Pharm exam 4 review
Document Content and Description Below
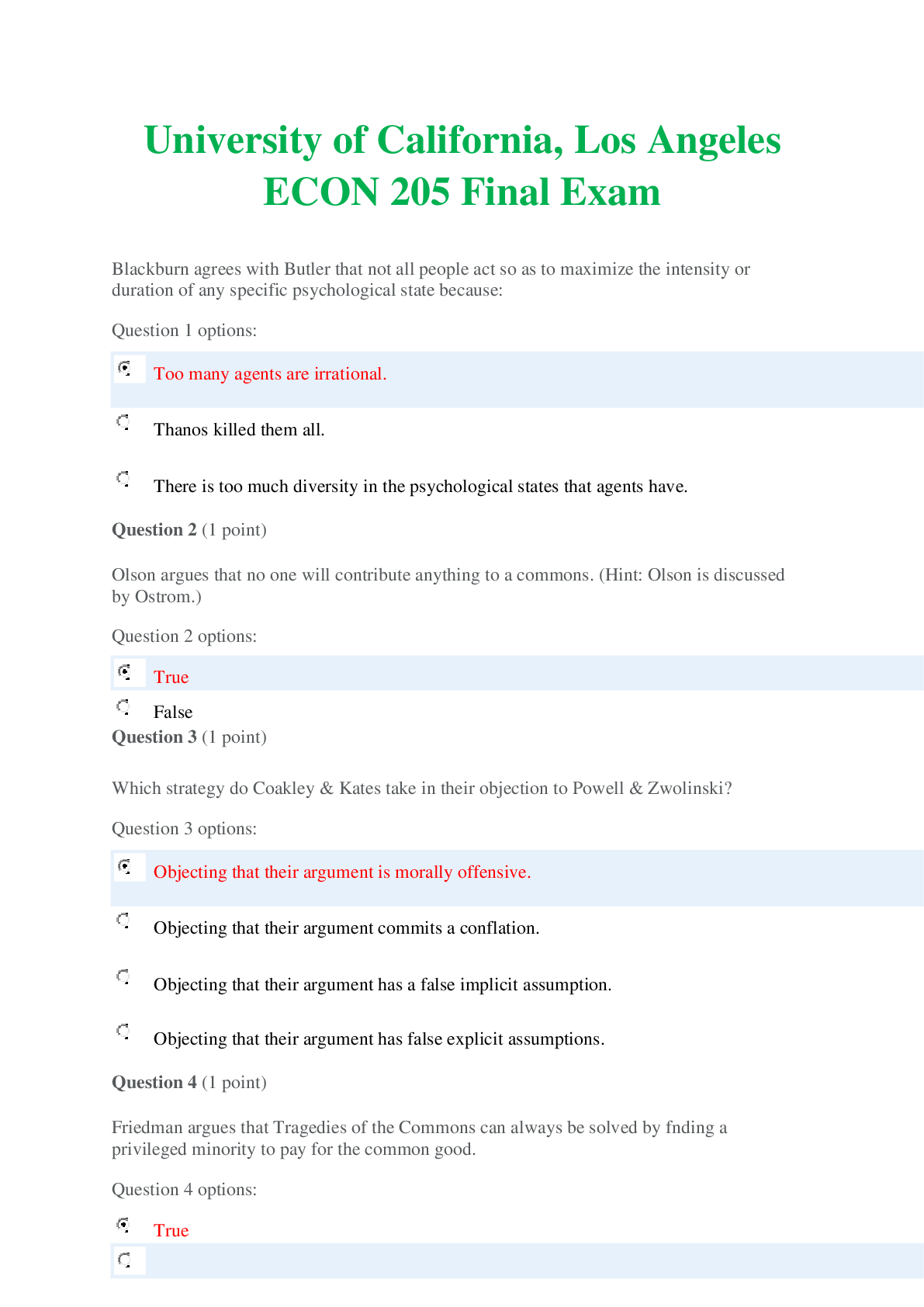
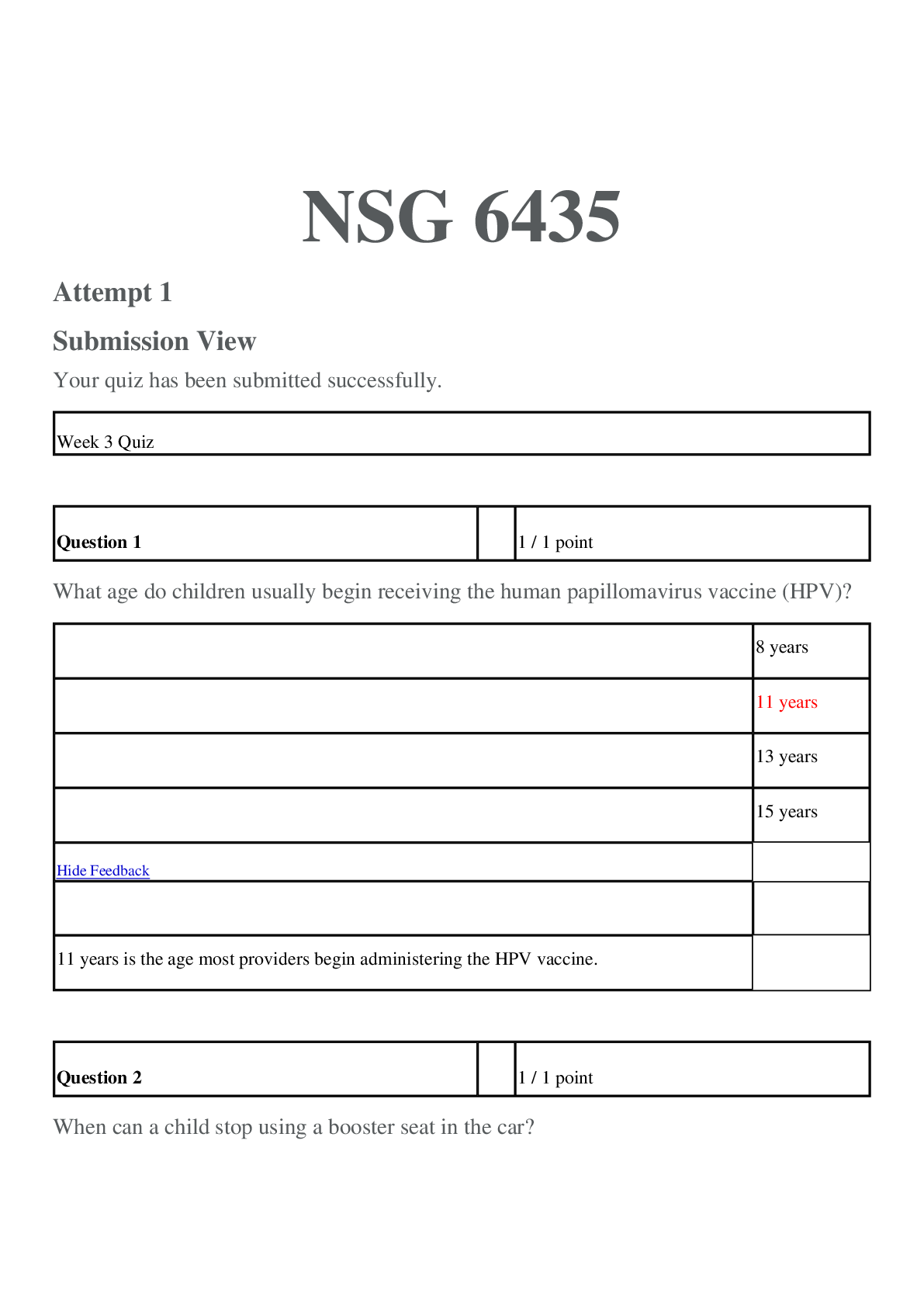
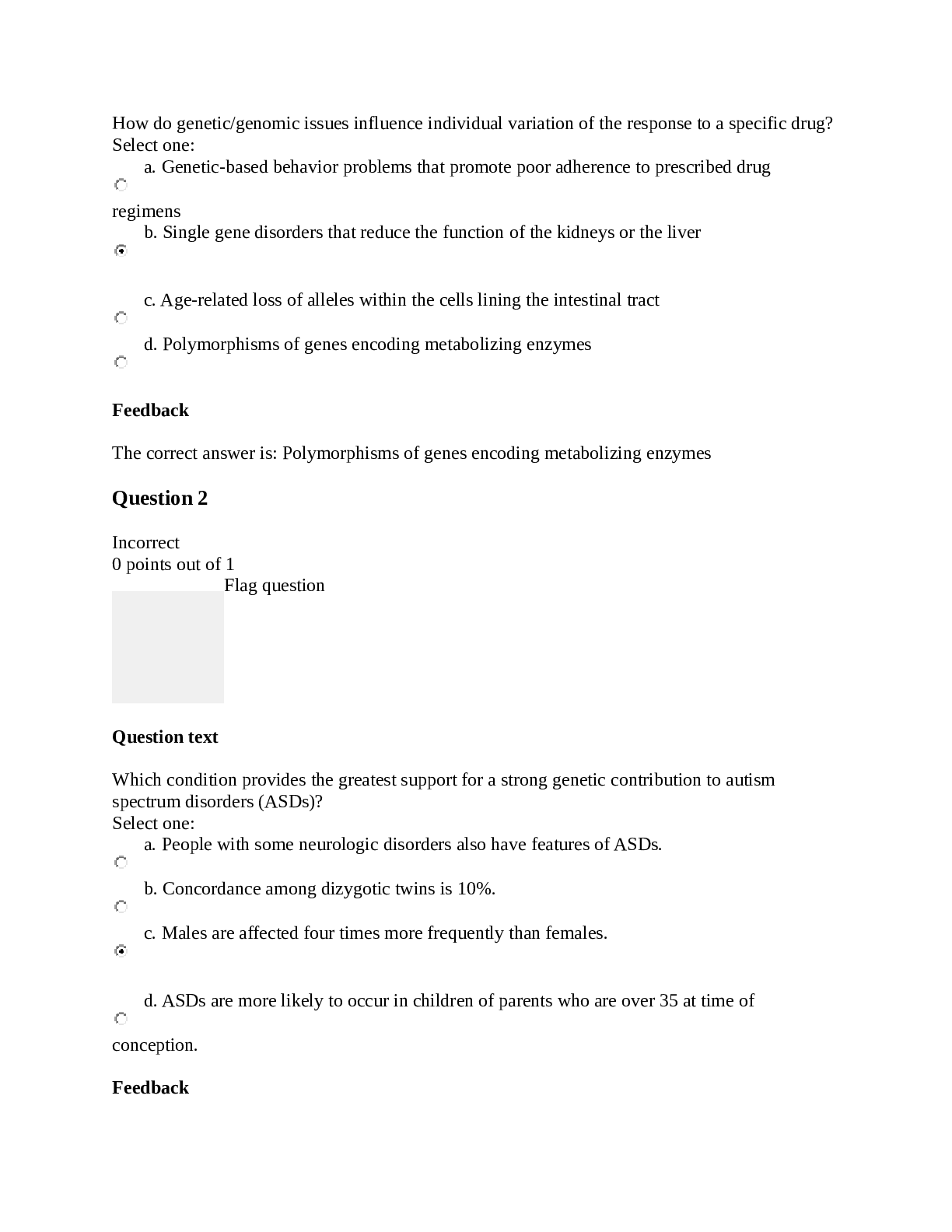
NURSING NSG6005 Pharm exam 4 review Pharm Study Guide Exam 4 Chapters 25, 26, 42, 43, 44, 45 (part of 45) Use the powerpoints as a study guide in conjunction with your text. This is a general stu... dy guide and is not all inclusive. Review your textbook, textbook study guide, ATI Pharmacology Made Easy and ATI book. Labs Sodium: 135-145 mEq/L Potassium: 3.5-5 mEq/L Chloride: 98-106 mEq/L Digoxin level 0.5-0.8 ng/mL Chapter 25 - Antiinflammatory Identify NSAIDs- NSAIDs are aspirin and aspirin-like drugs that inhibit the enzyme COX, which is needed for the biosynthesis of prostaglandins. Side/adverse effects of NSAIDs- GI upset, dizziness, rash, heartburn, and occult blood loss. Contraindications of NSAIDs- anti-coagulant drugs (warfarin), pregnancy, nursing, renal disease, asthma, angioedema. What organ does NSAIDs effect? Kidney (renal toxicity) What is the antidote for aspirin? Vitamin K (Sodium bicarbonate is a treatment for it not an antidote) Acetaminophen – is an analgesic;It can treat minor aches and pains, and reduces fever. (Not for inflammation) Side/adverse effects of acetaminophen- nausea, dark urine, upper stomach pain, loss of appetite, and jaundice. Organ affected of acetaminophen- Liver (hepatotoxicity)Antidote of acetaminophen- N-acetylcysteine/mucomyst Corticosteriods- Corticosteroids such as prednisone, prednisolone, and dexamethasone are frequently used as anti-inflammatory agents. This group of drugs controls inflammation by suppressing or preventing many of the components of the inflammatory process at the injured site. Corticosteroids have been widely prescribed for arthritic conditions, and although they are not the drug of choice for arthritis because of their numerous side effects, they are frequently used to control arthritic flare-ups. DMARDs- include immunosuppressive agents, immunomodulators, and antimalarials. DMARDs help alleviate the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis for the 2 million persons in the United States affected by the disorder. Antimalarials- Antimalarial drugs may be used to treat rheumatoid arthritis when other methods of treatment fail. The mechanism of action of antimalarials in suppressing rheumatoid arthritis is unclear. The effect may take 4 to 12 weeks to become apparent, and antimalarials are usually used in combination with NSAIDs in patients whose arthritis is not under control. Colchicine- The first drug used to treat gout was colchicine, introduced in 1936. This anti-inflammatory gout drug inhibits the migration of leukocytes to the inflamed site. Allopurinol- is not an anti-inflammatory drug; instead, it inhibits