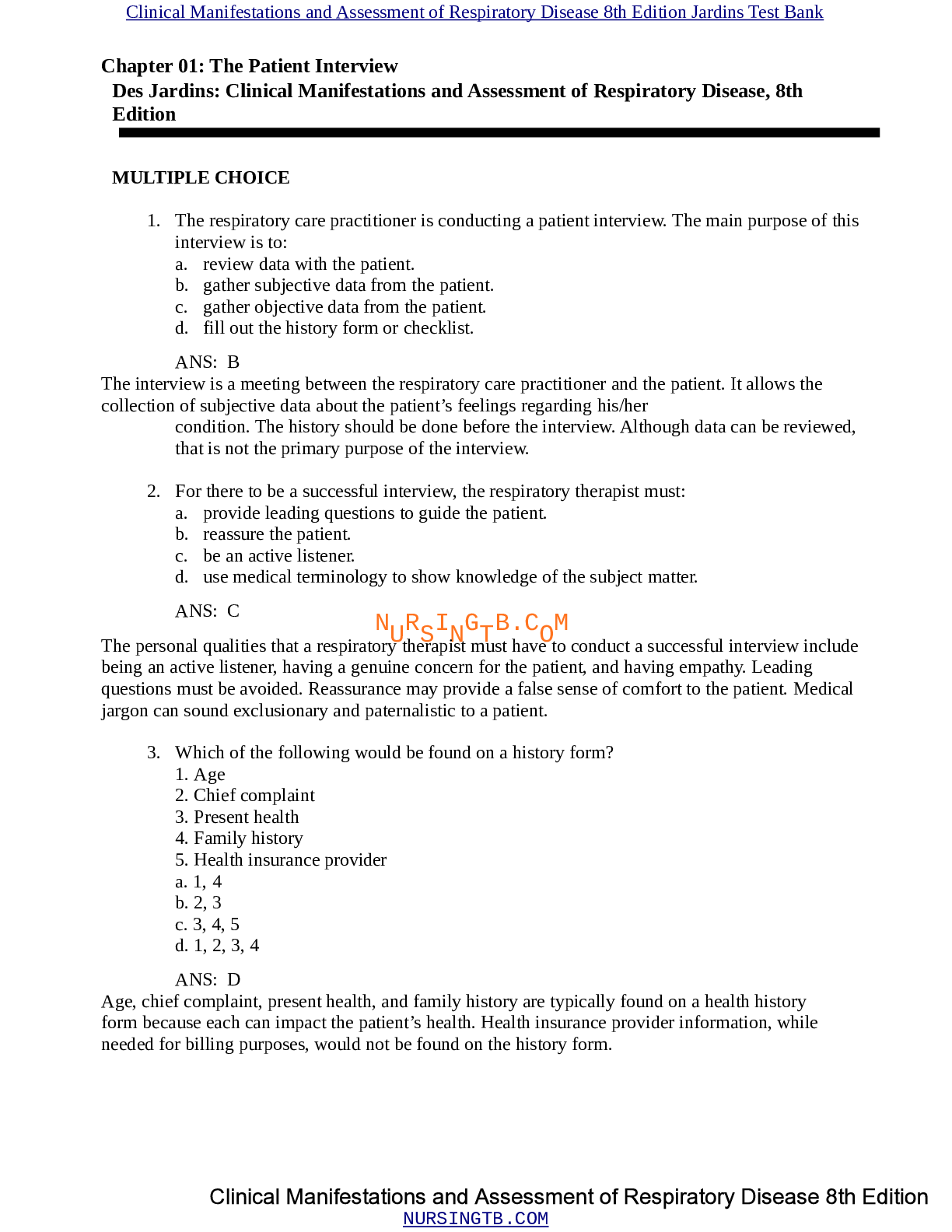*NURSING > TEST BANK > Pulmonary Function Testing Des Jardins: Clinical Manifestations and Assessment of Respiratory Diseas (All)
Pulmonary Function Testing Des Jardins: Clinical Manifestations and Assessment of Respiratory Disease, 8th Edition,100% CORRECT
Document Content and Description Below
Pulmonary Function Testing Des Jardins: Clinical Manifestations and Assessment of Respiratory Disease, 8th Edition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Pulmonary function studies are done for which of the follo... wing measurements? 1. The patient’s carbon monoxide level 2. Lung volumes and capacities 3. Pulmonary diffusion capacity 4. Forced expiratory flowrates a. 1 b. 2, 3 c. 2, 3, 4 d. 1, 2, 3 ANS: C A blood sample must be analyzed by a cooximeter to determine a patient’s carbon monoxide level. All of the other listed options can be measured on a pulmonary function test. 2. In response to a restrictive lung disorder, which of the following is typically found? 1. Decreased lung compliance 2. Increased ventilatory rate 3. Decreased tidal volume 4. Decreased lung rigidity a. 1 b. 2, 3 c. 2, 3, 4 d. 1, 2, 3 ANS: D With a restrictive lung disorder, there will be increased lung rigidity. This causes decreased lung compliance. As a result, the patient breathes faster and with a smaller tidal volume. 3. A special indirect measurement procedure must be done to find which of the following? a. Inspiratory reserve volume b. Residual volume c. Expiratory reserve volume d. Inspiratory capacity ANS: B Because the residual volume cannot be measured by spirometry, special procedures and equipment must be used to indirectly measure it. The other listed options can be directly measured by spirometry. 4. In a healthy individual, which of the following is considered a normal expiratory time necessary to perform a forced vital capacity? a. Less than 4 seconds b. 4 to 6 seconds c. 6 to 8 seconds d. 8 to 10 seconds ANS: B A normal adult will exhale a forced vital capacity (FVC) within 4 to 6 seconds. 5. Overall characteristics of pulmonary function testing results on a patient with obstructive lung disease include that the FEV1: a. is reduced and FEV1% is normal. b. and FEV1% are both increased. c. and FEV1% are both reduced. d. is increased and FEV1% is decreased. ANS: C Because of airway narrowing problems, a patient with obstructive lung disease will have a reduced FEV1 volume and FEV1% flow. A patient with restrictive lung problems may have FEV1 reduced and FEV1% normal. The other combinations are not seen. 6. The FEF25%-75% is used to evaluate: a. flow in large airways. b. lung volumes. c. maximum breathing effort. d. flow in medium-size to small airways. ANS: D The forced expiratory flow 25%-75% (FEF25%-75%) is the average flowrate generated by the patient during the middle 50% of an FVC measurement. This expiratory maneuver is used to evaluate the status of medium-to-small airways in obstructive lung disorders. Other tests would be needed to assess the other listed options. 7. Which of the following are true of the peak expiratory flowrate test? 1. It is effort dependent. 2. It is taken from the FVC test results. 3. It is taken from the MVV test results. 4. It assesses large upper airways. a. 1, 3 b. 1, 2, 4 c. 2, 3, 4 d. 1, 2, 3 ANS: B The maximum voluntary ventilation (MVV) test is used to measure the maximum amount of air that can be breathed in a minute. The peak flow requires maximum effort from the patient, is taken from the FVC test, and assesses flow through the large upper airways. 