Marketing > STUDY GUIDE > C712 Marketing Fundamentals Study Guide Questions and Answers. (for All Chapters 1-18) (All)
C712 Marketing Fundamentals Study Guide Questions and Answers. (for All Chapters 1-18)
Document Content and Description Below
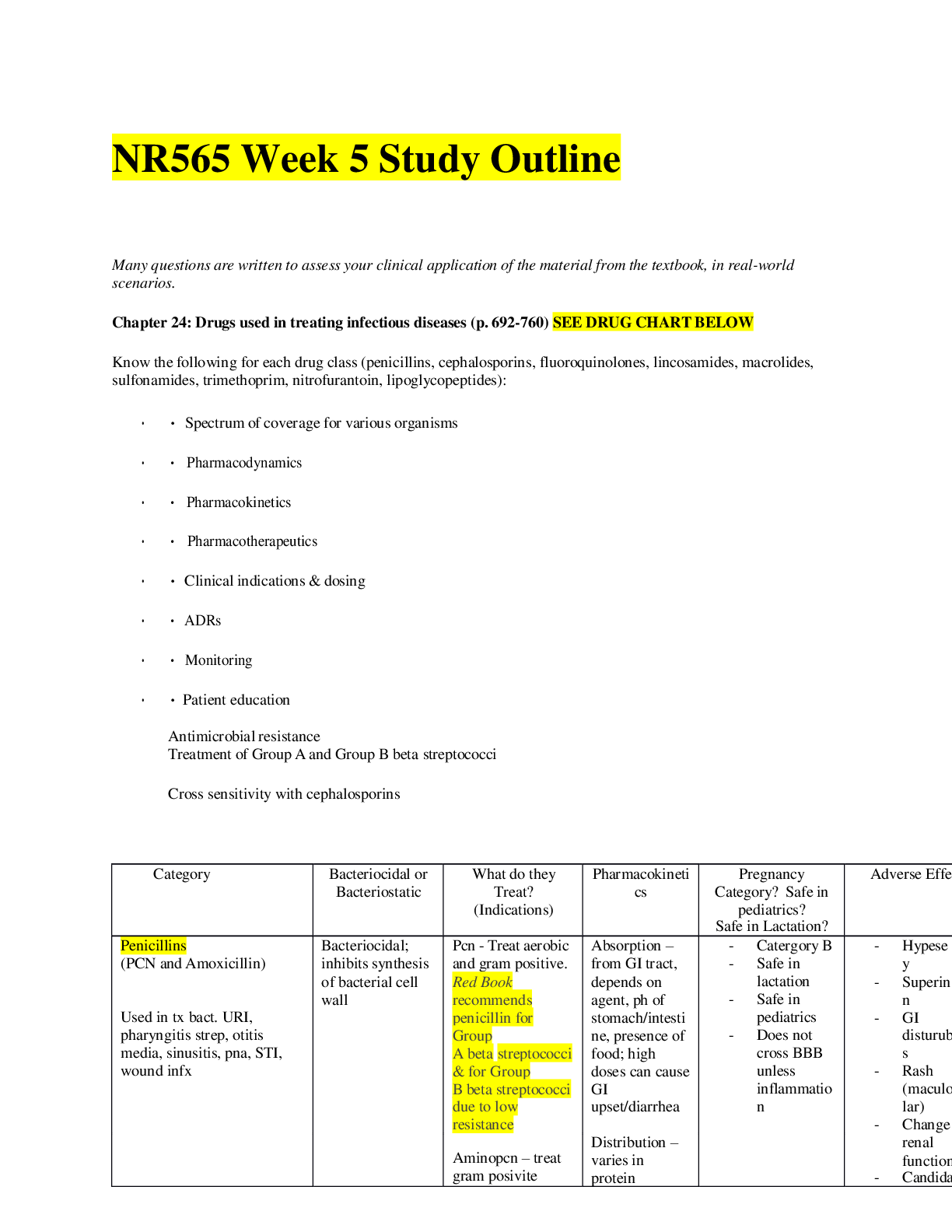
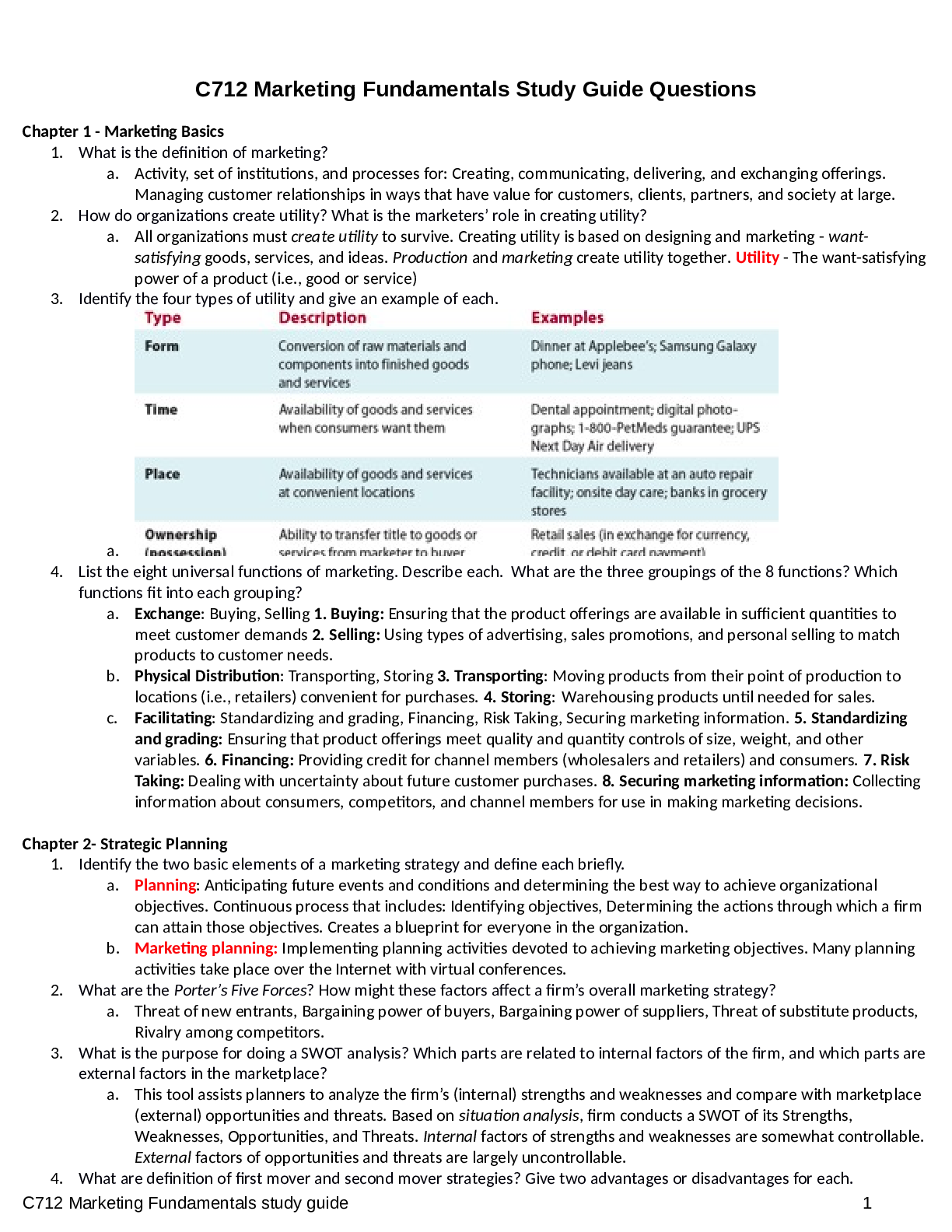
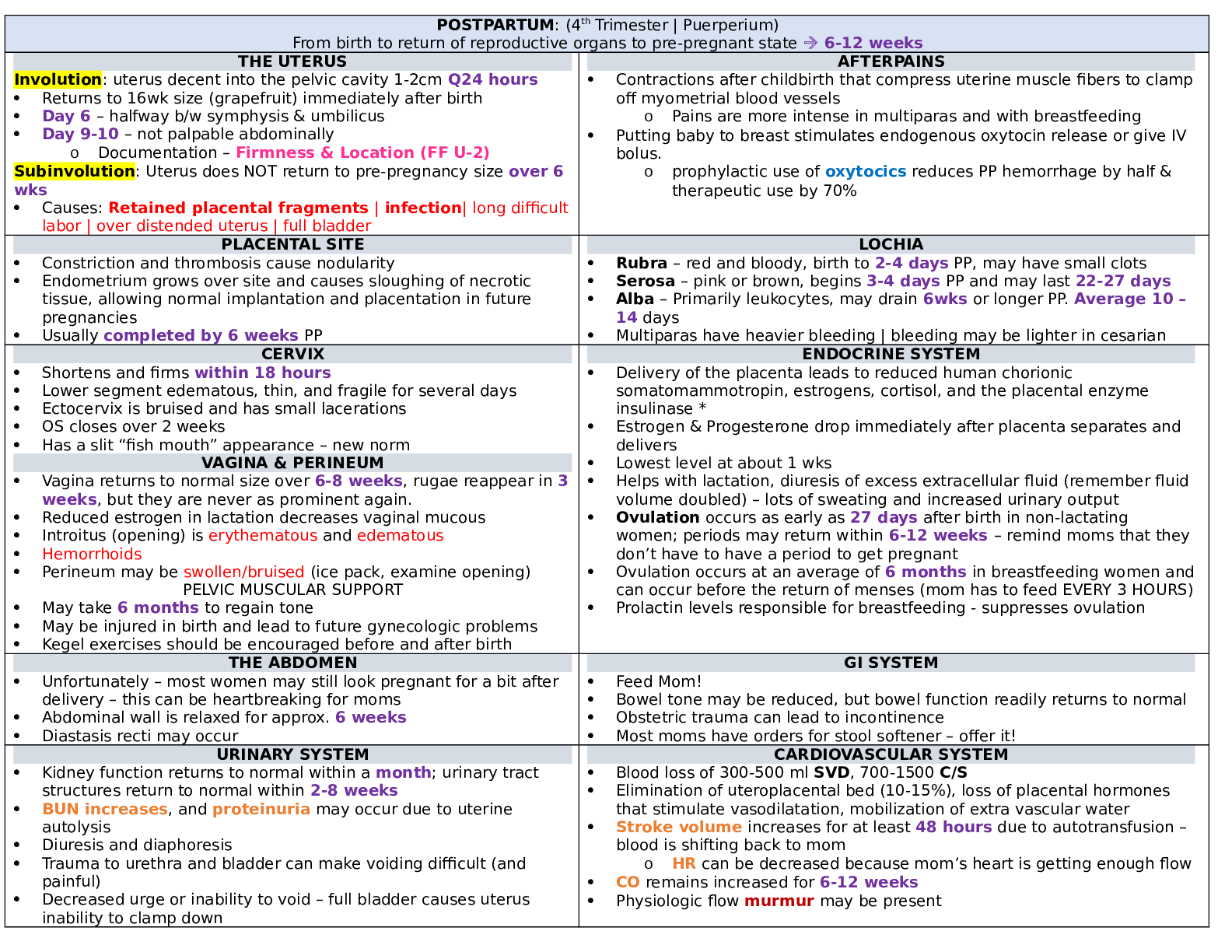
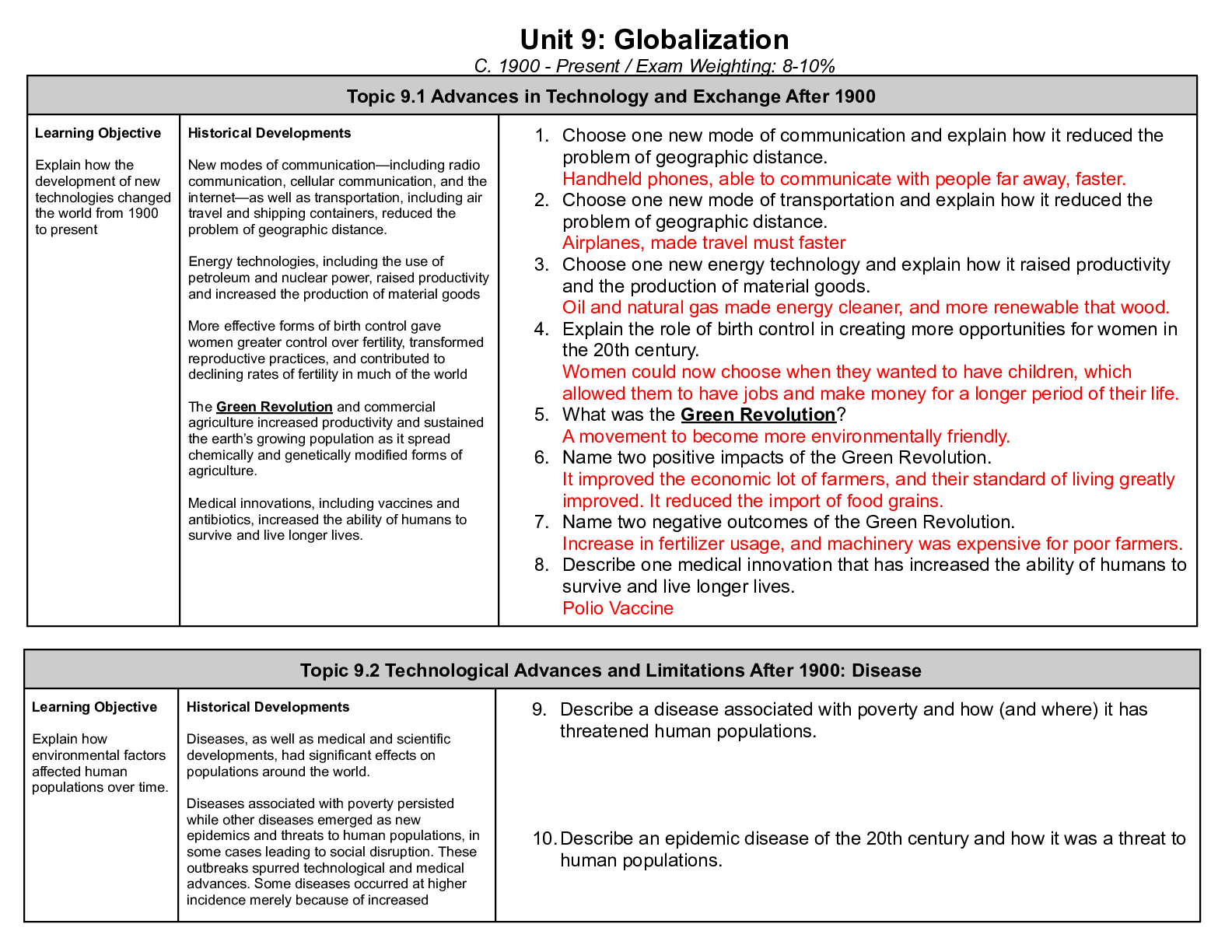
C712 Marketing Fundamentals Study Guide Questions Chapter 1 - Marketing Basics 1. What is the definition of marketing? a. Activity, set of institutions, and processes for: Creating, communicating, ... delivering, and exchanging offerings. Managing customer relationships in ways that have value for customers, clients, partners, and society at large. 2. How do organizations create utility? What is the marketers’ role in creating utility? a. All organizations must create utility to survive. Creating utility is based on designing and marketing - wantsatisfying goods, services, and ideas. Production and marketing create utility together. Utility - The want-satisfying power of a product (i.e., good or service) 3. Identify the four types of utility and give an example of each. a. 4. List the eight universal functions of marketing. Describe each. What are the three groupings of the 8 functions? Which functions fit into each grouping? a. Exchange: Buying, Selling 1. Buying: Ensuring that the product offerings are available in sufficient quantities to meet customer demands 2. Selling: Using types of advertising, sales promotions, and personal selling to match products to customer needs. b. Physical Distribution: Transporting, Storing 3. Transporting: Moving products from their point of production to locations (i.e., retailers) convenient for purchases. 