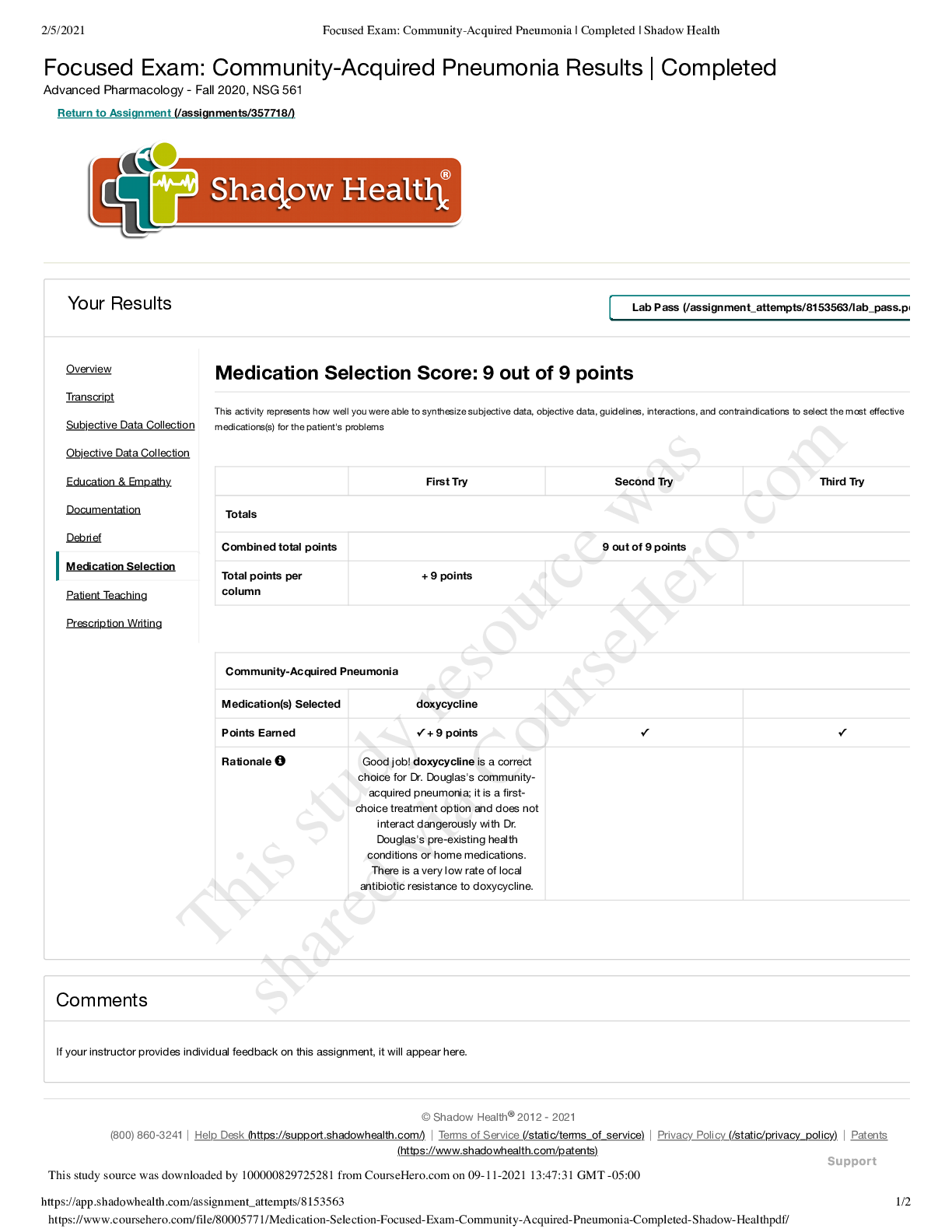
Physiology > EXAM > Abnormal Psychology Chapters 1-4 Exam Review Graded A+ (All)
Abnormal Psychology Chapters 1-4 Exam Review Graded A+
Document Content and Description Below
Acute - ANSWER Term used to describe a disorder of sudden onset, usually with intense symptoms (short in duration). Chronic - ANSWER Term used to describe a long-standing or frequently recurring di... sorder, often with progressing seriousness (long in duration). Case Study Method - ANSWER An in-depth examination of an individual or family that draws from a number of data sources, including interviews and psychological testing. Comorbidity - ANSWER Occurrence of two or more identified disorders in the same psychologically disordered individual. Comparison or Control Group - ANSWER Group of subjects who do not exhibit the disorder being studied but who are comparable in all other respects to the criterion group. Also, a comparison group of subjects who do not receive a condition or treatment the effects of which are being studied. Correlation - ANSWER The tendency of two variables to change together. With positive correlation, as one variable goes up, so does the other; with negative correlation, one variable goes up as the other goes down. Correlational Method/Correlational Research - ANSWER A research strategy that examines whether and how variables go together (covary) without manipulating (changing) any variables. Correlation Coefficient - ANSWER A statistic that ranges from +1.0 to -1.0 and reflects the degree of association between two variables. The magnitude of the correlation indicates the strength of the association, and the sign indicates whether the correlation is positive or negative. Criterion Group - ANSWER Group of subjects who exhibit the disorder under study. Dependent Variable - ANSWER In an experiment, the factor that is observed to change with changes in the manipulated (independent) variables. Direct Observation - ANSWER Method of collecting research data that involves directly observing behavior in a given situation. Effect Size - ANSWER A statistical term referring to the strength of the relationship between two variables in a statistical population. Epidemiology - ANSWER Study of the distribution of diseases, disorders, or health-related behaviors in a given population. Mental health epidemiology is the study of the distribution of mental disorders. Etiology - ANSWER Factors that are related to the development (or cause) of a particular disease. Experimental Research - ANSWER Research that involves the manipulation of a given factor or variable with everything else held constant. External Validity - ANSWER The extent to which the findings from a single study are relevant to other populations, contexts, or times. Family Aggregation - ANSWER The clustering of certain traits, behaviors, or disorders within a given family. Family aggregation may arise because of genetic or environmental similarities. Generalizability - ANSWER The extent to which the findings from a single study can be used to draw conclusions about other samples. Hypothesis - ANSWER Statement or proposition, usually based on observation, that is tested in an experiment; may be refuted or supported by experimental results but can never be conclusively proved. Incidence - ANSWER Occurrence (onset) rate of a given disorder in a given population. 1-Year Prevalence - ANSWER The total number of cases of a health-related state or condition in a population for a given year. Prevalence - ANSWER In a population, the proportion of active cases of a disorder that can be identified at a given point in time or during a given period. Point Prevalence - ANSWER The number of cases of a specific condition or disorder that can be found in a population at one given point in time. Lifetime Prevalence - ANSWER The proportion of living persons in a population who have ever had a disorder up to the time of the epidemiological assessment. Independent Variable - ANSWER Factors whose effects are being examined and which is manipulated in some way, while other variables are held constant. Internal Validity - ANSWER The extent to which a study is free of confounds, is methodologically sound, and allows the researcher to have confidence in the findings. Labeling - ANSWER Assigning a person to a particular diagnostic category, such as schizophrenia. Longitudinal