*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > Ob ATI proctored study (All)
Ob ATI proctored study
Document Content and Description Below
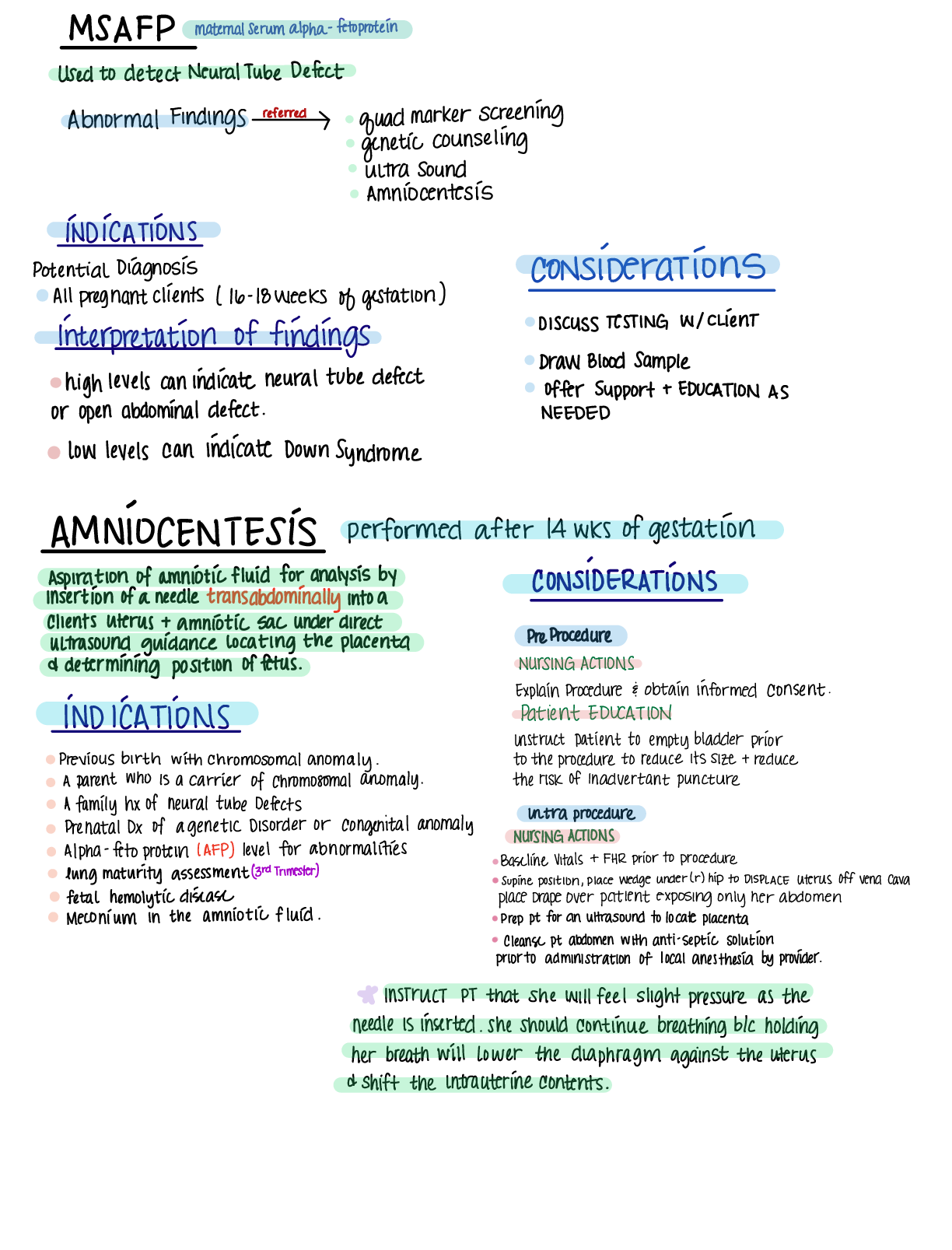
Ob ATI proctored study 1) Cytomegalovirus – is an infection contracted by mother during pregnancy that causes neonate implications of IUGR, Encephalopathy Exposure to toxoplasmosis, rubella, cyto... megalovirus, herpes simplex, and hepatitis B may adversely affect pregnancy and fetal outcome. TORCH Cytomegalovirus (CMV) belongs to the herpes simplex virus group and causes both congenital and acquired disorders. The significance of this virus in pregnancy is related to its ability to be transmitted by asymptomatic women across the placenta to the fetus or by the cervical route during birth. the virus is usually innocuous in adults and children,itmaybefataltothefetus. Asymptomatic CMV infection is particularly commoninchildrenandgravidwomen.Transmissioniscommon indaycarecenters 2) Who see first? 190 sugar, FHR 160 3) Which food has highest fiber? Oatmeal, asparagus A: oatmeal, avavados, bananas, pears, split peas, lentils 4) Client who reported abdominal pain upon breast feeding Why Does It Happen? The uterus is a muscle, and each pregnancy over-stretches the muscle. Nipple stimulation during breastfeeding causes a hormone known as oxytocin to be released into your bloodstream. This hormone causes the contraction of all smooth muscles and helps your uterus contract back into its pre-pregnancy shape and size. These contractions also help reduce postpartum blood loss, so although you may be uncomfortable, this cramping is helping your body heal. What Can You Do? Don’t be afraid to ask for pain medication while still in the hospital – it will be safe for you and your baby. You can also give yourself a gentle lower-stomach massage. These afterbirth pains almost always subside within a few days, but if they continue longer than that or if the pain becomes intense, reach out to your healthcare provider.5) Signs of neonate abstinent syndrome - NAS may occur when a pregnant woman takes drugs such as heroin, codeine, oxycodone (Oxycontin), methadone, or buprenorphine. Tremors (trembling) Irritability (excessive crying) Sleep problems. High-pitched crying Tight muscle tone. Hyperactive reflexes. Seizures. Yawning, stuffy nose, and sneezing. 6) Place test in order alpha-protien, 1 hour glucose Gestational diabtes test: To take the glucose screening test you will drink a sugar solution (which tastes like a thick, flat cola—I'm not saying it's delicious, but it's not all that awful either). An hour later, a blood sample will be taken and the blood sugar level will be checked. If the reading is abnormal (which occurs about 20 percent of the time) you'll go home and come back at a later date for a diagnostic exam, called a three-hour glucose tolerance test, to verify the results. Alpha fetoprotien - screening test for congenital disabilities, chromosomal abnormalities - Alpha-fetoprotein levels in men and non-pregnant women vary for age and race but mostly range from 0 ng/ml to 40 ng/ml. Maternal AFP levels in pregnancy start to rise from about 14th week of gestation up until about 32 weeks gestation. Between week 15 and 20 weeks, levels usually range between 10 ng/ml to 150 ng/ml. -elevated levels imply a significant risk of having birth defects 7) Report HR with – 150/155/135 – acceleration. Decleration, variability