the final steps of uric acid biosynthesis and therefore lowers serum uric acid levels, preventing the precipitation of an attack. This drug is frequently used as a prophylactic to prevent gout. It is a drug of choice for patients with chronic tophaceous gout. Uricosurics- increase the rate of uric acid excretion by inhibiting its reabsorption. These drugs are effective in alleviating chronic gout, but they should not be used during acute attacks. Probenecid (Benemid) is a uricosuric that has been available since 1945. It blocks the reabsorption of uric acid and promotes its excretion. Chapters 26 - Opioids Recognize the drugs classified as opioid agonist- are prescribed for moderate and severe pain such as acetaminophen, NSAID’s (such as aspirin,ibuprofen), Side and adverse effects? Hepatotoxicity or renal toxicity Use of Fentanyl- patients who suffer from chronic pain Recognize the drugs classified as agonist-antagonist opioids – difference with opioids – side effects (Nalbuphine, buprenorphine HCl (Buprenex), butorphanol tartrate, nalbuphine HCl (Nubain), and pentazocine lactate) medications in which an opioid antagonist (e.g., naloxone [Narcan]) is added to an opioid agonist, weredeveloped in hopes of decreasing opioid abuse. Side effect Dizziness, confusion, hallucinations, blurred vision, headache, flushing, sedation, nervousness, restlessness, euphoria, depression, crying, dysphoria, unusual dreams, dry mouth, bitter taste, nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, clammy skin, and urinary urgency Opioid antidote- Naloxone Antimigraine medications: Ergot Alkaloids and Triptans – side/adverse effects; dosing: These are given for migraine and clustered headaches side effect dysrhythmia and tachycardia (triptan causes chest pain which make you think you are having and MI also don’t take if taking anti-depressant), Dosage Ergot 1 spray in each nostril; may repeat in 15 min; max: 4 sprays and Triptan PO: 25-50 mg for 1 dose, may repeat once after 2 h, max: 200 mg/d. Chapter 42 1. Digoxin improves the heart’s pumping effectiveness, and increases cardiac output and stroke volume. It decreases heart rate by slowing depolarization through the SA node, thus allowing more time for the ventricles to fill with blood. 2. Therapeutic Use: Digoxin is used to treat heart failure, atrial fibrillation and some other tackydysrhytmias 3. Side / Adverse Effects: CNS effects (fatigue and weakness), visual effects (yellowtinged vision, halos around lights and diplopia). Pulse rate less than 60 min in adults, or skipped beats when checking the pulse 4. Drug interactions • Diuretics • Glucocorticoids • Antacids • Herbal interactions • Hypokalemia 5. Digitalis toxicity a. Anorexia, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, bradycardia, premature ventricular contractions, cardiac dysrhythmias, headaches, malaise, blurred vision, visual illusions, confusion, and delirium.6. Drug level: range is 0.5 to 2.0 ng/mL. Signs of toxicity may appear at levels less than 1.75 ng/ml. Very important the nurse should monitor ECG and serum potassium levels because hypokalemia can cause dysrhythmias especially in older adult. 