*NURSING > EXAM REVIEW > NURS 623 Health Assessment Final Review Exam with complete solution 2020 (All)
NURS 623 Health Assessment Final Review Exam with complete solution 2020
Document Content and Description Below
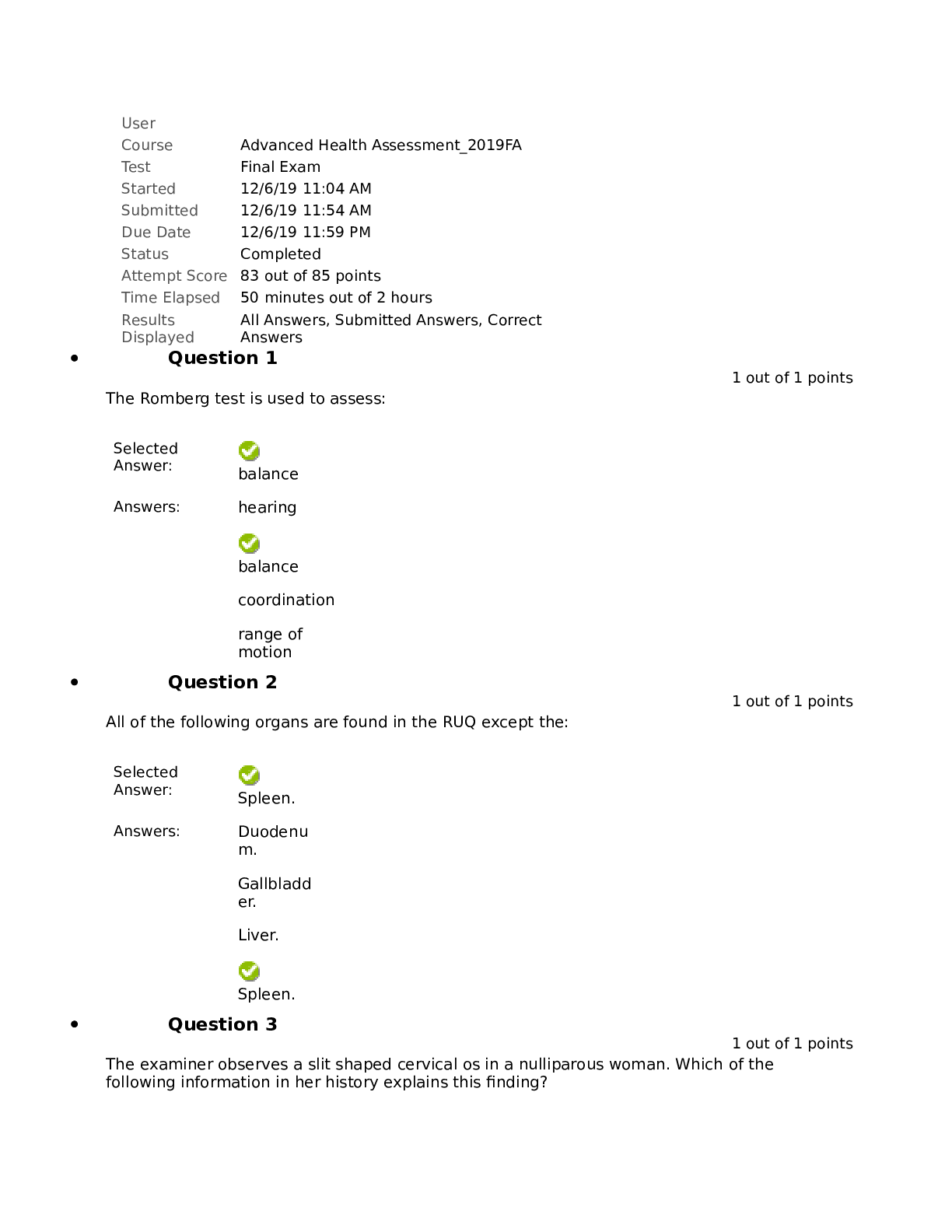
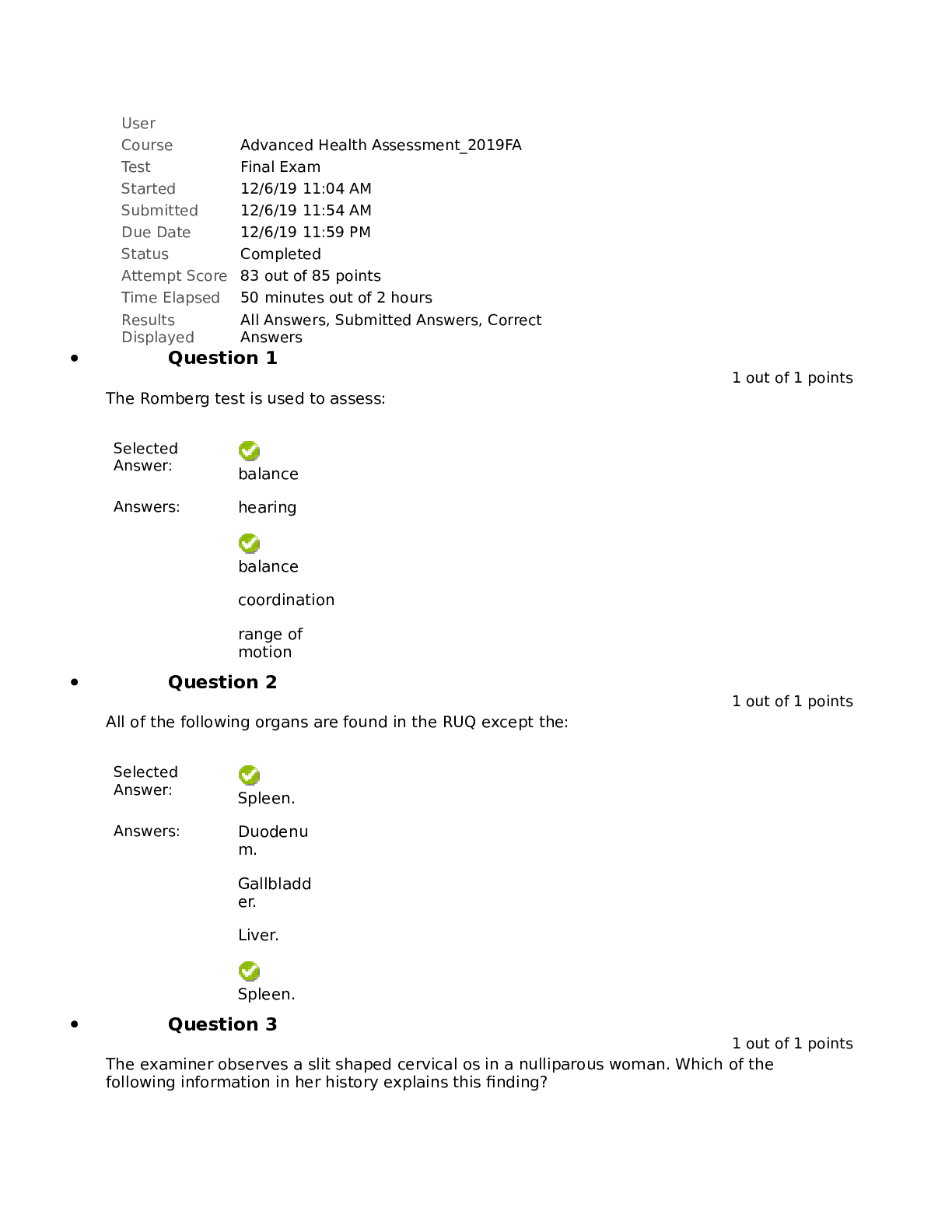
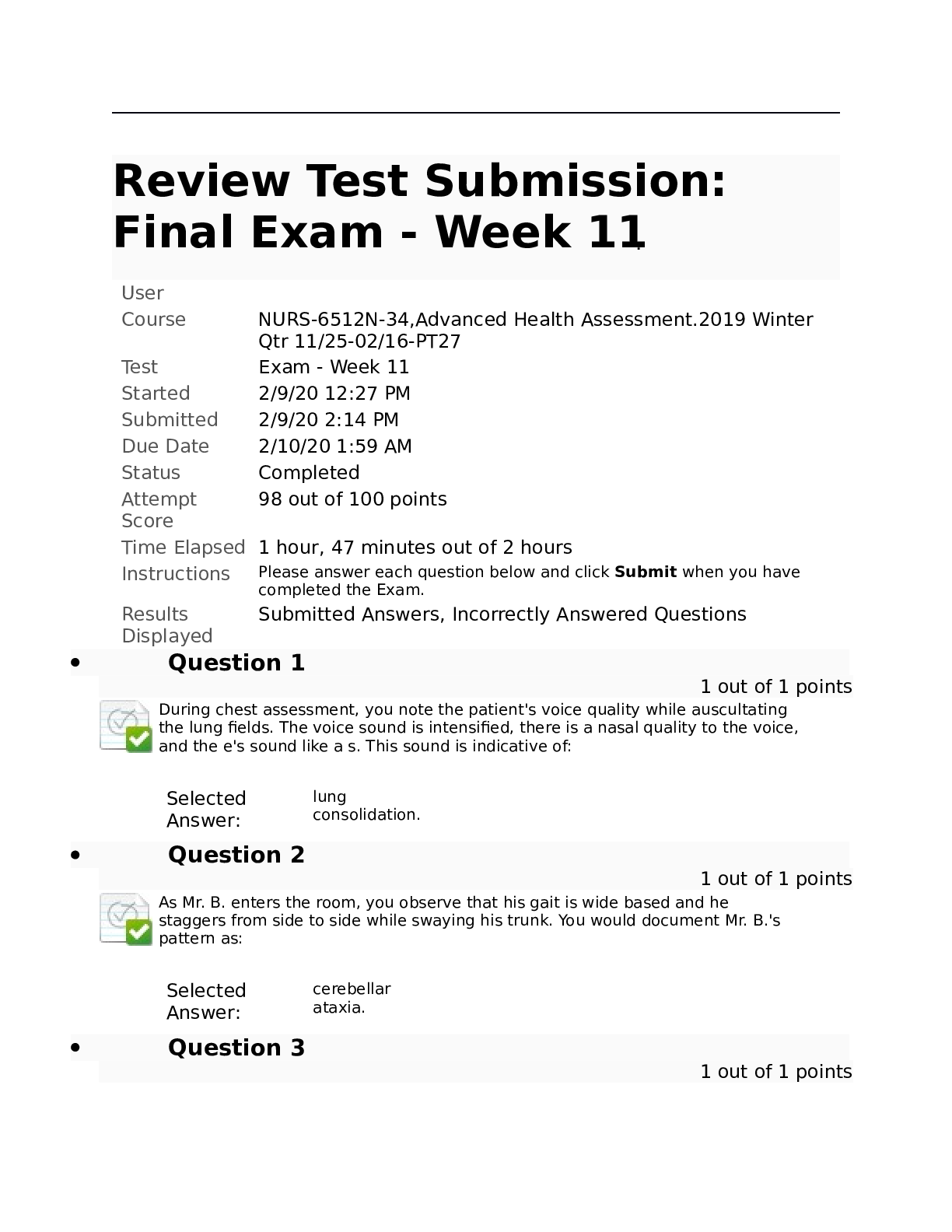
Health Assessment Final Review Exam 1. Assessing orientation to person, place, and time helps determine 2. Under most conditions, adult patients should be able to repeat a series of _____... numbers. 3. Recent memory may be tested by 4. Which condition is considered progressive rather than reversible? 5. An older adult is administered the Set Test and scores a 14. The nurse interprets this score as indicative of 6. Which of the following is usually related to structural diseases of the brain? 7. A state of impaired cognition, consciousness, mood and behavioral dysfunction of acute onset refers to 8. The Mini-Mental State Examination should be administered for a patient who 9. The Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) 10. While interviewing a 70-year-old female clinic patient, she tells you that she takes ginkgo biloba and St. John’s wort. You make a short note to check for results of the 11. For purposes of examination and communication of physical findings, the breast is divided into 12. When conducting a clinical breast examination, the examiner should 13. Which breast change is typical after menopause? 14. In a woman complaining of a breast lump, it is most important to ask about 15. A 50-year-old woman presents as a new patient. Which finding in her personal and social history would increase her risk profile for developing breast cancer? 16. To begin the clinical breast examination (CBE) for a man, ask him to: 17. Inspection of the breasts usually begins with the patient in which position? 18. Which finding, found on inspection, is related to fibrotic tissue changes that occur with breast carcinoma? 19. Venous patterns on breasts are suggestive of pathology when they are 20. In patients with breast cancer, peau d’orange skin is often first evident 21. Recent unilateral inversion of a previously everted nipple suggests 22.You are conducting a clinical breast examination for a 30-year-old patient. Her breasts are symmetrical with bilateral, multiple tender masses that are freely moveable with well-defined borders. You recognize that these symptoms and assessment findings are consistent with 23. When palpating breast tissue, the examiner should use the _____ at each site. 24.The largest amount of glandular breast tissue lies in the 25. The tail of Spence extends 26. When examining axillary lymph nodes, the patient’s arm is 27. Lymphatic flow of the breast primarily drains 28. The greatest concern for breast cancer is when you palpate _____ nodes. 