Cord compression associated with decelerations Baseline Fetal Heart Rate• Normal baseline FHR = 110 – 160 Accelerations/decelerations are compared to the baseline of the infants HR Late and variable decelerartions are the most risk for fetus because of head or cord compression 8) Induction with misoprototesol Taken orally used to soften and ripen the cervix and to induce labor Women who receive Cytotec to in Guidelines for misoprostol induction include (ACOG, 2009a): ■ The initial dosage should be 25 mcg. ■ Recurrent administration should not exceed dosing intervals of more than 3 to 6 hours. ■ Pitocin should not be administered less than 4 hours after the last Cytotec dose. ■ Cytotec should only be administered where the uterine activity and fetal heart rate (FHR) can be monitored continuously for an initial observation period. Contraindications: : ■ Nonreassuring FHR tracing. ■ Frequent uterine contractions of moderate intensity.duce labor typically deliver within 24 hours of administration. reasons for induction include being overdue, pre-labour rupture of membranes and high blood pressure. Prostaglandins are hormones that are naturally present in the uterus (womb); they soften the cervix and stimulate contractions in labour. 9) Risk for which condition -ectopic pregnancy - Who is at risk for an ectopic pregnancy? All sexually active women are at some risk for an ectopic pregnancy. Risk factors increase with any of the following: maternal age of 35 years or older. -postpartum hemmorage Conditions that may increase the risk for postpartum hemorrhage include the following: Placental abruption. The early detachment of the placenta from the uterus. Placenta previa. ... Overdistended uterus. ... Multiple pregnancy. ...Gestational hypertension or preeclampsia. ... Having many previous births. Prolonged labor. Infection. 10) Mother Rh neg, baby RH postitive? Rh incompatibility is a condition that develops when a pregnant woman has Rh-negative blood and the baby in her womb has Rh-positive blood. You can prevent the effects of Rh incompatibility by getting an injection of Rh immune globulins (RhIg) during your first trimester, A positive indirect Coombs test is a sign of Rh incompatibility 11) 28 weeks gestation with no children. Which is vaccine received? -rebulla . - NO -tetanur or tdap - YES -hpv – NO 11) Dinoprosterone - It can help dilate the opening of the uterus (cervix) in pregnant women. Inserted vaginally Contraindications or dinoprsterone: diabetes; high or low blood pressure; placenta previa; a seizure disorder; six or more previous term pregnancies; glaucoma or increased pressure in the eye Symptoms associated with drug: unpleasant vaginal discharge continued fever chills and shivering increase in vaginal bleeding several days after treatment chest pain or tightness 13)Bilirunib normal leves, urine gravity normal, swelling of breastEXHIBIT: bilirubin 18 USG 1.0 Normal indirect bilirubin in a newborn would be under 5.2 mg/dL Normal bilirubin: 0.1 - 1.2 mg/dL - A specific gravity greater than 1.035 is consistent with frank dehydration. 12) Mother had hepatitis B during pregnancy Babies born to a mother with hepatitis B have a greater than 90% chance of developing chronic hepatitis B if they are not properly treated at birth If you test positive for hepatitis B, then your newborn must be given two shots immediately in the delivery room: first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine one dose of the Hepatitis B Immune Globulin (HBIG). if these two medications are given correctly, a newborn has more than a 90% chance of being protected against a lifelong hepatitis B infection. 