7. Antidote: Digibind. 8. Antidote for digitalis toxicity: digoxin immune Fab (ovine, Digibind) 9. Treatment cardiotoxicity a. Phenytoin b. Lidocaine 10. Nursing implications: Ascertain apical pulse rate before administering digoxin. Do not administer if pulse rate <60 beats/min. ▪ Determine signs of peripheral and pulmonary edema, which indicate HF is present. ▪ Monitor serum digoxin level (normal therapeutic drug range is 0.8 to 2 ng/mL). A serum digoxin level greater than 2 ng/mL is indicative of digitalis toxicity. ▪ Monitor serum potassium level (normal range is 3.5 to 5.3 mEq/L), and report if hypokalemia (<3.5 mEq/L) is present. 11. Milrinone: MOA: Short term treatment of HF unresponsive to conventional therapy with digoxin, diuretics and vasodilators. Increase cardiac output (inotropic effect) IV administration Side/ adverse effect: headache, ventricular arrhythmias, hypotension, increase liver enzymes, hypokalemia and thrombocytopenia. Nursing Interventions: Monitor electrolytes and renal function, check for hypokalemia, monitor platelet count during therapy. Monitor intake and output and daily weight. Milrinone lactate (Primacor) Positive inotrope Used to treat acute HF Action • Increase stroke volume and cardiac output and promote vasodilation Caution: Administered IV for no longer than 48 to 72 hours to avoid severe cardiac dysrhythmias 12. Nesiritide (Natrecor) a. Inhibits antidiuretic hormone (ADH) by increasing urine sodium loss b. Promotes vasodilation, natriuresis, and diuresis c. Used for treatment of acute decompensated HF with dyspnea at rest, dyspnea with little physical exertion d. It is useful for treating patients who have acute decompensated HF( Hydrogen Fluoride) 13. Nitroglycerin: First agents used to relieve angina Action: Generalized vascular and coronary vasodilation Side effects and adverse reactions: Headache, hypotension, dizziness, weakness, and faintness Julio Nitroglycerin should not be taken by men using sildenafil (Viagra) because of the risk of hypotension. (: Sublingual, topical (ointment, transdermal patch), buccal extended-release tablet, oral extended-release capsule and tablet, aerosol spray (inhalation), and IV Nursing implication: caution the patient to change position to minimize orthostatic hypotension. Avoid alcohol. Aspirin or acetaminophen may ordered to treat headaches. Notified the provider if dry mouth or blurred vision occurs. Antidysrhythmics Class I Sodium channel