29. You are performing a clinical breast examination for a 55-year-old woman. While palpating the supraclavicular area, you suspect that you felt a node. To improve your hooked technique, you should 30. You are conducting a clinical breast examination for a 30-year-old patient. Her breasts are symmetrical with bilateral, multiple tender masses that are freely moveable with well-defined borders. You recognize that these symptoms and assessment findings are consistent with 31. What structures are located at the 5 o’clock and the 7 o’clock positions of the vaginal orifice and open onto the sides of the vestibule in the groove between the labia minora and the hymen? 32. Which factor is associated with an increased risk of cervical cancer? 33. The risk of ovarian cancer is increased by a history of 34. During digital examination of the vagina, the cervix is noted to be positioned posteriorly. Upon bimanual examination of this woman, you would expect to palpate a(n) _____ uterus. 35. The presence of cervical motion tenderness may indicate 36. During a routine vaginal examination, you insert the speculum and visualize the cervix. The cervix projection into the vaginal vault is approximately 5 cm. Upon bimanual examination, you would expect to find the uterus 37. Small, pale yellow, raised, and rounded areas are visualized on the surface of the cervix. You should 38. The assessment of which structure is not part of the bimanual examination? 39. When a woman is not sexually active, cervical cancer screening should begin 40. During a pelvic examination for a postmenopausal woman, you would expect to assess 41. Which of the following is a risk factor for testicular cancer? 42. The most common cancer in young men age 15 to 30 years is . 43. Self-examination of the male genitalia 44. Mr. L. has an unusually thick scrotum with edema and pitting. He has a history of cardiac problems. The appearance of his scrotum is more likely a(n) 45. An enlarged, painless testicle in an adolescent or adult may indicate 46. You palpate a soft, slightly tender mass in the right scrotum of a man. You attempt to reduce the size of the mass, and there is no change in the mass size. Your next assessment maneuver is to 47. An adolescent male is being seen for acute onset of left testicular pain. The pain started 3 hours ago. He complains of nausea and denies dysuria and fever. Your prioritized assessment should be to 48. A 12-year-old boy says that his left scrotum has a soft swollen mass. The scrotum is not painful upon palpation. The left inguinal canal is without masses. The mass does transilluminate with a penlight. This collection of symptoms is consistent with 49. A cremasteric reflex should result in 50. Which technique is appropriate to detect an inguinal hernia? 