*NURSING > ATI > West Coast University, ATI|NURS 100 Nursing Fundamental Final Study Guide,100% CORRECT (All)
West Coast University, ATI|NURS 100 Nursing Fundamental Final Study Guide,100% CORRECT
Document Content and Description Below
West Coast University, ATI|NURS 100 Nursing Fundamental Final Study Guide WEEK 1 - Medical Asepsis – CLEAN TECHNIQUE - Surgical asepsis – STERILE TECHNIQUE - Clean the last soiled areas firs... t to prevent moving more contaminate - Vital Signs o BP: Less than 120/80 NORMAL o NOTE: 120/80 is considered prehypertension - Oxygen Saturation: 95-100 unless COPD then it is okay to be normal. o Example – if a patient that has COPD and is on oxygen and their O2 saturation is 99% that’s a problem since its too damn high for COPD - Respiratory Rate: 12-20 Breaths/minute o NORMAL - Pulse Rate: 60-100 Beats/Minute o Normal - Temperature: 96.8-100.4 o Rectal Temp is 0.9F higher than oral and tympanic o Axillary temp is 0.9F lower than oral and tympanic o Temporal is 1F higher than oral and 2F higher than axillary - Know PQRST for assessing patient with pain o Provocation: What caused it? o Quality: What does it feel like? o Radiate:where does it hurt?location? o Scale:Severity 0-10 o Time-how long has it been hurting - Prioritizing vital signs; who to assess first(Remember ABC) o Baby with high fever and diarrhea for three days o Older patient with diarrhea for days and cant breath. - Korotkoff Sounds o Phase 1: Characterized by first appearance of faint; first sound of systolic o Phase 2: Characterized by muffle/swishing. Sounds may also temporarily disappear also called auscultatory gap o Phase 3: Characterized by distinct, loud sound as blood flows relatively free through an increasingly open artery o Phase 4: Characterized by distinct, abrupt, muffling sound with sound, blowing quality. Considered to be the first diastolic pressure o Phase 5: The last sound heard before period of continuous silence. Also the second diastolic pressure - Communication(therapeutic/non therapeutic) o Do not ask WHY o Use open ended questions and o Touch is therapeutic ▪ Sympathetic touch on a patient who just found out they have cancer WEEK 2 - Know Head to toe assessment and know why you’re checking them – BRADEN SCALE - Skin turgor o Use to check for dehydration o Grasp a skin fold on the chest under the clavicle, release it, and note whether it springs back. o If you see “tenting” occur, it can mean that patient is dehydrated o LOOK AT STERNAL BORDER (so CLAVICLE is CLOSEST to STERNUM) - PERRLA o P: Pupil clear o E: Equal and between 3-7 mm in diameter o R: Round o RL: Reactive to light o A: Accommodation - Abnormal breath Sound o Crackles: Coarse bubbly sound like rice Krispy; usually with pneumonia, HF, bronchitis, when there's fluid in the lungs o Wheezing: High pitched whistling; usually with asthma, tumors or buildup secretion o Rhonchi: Coarse, loud, low pitch; snoring/COPD patients o Absence of breath: from lung collapse of atelectasis (do not hear lung sounds) o Stridor: Airway obstruction in children; barking sound(choking); is an Emergency - 5 landmarks for heart (APETM) o Aortic; Right 2nd intercostal o Pulmonic; Left 2nd Intercostal o Erb; left 3rd intercostal o Tricuspid; left 4th intercostal o Mitral; Left 5th intercostal; also, site of maximal impulse AKA apical pulse - Abdomen Assessment: o Inspect, Auscultate, percuss, palpate (Big on abdomen) o Auscultate order: Right lower→ Right upper→ Left upper→ Left Lower - When checking for pulse; you PALPATE - When checking Capillary refill o When checking refill, it should refill within 2 seconds o If it takes 3-4 seconds, it is unexpected finding o Assess by applying firm pressure to the nail bed to blanch it. - Checking for Edema o Compress skin for at least 5 seconds over bony prominence o 1+= Trace, 2mm o 2+=Mild, 4mm o 3+=Moderate, 6mm o 4+=Severe, 8mm - All pusles except for Carotid you can check bilaterally o (do not check carotid at the same time or bilaterally) - Safety Questions o Bed at lowest position o Make sure Brakes are on o No clutter on floor o Make sure oxygen works - RACE(Rescue, Pull alarm, Confine fire, Extinguish) - Restraints o Last resort o Check for circulation at least every 2 hours o Only use it if everything else fails o Make sure restraint is loose enough to fit 2 fingers o 