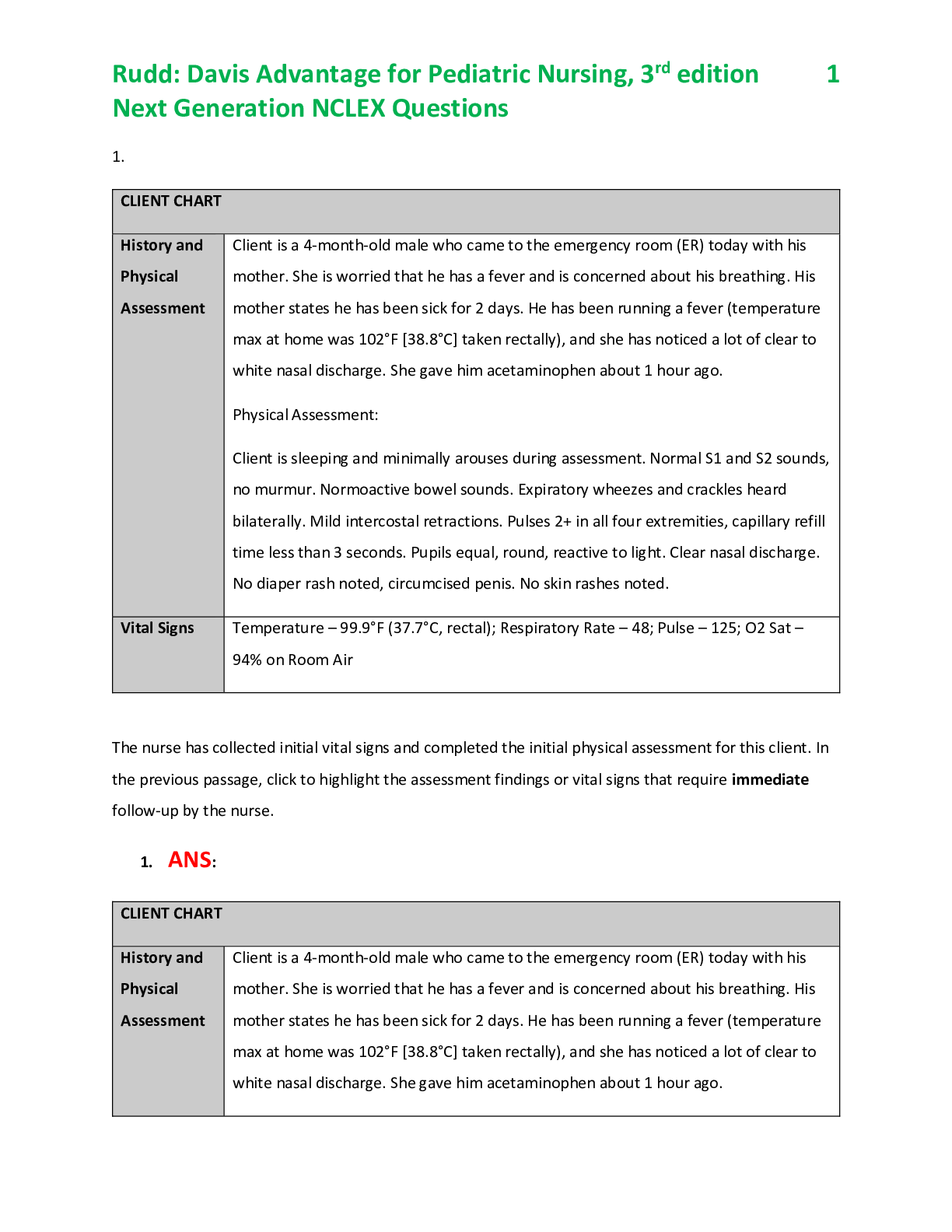
1. A patient is seen in the Emergency Department suspected of an ectopic pregnancy. Which of the following manifestations are most consistent with this condition? A. Abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding,... and a positive pregnancy test. B. Abdominal tenderness, hyperemesis and weight loss. C. Nauseas, amenorrhea and a negative pregnancy test. D. Copious discharge of clear mucus and prolonged epigastric pain. 2. A client is 22 weeks pregnant with her first child. Her weight gain is normal, but she complains of constipation. What’s the most effective recommendation the nurse can make? a. Take a mild laxative daily. b. Increase intake of fluids and high-fiber foods. c. Relax when trying to move the bowels. d. Start a strenuous exercise program. 3. Which statement by the nurse is the most accurate as part of a prenatal nutritional teaching program for a 17-year old primigravida who is concerned about weight gain? a. If you stay away from fast foods, your weight gain will be minimal. b. Since you’re young, the pregnancy weight gain will be easily lost after the baby is born. c. During pregnancy, a woman’s caloric needs increase by about 300 calories per day. d. Keep your caloric intake to around 1,000 calories per day. 4. A multigravida at 34 weeks’ gestation presents in the emergency department complaining of vaginal bleeding. What should be the nurse’s first action? a. Establish I.V. access. b. Assess fetal heart rate (FHR) and maternal blood pressure. c. Prepare the client for a cesarean birth. d. Assess maternal heart rate and respiratory rate. 5. A 17-year-old primigravida with severe gestational hypertension has been receiving magnesium sulfate I.V. for 3 hours. The nurse assesses deep tendon reflexes (DTR), vital signs, and fetal heart tones every 15 minutes and urine output hourly. The latest assessment yields the following data: DTR, +1 blood pressure, 150/100 mm Hg; pulse, 92 beats/minute; respiratory rate, 10 breaths/minute; and urine output, a. Take no action; continue monitoring per standards of care. b. Discontinue the magnesium sulfate infusion. c. Increase the infusion rate by 5 gtt/minute. d. Decrease the infusion rate by 5 gtt/minute. 6. A client whose pregnancy is confirmed at a clinic says her husband will be excited by the news. She reports concern because she isn’t excited. She fears her ambivalence may mean she’ll be a bad mother. What action by the nurse is the most therapeutic? a. Refer her to prenatal counselor. b. Advise the client that such feelings are normal in the beginning of pregnancy. c. Explore the underlying issues with the couple’s relationship. d. Encourage the client to discuss concerns with her partner about her potential lack of readiness for pregnancy. 