*NURSING > TEST BANK > NURSE-UN 70 Cell Function Test Bank Patton: Anatomy and Physiology 9th Edition,100% CORRECT (All)
NURSE-UN 70 Cell Function Test Bank Patton: Anatomy and Physiology 9th Edition,100% CORRECT
Document Content and Description Below
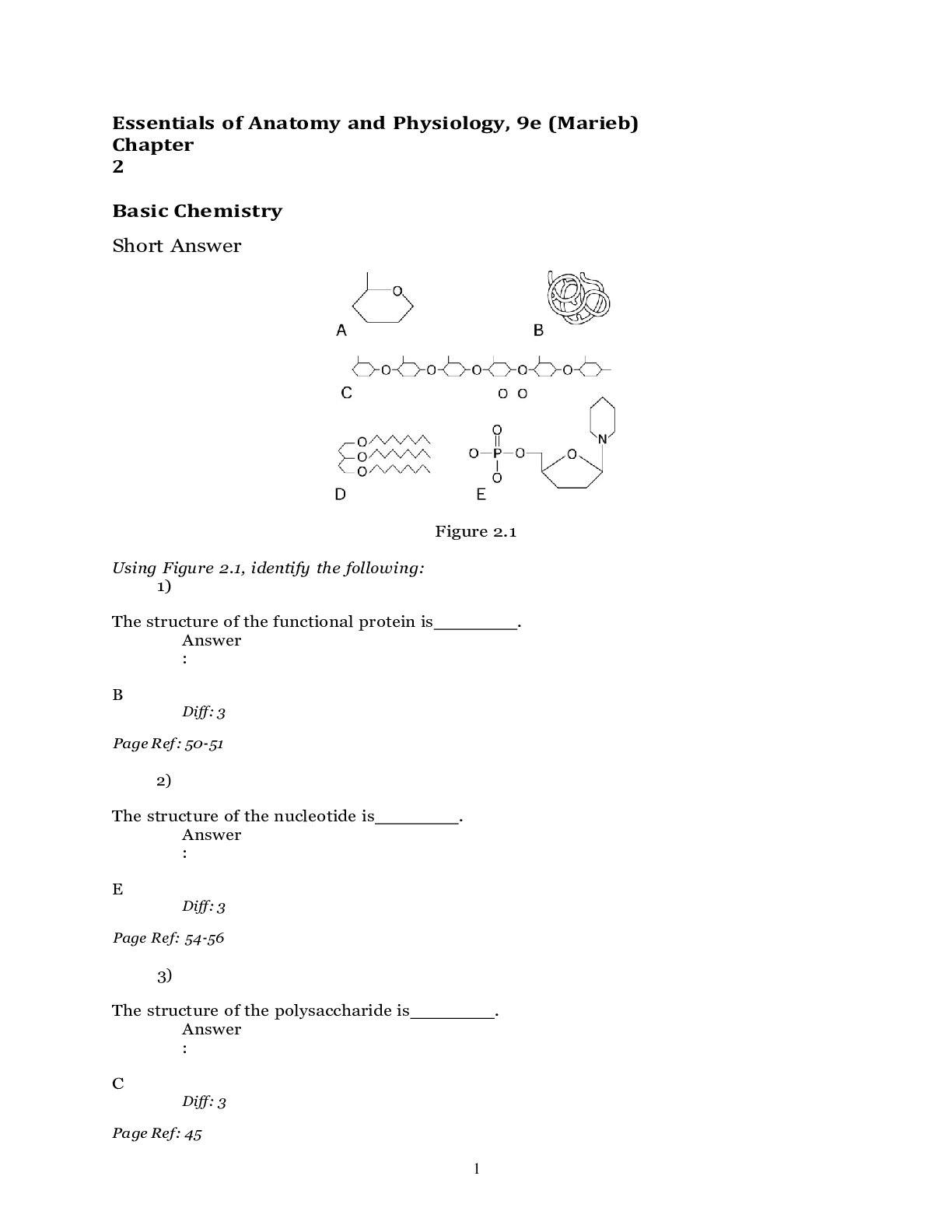
NURSE-UN 70 Cell Function Test Bank Patton: Anatomy and Physiology 9th Edition Chapter 06: Cell Function Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Diffusion of particles through a membrane by means of a carri... er molecule is called: a. pinocytosis. b. osmosis. c. facilitated diffusion. d. dialysis. ANS: C DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Facilitated Diffusion 2. Diffusion requires: a. a semipermeable membrane. b. a concentration gradient. c. ions. d. none of the above. ANS: B DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Diffusion 3. All of the following are examples of passive transport except: a. filtration. b. osmosis. c. endocytosis. d. dialysis. ANS: C DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Passive Transport Processes 4. A saline solution that contains a higher concentration of salt than a red blood cell would be: a. isotonic. b. hypotonic. c. hypertonic. d. hydrostatic. ANS: C DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Osmosis 5. Materials can be moved from a low concentration to a high concentration through: a. facilitated diffusion. b. filtration. c. osmosis. d. active transport. ANS: D DIF: Application REF: TOP: Active Transport Processes 6. Which of the following is not true of diffusion? a. Uses cellular energy b. Can occur in living and nonliving cells c. May occur both into and out of the cell d. Energy source is cellular ANS: A DIF: Application REF: TOP: Diffusion 7. A membrane carrier structure attracts a solute to a binding site, changes shape, and releases the solute on the other side of the cell membrane. This describes the process of: a. endocytosis. b. the sodium and potassium pump. c. channel-mediated transport. d. carrier-mediated transport. ANS: D DIF: Application REF: TOP: Facilitated Diffusion 8. The physical process by which water and solute move through a mem- brane when a hydrostatic pressure gradient exists across the membrane is the process of: a. dialysis. b. osmosis. c. diffusion. d. filtration. ANS: D DIF: Application REF: TOP: Filtration 9. Which is not true about the sodium and potassium pump? a. It uses cellular energy. b. Sodium moves into the cell and potassium moves out of the cell. c. A carrier system is used. d. It can move substances against their concentration gradient. ANS: B DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Active Transport Processes 10. Which is true about the sodium and potassium pump? a. Two sodium ions are taken into the cell. b. Three sodium ions are taken out of the cell. c. Three potassium ions are taken into the cell. d. Two potassium ions are taken out of the cell. ANS: C DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Active Transport Processes 11. Two solutions of different concentrations of glucose are separated by a membrane that allows both glucose and water to pass through. When dy- namic equilibrium is reached, there will be: a. no movement of water or glucose. b. movement of glucose but not water. c. movement of water but not glucose. d. an even exchange of material across the membrane. ANS: D DIF: Synthesis REF: TOP: Diffusion 12. Phagocytosis is an example of: a. exocytosis. b. endocytosis. c. passive transport. d. facilitated diffusion. ANS: B DIF: Application REF: TOP: Transport by Vesicles 13. Water will move through the cell membrane by: a. dialysis. b. diffusion. c. facilitated diffusion. d. osmosis. ANS: B DIF: Synthesis REF: TOP: Diffusion 14. NaCl would move through the cell membrane in which direction? a. Both into and out of the cell b. Into the cell c. Out of the cell d. Neither into nor out of the cell ANS: A DIF: Synthesis REF: TOP: Diffusion 15. The small water channels in the cell membrane are called: a. phospholipid molecules. b. transport pumps. c. aquaporins. d. transport vesicles. ANS: C DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Osmosis 16. If a cell were placed in a hypotonic solution: a. there would be a net gain of water into the cell. b. there would be a net loss of water out of the cell. c. no water would move into or out of the cell. d. water would move into and out of the cell in equal amounts. ANS: A DIF: Application REF: TOP: Osmosis 17. If a cell were placed in a hypertonic solution: a. there would be a net gain of water into the cell. b. there would be a net loss of water out of the cell. c. no water would move into or out of the cell. d. water would move into and out of the cell in equal amounts. ANS: B DIF: Application REF: TOP: Osmosis 18. Potential osmotic pressure can be measured by determining the: a. concentration on either side of a membrane. b. strength of the concentration gradient. c. permeability of the membrane. d. There is no direct means of measurement. ANS: D DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Osmosis 19. Which of the following is not a passive transport process? a. Dialysis b. Osmosis c. Filtration d. Phagocytosis ANS: D DIF: Application REF: TOP: Passive Transport Processes 20. Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane in the presence of at least one impermeable solute is referred to as: a. diffusion. b. osmosis. c. phagocytosis. d. pinocytosis. ANS: B DIF: Application REF: TOP: Osmosis 21. The engulfing of microbes by white blood cells is an example of: a. pinocytosis. b. exocytosis. c. phagocytosis. d. “cell drinking.” ANS: C DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Transport by Vesicles 22. A hypertonic solution contains concentration of solute the cell. a. a greater; than b. the same; as c. a lesser; than d. None of the above is correct. ANS: A DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Osmosis 23. The force of a fluid pushing against a surface could be described as pressure. a. facilitated. b. hydrostatic. c. hypostatic. d. diffused. ANS: B DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Filtration 24. If a 20% glucose solution were separated from a 10% glucose solution by a permeable membrane: a. glucose would move from the 20% solution to the 10% solution. b. water would move from the 10% solution to the 20% solution. c. water would move from the 20% solution to the 10% solution. d. both A and B would occur. ANS: D DIF: Application REF: TOP: Diffusion 25. The proteins in the cell membrane that can open and close are called: a. enzymes. b. gated channel proteins. c. glycoproteins. d. both A and B. ANS: B DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Channel-Mediated Passive Transport 26. Hydrostatic pressure in the blood is: a. generated by the contraction of the heart. b. generated by gravity. c. important to the functioning of the kidney. d. all of the above. ANS: D DIF: Application REF: TOP: Filtration 27. Gated channels in the cell membrane can be “opened” by: a. electrical changes or voltage. b. chemicals. c. light. d. all of the above. ANS: D DIF: Application REF: TOP: Channel-Mediated Passive Transport 28. After phagocytosis occurs, enzymes from which organelle can digest what is in the vesicle? a. Lysosome b. Golgi apparatus c. Mitochondria d. Cytoskeleton ANS: A DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Transport by Vesicles 29. The location at which the enzyme molecule binds to the substance it acts on is called the: a. substrate. b. coenzyme. c. active site. d. cofactor. ANS: C DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: The Role of Enzymes 30. Which of the following is not true of glycolysis? a. It occurs in the cytoplasm. b. It does not require oxygen. c. The energy is transferred to NADH. d. It is able to get almost all of the energy out of a glucose molecule. ANS: D DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Glycolysis 31. In aerobic respiration, the function of oxygen is to combine with: a. pyruvic acid in glycolysis. b. NADH in the citric acid cycle. c. electrons and hydrogen at the end of the electron transport system. d. lactic acid in glycolysis. ANS: C DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Electron Transport System 32. Which of the following is not true of enzymes? a. They increase the activation of a reaction. b. They are unchanged by the chemical reaction. c. They frequently require a cofactor or coenzyme to function. d. All of the above are true of enzymes. ANS: A DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: The Role of Enzymes 33. A molecule or other agent that alters enzyme function by changing the enzyme’s shape is called a(n): a. cofactor. b. coenzyme. c. allosteric effector. d. proenzyme. ANS: C DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: General Functions of Enzymes 34. Which of the following is not true of the citric acid cycle? a. Occurs in the mitochondria b. Directly releases 36 ATPs of energy c. Has acetyl CoA as a starting product d. All of the above are true of the citric acid cycle. ANS: B DIF: Application REF: TOP: Citric Acid Cycle 35. Digestive enzymes belong to which group? a. Hydrases