4. Storing: Warehousing products until needed for sales. c. Facilitating: Standardizing and grading, Financing, Risk Taking, Securing marketing information. 5. Standardizing and grading: Ensuring that product offerings meet quality and quantity controls of size, weight, and other variables. 6. Financing: Providing credit for channel members (wholesalers and retailers) and consumers. 7. Risk Taking: Dealing with uncertainty about future customer purchases. 8. Securing marketing information: Collecting information about consumers, competitors, and channel members for use in making marketing decisions. Chapter 2- Strategic Planning 1. Identify the two basic elements of a marketing strategy and define each briefly. a. Planning: Anticipating future events and conditions and determining the best way to achieve organizational objectives. Continuous process that includes: Identifying objectives, Determining the actions through which a firm can attain those objectives. Creates a blueprint for everyone in the organization. b. Marketing planning: Implementing planning activities devoted to achieving marketing objectives. Many planning activities take place over the Internet with virtual conferences. 2. What are the Porter’s Five Forces? How might these factors affect a firm’s overall marketing strategy? a. Threat of new entrants, Bargaining power of buyers, Bargaining power of suppliers, Threat of substitute products, Rivalry among competitors. 3. What is the purpose for doing a SWOT analysis? Which parts are related to internal factors of the firm, and which parts are external factors in the marketplace? a. This tool assists planners to analyze the firm’s (internal) strengths and weaknesses and compare with marketplace (external) opportunities and threats. Based on situation analysis, firm conducts a SWOT of its Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. Internal factors of strengths and weaknesses are somewhat controllable. External factors of opportunities and threats are largely uncontrollable. 