13) Magnesium sulfide during pregnancy by continuos IV, what lab should be monitored? Monitoring. The Assessing toxicity patient’s vital signs, oxygen saturation, deep tendon reflexes, and level of consciousness should be monitored. Monitoring of fetal heart rate and maternal uterine activity is also essential if the drug is used for preterm labor. The patient should be assessed for signs of toxicity (e.g., visual changes, somnolence, flushing, muscle paralysis, loss of patellar reflexes) or pulmonary edema. If these signs are observed, a physician must be notified. During bolus administration, a staff member should remain at the patient’s bedside to oversee continuous monitoring. Subsequent assessment intervals of 15 minutes are suggested for the first hour, 30 minutes for the second hour, and then hourly magnesium sulfate for treating preterm labor and pre-eclampsia 14) Which image erythema toxicum is a common rash in neonates. It appears in up to half of newborns carried to term, usually between day 2–5 after birth; it does not occur outside the neonatal period.16)Yellow discharge forming at circumcision site Yellow discharge typically goes away within one week. This is not pus or a sign of infection17) Client has cocaine disorder, monitor for potential complications? -abrupto placenta - Placental abruption (separation of the placenta from the uterine wall). -chorioamnio – yes if multiple choice chronic villitis – yes if multiple choice 18) Client who is breast feeding, instructions nurse include? Breastfeed 8-12 min in 24 hour period -newborns who are breastfed will average 15-20 min per breast -feedings should be on demand every 2-3 hours -no other fluids offered to newborn unless instructed by doctor -specific timing feedinds should be avoided and only on demand -most newborns spit up small amounts of milk after feedings and should be sat up and kept quiet for a few minutes after feedings -breastfed newborns should have 3 or more BM’s per day and 6 or more wet diapers 19) Client mitral valve stenosis? rheumatic mitral stenosis is the most common cardiac disease found in women during pregnancy. The typical increased volume and heart rate of pregnancy are not well tolerated in patients with more than mild stenosis. - Maternal complications of atrial fibrillation and congestive heart failure can occur -Labour and delivery goals include reducing tachycardia by adequate pain control and minimized volume shifts - adverse maternal events in women with mitral stenosis include pulmonary edema, arrhythmia and thromboembolism Adverse fetal outcomes associated with mitral stenosis include preterm delivery, intrauterine growth retardation, low birth weight and fetal or neonatal death Management: patients with mild-moderate mitral stenosis may first become symptomatic and be diagnosed during pregnancy when increased plasma volume and resting heart rate stress20) Phenylketonuria - A birth defect that causes an amino acid called phenylalanine to build up in the body. Without the enzyme necessary to process phenylalanine, a dangerous buildup can develop when a person with PKU eats foods that contain protein or eats aspartame, an