Design - ANSWER A research design in which people are followed over time. Meta-Analysis - ANSWER A statistical method used to combine the results of a number of similar research studies. The data from each study are transformed into a common metric called the effect size. This allows the data from the various studies to be combined and then analyzed. You can think of a meta-analysis as being like research that you are already familiar with, except that the "participants" are individual research studies, not individual people. Negative Correlation - ANSWER A relationship between two variables such that a high score on one variable is associated with a low score on another variable. Nomenclature - ANSWER A formalized naming system. Placebo Treatment - ANSWER An inert pill or otherwise neutral intervention that produces desirable therapeutic effects because of the subject's expectations that it will be beneficial. Positive Correlation - ANSWER A relationship between two variables such that a high score on one variable is associated with a high score on another variable. Prospective Research - ANSWER Method that often focuses on individuals who have a higher-than-average likelihood of becoming psychologically disordered before abnormal behavior is observed. Sampling - ANSWER The process of selecting a representative subgroup from a defined population of interest. Self-Report Data - ANSWER Data collected directly from participants, typically by means of interviews or questionnaires. Statistical Significance - ANSWER A measure of the probability that a research finding could have occurred by chance alone. Stereotyping - ANSWER The tendency to jump to conclusions (often negative) about what a person is like based on the beliefs about that group that exist (often incorrectly) in the culture (e.g., French people are rude, homosexuals have good taste in clothes, mental patients are dangerous, etc.). Stigma - ANSWER Negative labeling. Third Variable Problem - ANSWER Refers to the problem of making causal inferences in correlational research, where the correlation between two variables could be due to their shared correlation with an unmeasured third variable. Asylums - ANSWER Historically, these were institutions meant solely for the care of the mentally ill. Behavioral Perspective - ANSWER A theoretical viewpoint organized around the theme that learning is central in determining human behavior. Behaviorism - ANSWER School of psychology that formerly restricted itself primarily to the study of overt behavior. Catharsis - ANSWER Discharge of emotional tension associated with something, such as by talking about past traumas. Classical Conditioning - ANSWER A basic form of learning in which a neutral stimulus is paired repeatedly with an unconditioned stimulus (US) that naturally elicits an unconditioned response (UR). After repeated pairings, the neutral stimulus becomes a conditioned stimulus (CS) that elicits a conditioned response (CR). Deinstitutionalization - ANSWER Movement to close mental hospitals and treat people with severe mental disorder in the community. Dream Analysis - ANSWER Method involving the recording, description, and interpretation of a patient's dreams. Exorcism - ANSWER Religiously inspired treatment procedure designed to drive out evil spirits or forces from a "possessed" person. Free Association - ANSWER Method for probing the unconscious by having patients talk freely about themselves, their feelings, and their motives. Insanity - ANSWER Legal term for mental disorder, implying lack of responsibility for one's acts and inability to manage one's affairs. Lycanthropy - ANSWER Delusion of being a wolf. Mass Madness - ANSWER Historically, widespread occurrence of group behavior disorders that were apparently cases of hysteria; a whole group of people panic/get scared and develop psychological symptoms as a result. Mental Hygiene Movement - ANSWER Movement that advocated a method of treatment focused almost exclusively on the physical well-being of hospitalized mental patients. Mesmerism - ANSWER Theory of "animal magnetism" (hypnosis) formulated by Anton Mesmer. Moral Management - ANSWER Wide-ranging method of treatment that focuses on a patient's social, individual, and occupational needs. Nancy School - ANSWER Group of physicians in nineteenth-century Europe who accepted the view that hysteria was a sort of