*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > Geology 101 Midterm Exam Study GuidE (All)
Geology 101 Midterm Exam Study GuidE
Document Content and Description Below
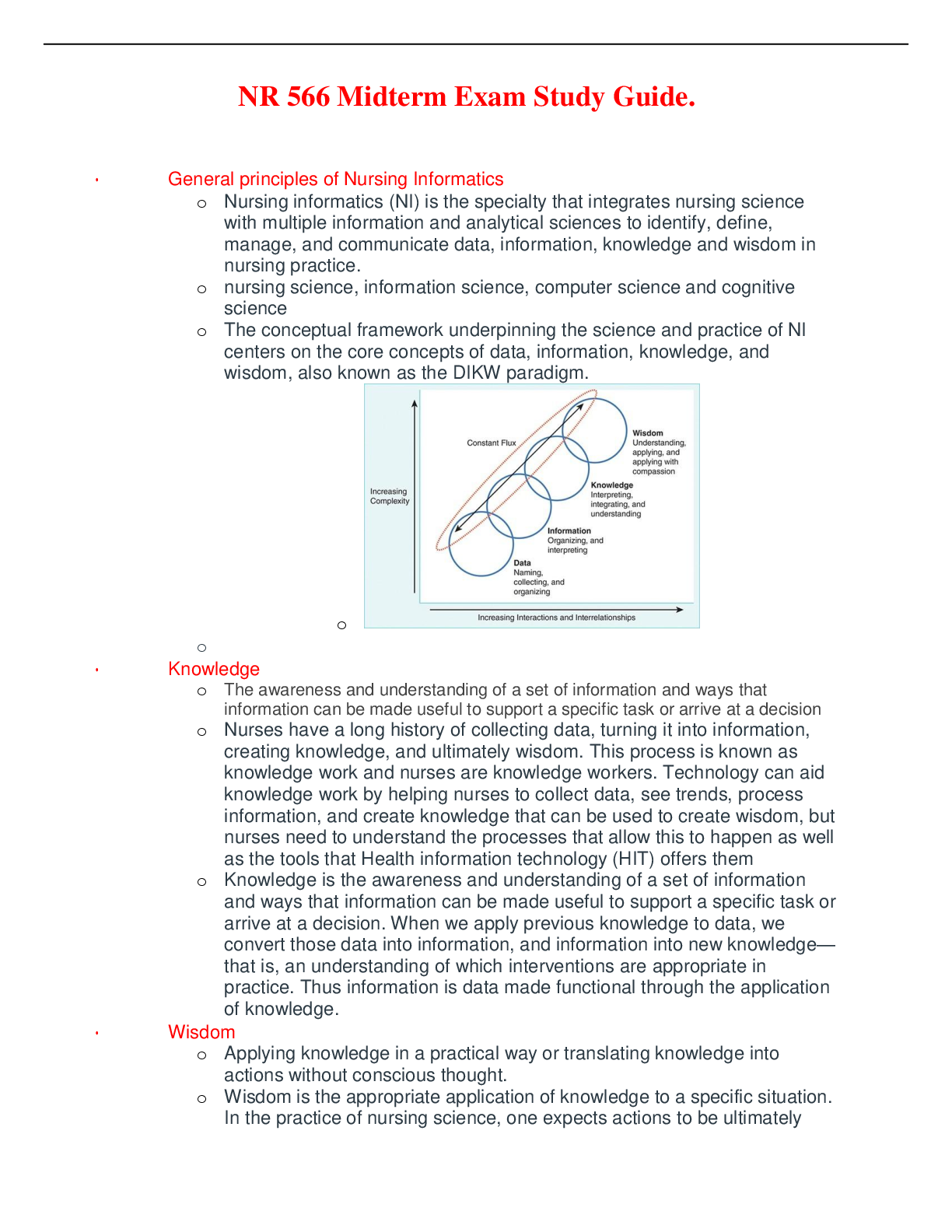
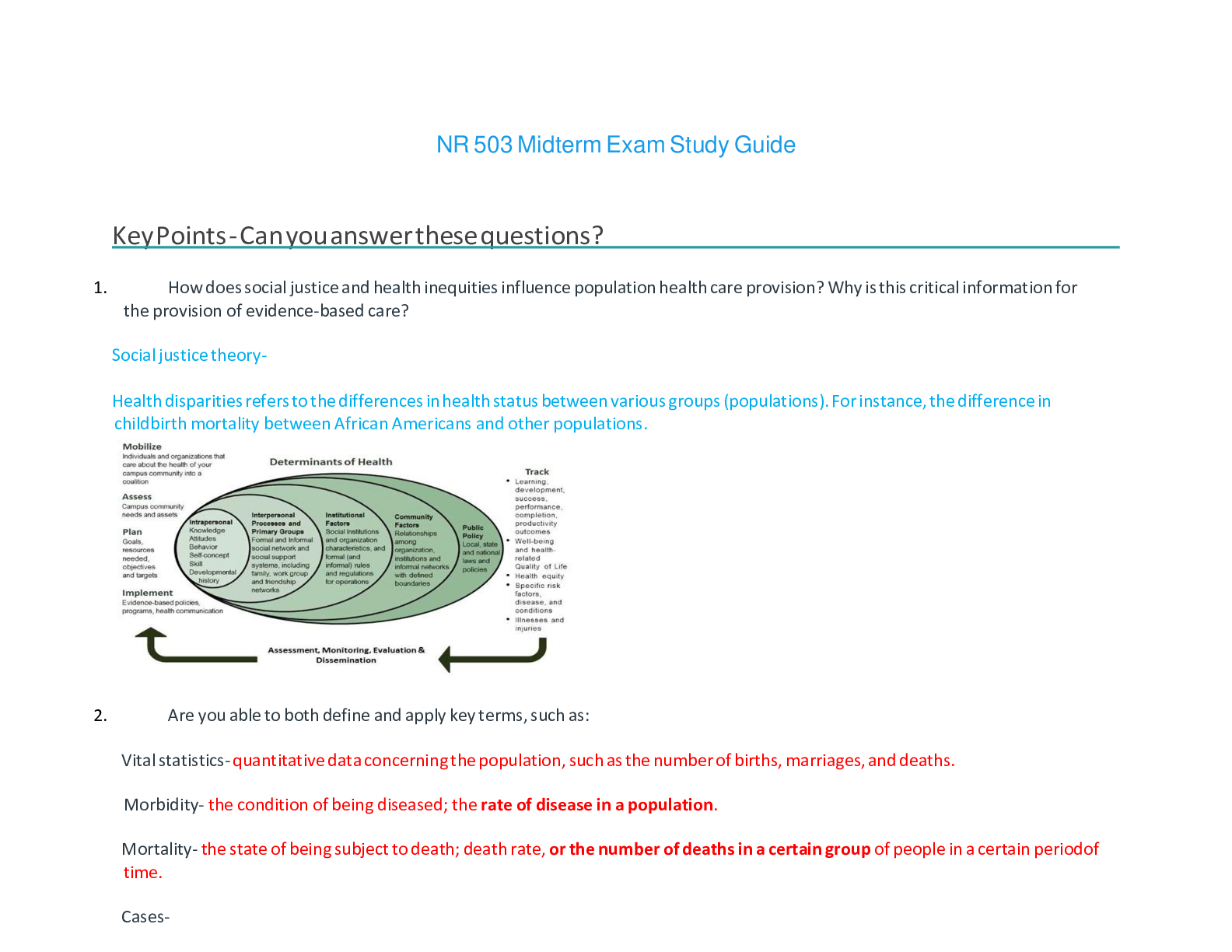
Geology 101 Midterm Exam Study Guide The Midterm Exam will cover Introduction to Geology, The Rock Cycle, Minerals, Bowens Reaction, Volcanoes and Igneous Activity, Weathering and Sedimentary Envir... onments and Metamorphism. Essay questions will be pulled from the following questions. Multiple choice questions will also cover lecture and lab materials covered in class. Introductions and Minerals • Define “hypothesis” and describe how a hypothesis becomes a scientific theory A hypothesis is a tentative explanation that can be tested by further investigation If a refined hypothesis survives all attacks on it and is the best existing explanation for a particular phenomenon, it is then elevated to the status of a theory. • Describe and atom and its basic components. Key Terms: electron, neutron, proton, nucleus, orbital, charge. Atoms consist of three basic particles: protons, electrons, and neutrons. The nucleus (center) of the atom contains the protons (positively charged) and the neutrons (no charge). The outermost regions of the atom are called electron shells and contain the electrons (negatively charged). • Describe the basic framework of a silicate mineral. Key Terms: silica tetrahedron, sharing, cations, crystalline. The simplest silicate structure, that of the mineral olivine, is composed of isolated tetrahedra bonded to iron and/or magnesium ions. • What physical characteristics can you use to identify minerals (i.e. mineral properties)? hardness, luster, color, streak, specific gravity, cleavage, fracture, and tenacity. Igneous Activity • Magma is generated in three (3) ways. List and give a description of each method. Be sure to note HOW the parameter has to change in order to induce melting. Magma and lava contain three components: melt, solids, and volatiles. The melt is made of ions from minerals that have liquefied. This study source was downloaded by 100000827141222 from CourseHero.com on 07-13-2022 07:32:49 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/137479973/Midterm-Exam-Study-Guide-2022-completepdf/ • Look at the diagram of Bowen’s Reaction