4hr=adult; 2hr=age 9-17 and 1 hour for clients younger than 9 - Infection Control o Wash 15-20 seconds o 3 to 5 mL of soap o Infection control is important to prevent micro organisms o The nurse washes with her hands held higher than her elbows. - PPE Removal (Gloves→ Eyewear(goggle)→ Gown→ Mask→ Hand wash) - Airborne o Use for MTV, measles, tuberculosis, varicella o N95, negative pressure, private room, mask) - Droplet o Use for pertussis, mumps, pneumonia o Private Room and Mask - Contact o Wound infection, herpes, RSV, MRSA o Gown, Gloves, Private Room, disposal of infectious dressing items. - If IMMUNOCOMPROMISED – PROTECTIVE precaution - Asepsis and Sterile Technique Principles o Clean the last soiled areas first to prevent moving more contaminate o DO NOT REACH across or above the sterile field o DO NOT TURN YOUR BACK on sterile field o NOTHING BELOW YOUR WAIST when in sterile field o STERILE CAN TOUCH STERILE o The outer wrapping and 1 inch edge is not sterile o Open flap AWAY from the body - Hygiene o When Bathing patient ; Ask them when they prefer to take baths and see if they can do it by themselves, always try to keep them independence WEEK 3 - Bed Position for patient o Semi Fowler: 15-45; prevent regurgitation and aspiration; also when measuring respiratory rate and dyspnea o Fowler: 45-60; NG tube and suctioning; maximum breathing o High fowler: 60-90; promote lung expansion and relief severe dyspnea o Prone: Patient lie flat on abdomen; promote drainage and help prevent hip flexion; use after throat or oral surgery or lower extremity amputation o Lateral or side: Lies on side with most of his weight; help with pressure injuries o Sims: Patient is on his side halfway; promote oral drainage, used for ENEMA and rectal o Orthopneic: Patient sits on side of bed and rest arm over pillows on top of bedside table; help with COPD o Modified Trendelenburg: Treat hypovolemia and shock o - Body Mechanic o Bend hips and knee o Spread your feet apart to lower center of gravity o When lifting an object, flex your hips, knee and back. o Always hold the object as close as possible to your body - Sleep Apnea o Condition in which you stop breathing o Is life threatening o Include hallucination and sudden Sleep attacks o use CPAP to help with condition o - Sensory function o Auditory (Hearing) o Olfactory (Smell) o Gustatory (Taste) o Tactile (Touch) o - 4 Stages of Pressure Ulcer o STAGE 1: non-blanchable erythema; if it does not turn white and its constantly red, it is stage 1 <-- transparent wound dressing o STAGE 2: partial thickness skin loss with exposed dermis(can be serum filled blister, fat is not visible on this stage, no slough) o STAGE 3: Full thickness skin lost(Fat is visible, slough may be present and can be undermining and tunneling) o STAGE 4: full thickness skin and tissue lost(exposed bone/tendon, slough and dead tissue, escar) o Intervention: Turn the patient Q2(2 hours), Proper diet of high protein, hydrate patient o Do not use powder or cornstarch to prevent friction or repel moisture due to their abrasive grit o Do not massage bony prominences - Bowel Elimination - Flatus: Gas generated in the intestinal tract or gas passed through the anus. (A good sign that the GI is moving stuff through) - Peristalsis: series of wavelike muscle contractions that helps us move the food we eat throughout the body to other organs - Paralytic ileus: Where there’s no movement/activity, usually right after surgery - Encourage patient to walk to promote gas - Promoting bowel habits for constipation - Promoting patient who can’t move though movement/physical activity (ROM exercises and change of position) - Hydrating patient by increasing water consumption - Promote high fiber - Give bulk forming products like whole grain, fresh fruit, wheat bread - If patients have diarrhea, DO NOT GIVE STOOL SOFTENER - Enemas are last resort Week 5 - Med administration o 6 Rights o Right Patient, dose, time, route, medication, documentation) o Pt do have the right to refuse but as nurses, you want to ask them why they are refusing it to maybe order something different or give an alternative - Types of Orders - STAT (Carried out immediately) - NOW (90 minutes time frame) - PRN (As needed) - Single (one time prescription such as analgesic before surgery) - - Insulin o INJECT AIR Cloudy Clear, DO