7. A nurse is providing care for a pregnant woman who asks the nurse how she can best deal with her fatigue. The nurse should instruct her to: a. Take sleeping pills for a restful night’s sleep. b. Try to get more rest by going to bed earlier. c. Take her prenatal vitamins. d. Not to worry because the fatigue will go away soon. 8. A nurse is providing care for a pregnant 16-year-old who says that she’s concerned she may gain too much weight and wants to start dieting. The nurse respond by saying: a. Now isn’t a good time to begin dieting because you’re eating for two. b. Let’s explore your feelings further. c. Nutrition is important because depriving your baby of nutrients can cause developmental and growth problems. d. The prenatal vitamins should ensure the baby gets all the necessary nutrients. 9. A primipara client is 6 weeks pregnant. At he first prenatal visit, she says to the nurse, “I just can’t believe I’m really pregnant. I hope this baby is a good idea.” What should the nurse infer from the client’s statement? a. The client is afraid of pregnancy and birth. b. The client should have waited until she was committed to have a baby. c. The client is experiencing normal ambivalence about being pregnant. d. The client may have problems attaching to the baby after birth. 10. A nurse instructs a prenatal class about the importance of doing Kegel exercises frequently. Kegel exercises help to: a. Promote better breathing by strengthening the diaphragm muscle. b. Maintain a good perineal muscle tone by tightening the pubococcygeus muscle. c. Minimize leg crams by strengthening the calf muscles. d. Prepare the mother for pushing by strengthening the abdominal muscles. 11. A client is admitted to the labor and delivery unit in active labor. She has had no prenatal care, but appears to be between 32 and 35 weeks gestation. History reveals that she’s gravida 5, para 1. She tells the nurse she thinks her friend gave her a cigarette containing crack cocaine just prior to the onset of her contractions. What should the nurse do next? a. Move the precipitant delivery cart [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 50 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jun 30, 2022
Number of pages
50
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jun 30, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
44

.png)