4. What are definition of first mover and second mover strategies? Give two advantages or disadvantages for each. C712 Marketing Fundamentals study guide 1a. First mover strategy: The company first to offer a product in a marketplace will be the long-term market winner. Second mover strategy: Observing the innovations of first movers and then improving on them to gain advantage in the marketplace 5. Define planning. How does marketing planning differ between top managers, middle-level managers, and supervisors? 6. State whether each of the following illustrates strategic or tactical planning: a. Global automakers begin setting up manufacturing plants in China b. Play N Trade Video Games and Dimensions Games Corporation merge c. The Cleveland Browns give up draft picks to obtain QB Johnny Manziel (“Johnny Football”) d. A regional airline looks for ways to expand to other markets. Chapter 3 Marketing Environments 1. Why is environmental scanning an important activity for marketers? a. Collecting external marketing environment information to identify and interpret potential trends. Trends represent significant opportunities or threats to the company. Example: Consumer Product Safety Commission issued a recall of children’s books due to choking and laceration hazards. 2. Describe an industry or firm that you think might be able to weather an economic downturn and explain why. a. Deflation can cause: A freefall in business profits, Lower returns on most investments, Widespread job layoffs. b. Unemployment - Proportion of people in the economy actively seeking work but do not have jobs. Rises during recession and declines during recovery and prosperity 3. Why do