NOT TAKE OUT OF CLEAR, withdraw from CLEAR cloudy - Injection and the Sites o Dermis/epidermis o SubQ o IM o Adipose - Idiosyncratic Effect: Opposite Effect of intended desire - Know that nurses are the ones responsible when administering medication - If something doesn’t sound right, call the provider - Medication Policies o if you spill the med before giving it; send back to pharmacy o If you spill the med after giving it; have second nurse, verify o always have second nurse verify for insulin o if disposing mediation; have second nurse verify - AC-Before meal - PC-After meal - HS-Bedtime - - Week 6 - Clear liquid (Cranberry, grape juice, broth, hard candy, jello, gelatin, black coffee no cream) - full liquid (Ice cream, yogurt, Lemon Sherbet, Custard) - Pureed (For patients with dysphagia, scrambled eggs) - 1800 calories for diabetic (ADA diet) - Provide 30 minute rest before meal - Sit patient upright in chair - If bed rest is mandatory, elevate head of bed to 90 - Avoid rush/force feed NG Tube ○ Chest x ray to verify ○ Start at nose→ Ear→ Xiphoid process ○ You want to Pinch the NG tube while removing the tube 1)Perform hand hygiene, and apply clean gloves. 2)Insert tip of syringe into NG tube, and slowly inject 30 mL saline 3)Reconnect the NG tube to suction. 4)Slowly aspirate the syringe. 5)Clamp and disconnect the NG tube ● Fluid Volume Deficit(Hypovolemia) ○ Cause ■ NG suctioning, Diaphoresis, Loss of fluids from wound, Impaired swallowing, Vomiting, Anorexia ○ Signs ■ Thready Pulse, flattened neck veins, hypotension, skin turgor, diminished cap refill, cool clammy skin, confusion ● Fluid Volume Overload(Hypervolemia) ○ Cause ■ HF, Cirrhosis, Increased glucocorticosteroids, Kidney failure, hypertonic fluids, burns, excessive sodium intake from IV ○ Signs ■ Bounding Pulse, Distended neck veins Hypertension, tachycardia, muscle weakness, weight gain, Dyspnea, Crackle, orthopnea, edema ● Hyperkalemia (Potassium greater than 5.0) ○ Cause ■ Ace inhibitors, kidney failure, diabetic ketoacidosis, IV ○ Signs ■ Slow irregular Pulse, Peaked T waves, Widened QRS, cardiac arrest, increased motility, diarrhea, hyperactive bowel sounds, Confusion, lack of reflex, abdominal cramps ○ Never Give IV push/bolus because it can cause cardiac arrest ● Hypokalemia (Potassium less than 3.5) ○ Cause ■ GI Loss-Vomiting, Diarrhea, Ng Tube ■ Kidney Loss- Diuretics Nursing Fundamental Final Study Guide ■ Skin Loss- Diaphoresis, wound loss ○ Signs ■ Weak irregular Heart, Flattened T waves, ST depression, decreased motility, vomiting, hyperthermia, hypotension, orthostatic hypotension, respiratory distress ○ If you give IV fluid, give it with dextrose ● Foley catheter ○ If patient complain about having to urinate, you want to check the kink and make sure it's off the floor to prevent urinary infection ● Stress Incontinence ○ When they laugh/sneeze/cough;pees come out ○ Most common in the hospital ○ Hematuria(Blood in urine) ○ Voiding(Peeing) ○ Incontinence(Inability to control pee) WEEK 7(33, Oxygenation) ● Nasal cannula ○ Tubing with two small prongs for insertion into nares ○ Low flow oxygen delivery system ○ Delivers an FIO2 of 24% to 44% at a flow rate of 1-6L/min ○ Pros: Safe and simple, comfy and well tolerated, pt can eat, talk and ambulate ○ Cons: Can cause skin breakdown and dry mucous, tubing is easily dislodged and FIO2 varies with flow rate ○ Interventions: Assess patency of nares, ensure that prong fits properly, use water soluble gel to prevent dry nares, provide humidification for flow rates of 4L/min and greater ● Making sure that if patient is in respiratory distress after surgery, first thing you want to do is elevate the head ● Incentive spirometer ○ Prevent atelectasis and prevent pulmonary infection ○ Also use after surgery to prevent pulmonary infection ○ Promote Lung expansion ○ You tell the patient to Inhale when using it ● Types of MDI ○ Bronchodilators(Open airway) ○ Expectorants(Make you cough up all the mucous and secretion) ■ Use for congestion cold and cough ○ Mucolytic(Liquify and loosen secretion) Nursing Fundamental Final Study Guide ○ Corticosteroids(Reduce inflammation) Week 8(Loss, Grieve, Dying) ● 5 stages of Kubler-Ross Model ○ Denial: Patient has difficulty believing a terminal diagnosis or loss ○ Anger: Patient lashes out at other people or things ○ Bargaining: Patient negotiate for more time or a cure ○ Depression: Patient is overwhelmingly saddened by inability to change the situation ○ Acceptance: Patient acknowledge what is happening and plans fo the future by moving forward ● 2 types of advanced directives ○ Allows patient to specify instruction for health care treatment should they be unable to communicate ○ 1) Living will: Provide specific instruction about the kinds of health care that should be provided or foregone in a particular situation ○ 2) Durable Power of Attorney(DPOA): Appoints an agent the person trust to make decision in the event of subsequent incapacity ● Facilitate mourning ○ Grant time for grieving process ○ Identify expected grieving behaviors such as crying, somatic manifestation and crying ○ Use therapeutic communication such as “ You sound as though you are angry” ○ Use active listening, open ended questions, paraphrasing, clarifying ○ Use silence and personal presence ○ Do not offer false reassurance, giving advice, changing the subject and taking focus away from grieving individual ● Preparation of body ○ Maintain privacy ○ Remove all tubes unless organs are to be donated ○ Remove all personal belongings and give to family ○ Brush/comb patient’s hair ○ Remove excess supplies, equipments, and soiled linens from room Nursing Fundamental Final Study Guide ● BEEFY RED IS NORMAL COLOR for stoma and Purple require surgical intervention ● After diarrhea stops, suggest patient to eat yogurt to help establish intestinal balance ● Food like red meat, citrus fruit, raw veggies and meds can cause false positive result ● BLEEDING IS AN INDICATION OF CANCER ● Blue color indicate that the stool is positive for blood ● when patient has blood and cramping you need to STOP IT - for enemas ● If cramping or fluid leak around the tube at the anus, you slow down the flow of solution by lowering the container; Blood is red flag to stop ● If question say patient is cramping, answer is to slow down solution ● best position is fowler to use for bed pen *important for back to be elevated ● Most common place is sacral coccyx area for pressure ulcers ● Salem Stump= Use for DECOMPRESSION Nursing Fundamental Final Study Guide ● Priority if you see patient’s organ pop out is to get a clean towel and put on top of organ ● Evisceration=Popping and Dehiscence=wound separation ● IM injection Solution volume is usually between 1-3 mL ● Solution for deltoid should be limited to 1 mL but up to 2 mL depending on size ● Kidney excretes most drugs through the urine ● If patient is vomiting; administer IV First ● Know that a spacer decreases amount of med in the oral pharynx ● Hypokalemia affect the heart and causes arrhythmia, ● Patient with hyperkalemia can go into cardiac arrest ● Phlebitis-inflammation of the wall of a vein; usually have redness(erythema), discomfort, pain or swelling ● Infiltration-When needle is no longer in vein and fluid starts to build up which causes edema, skin will feel cool, pale discomfort and swelling. ● First thing you do is STOP IV pump infusion from flowing for either phlebitis or infiltration ● pt w/ dysphagia need THICK LIQUID DIET and make sure they’re TILTING HEAD FORWARD ● Encourage patient to deep breath and cough if they have hypoventilation ● If patient have crackles in left lung, encourage coughing ● Instruct the patient to make each breath deep enough to move the bottom ribs. ● People with dyspnea and orthopnea are most comfortable in a high Fowler’s position because accessory muscles can easily be used to promote respiration. ● Encourage patients to breathe through the nose, with the mouth closed. PALS TUTOR FOR FINAL ● Remember APETM (APE To Man) ● Aortic; right 2nd intercostal ● pulmonic; Left 2nd intercostal ● Erbs; Left 3rd intercostal ● Tricuspid; Left 4th intercostal ● Mitral; Left 5th intercostal ● Use bell to listen to murmur ● For Orthostatic Hypertension, assess by lying sitting standing and check pressure each time - Drop of 20 systolic and 10 in diastolic indicate orthostatic ● have patient slowly get up and sit on edge of bed and dangle their feet ● Patient with orthostatic tend to have Dizziness or nausea Nursing Fundamental Final Study Guide ● If patient are at risk; lock the brake when ambulating, put sign at door, yellow slip socks, lower the bed, use hand rail in