*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > South University > NURSING > EXAM. SOUTH UNIVERSITY NURSING 682/NRSG 682 Assessment Final Exam(ALREA (All)
South University > NURSING > EXAM. SOUTH UNIVERSITY NURSING 682/NRSG 682 Assessment Final Exam(ALREADY GRADED A)
Document Content and Description Below
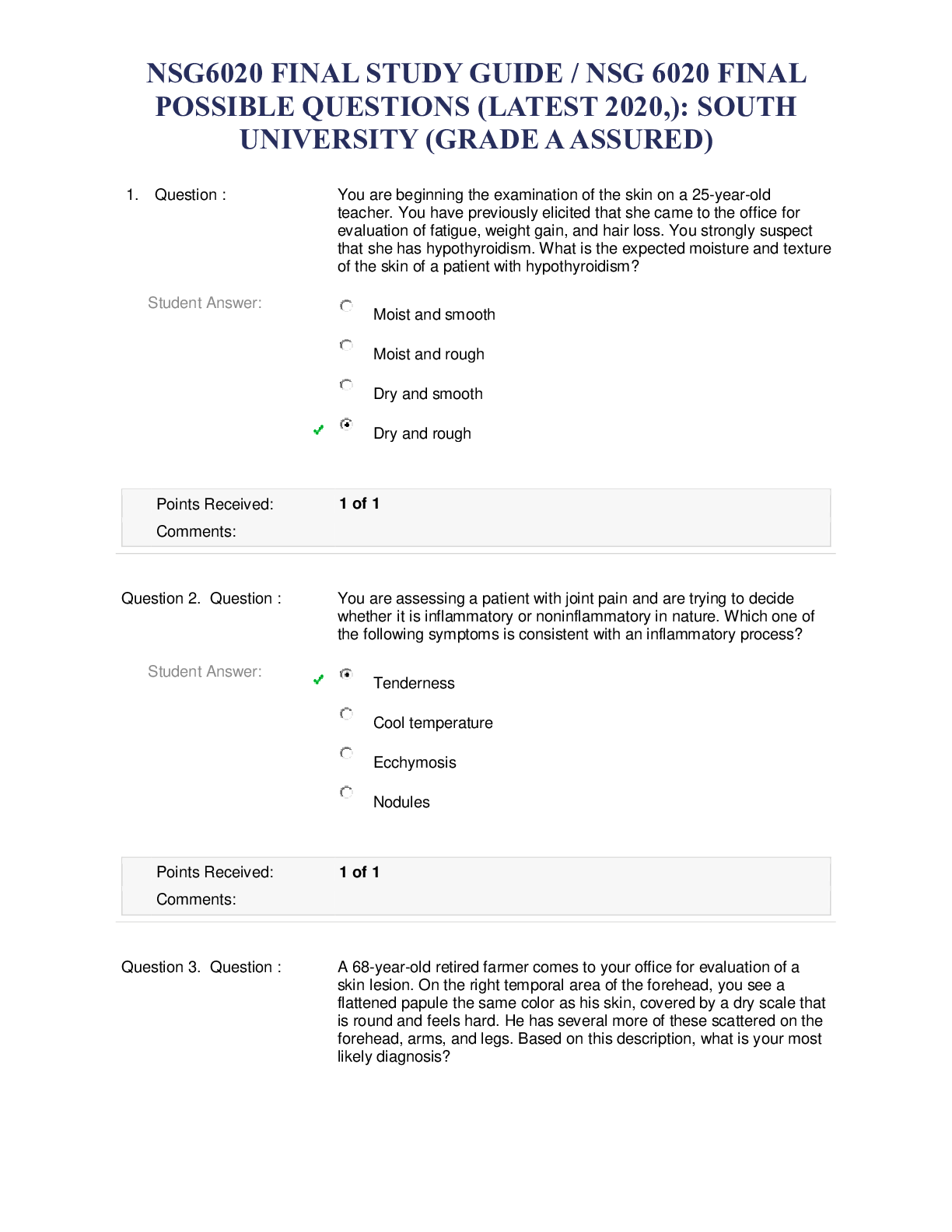
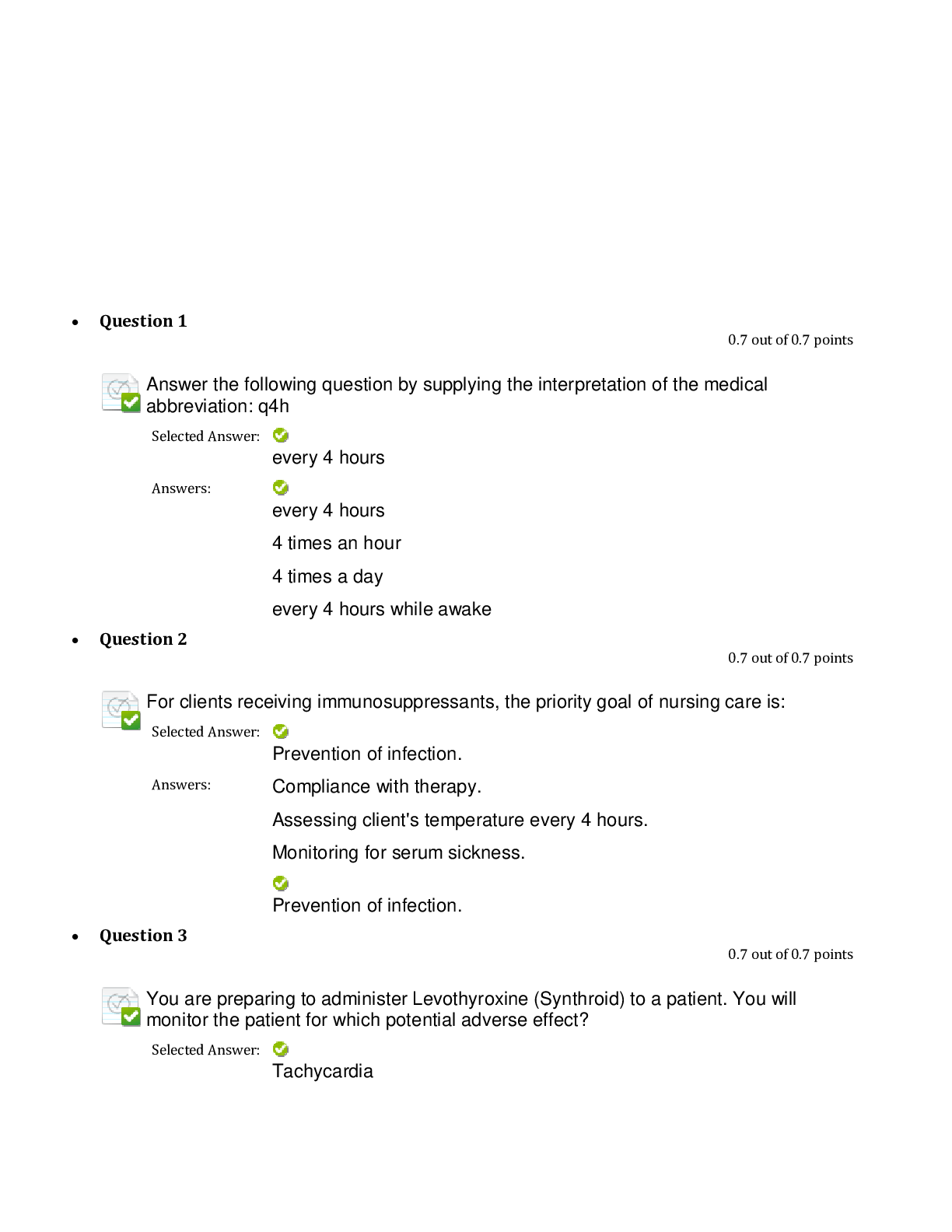
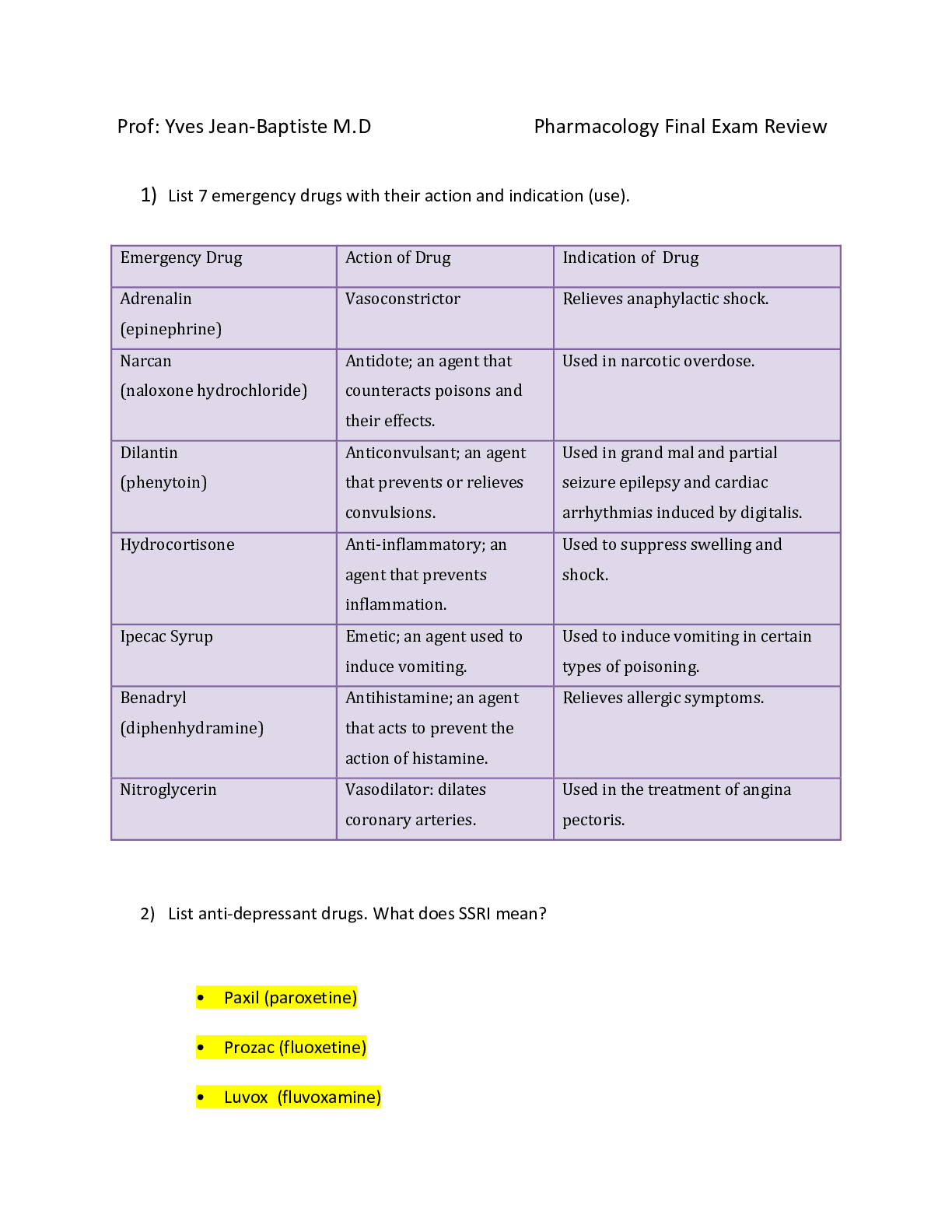
NURSING 682 Assessment Final Exam 1. The components of the health history include all of the following except: 2. The following information is best placed in which category: “The patient had a s... tent placed in the left anterior descending artery (LAD) in 1999” 3. The following information is recorded in the health history: “I feel really tired.” Which category does it belong to? 4. The following information is recorded in the health history: “The patient has had abdominal pain for 1 week. The pain lasts for 30 minutes at a time; it comes and goes. The severity is 7 to 9 on a scale of 1 to 10. It is accompanied by nausea and vomiting. It is located in the mid-epigastric area.” Which of these categories does it belong to? 5. Steve has just seen a 5-year-old girl who wheezes when exposed to cats. The patient’s family history is positive for asthma. You think the child most likely has asthma. What have you just accomplished? 6. You are seeing an elderly man with multiple complaints. He has chronic arthritis, pain from an old war injury, and headaches. Today he complains of these pains, as well as dull chest pain under his sternum. What would the order of priority be for your problem list? 7. A 22-year-old advertising copywriter presents for evaluation of joint pain. The pain is new, located in the wrists and fingers bilaterally, with some subjective fever. The patient denies a rash; she also denies recent travel or camping activities. She has a family history significant for rheumatoid arthritis. Based on this information, which of the following pathologic processes would be the most correct? 8. Ms. Washington is a 67 year old who had a heart attack last month. Now she complains of shortness of breath and not being able to sleep in a flat position (orthopnea). On examination you note increased jugular venous pressure, a S3 gallop, crackles low in the lung fields, and swollen ankles (edema). This is an example of a: 9. Mr. Curtiss has a history of obesity, diabetes, osteoarthritis of the knees, HTN, and obstructive sleep apnea. His BMI is 43 and he has been discouraged by his difficulty in losing weight. He is also discouraged that his goal weight is 158 pounds away. What would you tell him? 10. A 50 year old body builder is upset by a letter of denial from his life insurance company. He is very lean but has gained 2 pounds over the past 6 months. You personally performed his health assessment and found no problems whatsoever. He says he is classified as “high risk” because of obesity. What should you do next: 11. You are seeing an older patient who has not had medical care for many years. Her vital signs taken by your office staff are: T 37.2, HR 78, BP 118/92, and RR 14, and she denies pain. You notice that she has some hypertensive changes in her retinas and you find mild proteinuria on a urine test in your office. You expected the BP to be higher. She is not on any medications. What do you think is causing this BP reading, which doesn’t correlate with the other findings? 12. You are observing a patient with heart failure and notice that there are pauses in his breathing. On closer examination, you notice that after the pauses the patient takes progressively deeper breaths and then progressively shallower breaths, which are followed by another apneic spell. The patient is not in any distress. You make the diagnosis of: 13. In obtaining a history, you note that a patient uses the word “largely” repeatedly, to the point of being a distraction to your task. Which word best describes this speech patter? 14. Susanne is a 27 year old who has had headaches, muscle aches, and fatigue for the last 2 months. You have completed a thorough history, examination, and laboratory workup but have not found a cause. What would your next action be: 15. A 72 year old African American male is brought to your clinic by his daughter for a follow up visit after his recent hospitalization. He had been admitted to the local hospital for speech problem and weakness in his right arm and leg. On admission his MRI showed a small stroke. The patient was in rehab for 1 month following his initial presentation. He is now walking with a walker and has good use of his arm. His daughter complains, however, that everyone is still having trouble communicating with the patient. You ask the patient how he is doing. Although it is hard for you to make out his words you believe his answer is “well… fine… okay.” His prior medical history involved high blood pressure and coronary artery disease. He is a widower and retired handyman. He has three children who are healthy. He denies tobacco, alcohol, or drug use. He has no other current symptoms. On examination he is in no acute distress but does seem embarrassed when it takes him so long to answer. His blood pressure is 150/90 and his other vital signs are normal. Other than his