*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > NUR-641E Study Guide 1.Midterm (2019/2020). (All)
NUR-641E Study Guide 1.Midterm (2019/2020).
Document Content and Description Below
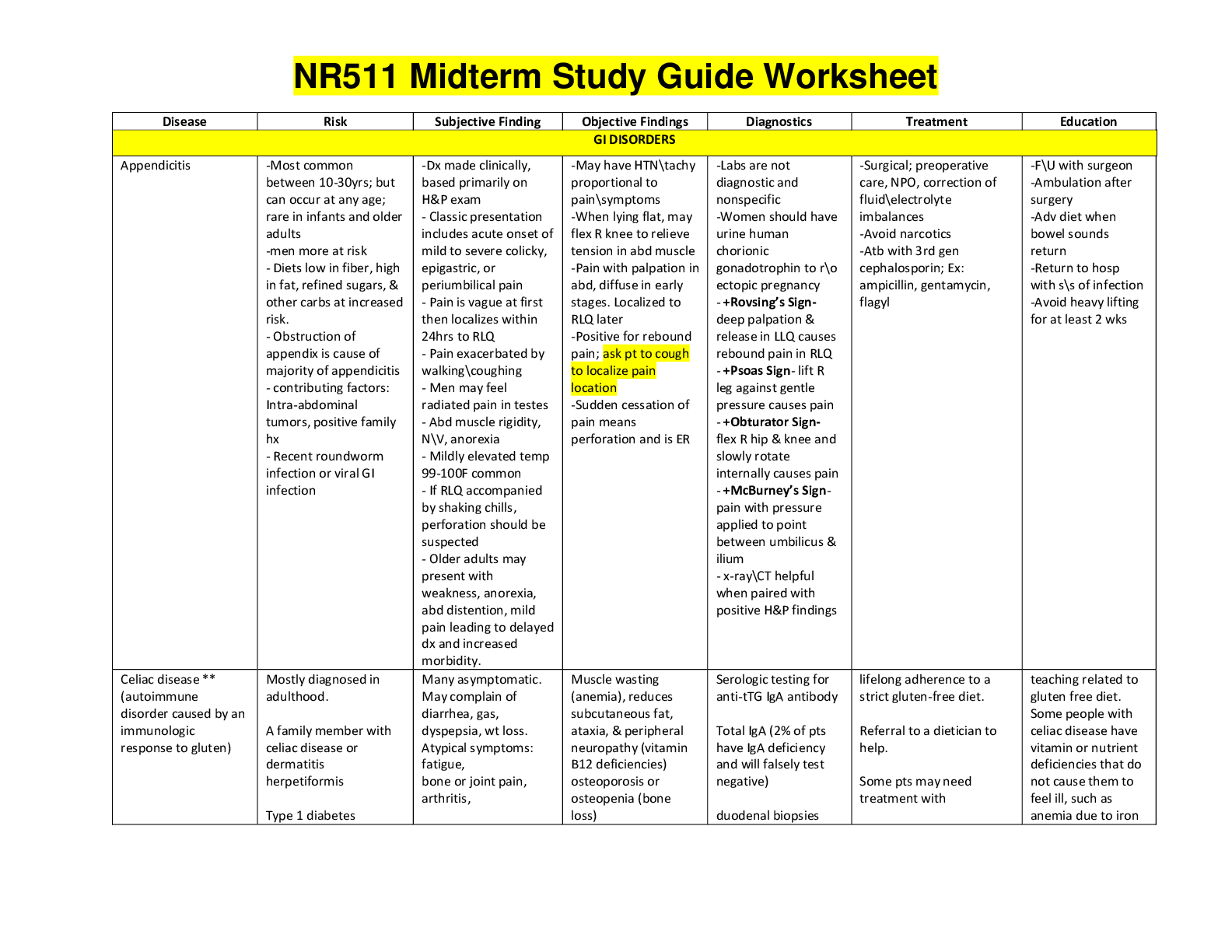
NUR-641E Mid-Term Exam Study Guide Note: Read the questions: the questions only have one answer unless the question specifically states there is more than one correct answer. ANSWERED SO FAR Understan... d what a prodrug is, and activation/inactivation by liver enzymes, and how it differs from active drugs. Know what Bioavailability (BA) Bioavailability is affected by chemical instability, solubility and first-pass metabolism Bioequivalence does not affect bioavailability Understand what the Cytochrome P450 system is in the liver A drug’s half-life determines how often the drug is administered? . Steady state of a drug is reached in approximately 5 to 6 times the half-life Inhalation, oral and parenteral drug action and onset of effects? Know the mechanism of action of anticoagulants (e.g., warfarin, apixaban, heparin). Heparin produces rapid anticoagulation by binding with antithrombin III, and inhibits factors IXa, Xa, XIIa, and XIII. Monitor heparin with a PTT Warfarin inhibits vitamin K-dependent blood factors II, VII, IX and X; takes several days for its anticoagulant effect. Monitor the International Normalized Ratio (INR) when warfarin is used. Blood Factor IIa inhibitor (direct thrombin inhibitor): dabigatran (Pradaxa). An antidote to dabigatran-induced hemorrhage is idarucizumab. Blood Factor Xa inhibitors: apixaban (Eliquis), edoxaban (Savaysa), rivaroxaban (Xarelto), fondaparinux (Arixtra). Know what pulmonary emboli are, where they come from and what these emboli do in the body Know the risk factors for cerebrovascular accident (CVA) Know the elements involved in the action potential of myocardial tissue Know what tuberculosis is and its epidemiology in the world. Isoniazid (INH) is famous for causing jaundice when combined with other drugs in a multidrug combination for treating TB. Be able to explain the side effects of multidrug therapy/polypharmacy Know the difference between vertical and horizontal transmission of organisms Know how empiric antimicrobial therapy is selected Antibiotic drugs that inhibit cell wall integrity include penicillins, ampicillin, cephalosporins, and carbapenems Antibiotic drugs that inhibit bacterial protein synthesis include the aminoglycoside, tetracyclines, fluoroquinolondes and tetracyclines. Endotoxic and exotoxic bacteria . Invasion period is when the immune and inflammatory responses are initiated Explain the cause of upper and lower respiratory tract infections, especially pneumonia