8. A patient has restrictive lung disease. In response to this, which of the following are typically found? 1. Decreased lung compliance 2. Increased ventilatory rate 3. Increased tidal volume 4. Decreased ventilatory rate a. 3, 4 b. 2, 3 c. 1, 2 d. 1, 3, 4 ANS: C Restrictive lung disorders result in an increase in lung rigidity, which in turn decreases lung compliance. When lung compliance decreases, the ventilatory rate increases and the tidal volume decreases. 9. The pulmonary diffusion capacity of the carbon monoxide test is used to: a. assess the patient’s blood carbon monoxide level. b. remove carbon monoxide from the patient’s blood. c. measure the residual volume. d. assess the alveolar-capillary membrane. ANS: D Alveolar-capillary membrane function is measured by the pulmonary diffusion capacity of the carbon monoxide test. A very small amount of carbon monoxide (CO) is inhaled by the patient to perform the test. But the CO level is not measured in the blood, and CO is not removed from the blood. 10. Total lung capacity is composed of which of the following? 1. IRV 2. IC 3. ERV 4. RV a. 3, 4 b. 2, 3 c. 1, 2 d. 2, 3, 4 ANS: D Total lung capacity (TLC) can be calculated by adding IC, ERV, and RV. 11. A respiratory therapist has just performed a pulmonary function study and notes that the results show obstructive lung disease with a decreased DLCO value. Which of the following is the best interpretation of these results? a. The patient has pulmonary fibrosis. b. The patient has asthma. c. The patient has cystic fibrosis. d. The patient has emphysema. ANS: D A decreased DLCO is a hallmark clinical manifestation in emphysema because of the destruction of the alveolar pulmonary capillaries and decreased surface area for gas diffusion associated with the disease. The DLCO is usually normal in all other obstructive lung disorders. Pulmonary fibrosis is a restrictive disease, not an obstructive disease. 12. The respiratory therapist is called to the neurologic care unit to assess the muscle strength of a patient diagnosed with myasthenia gravis. Which of the following tests should the therapist recommend to assess the patient’s respiratory muscle strength? a. Maximum inspiratory pressure (MIP) b. Maximum inspiratory flowrate (MIFR) c. Maximum expiratory flowrate (MEFR) d. Vital capacity (VC) ANS: A The most commonly used tests to evaluate the patient’s respiratory muscle strength at the bedside are maximum inspiratory pressure (MIP) and maximum expiratory pressure (MEP), forced vital capacity (FVC), and maximum voluntary ventilation (MVV). 13. The respiratory therapist is performing a pulmonary function study on a patient who has periodic symptoms of asthma. The pulmonary function results are within normal limits. What further testing can the therapist recommend to aid in either confirming or negating the possible diagnosis? a. Inhaled methacholine challenge testing b. Body plethysmography c. Inhaled digitalis d. Warm, humid air challenge ANS: A Because some patients have clinical manifestations associated with asthma, but otherwise normal lung function between asthma episodes, measurements of airway responsiveness to inhaled methacholine or histamine, or an indirect challenge test to inhaled mannitol, or to an exercise or cold air challenge may be useful in confirming a diagnosis of asthma. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 5 pages
Instant download

Instant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Feb 17, 2023
Number of pages
5
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Feb 17, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
30