blockers• 1A: slow conduction, prolongs repolarization (quinidine, procainamide, disopyramide) • 1B: slow conduction, shortens repolarization (lidocaine, mexiletine) • 1C: prolonged conduction with little/no effect on repolarization (flecainide, propafenone) Class II Beta-adrenergic blockers • Reduce calcium entry, decrease conduction velocity, automaticity, and recovery time • Propranolol (Inderal) • Acebutolol (Sectral) • Esmolol (Brevibloc) . Sotalol (Betapace Class III Prolong repolarization Amiodarone (Cordarone) Class IV Block calcium influx (calcium channel blockers) Verapamil (Calan, Isoptin) Diltiazem (Cardizem) Adenosine: (Adenocard, Adenoscan) MOA: slows conduction through AV node, can interrupt reentry pathways through AV node, and can restore normal sinus rhythm in patients with supraventricular tachycardia (SVT). Side Effects: nausea, metallic taste, chest pressure, hyperventilation, sweating, palpitation, hypotension, facial flushing, numbness. Warning hypersensitivity 2nd and 3rd degree heart block, AV block, sick sinus syndrome, atrial flutter, atrial fibrillation. Nurse Intervention:Advise to report facial flashing, dizziness for a sitting or standing position to prevent orthostatic hypotension. Remember this. DON’T ADMINISTER CAFEINE ALOE THEOPHYLLINE (bronchodilator) SMOKING. Chapter 43 - Diuretics *****Chloride to the diuretics, fluid excreted. Chloride follow sodium****** 1. High ceiling Loop Diuretics a. Mechanism of action: Loop diuretics act on the ascending loop of Henle, in the renal tubules blocking reabsorption of sodium and chloride. This promote excretion of sodium and chloride, which carry water with them. As a result of these actions, urine output is increase and potassium is excreted. b. What electrolytes are excreted: sodium water, and potassium Therapeutic uses – most powerful: are powerful diuretics that treat pulmonary edema in heart failure, edema caused by renal hepatic or cardiac failure not affected by other diuretics, as well as hypertension that is not controlled by other types of diuretics. c. Furosemide (Lasix); prototype drug for Loop Diuretics. Ethacrynic acid other drugs in this category d. Adverse effects – know: Include electrolyte imbalance, such as hyponatremia, hypochloremia, severe fluid loss or dehydration, hypokalemia, Hypertension, Ototoxicity e. Know hypokalemia can increase risk for digoxin toxicity f. Know signs of hypokalemia: weakness, fatigue, constipation, and muscle cramping. In more severe cases, heart arrhythmias, or abnormal rhythms may occur – lab ranges for K: 3.5 to 5 g. Use with caution in diabetics and gout: Furosemide’s ability to block the release of insulin and cause Hyperglycemia, especially in patients who are diabetic. Increase uric acid levels, or hyperuricemia can occur in patients who