51. Which type of hernia lies within the inguinal canal? 52. What structure of the male genitalia travels through the inguinal canal and unites with the seminal vesicle to form the ejaculatory duct? 53. A normal vas deferens should feel 54. An adolescent male is being seen for acute onset of left testicular pain. The pain started 3 hours ago. He complains of nausea and denies dysuria and fever. Your prioritized assessment should be to 55. The most emergent cause of testicular pain in a young male is 56. The most common type of hernia occurring in young males is 57. Percussion of the abdomen begins with establishing 58. Before performing an abdominal examination, the examiner should 59. When examining a patient with tense abdominal musculature, a helpful technique is to have the patient 60. After thorough inspection of the abdomen, the next assessment step is to 61. How long do you auscultate for BS? (pg380) 62. What is the technique for percussing the liver border? Where to start, how you move, what are you listening for?(pg381) 63. Percussion at the right midclavicular line, below the umbilicus, and continuing upward is the correct technique for locating the 64. When palpating the abdomen, you should note whether the liver is enlarged in the 65. An examiner can recognize a friction rub in the liver by a sound that is 66. Costovertebral angle tenderness should be assessed whenever you suspect the patient may have 67. The autonomic nervous system coordinates which of the following? 68. The major function of the sympathetic nervous system is to 69. The parasympathetic nervous system maintains the day-to-day function of 70.The motor cortex of the brain is in the 71. The thalamus is the major integration center for perception of 72. Which area of the brain is responsible for perceiving sounds and for determining their source? 73. Nerves that arise from the brain rather than the spinal cord are called 74. If a patient cannot shrug the shoulders against resistance, which cranial nerve (CN) requires further evaluation? 