bedroom and provide night light if they wake up to urinate ○ Keep them close to nurses station if they are at risk for falls ○ Use gait belt for ambulating if patient at risk for fall Atelectasis ○ Good intervention for atelectasis postoperative patients is to encourage them to deep breathe or cough, If it doesn’t work, provide incentive spirometry ○ atelectasis patient will have no lung sounds Lung Sounds ○ Barking-stridor which indicate obstruction/choking - heard at inhalation ○ Ronchi-Loud, low pitched snoring sound ○ Crackles-Rice crispy ○ Wheezing- High pitched sounds at exhale - Musical sounds Inspections of Body Parts ○ For abdomen: Inspect, auscultate, percuss, palpate ○ For normal:Inspect, Percuss, palpate, auscultate ○ For dark skin patient, check their oral mucosa, soles of feet and conjunctivae Precautions ○ used airborne precautions for Tb patients along with negative air pressure ○ Give patient surgical mask if transferring out of room ○ For whooping cough, use droplet precaution PPE ● When removing PPE- Gloves—->Eyewears—>Gowns—->mask ● For MRSA, when cleaning you want to use clean gloves Restraints ● Restraints- Quick release knob, always check pulse site and that you can put 2 fingers and for adults make sure you renew every 24 hours but you can keep it on for 4 hours for adults ● Request one on one, dim the lights, give distraction before using restraints Nursing Fundamental Final Study Guide Positioning the patients ● Fowlers is 45-60 ● High fowler is used for difficult breathing because it promote lung expansions ● Put patient on fowler when eating Delegations ● LVN/CNA cant not EAT(Explain, assess and teach) ● CNA usually perform activities of daily(ADL) living like ambulating ● Nurse can give 2L oxygen of nasal cannula without doctor’s order ● Apnea-absence of breath sounds ● cheyne stoke- Periods of hyperventilation with apnea(indicate of patient almost dying) - Kene stroke – a deep breath, a shallow breath, then no breath (apnea) Narcolespy ● Narcolespy-vivid dream and sudden sleep attack and REM ● Encourage nap throughout the day for narcoleptic patient Braden Scale ● For skin, braden scale is used for pressure ulcer ● Lower the number, the higher the chance ● Higher the number, the lower the chance ● Assess the scale every shift ● Patient at risk for skin breakdown: Turn the patient every 2 hour, increased fluids of 2-3L a day, increased protein, calcium intake ● For UTI; Wipe front to back with female and give cranberry juice for preventive, Have females pee after sex. E Coli is number 1 caused factor ● polyuria- too much urine ● Guiac/fecal occult test assess for blood in stool ● For colonoscopy- checks for cancer Nursing Fundamental Final Study Guide ● For ampules, tap the top then break it towards your body and clean with pad ● Most common meds given sublingual are nitroglycen(Used for chest pain) ● IM=90 Subcutaneous=45 ● Now prescriptions=90 minutes ● Acceptable identifiers are name, date of birth ● Need another nurse to witness if you want to dispose items ● If you have needle injury, wash with soap/water ● Hard candy and lemon sherbet is a clear liquid diet ● Ice cream and yogurt is a full liquid diet ● Signs of dehydration include tachycardia, flat veins, tenting, thready ● Swollen, red for IV means you have to remove it and put it at a different site ● Tie bed frame for restraint knob ● Use 4-5 mL of soap for hand wash ● If patient mastectomy sign that shows patient has it is if they won’t look at it ● AC-Before meal ● PC-After Meal ● HS-Bedtime ● If patient doesn’t speak english, call a translator ● Fastest route for med is IV ● Order EKG for hypokalemia/hyperkalemia patient ● Signs of choking is weak cough; use hemlick ● Pyridium turns secretion, sweats and tears to orange; use to treat tb ● If you dropped the medication, you want a second nurse to verify ● For Insulin, heparin, opioids; you always want a second nurse to verify before administering, withdrawing and administer ● If you spill a bottle and you haven't used it or labeled gets messed up, you would send it back to the pharmacy ● Spacer is used to help decreased the amount of meds delivered to your lungs ● For Hinduism, you’re not able to touch their lips when giving medication ● Hospice is end of life(6 months of life or less), pain management, keep them comfy, don’t do