artificial sweetener. This can eventually lead to serious health problems. PKU signs and symptoms can be mild or severe and may include: A musty odor in the breath, skin or urine, caused by too much phenylalanine in the body Neurological problems that may include seizures Skin rashes (eczema) Fair skin and blue eyes, because phenylalanine can't transform into melanin — the pigment responsible for hair and skin tone Abnormally small head (microcephaly) - Babies born to mothers with high phenylalanine levels don't often inherit PKU. But they can have serious consequences if the level of phenylalanine is high in the mother's blood during pregnancy. Complications at birth may include: Low birth weight Delayed development Facial abnormalities Abnormally small head Heart defects and other heart problems Intellectual disability Behavioral problems -Prevention: If you have PKU and are considering getting pregnant: Follow a low-phenylalanine diet. Women with PKU can prevent birth defects by sticking to or returning to a low-phenylalanine diet before becoming pregnant 21) 21 weeks gestation and has trichomoniasis Trichomoniasis – is an STI transmitted through skin to skin contactIf a trichomoniasis infection is left untreated during pregnancy, it can increase a woman’s chances of a pre-term delivery and low birth weight. Both of these can affect the baby’s development, overall health, and time spent in the hospital after birth. treatment for trichomoniasis is a large single dose of antibiotics, typically metronidazole or tinidazole. Common brand names for these are Flagyl or Tindamax. 22) Nurse caring for newborn who is 2 days old -babinski reflex 23) Who has a prescription for rubella immunization -not during pregnancy especially in early pergnancy 24) Hct of 25% Hematocrit 44% - 64% are normal values in newborn. This is low. High hct indicates dehydration. Reasons for low hct: The baby’s body does not produce enough red blood cells. The body breaks down red blood cells too quickly. 25) Full term newborn admitted to nursery, report what condition? 26) ) Client has a contraindication for a contraction stress test? A: Reasons CSTs should not be performed prior to 28 weeks gestation 1. In light of positive test, birth and extrauterine survival would be questionable at such an early gestational age 2. Research has not been performed to show that the test applies to early gestations 27) Client has 4th degree laceration of perineum fourth degree tear goes through the anal sphincter all the way to the anal canal or rectum. These tears require surgical repair and it can take approximately three months before the wound is healed and the area comfortable. 28) Teaching to client about post-partum care29) nonpharm pain management during labor 30) Newborn whos mother has a cocaine disorder APGARS - Evaluation tool only! Intervention should start prior to 1 minute as needed. Done at 1 and 5 minutes and 10 mins if APGAR at 5 mins < 7 APGAR Results - 0 to 3 indicate severe distress - 4 to 6 indicates moderate difficulty - 7 to 10 indicates that the newborn is having minimal or no difficulty adjusting to extrauterine life Thermoregulation - Normal Axillary Range > 36.5C (97.7F) to < 38.0C (100.4F) Skin Color - Mottled -lacy pattern of dilated blood vessel under the skin. -result of general circulation fluctuations or when newborn is cold. Normal Heart Rate Range - 110 to 160 bpm - Normally the heart