weak right arm and leg his physical examination is unremarkable. What disorder of speech does he have? 16. A 26 year old violinist comes to your clinic, complaining of anxiety. He is a first chair violinist in the local symphony orchestra and has started having symptoms during performances, such as sweating, shaking and hyperventilating. It has gotten so bad that he has thought about giving up his first chair status so he does not have to play the solo during one of the movements. He says that he never has these symptoms during rehearsals or when he is practicing. He denies having any of these symptoms at any other time. His past medical history is unremarkable. He denies any tobacco use, drug use, or alcohol abuse. His parents are both healthy. On examination you see a young man who appears worried. His vital signs and physical appearance are unremarkable. What type of anxiety disorder best describes the situation? 17. A patient presents with a daily headache, which has worsened over the past several months. On funduscopic examination, you notice that the disk edge is indistinct and the veins do not pulsate. Which is most likely? 18. A 77 year old retired school superintendent comes to your office, complaining of unsteady hands. He says that for the past 6 months, when his hands are resting in his lap they shake uncontrollably. He says when he holds them out in front of his body the shaking diminishes, and when he uses his hands the shaking is also better. He also complains of some difficulty getting up out of his chair and walking around. He denies any recent illnesses or injuries. His past medical history is significant for high blood pressure and coronary artery disease, requiring a stent in the past. He has been married for over 50 years and has five children and 12 grandchildren. He denies any tobacco, alcohol, or drug use. His mother died of a stroke in her 70s and his father died of a heart attack in his 60s. He has a younger sister who has arthritis problems. His children are all essentially healthy. On examination you se a fine, pill rolling tremor of his left hand. His right shows less movement. His cranial nerve examination is normal. He has some difficulty rising from his chair, his gait is slow, and it takes him time to turn around to walk back toward you. He has almost no “arm swing” with his gait. What type of tremor is he most likely to have? 19. You are examining a child with severe cerebral palsy. When you suddenly move his foot dorsally, a sustained “beating” of the foot against you hand ensues. What does this represent? 20. You are conducting a mental status examination and note impairment of speech and judgment, but the rest of your examination is intact. Where is the most likely location of the problem 21. Steve has had a stroke and comes to you for a follow-up today. On examination you find that he has increased muscle tone, some involuntary movements, an abnormal gait, and a slowness of response in movements. He most likely has involvement of which of the following 22. You are beginning the examination of the skin on a 25 year old teacher. You have previously elicited that she came to the office for evaluation of fatigue, weight gain, and hair loss. You strongly suspect that she has hypothyroidism. What is the expected moisture and texture of the skin of a patient with hypothyroidism 23. You are speaking to an 8th grade class about health prevention and are preparing to discuss the ABCDEs of melanoma. Which of the following descriptions correctly defines the ABCDEs? 24. A 19 year old construction worker presents for evaluation of a rash. He notes that it started on his back with a multitude of spots and is also on his arms, chest, and neck. It itches a lot. He does sweat more than before because being outdoors is part of his job. On physical examination, you note dark tan patches with a reddish cast that has sharp borders and fine scales, scattered more prominently around the upper back, chest, neck, and upper arms as well as under the arms. Based on this description, what is most likely your diagnosis 25. A 28 year old patient comes to the office for evaluation of a rash. At first there was only one large patch, but then more lesions erupted suddenly on the back and torso; the lesions itch. On physical examination, you note that the pattern of eruption is like a Christmas tree and that there are a variety of erythematous papules and macules on the cleavage lines of the back. Based on this description, what is the most likely diagnosis? 26. A 22 year old nurse comes to your clinic, complaining of severe constipation and pain during defecation. She has also seen blood on the toilet paper. She states that she eats a healthy diet and does some light exercising. She is currently at the beginning of her third trimester of an unremarkable pregnancy. Her past medical history is unremarkable. Her mother has high cholesterol but her father is in good health. She does not smoke, drink alcohol or use illegal drugs. She is married and expecting her first child. On examination she appears healthy and is afebrile, with a blood pressure of 110/60. Her abdominal examination reveals a gravid uterus but is otherwise unremarkable. On visualization of the anus there is a slight red, moist-appearing protrusion from the anus. As you have her bear down, the protrusion grows larger. On digital rectal examination you can feel an enlarged tender area on the posterior side. There is some blood on the glove after the examination. What disorder of the anus or rectum best fits this presentation? 