Series. Explain what the series tells you about order of crystallization of minerals in magma, and what minerals you might expect to find in rocks of mafic, intermediate, and felsic compositions. Finally, (1) comment on the relative stability of these minerals on the Earth’s surface (which ones weather easily or are fairly resistant to weathering). Mafic: A mafic (portmanteau of "magnesium" and "ferric") mineral or rock is a silicate mineral or igneous rock rich in magnesium and iron. Most mafic minerals are dark in color, and common rock-forming mafic minerals include olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, and biotite. Common mafic rocks include basalt, diabase and gabbro. Intermediate: Intermediate rocks are roughly even mixtures of felsic minerals (mainly plagioclase) and mafic minerals (mainly hornblende, pyroxene, and/or biotite). There is little or no quartz. Felsic rocks are mostly feldspar (especially K-feldspar), at least 10% quartz, and less than 15% mafic minerals (biotite, hornblende). Felsic: In geology, felsic is an adjective describing igneous rocks that are relatively rich in elements that form feldspar and quartz. Common felsic minerals include quartz, muscovite mica, and the orthoclase feldspars. Rocks and the Rock Cycle • Describe two (2) reasons sedimentary rocks are important to science (as covered in lecture). coal, fossil fuels, drinking water and ores. Used for buildings in construction. Asphalt • Weathering, physical vs. chemical weathering, examples? Physical, or mechanical, weathering happens when rock is broken through the force of another substance on the rock such as ice, running water, wind, rapid heating/cooling, or plant growth. Chemical weathering occurs when reactions between rock and another substance dissolve the rock, causing parts of it to fall away. • What is erosion? Erosion is the geological process in which earthen materials are worn away and transported by natural forces such as wind or water • Transportation, how is sediment transported [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 5 pages
Instant download

Instant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jul 13, 2022
Number of pages
5
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jul 13, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
80



.png)

.png)






.png)














.png)