are susceptible to gouty arthritis. h. Drug interactions: Patients who are on digoxin are at an increased risk of digoxin toxicity if they become potassium deficient so patient on loop diureticsand digoxin need to carefully watch their potassium levels. Giving a loop diuretic with other diuretics increase their diuretics effects, while giving them with NSAIDs may decrease the diuretic effect. And lithium toxicity may occur in patients taking lithium for a mood disorder. amphotericin B and corticosteroids also increase the risk for hypokalemia when they take them concurrently with a loop diuretic. 2. Thiazide a. Mechanism of action: Thiazide diuretics act on the early distal convoluted tubules in the kidneys by blocking reabsorption of sodium, chloride and water. This promotes excretion of sodium and chloride which carry water along with them. As a result of these actions, urine output is increase and potassium is excreted. Adequate kidney perfusion and glomerular filtration rate is needed for this type of drug to work. b. What electrolytes are excreted: sodium water, and potassium c. Therapeutic uses: are used with other drugs as part of the treatment for heat failure. They also treat hypertension, cirrhosis of the liver, and renal failure. d. Not effective when urine flow is scant e. Hydrochlorothiazide (Hydrodiuril): prototype drug for the thiazide f. Adverse effects – know: Fluid and electrolyte imbalance, in particular Hyponatremia (low sodium), Hypochloremia (low chloride), dehydration (severe fluid loss), and Hypokalemia (low potassium). Hyperglycemia and Hyperuricemia (increase uric acid levels). g. Know hypokalemia can increase risk for digoxin toxicity h. Know signs of hypokalemia: weakness, fatigue, constipation, and muscle cramping. In more severe cases, heart arrhythmias, or abnormal rhythms may occur. i. Drug interactions: Take Thiazide concurrently with lithium may cause lithium toxicity. Also an increase in the risk of Digoxin toxicity with either potassium or magnesium deficiency, patients on thiazide and digoxin need to carefully watch for their potassium levels. Thiazide with corticosteroids and amphotericin B increase the risk for hypokalemia. 3. Osmotic a. Mechanism of action: Work on the proximal tubule and loop of Henle by increasing the osmolality (concentration) and sodium reabsorption. b. Therapeutic uses – know unique uses: is used to prevent kidney failure, to decrease intracranial pressure (ICP) (edema in brain), and to decrease intraocular pressure (IOP).c. Mannitol: Draw with filter needle. Crystallization of mannitol in the vial may occur when the drug is exposed to a low temperature. The vial should be warmed to dissolve the crystals. The mannitol solution should not be used for IV infusion if crystals are present and have not been