27. A 24 year old graduate student comes to your clinic, complaining of burning during urination and increased urinary frequency. He has had a low grade fever (100.5) and does not feel very well. He is very worried about STDs because he had a drunken encounter 2 weeks ago and did not use a condom. He has had no recent weight loss, weight gain, or night sweats. His past medical history includes knee surgery in HS and genital warts in college. He does not smoke but drinks six beers every Friday and Saturday night. He denies using any IV drugs but has tried marijuana in the past. His father has high cholesterol but his mother is healthy. On examination he appears tired. His temperature is 99.5 degrees and his BP is 110/70. His abdominal examination is normal. Visualization of the anus shows no masses, inflammation, or fissures. DRE reveals a warm, boggy, tender prostate. No discrete masses are felt and there is no blood on the glove. The scrotum and penis appear normal. Urinalysis shows moderate amounts of WBCs and bacteria. What d/o of the anus, prostate, or rectum best describes this situation? 28. A 55 y/o retired property manager comes to your clinic, concerned that she may have a tumor in her rectum. When asked why, she stakes that after straining at a bowel movement she felt a mass around her rectum. She denies any blood in her stool, black stools, or pain with defecation. She admits to having had chronic constipation for 30 years. She often uses laxatives to be able to have a VM. She denies any recent weight gain, weight loss, fever, or night sweats. Her PMhx consists of hypothyroidism, and she has had 2 spontaneous vaginal deliveries. Her mother died recently of colon CA and her father has HTN but is otherwise healthy. She denies any smoking and only occasionally drinks ETOH. On examination she seems nervous. Her BP is 140/90 and her HR is 100. Her cardiac, lung, and abdominal examinations are normal. On visualization of her anus, no inflammation, masses, or fissures noted. When she is asked to bare down, you see a rosette of red mucosa prolapsing from the anus. On DRE there are no masses and no blood is found on the glove. What disorder of the anus or rectum is this likely to be? 29. A 50 year old truck driver comes to your clinic for a work physical. He has had no upper respiratory, cardiac, pulmonary, GI, UI, or musculoskeletal system complaints. His past medical hx is significant for mild arthritis and prior knee surgery in college. He is married and just changed jobs, working for a different trucking company. He smokes one pack of cigarettes a day, drinks less than 6 beers a week, and denies using any illegal drugs. His mother has HTN and arthritis and his father died of lung CA in his 60’s. on examination, his BP is 130.80 and his HR is 80. His cardiac, lung, and abdominal examinations, are normal. He has no inguinal hernia, but on his DRE you palpate a soft, smooth, nontender peduculated mass on the posterior wall of the rectum. What anal, rectal, or prostate disorder best fits his presentation? 30. A 75 year old retired construction worker comes to your clinic, complaining of bright red blood in the toilet for the last several months. He has no pain with defecation but has occasional constipation. He states he eats a healthy diet with fruits and vegetables and walks 2 miles a day. He has had a 10 pound weight loss over the last 3 months. He denies fever or night sweats. His medical hx includes high blood pressure, coronary artery dz, and arthritis. HeA has also had a n appendectomy. He smoked for 40 years, two packs a day, but quit 15 years ago. He used to drink alcohol but doesn’t now. His father died in his 60s of a MI and his mother had breast CA in her 70’s. on examination he appears his stated age and sits comfortably on the examining table. His BP is 150/85 and his pulse is 88. He is afebrile. His cardiac, lung, and abdominal examinations are normal. Visualization of the anus shows no erythema, masses, or inflammation. Digital rectal exam elicits an irregular, firm mass on the posterior side of the rectum. After you remove your finger you notice frank blood on your glove. What anal or rectal disorder is this patient most likely to have? 31. Dawn is a 55 year old woman who comes in today for her yearly wellness exam. You arefully perform the rectal exam in the lithotomy position and feel a mass against the bowel wall which is firm and immobile. Which of the following is most likely? 32. A 19 year old college sophomore comes to the clinic for evaluation of joint pains. The student has been back from spring break for 2 weeks; during her holiday, she went camping. She notes that she had a red spot, shaped like a target, but then it started spreading, and then the joint pains started. She used insect repellant but was in an area known to have ticks. She has never been sick and takes no medications routinely; she has never been sexually active. What is the most likely cause of her joint pain? 33. A 38 year old woman comes to you and has multiple small joints involved with pain, swelling, and stiffness. Which of the following is the most likely explanation? 