Portage Learning A&P I Final Exam Answered
Document Content and Description Below
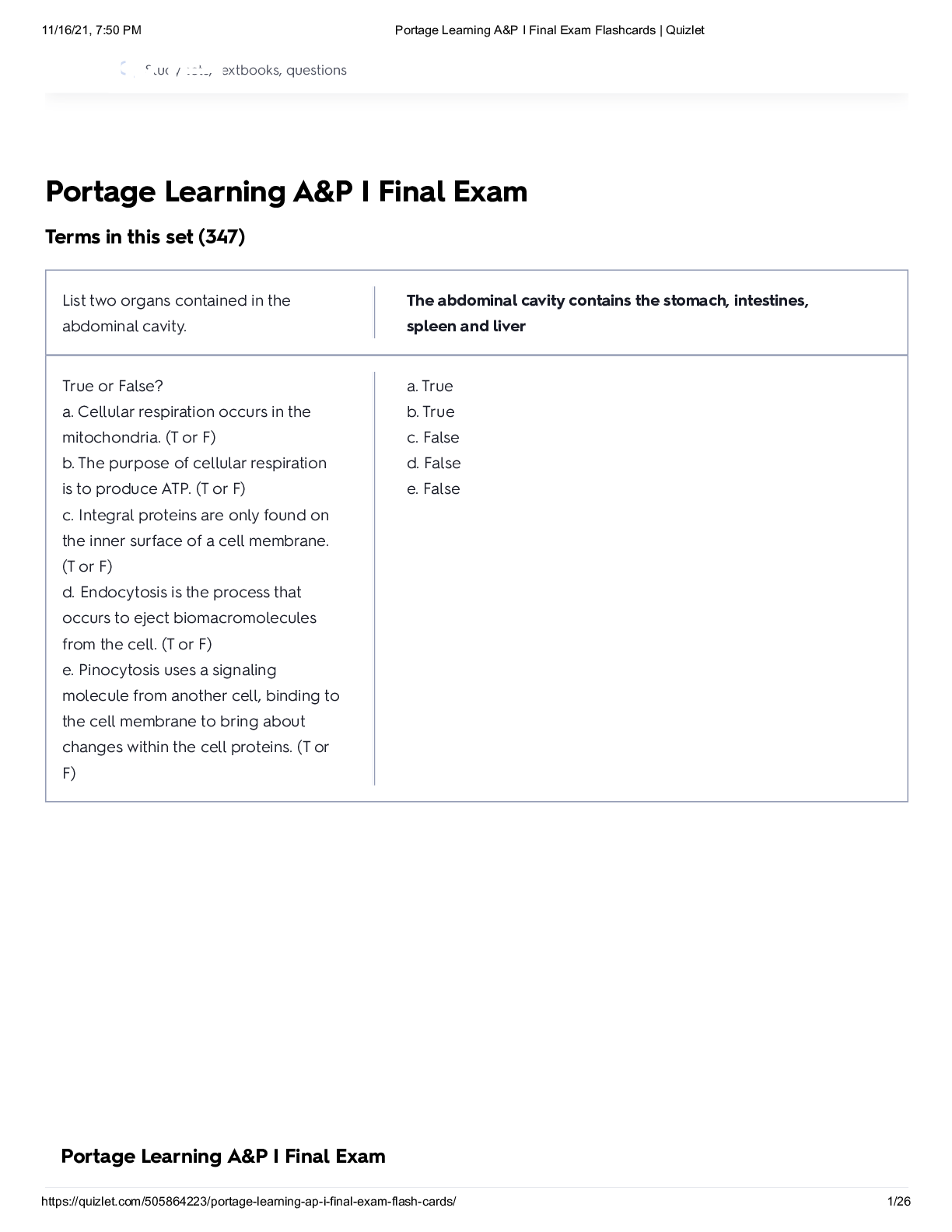
List two organs contained in the abdominal cavity. - ANSWER The abdominal cavity contains the stomach, intestines, spleen and liver True or False? a. Cellular respiration occurs in the mitochondri... a. (T or F) b. The purpose of cellular respiration is to produce ATP. (T or F) c. Integral proteins are only found on the inner surface of a cell membrane. (T or F) d. Endocytosis is the process that occurs to eject biomacromolecules from the cell. (T or F) e. Pinocytosis uses a signaling molecule from another cell, binding to the cell membrane to bring about changes within the cell proteins. (T or F) - ANSWER a. True b. True c. False d. False e. False You are observing two cells under the microscope. They are the same type of eukaryotic cell but one appears much larger. Based on appearance alone, which one would you expect to be carrying out respiration at a more active rate, the larger or smaller cell? Explain why. - ANSWER I believe it is the smaller cell that will breathe at a more active rate because in order for respiration to occur efficiently and more actively the surface area to volume ratio is very critical; also, if the larger surface area is present then the diffusion of gases occur at a higher rate; so, larger cells will have a smaller surface to volume ratio and diffusion that will occur at a slower rate creating a less active respiration; and, on the other hand smaller cells will have a larger surface area to volume ratio and an improved diffusion rate, so the higher rate and more active respiration. The smaller cell. Cells need to remain relatively small because as a cell expands the amount of surface area relative to the volume of the cell decreases. The smaller cell is more active because relative to its volume, its surface area is larger than a bigger cell. With a larger surface area (relative to its volume) this allows the metabolic processes to occur faster. Note: Essay answers must clearly be in your own words. Explain what happens to the epiglottis during swallowing. Why? - ANSWER During swallowing the epiglottis moves inferiorly to close off and prevent aspiration by covering the trachea and creating a passage for liquid, food, or bolus into the esophagus; and, preventing these things from entering into the lungs. Air and food pass in which one of the following areas: - ANSWER Oropharynx Label the following five items from the diagram: Label B- ___________ Label D- __________ Label E- __________ Label F- __________ Label G- __________ - ANSWER B - Oral Cavity D - Epiglottis E - Glottis F - Trachea G - Esophagus From widest to narrowest, the branches of the bronchial tree are: - ANSWER Primary bronchi, secondary bronchi, tertiary bronchi, bronchioles Explain why someone who has hypergastrinemia (excessive secretion of gastrin) might develop gastric/stomach ulcers. - ANSWER Hypergastrinemia leads to excess secretion of the gastrin hormone, which induces excess secretion of hydrochloric acid in the stomach; and, the excess acid then acts as a protective mucousa layer causing disruption that can lead to those ulcers. Gastrin stimulates the secretions of pepsinogens and hydrochloric acid. Excess amounts would lead to erosion of the stomach lining. Look carefully at the diagram below. Label the following 5 organs of the digestive system. To receive credit for the intestines you must label the specific region. 3: ___________ 4: ___________ 7: ___________ 9: ___________ 10: ___________ - ANSWER 3. Stomach 4. Gallbladder 7. Jejunum 9. Appendix 10. Rectum Note: Essay answers must clearly be in your own words. Answer the following essay question: Describe parietal cells and chief cells: name their location, secretions and purposes. - ANSWER Parietal and chief cells are located in the stomach wall and they secrete gastric juices and mucous, secrete hormones that regulate digestive activity; also, parietal cells produce HCl in the stomach; and, chief cells secrete te enzymes pepsinogen, rennin, and gastric lipase. The parietal cells (located in the wall of the stomach body) secrete hydrochloric acid, generating a pH of 1.3-3.5. This very acidic pH kills many of the bacteria ingested along with food. In addition, the low pH stops the activity of salivary amylase. The secretion of hydrochloric acid is essential in the activation of pepsin. Chief cells: secrete pepsinogen. Pepsinogen (a pre-enzyme) is secreted by the chief cells in the stomach. Hydrochloric acid converts the inactive pepsinogen (secreted by the chief cells) into the active enzyme pepsin which begins the breakdown of proteins. Label the following bones of the skeleton from the figure below: 1: ____________ 3:____________ 5:____________ 7: ____________ 8: ____________ - ANSWER 1: Frontal bone/frontal sinuses 3: Maxilla [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 55 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Aug 02, 2022
Number of pages
55
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Aug 02, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
51











.png)






.png)
.png)