b. Phosphorylating enzymes c. Hydrolases d. Isomerases ANS: C DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Classification and Naming of Enzymes 36. Which enzymes rearrange atoms within a molecule? a. Hydrases b. Phosphorylating enzymes c. Oxidation-reduction enzymes d. Isomerases ANS: D DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Classification and Naming of Enzymes 37. Which factor can have an effect on the functioning of an enzyme? a. Temperature b. pH c. An increase in the amount of end product produced by a reaction d. All of the above ANS: D DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: General Functions of Enzymes 38. Which of the following is not true of the exocytosis? a. The vesicles containing the protein were formed by the rough endoplasmic reticulum. b. The vesicles are pulled to the cell membrane by the cytoskeleton. c. The vesicles add to the structure of the cell membrane. d. All of the above are true of exocytosis. ANS: A DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Exocytosis 39. Which of the following is true of catabolic pathways? a. They turn larger molecules into smaller ones. b. They turn smaller molecules into larger ones. c. They require energy from the cell. d. Both B and C are true. ANS: A DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Cell Metabolism 40. Which of the following is true of anabolic pathways? a. They turn larger molecules into smaller ones. b. They turn smaller molecules into larger ones. c. They require energy from the cell. d. Both B and C are true. ANS: D DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Cell Metabolism TRUE/FALSE 1. Dialysis is a form of filtration that results in a separation of small and large solute particles. ANS: T DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Dialysis 2. For osmosis to occur, a selectively permeable membrane must be present. ANS: T DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Osmosis 3. The physical movement of water and solutes through a membrane when a hydrostatic pressure gradient exists is called filtration. ANS: T DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Filtration 4. Active transport processes that use protein carrier molecules, or pumps, do not use cellular energy but rely instead on concentration gradients. ANS: F DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Active Transport Processes 5. Most enzymes cannot catalyze a reaction in both directions. ANS: F DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: General Functions of Enzymes 6. Glycolysis does not require oxygen and is therefore termed anaerobic. ANS: T DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Glycolysis 7. The citric acid cycle and electron transport system are located in the Golgi apparatus. ANS: F DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Citric Acid Cycle 8. Protein synthesis is an anabolic pathway for cells. ANS: T DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Anabolism 9. A semipermeable membrane is needed for diffusion to occur. ANS: F DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Diffusion 10. A 10% solution of NaCl has a higher concentration of water than a 10% solution of glucose. ANS: F DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Diffusion 11. A solution may be defined as various solutes dissolved in a solvent. ANS: T DIF: Application REF: TOP: Dialysis 12. Red blood cells placed in a hypertonic solution may be destroyed be- cause the blood cells will lyse. ANS: F DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Osmosis 13. A hypertonic solution has a higher amount of osmotic potential than any other type of solution. ANS: T DIF: Application REF: TOP: Osmosis 14. For osmosis to occur there must be at least one impermeable solute present. ANS: T DIF: Application REF: TOP: Osmosis 15. One of the advantages of active transport is that it can move materials up, or against, its concentration gradient. ANS: T DIF: Application REF: TOP: Active Transport Processes 16. The active transport process involving pumps requires both a carrier system and cellular energy. ANS: T DIF: Application REF: TOP: Active Transport Processes 17. Endocytosis and pinocytosis are both active transport processes, because they require a carrier system such as a pump. ANS: F DIF: Application REF: TOP: Transport by Vesicles 18. The process of pinocytosis may be viewed as the cell drinking. ANS: T DIF: Application REF: TOP: Transport by Vesicles 19. Facilitated diffusion is a metabolically inexpensive process. ANS: T DIF: Application REF: TOP: Facilitated Diffusion 