34. A 68 y/o retired banker comes to your clinic for evaluation of left shoulder pain. He swims for 30 minutes daily, early in the morning. He notes a sharp, catching pain and a sensation of something grating when he tries overhead movements of his arm. On physical examination, you note tenderness just below the tip of the acromion in the area of the tendon insertion. The drop arm test is negative and there is no limitation with shoulder shrug. The patient is not holding his arm close to his side, and there is no tenderness to palpation in the bicepital groove when the arm is at the pt’s side, flexed to 90 degrees, and then supinated against resistance. Based on this description, what is the most likely cause of his shoulder pain? 35. Louise, a 60 y/o complains of left knee pain associated with tenderness throughout, redness, and warmth over the joint. Which of the following is least helpful in determining if a joint problem is inflammatory? 36. Mark is a contractor who recently injured his back. He was told he had a bulging disc to account for the burning pain down his right leg and slight foot drop. The vertebral bodies of the spine involve which type of joint? • Cartilaginous 37. Ray works a physical job and notes pain when he attempts to lift his arm over his head. When you move the shoulder passively, he has full ROM without pain and there is no gross swelling or tenderness. What type of joint dz does this most likely represent? • Extra-articular 38. A 15 month old is brought to you for a fever of 38.6 degrees Celsius and fussiness. The ear examination is as follows: external ear, normal appearance and no tenderness and manipulation; canal, normal diameter without evidence of inflammation; tympanic membrane, bulging, erythematous, and opaque. Insufflation is deferred due to pain. What is your diagnosis? • Otitis Media 39. A 38 week gestation, 2500 gram infant is placed on your service. How would she be described? • Term, normal birth weight 40. A mother brings her 16 month old son in for an evaluation. She is afraid he is not meeting his developmental milestones and wants to know if he should be sent to therapy. He was the product of an uneventful pregnancy and a spontaneous vaginal delivery. His apgar scores were 7 and 9. Until reaching a year old the mother believes he was hitting his milestones appropriately. You decide to administer the Denver Developmental Screening Test. You find that he is using a spoon to eat with and can take off his own shoes and shirt. He can build a tower of two cubes and dump raisins. His vocabulary consists of at least 10 words. He can stand-alone and stoop and recover, but he is unable to walk without holding onto someones hand. What type of developmental delay does he have? • Gross Motor 41. A quiet 3 year old is brought in for a routine check-up when you notice a fresh bruise in the axilla and bilateral bruises over the upper back that appear slightly older. There are brown bruises over his shins as well. His mother said this happened when he fell off a couch. What dx should be considered? • Abuse 42. A toddler is able to jump in place and balance on one foot as well. She can also speak in full sentences and feed herself. What is the approximate developmental age of this child? • 3 43. You are observing an infant who is able to pull to a stand, uses “mama” and “dada” specifically, and indicates his wants by vocalization and pointing. Where would you place this child’s developmental age? • 8 months 44. A 19 y/o childcare worker comes to you for her first prenatal visit. She cannot remember when her last period was but thinks it was between 2 to 5 months ago. When she began gaining weight and felling something move down there, she did a home pregnancy test and it was positive. She states she felt the movement about a week ago. She has had no n/v, fatigue, or fevers. Her past medical hx is remarkable only for irregular periods. She has been dating the same young man for a year. She says they were not using condoms. On examination you see an overweight young lady appearing her stated age. Her head, eyes, ears, nose, throat, neck, thyroid, cardiac, and pulmonary exams are unremarkable. Her abdomen is nontender with normal bowel sounds, and the gravid uterus is palpated to the level of the umbilicus. Fetal heart tones are easily found with doptone, and with the bimanual exam the cervix is soft. Results of pap smear, cultures, and blood work are pending. You give the pt her due date and how far along she is, based on your clinical findings. An OB ultrasound to confirm her dates is ordered. With only the clinical exam, how many weeks pregnant did you tell the pt she is? • 18-20 wks 45. A pregnant woman finally comes in for her prenatal check up. She complains today of a headache and abdominal pain for several months’ duration. She appears somewhat hurried or nervous. What question do u ask next? • Do you feel safe at home 46. A woman in her 30th week has a cervical length estimated at 1 cm. should you be concerned? • Yes; she may be at risk for preterm labor 47. During cardiac examination you notice a new parasternal systolic murmur of 2/6 intensity. On palpation