dissolved. d. Adverse effects – know: fluid and electrolyte imbalance, pulmonary edema 4. Potassium Sparing a. Aldosterone antagonist (Spironolactone Aldactone): is a mineralocorticoid hormone that promotes sodium retention and potassium excretion. Spironolactone blocks the action of aldosterone and inhibits the sodium-potassium. b. Nonaldosterone antagonists (Triamterene and Amiloride): Amiloride (Midamor), triamterene (Dyrenium), are additional commonly prescribed potassium-sparing diuretics. Amiloride is effective as antihypertensive agent. Triamterene is useful in the treatment of edema caused by HF or cirrhosis of the liver. Amiloride and triamterene should not be taken with ACE inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) because they can also increase serum potassium levels. c. Mechanism of action: act primarily in the collecting duct renal tubules and late distal tubule to promote sodium and water excretion and potassium retention by blocking the action of aldosterone. d. What electrolytes are excreted: Sodium and water e. Therapeutic uses – know about use in heart failure: Is used to treat hypertension, edema cause by heart failure, cirrhosis of the liver, nephrotic syndrome and hypokalemia. f. Adverse effects – know: hyperkalemia GI disturbances (anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and numbness and tingling of the hands and feet. g. for accuracy before use. h. Know hyperkalemia (high potassium level) - lab ranges: 3.5 to 5 Potassium (K) greater than 5.0 mEq/L - hyperkalemia i. Drug interactions: Counteract the adverse effect of hypokalemia of loop and thiazide diuretics. It’s because of this interaction that patients often give these diuretics together. However, when patients are given a potassium-sparing diuretic with ACE inhibitors, ARBs, direct renin blockers, potassium supplements and potassium containing salt substitutes, the risk of hyperkalemia increases 5. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitor a. Therapeutic use: Is Used primarily to decrease intraocular pressure (IOP) in patients with open-angle (chronic) glaucomab. What can it cause? fluid and electrolyte imbalance, metabolic acidosis, nausea, vomiting, anorexia, confusion, orthostatic hypotension, crystalluria, hemolytic anemia, and renal calculi. Chapter 44 – Antihypertensives Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. More info in pg 634ACE Inhibitors: benazepril (Lotensin), captopril (Capoten), enalapril maleate (Vasotec), fosinopril (Monopril), lisinopril (Prinivil, Zestril), moexipril (Univasc), perindopril (Aceon), quinapril (Accupril), ramipril (Altace), and trandolapril (MavikMOA- ACE inhibitors inhibit ACE, which in turn inhibits the formation of angiotensin II (vasoconstrictor) and blocks the release of aldosterone therapeutic