20. The sodium-potassium pump is an example of a passive transport process. ANS: F DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Active Transport Processes 21. Cellular secretion can be achieved by endocytosis. ANS: F DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Transport by Vesicles 22. Diffusion is a form of filtration that results in the separation of small and large solute particles. ANS: F DIF: Application REF: TOP: Dialysis 23. The three processes that comprise cellular respiration are glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the proton transport system. ANS: F DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Overview of Cellular Respiration 24. The “lock-and-key model” is used to describe how mRNA and tRNA base pairs align. ANS: F DIF: Application REF: TOP: Chemical Structure of Enzymes 25. Protein anabolism is a rarely used cellular activity. ANS: F DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Anabolism 26. Diffusion is a characteristic of living things and will not occur in a nonliv- ing system. ANS: F DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Osmosis 27. Because of the phospholipid cell membrane, water cannot diffuse into or out of the cell. ANS: F DIF: Application REF: TOP: Diffusion 28. The measurement of potential osmotic pressure is easier to determine than actual osmotic pressure. ANS: F DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Osmosis 29. The size of the molecule is an important factor in both dialysis and filtra- tion. ANS: T DIF: Synthesis REF: TOP: Filtration 30. Facilitated diffusion and simple diffusion move substances in opposite di- rections. ANS: F DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Facilitated Diffusion 31. Endocytosis can occur when molecules bind to membrane receptor pro- teins. ANS: T DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Transport by Vesicles 32. A side effect of exocytosis is the addition of new membrane material to the cell membrane. ANS: T DIF: Synthesis REF: TOP: Transport by Vesicles 33. An inorganic substance, such as an ion, is called a coenzyme when it is part of an enzyme. ANS: F DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Chemical Structure of Enzymes 34. For an enzyme to function, the coenzyme must fit into the enzyme’s ac- tive site like a key fits into a lock. ANS: F DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Chemical Structure of Enzymes 35. The hydrolyzing enzyme sucrase joins two sucrose molecules together. ANS: F DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Classification and Naming of Enzymes 36. Lactic acid is the result of glycolysis and is the substance that enters the citric acid cycle. ANS: F DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Glycolysis, Citric Acid Cycle 37. Most of the chemical energy released by the citric acid cycle is in the form of ATP. ANS: F DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Citric Acid Cycle 38. The electron transport system makes ATP by the movement of electrons through the inner mitochondrial membrane. ANS: F DIF: Application REF: TOP: Electron Transport System 39. Both the citric acid cycle and the electron transport system occur in the mitochondria. ANS: T DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Citric Acid Cycle, Electron Transport System 40. Anaerobic respiration is about 17 times more efficient in producing ATP than is aerobic respiration. ANS: F DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Electron Transport System 41. One explanation of the action associated with isotonic solutions is that they all have the same potential osmotic pressure. ANS: T DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Osmosis 42. Gated membrane channels can be opened and closed only by chemical stimuli. ANS: F DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Channel-Mediated Passive Transport 43. Special membrane channels called aquaporins assist the diffusion of wa- ter across the cell membrane. ANS: T DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Osmosis 44. An enzyme is a catalyst. ANS: T DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: The Role of Enzymes 45. The “lock-and-key” model of enzyme function explains how the protein and substrate join. ANS: T DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Chemical Structure of Enzymes 46. All enzyme names end with the suffix “-ase.” ANS: F DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Classification and Naming of Enzymes 47. Allosteric effectors activate or inactivate enzymes by changing the shape of the enzyme’s