vitals that often ● Palliative care is relieving signs and care ● if patient have ankle injury; you rest, elevate, Ice and compress( RICE) ● If leg is swollen and red, you do not elevate it or ice it ● Patient can only use their own crutches because its fitted for them, also 6 inches ● move 6-12 inches in front of strong foot and then move the affected leg forward evenly with the cane then unaffected leg in front of cane, then cane ● Right crutch forward and left foot forward after ● If patient have black stool, ask if they are taking any iron supplement Nursing Fundamental Final Study Guide ● Give diuretics in the morning so patient will not get up in middle of the night to pee ● WBC will be elevated if there is infection, normal WBC is 5-10k ● Remember ABC’s for patient priority if there’s no ABC prioritize safety ● If patient is unresponsive and respiration is under 6, that is not a priority ● Occupational therapy helps with ADL like eating ● Physical is more for movement like ambulating ● HIPPA- For patient protection and privacy ● Discharge planning starts on admissions ● Wash face first when washing patient ● SBAR(Situation, background, assessment, recommendation) ● Race(Remove/rescue client, pull alarm, confine fire, Extinguish fire) ● Nocturia-Urinating at night ● Ask open ended questions to discuss feelings and concerns ● When was the last time you took your med, when was last time you had bowel? These types of closed ended are okay ● Modifying factors diet/exercise/weight ● Non Modifying: Things that can not be changed like allergies ● The nurse should instruct the client to move the cane and then advance his weak leg forward to the cane, followed by advancing the stronger leg past the cane. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 15 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Recommended For You
*NURSING> ATI > [NGN] 2023/2024 ATI PN COMPREHENSIVE EXIT EXAM NGN (Latest ) Questions & Answers/ Guaranteed A+ (All)

[NGN] 2023/2024 ATI PN COMPREHENSIVE EXIT EXAM NGN (Latest ) Questions & Answers/ Guaranteed A+
[NGN] 2023/2024 ATI PN COMPREHENSIVE EXIT EXAM NGN (Latest ) Questions & Answers/ Guaranteed A+//////[NGN] 2023/2024 ATI PN COMPREHENSIVE EXIT EXAM NGN (Latest ) Questions & Answers/ Guaranteed A+////...
By Rixx Dennis , Uploaded: Jul 27, 2023
$50.5
*NURSING> ATI > ATI EXIT RN Comprehensive Predictor Exam With NGN (Q&As) Graded A+) (All)

ATI EXIT RN Comprehensive Predictor Exam With NGN (Q&As) Graded A+)
• A nrse is reviewing the medical record of a client who has a prescription for intermittent heat therapy for a foot injury. Which if the following findings should the nrse identify as a contraindicat...
By Rixx Dennis , Uploaded: Apr 23, 2024
$45.5
*NURSING> ATI > ATI RN COMPREHENSIVE LATEST EXAM PREDICTOR QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS || 2024 GRADED A+ (All)

ATI RN COMPREHENSIVE LATEST EXAM PREDICTOR QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS || 2024 GRADED A+
1. Nurse Ronn is assessing a client with possible Cushing’s syndrome. In a client with Cushing’s syndrome, the nurse would expect to find: a. Hypotension. b. Thick, coarse skin. c. Deposits of adip...
By Rixx Dennis , Uploaded: Apr 23, 2024
$45.5
*NURSING> ATI > ATI - MedSurg Proctored test Bank updated for 2022-2023 (All)

ATI - MedSurg Proctored test Bank updated for 2022-2023
The ATI MedSurg Proctored Test Bank has been updated for 2022-2023. A nurse caring for a client receiving a blood transfusion notes bounding peripheral pulses, hypertension, and distended jugular vein...
By ProfXams , Uploaded: Nov 24, 2021
$16
*NURSING> ATI > ATI PHARMACOLOGY PROCTORED ASSESMENT & REVIEW, WELL STUDIED AND REVISED Q&A (All)

ATI PHARMACOLOGY PROCTORED ASSESMENT & REVIEW, WELL STUDIED AND REVISED Q&A
ATI Pharmacology – Proctored Review A patient newly diagnosed with hypothyroidism is prescribed Levothyroxine (Synthroid) 0.25 mg PO daily. After 6 weeks of treatment the nurse dtermines that the me...
By Anonymous 98%+ , Uploaded: Jun 14, 2021
$13
*NURSING> ATI > ATI Mental Health A B and C Graded Score 100% (All)

ATI Mental Health A B and C Graded Score 100%
ATI Mental Health A,B& C 1) A nurse is teaching a client who has schizophrenia about her new prescription for risperidone. Which of the following statements should the nurse include in the teac...