the PMI is slightly higher than usual. What do you suspect? • Mammary soufflé 48. Which of the following is a major effect of placental hormones? • Insulin resistance 49. You are examining for fetal heart tones with a fetoscope and are unable to hear any. Using a doptone, you measure the rate at 164. Which gestational age is most likely? • 20 wks 50. A 70 year old retired auto mechanic comes to your office because his neighbor is concerned about his memory. The patient himself admits to misplacing his keys more often and forgets what he is supposed to buy from the grocery store and where he has parked the car. He denies getting lost in familiar places. Upon further questioning, he states that his wife of 40 years died 8 months ago; his three children live in three different states; and he has limited his activities because the people he interacted with were “his wife’s friends, not his.” He drinks a six-pack of beer daily; he does not smoke or use illicit drugs. You perform a mini-mental state examination and obtain a total score of 24 out of 28. Based on this information what is your most likely diagnosis? • Depression 51. A 79 year old retired banker comes to your office for evaluation of difficulty with urination; he gets up five to six times per night to urinate and has to go oat least that often in the daytime. He does not feel as if his bladder empties completely; the strength of the urinary stream is diminished. He denies dysuria or hematuria. This problem has been present for several years but has worsened over the last 8 months. You palpate his prostate. What is you expected physical examination finding, based on this description? • Enlarged size, smooth 52. An 89 year old retired school principal comes for an annual check-up. She would like to know whether or not she should undergo a screening colonoscopy. She has never done this before. Which of the following factors should not be considered when discussing whether she should go for this screening test? • Time interval until benefit from screening accrues 53. Mr. Chin is an 82 y/o man who comes to your office for a routine check. On examination, you notice a somewhat high-pitched murmur in the second right intercostal space during systole. It does not radiate and the rest of his examination is normal for his age. Which is true of the most likely cause of this murmur? • It carries with it increased risk for cardiovascular disease 54. Mrs. Stanton is a 79 y/o widow who presents to your office for a routine BP visit. You note a new pulsatile mass in the right neck at the carotid artery. Which of the following is the most likely cause for this? • Kinking of the artery 55. You are examining an elderly man and notice the following: decreased vibration sense in the feet and ankles, diminished gag reflex, right patellar reflex less than the left, and diminished abdominal reflexes. Which of these is abnormal? • Diminished right patellar reflex compared to the left 56. A 12 y/o presents to the clinic with his father for evaluation of a painful lump in the left eye. It started this morning. He denies any trauma or injury. There is no visual disturbance. Upon physical examination, there is a red raised area at the margin of the eyelid that is tender to palpation; no tearing occurs with palpation of the lesion. Based on this description, what is the most likely diagnosis? • Hordeolum 57. A 73 y/o nurse comes to your office for evaluation of new onset tremors. She is not on any medication and does not take herbs or supplements. She has no chronic medical conditions. She does not smoke or drink alcohol. She walks into the exam room with slow movements and shuffling steps. She has decreased facial mobility and a blunt expression, without any changes in hair distribution on her face. Based on this description, what is the most likely reason for the pt’s symptoms? • Parkinson’s Disease 58. A college student presents with a sore throat, fever, and fatigue for several days. You notice exudates on her enlarged tonsils. You do a careful lymphatic exam and notice some scattered small, mobile lymph nodes just behind her sternocleoidomastoid muscles bilaterally. What group of nodes is this? • Posterior cervical 59. A pt is examined with the opthalmoscope and found to have red reflexes bilaterally. Which of the following have you essentially excluded from your differential? • Hypertensive Retinopathy 60. Glaucoma is the leading cause of blindness in AAs and the second leading cause of blindness overall. What features would be noted on funduscopic examination? • Increased cup-to-disc ratio 61. Sudden, painful unilateral loss of vision may be caused by which of the following conditions? • Optic neuritis 62. Very sensitive methods for detecting hearing loss include which of the following? • The tuning fork test 63. You feel a small mass that you think is a lymph node. It is mobile in both the up and down and side to side directions. Which of the following is most likely? • Lymph node 64. You note that a pt has anisocoria on exam. Pathologic causes of this include which of the following? • Horner’s syndrome 65. A 17 y/o high school senior presents to your clinic in acute respiratory distress. Between shallow breaths he states he was home finishing his homework when he suddenly began having