active site. ANS: T DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: General Functions of Enzymes 48. Coenzymes join enzymes to form proenzymes. ANS: F DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: General Functions of Enzymes 49. Proenzymes are unable to act as a catalyst in any type of chemical reac- tion. ANS: T DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: General Functions of Enzymes 50. One possible end product of glycolysis is lactic acid. ANS: T DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Glycolysis 51. Phagocytosis and exocytosis are opposite processes. ANS: T DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Transport by Vesicles 52. An enzyme eliminates the activation energy needed for a reaction to oc- cur. ANS: F DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Role of Enzymes 53. Digestive enzymes belong to a group of enzymes called hydrases. ANS: F DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Classification and Naming of Enzymes 54. Both temperature and pH change can affect the allosteric site of an en- zyme. ANS: T DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: General Functions of Enzymes 55. Oxygen is used in the citric acid cycle in cell respiration. ANS: F DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Electron Transport System 56. Glycolysis produces very little ATP but produces several molecules of NADH and FADH2. ANS: F DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Citric Acid Cycle 57. The energy storage molecules NADH and FADH2 have their energy con- verted to ATP in the electron transport system. ANS: T DIF: Application REF: TOP: Electron Transport System 58. Because a living cell membrane can limit the diffusion of some sub- stances by opening and closing channels, the membrane can be called selec- tively permeable. ANS: T DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Channel-Mediated Passive Transport 59. When molecules pass directly through the cell membrane, the process is called filtration. ANS: F DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Simple Diffusion 60. If a blood cell was placed in a solution and the cell began to swell and take in water, the solution would be called hypotonic to the cell. ANS: T DIF: Application REF: TOP: Osmosis 61. The sodium-potassium pump in the cell membrane moves potassium into the cell and sodium out of the cell. ANS: T DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Transport by Pumps 62. To maintain homeostasis, the sodium-potassium pump moves equal amounts of sodium and potassium into and out of the cell. ANS: F DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Transport by Pumps 63. Phagocytosis can be translated to “cell eating.” ANS: T DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Transport by Vesicles 64. The vesicles used in exocytosis have broken off from the mitochondria and are pulled to the cell membrane by the cytoskeleton. ANS: F DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Transport by Vesicles 65. Activation energy is the amount of energy gained by the cell as a result of a catabolic pathway. ANS: F DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Role of Enzymes 66. The enzyme that catalyzes the formation of sucrose is probably specific to that reaction. ANS: T DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: General Functions of Enzymes 67. The process of end-product inhibition in a metabolic pathway is an example of a positive-feedback loop. ANS: F DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: General Functions of Enzymes 68. The process of glycolysis produces two molecules of pyruvic acid for ev- ery one molecule of glucose. ANS: T DIF: Application REF: TOP: Glycolysis 69. The process of glycolysis does not occur in a specific organelle. ANS: T DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Glycolysis 70. The most important end product in cellular respiration is oxygen. ANS: F DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Electron Transport System MATCHING Match the name of each enzyme with its function or description. a. Hydrases b. Hydrolases c. Phosphorylating enzymes d. Mutases or isomerases e. Carboxylases or decarboxylases f. Oxidases and hydrogenases 1. Add or remove phosphate groups 2. Add water to a molecule without splitting it 3. Digestive enzymes 4. Involved in oxidation-reduction reactions 5. Add or remove carbon dioxide 6. Rearrange atoms within a molecule 1. ANS: C DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Classification and Naming of Enzymes 2. ANS: A DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Classification and Naming of Enzymes 3. ANS: B DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Classification and Naming of Enzymes 4. ANS: F DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Classification and Naming of Enzymes 5. ANS: E DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Classification and Naming of Enzymes 6. ANS: D DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Classification and Naming of Enzymes Match each term with its description. a. Cytosol b. Citric acid cycle c. Pyruvic acid d. Acetyl coenzyme A e. NAD f. Mitochondria g. Lactic acid h. Electron transport system i. Anaerobic j. Glycolysis 7. First step in cellular respiration 8. Part of the cell in which glycolysis takes place 9. Part of the cell in which citric acid cycles take place 10. Converted from pyruvic acid if no oxygen is present 11. Last step in cellular respiration 12. Process also called the Krebs cycle 13. Carries the end product of glycolysis to the citric acid cycle 14. Describes a process that can take place without oxygen 15. Compound that carries high energy electrons to the electron transport system 16. End product of glycolysis 7. ANS: J DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Overview of Cellular Respiration 8. ANS: A DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Glycolysis 9. ANS: F DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Citric Acid Cycle 10. ANS: G DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Glycolysis 11. ANS: H DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Overview of Cellular Respiration 12. ANS: B DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Citric Acid Cycle 13. ANS: D DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Citric Acid Cycle 14. ANS: I DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Glycolysis 15. ANS: E DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Citric Acid Cycle 16. ANS: C DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Glycolysis OTHER 1. Compare and contrast the processes of diffusion and osmosis. ANS: Answers will vary. DIF: Application REF: TOP: Passive Transport Processes 2. Name the three types of vesicle-mediated transport and explain how they are different. ANS: Answers will vary. DIF: Synthesis REF: TOP: Transport by Vesicles 3. Describe a hypertonic solution and a hypotonic solution. Explain what would happen to a cell if it were put into each of these solutions. ANS: Answers will vary. DIF: Synthesis REF: TOP: Osmosis 4. Briefly explain the process of glycolysis. What energy molecules are pro- duced, and how many of each are produced? ANS: Answers will vary. DIF: Synthesis REF: TOP: Glycolysis 5. Briefly explain the citric acid cycle. Name the energy molecules produced, and explain how many of each are produced. ANS: Answers will vary. DIF: Synthesis REF: TOP: Citric Acid Cycle 6. Explain why the electron transport system is necessary to get all of the us- able energy out of the processes of glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. ANS: Answers will vary. DIF: Synthesis REF: TOP: Electron Transport System 7. Explain the classification system and naming system for enzymes. ANS: Answers will vary. DIF: Memorization REF: TOP: Classification and Naming of Enzymes 8. Explain how the allosteric site on an enzyme allows the enzyme to func- tion. Explain the types of allosteric effectors. ANS: Answers will vary. DIF: Application REF: TOP: General Functions of Enzymes ESSAY 1. A nurse was instructed to dissolve a pill in a small amount of liquid medication. As she dropped the capsule into the liquid, she was interrupted by a telephone call. On her return to the medication cart, she found the medication had completely dissolved and apparently scattered evenly throughout the liquid. This phenomenon did not surprise her, because she was aware from her knowledge of cell transport that had created this distribution. Explain this phenomenon. ANS: Diffusion (Explanations will vary.) DIF: Synthesis REF: TOP: Diffusion 2. Anne ran in the Boston marathon. During the race, she lost a large amount of hypotonic sweat. Would you expect her cells to shrink, swell, or remain the same? Explain your answer. ANS: Shrink (Explanations will vary.) DIF: Synthesis REF: TOP: Osmosis [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 61 pages
Instant download

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Dec 20, 2022
Number of pages
61
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Dec 20, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
37
















.png)