List the antibiotics that should and should not be used in children SHOULD: SHOULD NOT: fluoroquinolones and tetracyclines. Know how to interpret an arterial blood gas NOT COMPLETE YET Know the causes of respiratory acidosis Be able to explain COPD and stepwise therapy (additions to current COPD medications) in its treatment Be able to explain hypoxemia at altitude (reduced oxygen inspiration) Discuss how pulmonary arterial hypertension is associated with right ventricular hypertrophy and an enlarged pulmonary artery Be able to explain fluid and electrolyte disorders Know the laboratory values of magnesium, calcium, sodium and potassium. Be able to explain how aldosterone affects sodium and water Know the effects of atrial natriuretic factor (ANF) Be able to explain the relationship between edema and oncotic pressure Be able to differentiate corticosteroids by potencies, mechanism of action and pharmacokinetics. Be able to explain how angiotensin and affects the cardiovascular system Know the unique pharmacokinetics of amiodarone Amiodarone can cause thyroid and pulmonary toxicity. Know what drugs are used for angina: beta-adrenergic antagonists (beta-blockers), angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs), angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), nitrates, calcium channel blockers (CCBs). Remember that many heart failure patients have more than just heart failure; look for underlying hypertension, angina, etc. Be able to describe how electrolyte serum levels affect digoxin serum levels Know how hyperkalemia is caused by renal failure and Addison’s Disease. Know how hypercalcemia is treated with calcitonin salmon and Kayexalate (sodium polystyrene sulfate) What is compensatory hyperplasia What are the effects of Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) An NSAID safe for use in CAD patients is naproxen NSAIDs can cause GI bleeding (indicated by darkening of stools and epigastric pain); one recommendation is switch to a COX-2 inhibitor (i.e., celecoxib). Corticosteroids include glucocorticoids (e.g., prednisone, prednisolone, dexamethasone, hydrocortisone, methylprednisolone) and mineralocorticoids (e.g., aldosterone). Patients on corticosteroids should be monitored for changes in skin, muscle wasting, blood pressure, weight gain, blood glucose and vitamin D levels, and any vision changes. [Show less] [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 7 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jan 25, 2021
Number of pages
7
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jan 25, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
53

























.png)

 Rasmussen College.png)