marketers monitor the technological environment? a. Technology: An application of knowledge based on discoveries in science, inventions, and innovations to marketing. Technology leads to: New products, Improvements in existing products, Better customer service, Reduced prices. b. Sources of technology: Industry, Educational institutions, Not-for-profit institutions, Federal government. 4. How might marketers make the most of shifts in the social-cultural environment? a. The relationship between the marketer, society, and culture: Marketers must be sensitive to demographic shifts and changing values, Increasing importance of cultural diversity. b. Example: Univision and Telemundo face growing competition in Spanish-language television programming. 5. What is the function of the Federal Trade Commission? The Food and Drug Administration a. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has the broadest regulatory powers over marketing: Enforces laws regulating unfair business practices and stops false and deceptive advertising. Chapter 4 - Social Media 1. What is the definition of a social media platform? Describe each of the platforms listed: General definition: a. Social networking sites: Websites that provide virtual communities for people to: Share daily activities, Post opinions on various topics, Increase their circle of online friends, and more. b. Bookmarking sites: These give people a place to save, organize, and manage links to: Websites, Other resources on the Internet. C712 Marketing Fundamentals study guide 2c. Social news sites: People post news items or links to outside articles on such sites, then vote on which postings get the most prominent display—and viewed by the most readers d. Blogging sites and forums: Blog postings and comments are attached to such sites and typically focus on specific topics. e. Microblogs: Subscribers get a steady stream of brief updates from anyone ranging from a high-school friend to a celebrity. 