use- first-line antihypertensive therapy. primarily to treat hypertension; some of these agents are also effective in treating heart failure side/adverse effects- Irritating cough, insomnia, hyperkalemia, tachycardia nursing implications- African-American adults and older adults do not respond with ACEI monotherapy, but do respond when taken with diuretic. ContraindicationsPregnancy, Potassium-sparing diuretics such as spironolactone (Aldactone). Salt substitutes that contain potassium --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ARBs: Losartan (Cozaar), valsartan (Diovan), irbesartan (Avapro), candesartan cilexetil (Atacand), eprosartan (Teveten), olmesartan medoxomil (Benicar), and telmisartan (Micardis) MOA- ARBs block angiotensin II from the angiotensin I (AT1) receptors found in many tissues therapeutic use- To treat hypertension side/adverse effects- Dizziness, drowsiness, cough (rare), blurred vision, headache, diarrhea, insomnia, arthralgia, fatigue. adverse- Orthostatic hypotension, hypoglycemia, hyperkalemia, Life threatening: renal dysfunction nursing implications- Less likely to cause irritating cough. It is highly protein-bound and should not be given during pregnancy, especially during the second and third trimester. The half-life is 6 to 9 hours. The drug is excreted in urine and feces. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Direct Renin Inhibitor: Aliskiren (Tekturna) MOA- Aliskiren binds with renin, causing a reduction of angiotensin I, angiotensin II, and aldosterone levels. therapeutic use- effective for mild and moderate hypertension side/adverse effects- adverse effects include allergic reaction such as angioedema, and rash. Hyperkalemia, and diarrhea. nursing implications- Aliskiren can be used alone or with another antihypertensive agent. It has an additive effect in reducing blood pressure when combined with athiazide diuretic or an ARB. This drug, when used as monotherapy, has not proven to be as effective in reducing blood pressure in the African-American population. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Calcium Channel Blockers: Diphenylalkylamine (verapamil), benzothiazepines (diltiazem), and dihydropyridine (amlodipine and others) MOA- Decrease calcium levels and promote vasodilation therapeutic use- treat chronic hypertension, angina pectoris, and cardiac dysrhythmias. side/adverse effects- Flush, headache, dizziness, ankle edema, bradycardia, and AV block nursing implications- Calcium blockers are highly protein-bound but have a short half-life. Slow-release preparations decrease frequency of administration --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Combining blood pressure meds- patients at risk for hyperkalemia, at risk for hypotension, and at risk for dehydration. Amlodipine may be combined