self-hypnosis. Operant (or Instrumental) Conditioning - ANSWER Form of learning in which if a particular response is reinforced, it becomes more likely to be repeated on similar occasions. Psychoanalysis - ANSWER Methods Freud used to study and treat patients. Psychoanalytic Perspective - ANSWER Theory of psychopathology, initially developed by Freud, that emphasizes the inner dynamics of unconscious motives. Saint Vitus's Dance - ANSWER Name given to the dancing mania (and mass hysteria) that spread from Italy to Germany and the rest of Europe in the Middle Ages. Tarantism - ANSWER Dancing mania that occurred in Italy in the nineteenth century. Association Studies - ANSWER Genetic research strategy comparing frequency of certain genetic markers known to be located on particular chromosomes in people with and without a particular disorder. Attachment Theory - ANSWER Contemporary developmental and psychodynamic theory emphasizing the importance of early experience with attachment relationships in laying the foundation for later functioning throughout life. Attribution - ANSWER Process of assigning causes to things that happen. Biopsychosocial Viewpoint - ANSWER A viewpoint that acknowledges the interacting roles of biological, psychosocial, and sociocultural factors in the origins of psychopathology. Castration Anxiety - ANSWER As postulated by Freud, the anxiety a young boy experiences when he desires his mother while at the same time fearing that his father may harm him by cutting of his penis; this anxiety forces the boy to repress his sexual desire for his mother and his hostility toward his father. Cognitive-Behavioral Perspective - ANSWER A theory of abnormal behavior that focuses on how thoughts and information processing can become distorted and lead to maladaptive emotions and behavior. Contributory Cause - ANSWER A condition that increases the probability of developing a disorder but that is neither necessary nor sufficient for it to occur. Cortisol - ANSWER Human stress hormone released by the cortex of the adrenal glands. Developmental Psychopathology - ANSWER Field of psychology that focuses on determining what is abnormal at any point in the developmental process by comparing and contrasting it with normal and expected changes that occur. Developmental Systems Approach - ANSWER Acknowledgment that genetic activity influences neural activity, which in turn influences behavior, which in turn influences the environment, and that these influences are bidirectional. Diathesis - ANSWER Predisposition or vulnerability to developing a given disorder. Diathesis-Stress Model - ANSWER View of abnormal behavior as the result of stress operating on an individual who has a biological, psychosocial, or sociocultural predisposition to developing a specific disorder. Discrimination - ANSWER Ability to interpret and respond differently to two or more similar stimuli. Ego - ANSWER In psychoanalytic theory, the rational part of the personality that mediates between the demands of the id, the constraints of the superego, and the realities of the external world. Ego Psychology - ANSWER Psychodynamic theory emphasizing the importance of the ego-- the "executive branch of the personality" --in organizing normal personality development. Ego-Defense Mechanisms - ANSWER Psychic mechanisms that discharge or soothe anxiety rather than coping directly with an anxiety-provoking situation; usually unconscious and reality distorting. Also called defense mechanisms. Electra Complex - ANSWER Excessive emotional attachment (love) of a daughter for her father; the female counterpart of the Oedipus complex. Extinction - ANSWER Gradual disappearance of a conditioned response when it is no longer reinforced. Generalization - ANSWER Tendency of a response that has been conditioned to one stimulus to be elicited by other, similar stimuli. Hormones - ANSWER Chemical messengers secreted by endocrine glands that regulate development of and activity in various parts of the body. pituitary gland master gland producing variety of hormones that regulate other endocrine galnds Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis (HPA Axis) - ANSWER Brain endocrine system involved in responding to stress in which the hypothalamus and pituitary send messages to the adrenal gland which releases a stress hormone that feeds back on the hypothalamus. Id - ANSWER In