right sided chest pain and severe SOB. He denies any recent traumas or illnesses. His PMH is unremarkable. He doesn’t smoke but drinks several beers on the weekend. He has tried marijuana several times but denies any other illegal drugs. He is an honors student and is on the basketball team. His parents are both in good health. He denies any recent weight gain, weight loss, fever, or night sweats. On exam you see a tall, thin young man in obvious distress. He is diaphoretic and is breathing at a rate of 35 bpm. On auscultation you hear no breath sounds on the right side of his superior chest wall. On percussion he is hyperresonant over his right upper lobe. With palpation he has absent fremitus over his right upper lobe. What disorder of the thorax or lung best describes his symptoms? • Spontaneous pneumothorax 66. A 25 y/o accountant presents to your clinic, complaining of intermittent lower right sided chest pain for several days. He describes it as knifelike and states it only lasts for 3 to 5 seconds, taking his breath away. He states he feels like he has to breathe slowly to keep it from recurring. The only thing that makes it better is lying quietly on his right side. It is much worse when he takes a deep breath. He has taken some Tylenol and put a heating pad on his side but neither has helped. He remembers that 2 weeks ago he had an upper respiratory infection with a severe hacking cough. He denies any recent trauma. His PMH is unremarkable. His parents and siblings are in good health. He has recently married, and his wife has a baby due in 2 months. He denies any smoking or illegal drug use. He drinks two to three beers once a month. He states that he eats a healthy diet and runs regularly, but not since his recent illness. He denies any cardiac, GI, or musculoskeletal symptoms. On examination he is lying on his right side but appears quite comfortable. His temperature, BP, pulse, and respirations are unremarkable. During palpation the ribs are nontender. What d/o of the chest best describes his symptoms? • Pleural pain 67. A 47 y/o receptionist comes to your office, complaining of fever, SOB, and a productive cough with golden sputum. She says she had a cold last week and her symptoms have only gotten worse, despite using OTC cold remedies. She denies any weight gain, weight loss, or cardiac or GI symptoms. Her past medical hx includes type 2 DM for 5 years and high cholesterol. She takes an oral medication for both diseases. She has had no surgeries. She denies tobacco, alcohol, or drug use. Her mother had DM and HTN. Her father passed away from colon CA. on exam you see a middle aged woman appearing her stated age. She looks ill and her temperature is elevated at 101. Her BP and pulse are unremarkable. Her head, eyes, ears, nose, and throat exam are unremarkable except for edema of the nasal turbinates. On auscultation she has decreased air movement, and coarse crackles are heard over the left lower lobe. There is dullness on percussion, increased fremitus during plapation, and egophony and whispered pectoriloquy on ausculataion. What d/o of the thorax or lung best describes her symptoms? • Pneumonia 68. A 75 y/o retired teacher presents to your clinic, complaining of severe, unrelenting anterior chest pain radiating to her back. She describes it as if someone is “ripping out her heart”. It began less than an hour ago. She states she is feeling very nauseated and may pass out. She denies any trauma or recent illnesses. She states she is never had pain like this before. Nothing seems to make the pain better or worse. Her medical hx consists of difficult to control htn and CAD requiring two stents in the past. She is a widow. She denies any ETOH, tobacco, or illegal drug use. Her mother died of a CVA and her father died of a MI. she has one younger brother who has had bypass surgery. On exam you see an elderly female in a great deal of distress. She is lying on the table, curled up, holding her left and right arms against her chest and is restless, trying to find a comfortable position. Her BP is 180/110 in the right arm and 130/60 in the left arm, and her pulse is 120. Her right carotid pulse is bounding but the left carotid pulse is weak. She is afebrile but her respirations are 24 times a minute. On auscultation her lungs are clear and her cardiac exam is unremarkable. You call ems and have her taken to the hospitals ER for further evaluation. What d/o of the chest best describes her symptoms? • Dissecting aortic aneurysm 69. When crackles, wheezes, or rhonchi clear with a cough, which of the following is likely etiology? • Bronchitis 70. A 25 y/o optical tech comes to your clinic for eval of fatigue. As part of your physical exam, you listen to her heart and hear a murmur only at the cardiac apex. Which valve is most likely to be involved, based on the location of the murmur? • Mitral 71. Suzanne is a 20 y/o college student who complains of chest pain. This is intermittent and is located to the left of her sternum. There are no associated symptoms. On exam, you hear a short, high pitched sound in systole, followed by a murmur which increased in intensity until S2. This is heard over the apex. When she squats, this noise moves later in systole along with the murmur. Which of the following is the most