By AplusSuccessor , Uploaded: Apr 06, 2021
$16
*NURSING> ATI > ATI Maternity - Detailed practice Answer Key Updated for 2021/2022 (All)
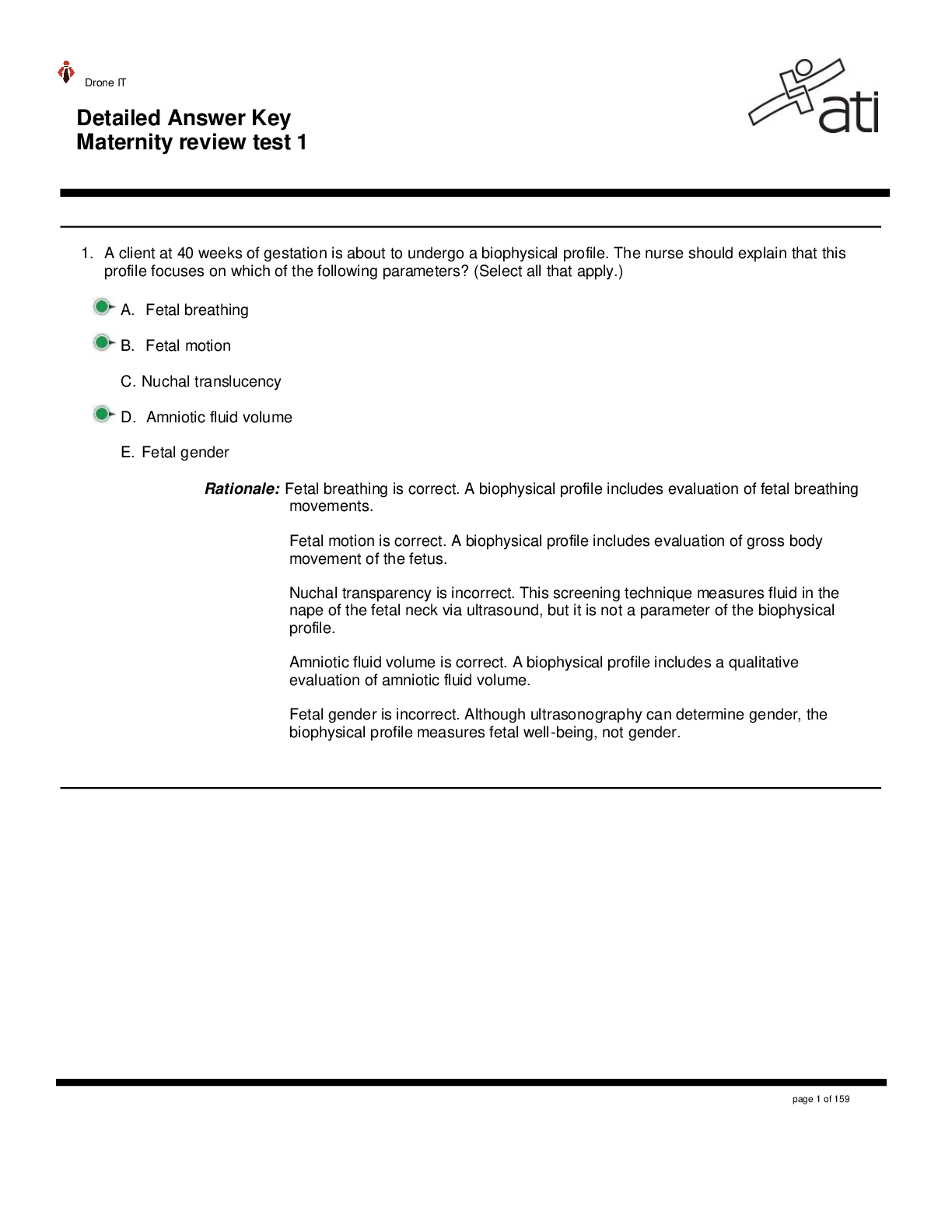
ATI Maternity - Detailed practice Answer Key Updated for 2021/2022
Boost your ATI Maternity Exam prep with our comprehensive Answer Key, tailored and updated for 2023/2024. Get detailed insights into topics like biophysical profiles, newborn care, postpartum assessme...