psychoanalytic theory, the reservoir of instinctual drives and the first structure to appear in infancy. Instrumental (Operant) Conditioning - ANSWER Reinforcement of a subject for making a correct response that leads either to receipt of something rewarding or to escape from something unpleasant. Interpersonal Perspective - ANSWER Approach to understanding abnormal behavior that views much of psychopathology as rooted in the unfortunate tendencies we develop while dealing with our interpersonal environments; it thus focuses on our relationships, past and present, with other people. Intrapsychic Conflict - ANSWER Inner mental struggles resulting from the interplay of the id, ego, and superego when the three subsystems are striving for different goals. Learning - ANSWER Modification of behavior as a consequence of experience. Libido - ANSWER In psychoanalytic theory, a term used to describe the instinctual drives of the id; the basic constructive energy of life, primarily sexual in nature. Linkage Analysis - ANSWER Genetic research strategy in which occurrence of a disorder in an extended family is compared with that of a genetic marker for a physical characteristic or biological process that is known to be located on a particular chromosome. Necessary Cause - ANSWER A condition that must exist for a disorder to occur. Neurotransmitters - ANSWER Chemical substances that are released into a synapse by the presynaptic neuron and that transmit nerve impulses from one neuron to another. Object-Relations Theory - ANSWER In psychoanalytic theory, this viewpoint focuses on an infant or young child's interactions with "objects" (i.e., real or imagined people), as well as how they make symbolic representations of important people in their lives. Observational Learning - ANSWER Learning through observation alone without directly experiencing an unconditioned stimulus (for classical conditioning) or a reinforcement (for instrumental conditioning). Oedipus Complex - ANSWER Desire for sexual relations with a parent of opposite sex; specifically, the desire of a boy for his mother, with his father a hated rival. Pleasure Principle - ANSWER Demand that an instinctual need be immediately gratified regardless of reality or moral considerations. Primary Process Thinking - ANSWER Gratification of id demands by means of imagery or fantasy without the ability to undertake the realistic actions needed to meet those instinctual demands. Protective Factors - ANSWER Influences that modify a person's response to an environmental stressor, making it less likely that the person will experience the adverse effects of the stressor. Reality Principle - ANSWER Awareness of the demands of the environment and adjustment of behavior to meet these demands. Reinforcement - ANSWER The process of rewarding desired responses. Resilience - ANSWER The ability to adapt successfully to even very difficult circumstances. Schema - ANSWER An underlying representation of knowledge that guides current processing of information and often leads to distortions in attention, memory, and comprehension. Secondary Process Thinking - ANSWER Reality-oriented rational processes of the ego for dealing with the external world and the exercise of control over id demands. Self-Schema - ANSWER Our view of what we are, what we might become, and what is important to us. Spontaneous Recovery - ANSWER The return of a learned response at some time after extinction has occurred. Stress - ANSWER Effects created within an organism by the application of a stressor. Sufficient Cause - ANSWER A condition that guarantees the occurrence of a disorder. Superego - ANSWER Conscience; ethical or moral dimensions (attitudes) of personality. Synapse - ANSWER Site of communication from the axon of one neuron to the dendrites or cell body of another neuron-- a tiny filled space between neurons. Temperament - ANSWER Pattern of emotional and arousal responses and characteristic ways of self-regulation that are considered to be primarily hereditary or constitutional. effects of temperament - ANSWER neuroticism/ negative emotionality extroversion/positive emotionality constraint/conscientiousness and agreeableness Zar - ANSWER A person who believes he or she is possessed by a spirit may experience a dissociative episode during which shouting, laughing, singing, or weeping may occur. The person may also show apathy and withdrawal, not eating or working. Actuarial Procedures - ANSWER Methods whereby data about subjects are analyzed by objective procedures or formulas rather than by human judgments. Aphasia - ANSWER Loss or impairment of ability to communicate and understand language symbols-- involving loss of power of expression by speech, writing, or signs, or loss of ability to comprehend written or spoken language-- resulting from brain injury or disease. Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale (BPRS) - ANSWER Objective method of rating clinical symptoms that provides scores on 18 variable (e.g., somatic concern, anxiety, withdrawal, hostility, and bizarre thinking). Clinical Diagnosis - ANSWER The process through which a clinician arrives at a general "summary classification" of the patient's symptoms by following a clearly defined system such as DSM-IV-TR or ICD-10. Computerized Axial Tomography (CAT) Scan - ANSWER Radiological technique used to locate and assess the extent of organic damage to the brain without surgery. Cultural Competence - ANSWER Refers to a psychologist's need to be informed of the issues involved in multicultural assessment. Dysrhythmia - ANSWER Abnormal brain wave pattern. Electroencephalogram (EEG) - ANSWER Graphical record of the brain's electrical activity obtained by placing electrodes on the scalp and measuring the brain wave impulses from various brain areas. Forensic - ANSWER Pertaining or used in the court of law. Functional MRI (fMRI) - ANSWER Internal scanning technique that measures changes in local oxygenation (blood flow) to specific areas of brain tissue that in turn depend on neuronal activity in those specific regions, allowing the mapping of psychological activity such as sensations, images, and thoughts. Intelligence Test - ANSWER Test used in establishing a subject's level of intellectual capability. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - ANSWER Internal scanning technique involving measurement of variations in magnetic fields that allows visualization of the anatomical features of internal organs, including the central nervous and particularly the brain. Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI/MMPI-2) - ANSWER Widely used and empirically validated personality scales. Neuropsychological Assessment - ANSWER Use of psychological tests that measure a person's cognitive, perceptual, and motor performance to obtain clues to the extent and locus of brain damage. Objective Personality Tests - ANSWER Structured tests, such as questionnaires, self-inventories, or rating scales, used in psychological assessment. Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scan - ANSWER Scanning technique that measures metabolic processes to appraise how well an organ is functioning. Presenting Problem - ANSWER Major symptoms and behavior the client is experiencing. Projective Personality Tests - ANSWER Techniques that use various ambiguous stimuli that a subject is encouraged to interpret and from which the subject's personality characteristics can analyzed. Psychological Assessment - ANSWER The use of psychological procedures such as behavioral observations, interview, and psychological tests to obtain a picture of a client's mental health symptoms and personality. Rating Scales - ANSWER Formal structure for organizing information obtained from clinical observation and self-reports to encourage reliability and objectivity. Reliability - ANSWER Degree to which a measuring device produces the same result each time it is used to measure the same thing or when two or more different raters use it. Role-Playing - ANSWER Form of assessment in which a person is instructed to play a part, enabling a clinician to observe a client's behavior directly. Rorschach Inkblot Test - ANSWER Use of 10 inkblot pictures to which a subject responds with associations that come to mind. Analysis of these responses enables a clinician to infer personality characteristics. Self-Monitoring - ANSWER Observing and recording one's own behavior, thoughts, and feelings as they occur in various natural settings. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 26 pages
Instant download

Instant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 06, 2022
Number of pages
26
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 06, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
38











.png)