likely dx? • Mitral valve prolapse 72. Which is true of a third hear sound (S3)? • It is caused by rapid deceleration of blood against the ventricular wall 73. Which of the following correlates with a sustained, high amplitude PMI? • HTN 74. Which of the following regarding jugular venous pulsation is a systolic phenomenon? • The downstroke of the “v” wave 75. You are examining a pt with emphysema in exacerbation and are having difficulty hearing his heart sounds. What should you do to obtain a good exam? • Listen in the epigastrium 76. You are performing a cardiac exam on a pt with SOB and palpitations. You listen to the heart with the pt sitting upright, then have him change to a supine position, and finally have him turn onto his left side in the left lateral decubitus position, which of the following valvular defects is best heard in this position? • Mitral 77. You find a bounding carotid pulse on a 62 y/o pt. which murmur should you search out. • Aortic insufficiency 78. You notice a pt has a strong pulse and then a weak pulse. This pattern continues. Which of the following is likely? • Severe left HF 79. A 77 y/o retired nurse has an ulcer on a lower extremity that you are asked to evaluate when you do your weekly rounds at a local long term care facility. All of the following are responsible for causing ulcers in the lower extremities except for which condition? • HTN 80. When assessing temperature of the skin, which portion of your hand should be used? • Backs of fingers 81. You are assessing a pt for peripheral vascular dz in the arms, secondary to the complaint of increased weakness and a hx of CAD and DM. you assess the brachial and radial pulses and note that they are bounding. What does that translate to on a scale of 0 to 3? • 3+ 82. You are performing a routine check-up on a 81 y/o retired cotton farmer in the vascular surgery clinic. You note that he has a hx of chronic arterial insufficiency. Which of the following physical examination findings in the lower extremities would be expected with this dz? • Thin, shiny, atrophic skin 83. You note a painful ulcerative lesion near the medial malleolus, with accompanying hyperpigmentation. Which of the following etiologies is most likely? • Venous insufficiency 84. A 19 y/o female comes to your office, complaining of a clear d/c from her right breast for 2 months. She states that she noticed it when she and her bf were “messing around” and he squeezes that nipple. She continues to have this discharge anytime she squeezes that nipple. She denies any trauma to her breast. Her past medical hx is unremarkable. She denies any pregnancies. Both of her parents are healthy. She denies any pregnancies. Both of her parents are healthy. She denies using tobacco or illegal drugs and drinks 3 to 4 beers a week. On examination her breasts are symmetric with no skin changes. You are able to express clear d/c from her right nipple you feel no discrete masses and her axillae are normal. The remainder of her heart, lung, abdominal, and pelvic examinations are unremarkable. A urine pregnancy test is negative. What cause of nipple d/c is most likely in her circumstances? • Benign breast abnormality 85. A 63 y/o nurse comes to your office, upset because she has found an enlarged lymph node under her right arm. She states she found it last week while taking a shower. She isn’t sure if she has any breast lumps because she doesn’t know how to do self exams. She states her last mammogram was 5 years ago and it was normal. Her past medical hx is significant for HTN and COPD. She quit smoking 2 years ago after a 55 packs/year hx. She denies using any illegal drugs and drinks alcohol rarely. Her mother died of a heart attack and her father died of a stroke. She has no children. On exam you see an older female appearing her stated age. On visual inspection of her right axilla you see nothing unusual. Palpating this area, you feel a 2cm hard, fixed lymph node. She denies any tenderness. Visualization of both breasts is normal. Palpation of her left axilla and breast is unremarkable. On palpation of her right breast you feel a nontender 1 cm lump in the tail of spence. What d/o of the axilla is most likely responsible for her symptoms? • Breast Cancer 86. A pt is concerned about a dark skin lesion on her anterolateral abdomen. It has not changed, and there is no d/c or bldg. On examination there is a medium brown circular lesion on the anterolateral wall of the abdomen. It is soft, has regular borders, is evenly pigmented, and is about 7 mm in diameter. What is this lesion? • Supernumerary nipple 87. Which of the following is most likely benign on breast exam? • One breast larger than the other 88. Which of the following lymph node groups is most commonly involved in breast cancer? • Central 89. A 24 year old travel agent comes to your clinic, complaining of pain and swelling in her vulvar area. She states that 2 days earlier she could feel a small tender spot on the left side of her vagina but now it is larger and extremely tender. Her last period was 1 year ago and she is sexually active now. She uses the Depo-Provera shot for contraception. She denies any n/v/d, constipation, pain with urination, or fever. Her past medical hx is significant for ankle surgery. Her mother is healthy and her