2. What are social media tools? Describe each of the tools listed: General definition: a. Media sharing: Services like YouTube and Flickr allow people to upload and share media such as photos and videos: Some videos have gone viral and shot their makers to fame, Marketers realize that a viral video can translate to a jump in demand—and sales—for their products. b. Blog and microblogging postings: Blogging allows people to communicate in greater detail than microblogging does. Microblogging offers short bursts of news. c. Apps: Short for application, it is a free or paid software download that links users to a wide range of goods and services, media and text content, social media platforms, search engines, and the like. d. QR codes: Short for quick response codes, Two-dimensional bar codes that can be read by some mobile phones with cameras, Information contained in the code is shared with the user: Might lead to a video, give details about a product, or offer a coupon. 3. What are the three essential features of social media marketing? a. 1. It creates a buzz, 2. It creates ways for customers or fans to engage in conversations with ach other and the organization, 3. It allows customers to promote the firm’s messages themselves 4. Why might B2B firms have a difficult time developing a loyal fan base using social media marketing? a. Businesses use social media to gather relevant market insights, improve search rankings, and form new business partnerships. 5. Why is it important for the goals of a social media marketing campaign to be both clear and flexible? a. Clear goals help marketers set the SMM campaign in the right direction. Flexible goals enable firms to adapt to changing circumstances. 6. How do social media marketers arrive at a target audience? a. Social media marketing efforts customize their approach to targeted audiences more than any other type of marketing because they are interactive, so it is important for marketers to link the targeted audience with the goals of the initiative. 7. Why must Social Media Marketing (SMM) content focus on the audience rather than the organization? a. Effective content has the following qualities: a strong brand focus; emphasis on the audience instead of the organization; targeted keywords; relevant information; shareworthy text and images; invitations to the audience to generate its own content; and offers for discounts or deals. The rules of engagement include: follow site-specific rules and guidelines; use social media channels as they were intended; and think before posting—or deleting. 8. Discuss why marketers need to have a SMM plan. How can social media be monitored to measure its effectiveness? a. Marketers often use social media analytics tools to help them track, measure, and interpret data related to the SMM effort. They calculate the return on investment (ROI) of the marketing campaign, typically measuring success in terms of share of voice, awareness of company or brand, level of audience engagement, influence created, and popularity. Marketers follow keywords and use tools, such as Trendrr and Brandwatch, to measure and manage specific activities. Flexibility and quick response are also vital to the management of SMM. [Show More]
Last updated: 11 months ago
Preview 1 out of 14 pages
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 29, 2023
Number of pages
14
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 29, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
49
















.png)