75. Normal changes of the aging brain include 76 .The area of body surface innervated by a particular spinal nerve is called a 77. A neurologic past medical history should include data about 78. When assessing superficial pain, touch, vibration, and position perceptions, you are testing 79. You are examining a patient in the emergency department who has recently sustained head trauma. To initially assess this patient’s neurologic status, you would 80. You are initially evaluating the equilibrium of Ms. Q You ask her to stand with her feet together and arms at her sides. She loses her balance. Ms. Q has a positive 81. The finger-to-nose test allows assessment of 82. You are performing a two-point discrimination test as part of a well physical examination. The area with the ability to discern two points in the shortest distance is the 83. As Mr. B enters the room, you observe that his gait is wide based and he staggers from side to side while swaying his trunk. You would document Mr. B’s pattern as 84. Deep pressure tests are used mostly for patients who are experiencing 85. To assess a cremasteric reflex, the examiner strokes the 86.You have asked a patient to close his eyes and identify an object placed in his hand. You are evaluating 87. The ability to recognize a number traced on the skin is called 88. To assess spinal levels L2, L3, and L4, which deep tendon reflex should be tested? 89. It is especially important to test for ankle clonus if 90.Which sign is associated with meningitis and intracranial hemorrhage? 91. When assessing a 17-year-old patient for nuchal rigidity, you gently raise his head off the examination table. He involuntarily flexes his hips and knees. To confirm your suspicions associated with this positive test result, you would also perform a test for the _____ sign. 92. On a scale of 0 to 4+, which deep tendon reflex score is appropriate for a finding of clonus in a patient? 93. Cranial nerve XII may be assessed in an infant by 94. A positive Babinski sign is normal until what age? 95.Which of the following is a concern, rather than an expected finding, in older adults? 96. Ipsilateral Horner syndrome indicates a cerebrovascular accident (CVA) occurring in the 97. An acute polyneuropathy that commonly follows a nonspecific infection occurring 10 to 14 days earlier and that primarily affects the motor and autonomic peripheral nerves in an ascending pattern is 98. The immune system attacks the synaptic junction between the nerve and muscle fibers blocking acetylcholine receptor sites in 99. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy will likely produce 100. Persons with Parkinson disease have an altered gait that is characterized by 101. A clinical syndrome of intracranial hypertension that mimics brain tumors is 102. Classic carpal tunnel syndrome would result in 103. You note that a child has a positive Gower sign. You know that this indicates generalized 104. A tingling sensation radiating from the wrist to the hand on striking the median nerve is a positive _____ sign. 105. Thrombosis of a leg vein should be suspected if the patient feels calf pain 106. Your patient presents with symptoms that lead you to suspect acute appendicitis. Which assessment finding is least likely to be associated with this condition? 