with the ACE inhibitor benazepril, forming Lotrel. Normally beta blockers are not prescribed with calcium blockers, because both drugs decrease myocardium contractility. Calcium blockers lower blood pressure better in African Americans than drugs in other categories. Chapter 45 review Heparin: MOA – Most commonly prescribed to prevent DVT and acute pulmonary embolism after orthopedic or abdominal surgery Side effects/ Adverse effect: bleeding, Heparin laboratory values: PTT 1.5 to 2 times control value (control 60 to 70 seconds) aPTT 30 to 85 seconds (control 20 to 35 seconds) Always give IV pump can be given deep sub Q, Antidote: Protomine sulfate. Low Molecular weight Heparins: Enoxaparin sodium (Lovenox), Dalteparin sodium (Fragmin), and tinzaparin sodium (Innohep), Contraindications: stroke, peptic ulcer, blood anomalies/ Patients having eye, brain, or spinal surgery, monitor platelet count Antidote: Protomine sulfateWarfarin: Oral anticoagulants: inhibit hepatic synthesis of vitamin K, thus affecting the clotting factors ll, Vll, IX, and X, Used mainly to prevent thromboembolic conditions such as thrombophlebitis, pulmonary embolism, and embolism formation caused by atrial fibrillation, which can lead to a stoke (CVA) Monitor therapeutic range: PT 1.25 to 2.5 times control value (11 to 15 seconds) INR 2 to 3 (normal 1.3 to 2) Antidote Vitamin K Direct thrombin inhibitors: Directly inhibit thrombin from converting fibrinogen to fibrin Administered intravenously: argatroban, bivalirubin, and lepirudin Administered subcutaneously: desirudin(iprivask) Oral anticoagulant that does not require routine coagulation/ No Antidote What does the PT, aPTT and INR mean? PT- The prothrombin time measures the speed of clotting by means of the extrinsic pathway (also known as the tissue factor pathway). Activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT or APTT) is a medical test that characterizes blood coagulation, International Normalised Ratio (INR) and is a measure of how much longer it takes the blood to clot when oral anticoagulation is used. For example, if your INR is 2 the blood is taking twice as long as normal to clot. • How to watch for signs of bleeding? : Look for bleeding from the gums, blood in your urine, bloody or dark stool, nosebleeds, or vomiting blood. • Women need to watch for extra bleeding during their period or between periods. • Dark red or black bruises may appear. If this happens, call your doctor right away When do you take warfarin? evening [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 14 pages
Instant download
.png)
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jan 19, 2021
Number of pages
14
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jan 19, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
51







.png)