has a toc-tic sound. - 90% of all murmurs are transient and considered normal. Half disappear by age 6 months. Respirations - Normal Respiratory Rate > 30 and < 60 bpm- Respirations are diaphragmatic, with associated rising and falling of abdomen. - Breath sounds are heard better when the newborn is crying. Respirations - Normal O2 Saturation Range - Term >90% - Preterm >90-95% Normal Cry Sounds - Cry-strong, lusty and medium pitched. - High pitched, shrill cry may indicate neurologic disorders or hypoglycemia Signs of Respiratory Distress - Rapid rate - Nasal flaring - Grunting Retractions Normal Blood Pressure - systolic >50 - diastolic >30 (if not >30, recheck later) Jaundice - First detectable on face where skin overlies cartilage and mucous membranes - Occurs in 50-60% of term newborns - Blanch tip of nose, forehead or gum line, area appears yellowish immediately after blanching - Pathologic within 24hrs or persisting for > 7 days - Physiologic after 24 hrsNewborn Feeding Readiness (Hunger Cues) - Rapid eye movement under lids - Sucking movements - Hand to mouth movements - Body movements - Small sounds - Rooting When to Initiate Newborn Feeding - Assess newborn breathing, suck & swallow - Breastfeeding - immediately after birth within first half hour - Bottle feeding - when newborn shows cues - Feed early, especially if newborn at risk for hypoglycemia LGA LGA >90th % for weight - Increase risk of birth trauma, hypoglycemia, hypocalcemia, hyperbilirubinemia, meconium aspiration, and polycythemia. SGA <10th % for weight - Increase risk of hypoglycemia, asphyxia, respiratory distress syndrome, meconium aspiration, intrauterine infection, and hyperbilirubinemia Breastfeeding Recommendations - First six months, up to two yearsAdvantages of Breast Milk for Baby Antibodies—Protects against infections Decreases risk of allergies Essentials for growth Protects against obesity Enhances cognitive development ( 8 IQ pts) Decreases risk for Diabetes Decreases risk of Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS) Breast Milk - Colostrum - First 2-3 days - Gold or yellow, Thick - Colostrum amount matches the size of the newborn's stomach - High protein content due to increased immunologic content; high levels of antibodies—passive immunity - Establishes normal GI track flora - Helps eliminate bilirubin as it has a laxative effect Breast Milk - Mature Milk - After 2 weeks - 10% solids (carbs, proteins, fats) for energy and growth - 90% water for hydration Steps to Latch On Positioning, pillows, pillows and more pillows Get mom and baby comfortable Stimulate rooting reflex Baby to open mouth WIDEBaby to latch onto the nipple + areola, not just the nipple Breastfeeding Assessment - LATCH Score Out of 10 L-Latch A-Audible swallowing T-Type of nipple (inverted, flat, everted) C-Comfort (breast and nipple) H-Hold (assistance and positioning) Bilirubin levels: in a newborn, higher bilirubin is normal due to the stress of birth. Normal indirect bilirubin in a newborn would be under 5.2 mg/dL Normal infant; Weight: 2,500-4000 grams (5.5-8-8 pounds) Length: 45-55 cm Head: 32-37 cm Chest: 30-33 cm [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 14 pages
Instant download

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jan 29, 2021
Number of pages
14
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jan 29, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
43