107. A patient presents with symptoms that lead you to suspect acute appendicitis. Which assessment finding is least likely to be associated with this condition early in its course? 108. Your patient returns to the office with multiple complaints regarding her abdomen. Which of the following are objective findings? (Select all that apply.) 110. Your patient is a 48-year-old woman with complaints of severe cramping pain in the abdomen and right flank. Her past medical history includes a history of bladder calculi. You diagnose her with renal calculi at this time. Which of the following symptoms would you expect with her diagnosis? (Select all that apply.) 111. A 45-year-old laborer presents with low back pain, stating that the pain comes from the right buttock and shoots down and across the right anterior thigh, down the shin to the ankle. Which examination finding is considered more indicative of nerve root compression? 112. A positive straight leg raise test usually indicates 113. The Thomas test is used to detect 114. When performing the drawer test, the examiner would place the patient in a supine position and flex the knee 45 to 90 degrees, placing the foot flat on the table, and then 115. Which one of the following techniques is used to detect a torn meniscus? 116. During a football game, a player was struck on the lateral side of the left leg while his feet were firmly planted. He is complaining of left knee pain. To examine the left knee, you should initially perform the _____ test. 117. Anterior cruciate ligament integrity is assessed via the _____ test. 118. You are initially evaluating the equilibrium of Ms. Q You ask her to stand with her feet together and arms at her sides. She loses her balance. Ms. Q has a positive 119. When assessing a 17-year-old patient for nuchal rigidity, you gently raise his head off the examination table. He involuntarily flexes his hips and knees. To confirm your suspicions associated with this positive test result, you would also perform a test for the _____ sign. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 10 pages
Instant download
.png)
Instant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Dec 03, 2020
Number of pages
10
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Dec 03, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
44






.png)

.png)


.png)







.png)