By ProfXams , Uploaded: Sep 20, 2021
$15
*NURSING> ATI > ATI Leadership Management Proctored Exam (NGN) 2024 | Screenshots (All)
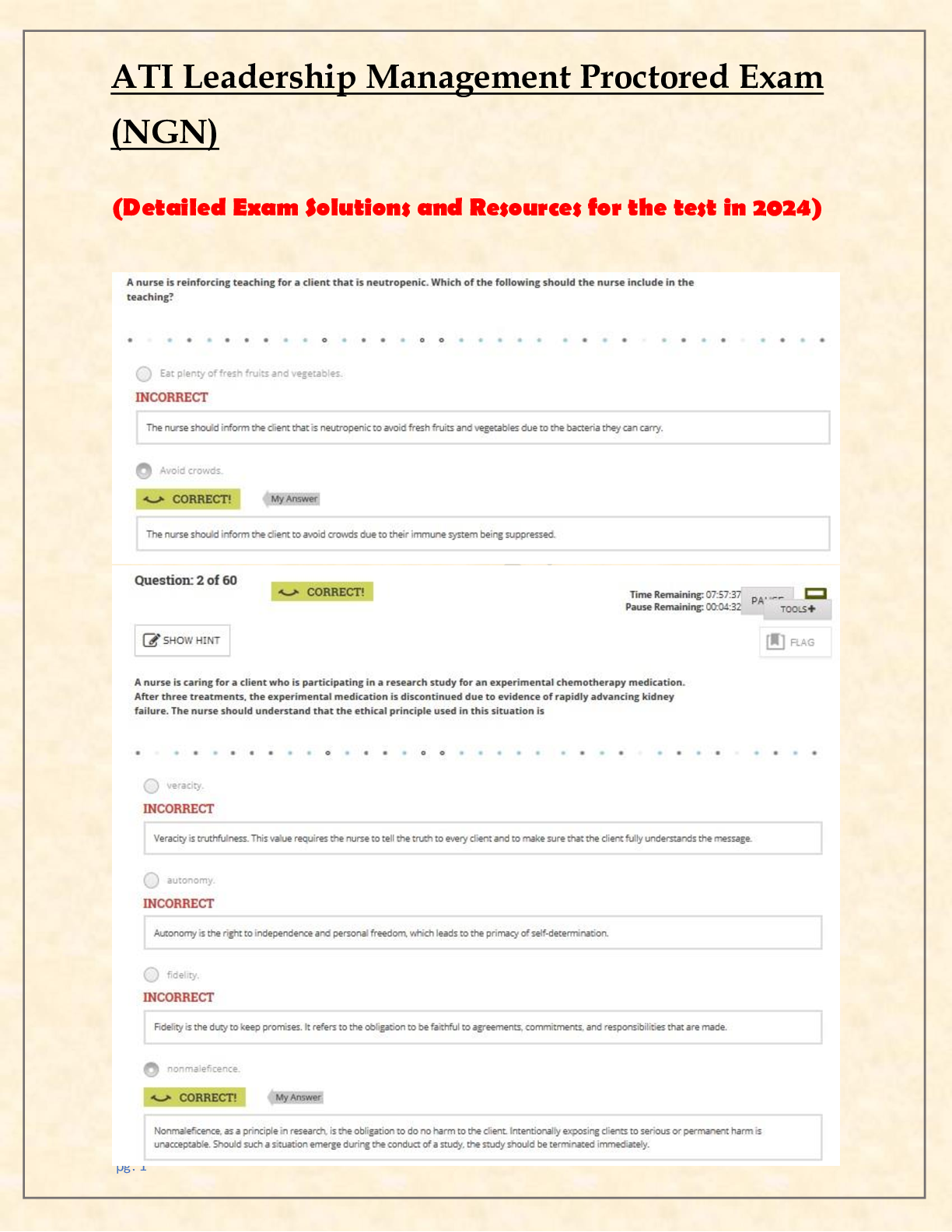
ATI Leadership Management Proctored Exam (NGN) 2024 | Screenshots
ATI Leadership Management Proctored Exam (NGN) 2024 | GOOD LUCK!!!!!///////////////////ATI Leadership Management Proctored Exam (NGN) 2024 | GOOD LUCK!!!!!///////////////////ATI Leadership Management...
By Rixx Dennis , Uploaded: Apr 02, 2024
$70
*NURSING> ATI > ATI PN PHARMACOLOGY PROCTORED LATEST EXAM RETAKE (GRADED A) 2024 (All)

ATI PN PHARMACOLOGY PROCTORED LATEST EXAM RETAKE (GRADED A) 2024
1.) A nurse is assessing a client who is receiving intravenous therapy. The nurse should identify which of the following findings as a manifestation of fluid volume excess? a. Decreased bowel sounds...
By Rixx Dennis , Uploaded: Mar 26, 2024
$60.5
*NURSING> ATI > ATI PHARMACOLOGY PROCTORED 2023/2024 EXAM RETAKE 1 (GRADED A) (All)

ATI PHARMACOLOGY PROCTORED 2023/2024 EXAM RETAKE 1 (GRADED A)
ATI PHARMACOLOGY PROCTORED 2023/2024 EXAM RETAKE 1 (GRADED A)
By Rixx Dennis , Uploaded: Sep 14, 2023
$65.5
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 24, 2023
Number of pages
15
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 24, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
42