father has type 2 diabetes. On examination she appears her stated age and is standing up. She states she cannot sit down without excruciating pain. Her BP, temperature, and pulse are unremarkable. On visualization of her perineum, a large, red, tense swelling is seen to the left of her introitus. Palpation of the mass causes a great deal of pain. What d/o of the vulva is most likely causing her problem? • Bartholin’s Gland Infection 90. A 30 year old paralegal analyst comes to your clinic, complaining of a bad smelling vaginal d/c with some mild itching, present for about 3 weeks. She tried douching but it did not help. She has had no pain with urination or with sexual intercourse. She has noticed the smell increases after intercourse and during her period last week. She denies any upper respiratory, GI, cardiac, or pulmonary symptoms. Her PMH consists of one spontaneous vaginal delivery. She is married and has one child. She denies tobacco, alcohol, or drug use. Her mother has HTN and her father died from heart dz. On examination she appears healthy and has unremarkable VS. On examination of the perineum there are no lesions noted. On palpation of the inguinal nodes there is no lymphadenopathy. On speculum examination a thing gray-white d/c is seen in the vault. The pH of the d/c is over 4.5 and there is a fishy odor when potassium hydroxide is applied to the vaginal secretions on the slide. Wet prep shows epithelial cells with stippled borders. What type of vaginitis best describes her findings? • Bacterial vaginosis 91. Abby is a newly married woman who is unable to have intercourse because of vaginismus. Which of the following is true? • Psychosocial reasons may cause this condition 92. An 18 year old college freshman comes to your clinic, complaining of severe left sided lower abdominal pain and a foul yellow discharge. The pain began last night while she was having intercourse with her b/f. Afterward the pain became more severe and the discharge started. By this morning she had a fever of 101 degrees and walking was making the pain worse. Only lying very still makes the pain better. She has tried ibuprofen and acetaminophen without any improvement. She denies any n/v/d or constipation. Her past medical hx is unremarkable. She has had two past sexual partners. She uses the birth control patch instead of condoms. She smokes a half pack of cigarettes a day and drinks four to five beers per weekend night. She denies any illegal drug use. Her parents both are healthy. On examination you find a young woman who appears ill. Her temperature is 102 degrees and her pulse is elevated at 110. She is tender in the LLQ but has no guarding or rebound. Speculum examination reveals yellow purulent drainage from the os. On palpation there is cervical motion tenderness and the left adnexa is swollen and tender. A urine analysis is unremarkable and the UPT is pending. What is the best choice of dx for this adnexal swelling? • Pelvic inflammatory disease 93. Which of the following is true of HPV? • It commonly resolves spontaneously in 1-2 years 94. A pt tells you about her experience with prolonged therapy for her breast cancer. You comment, “that must have been a very trying time for you.” What is this an example of? • Empathy 95. Jason is a 41 y/o electrician who presents to the clinic for evaluation of SOB. The SOB occurs with exertion and improves with rest. It has been going on for several months and initially occurred only a couple of times a day with strenuous exertion; however, it has started to occur with minimal exertion and is happening more than a dozen times per day. The SOB lasts for less than 5 minutes at a time. He has no cough chest pressure, chest pain, swelling in his feet, palpitations, orthopnea, or paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea. Which of the following symptom attributes was not addressed in this description? • Severity 96. Mrs. R. is a 92 y/o retired teacher who comes to your clinic accompanied by her daughter. You ask Mrs. R why she came to your clinic today. She looks at her daughter and doesn’t say anything in response to your question. This is an example of which type of challenging pt? • Silent pt 97. When using an interpreter to facilitate an interview, where should the interpreter be positioned? • Next to the pt, so the examiner can maintain eye contact and observe the nonverbal cues of the pt 98. You are performing a young woman’s first pelvic exam. You make sure to tell her verbally what is coming next and what to expect. Then you carry out each maneuver of the exam. You let her know at the outset that if she needs a break or wants to stop, this is possible. You ask several times during the exam, “how are you doing, Brittney?” What are you accomplishing with these techniques? • Increasing the pt’s sense of control • Increasing the pt’s trust in you as a caregiver • All of the above 99. Cody is a teenager with a hx of leukemia and an enlarged spleen. Today he presents with fairly significant LUQ pain. On exam of this area a rough grating noise is heard. What is this sound? 100. Which is the proper sequence of exam for the abdomen? • [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 22 pages
Instant download

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 12, 2020
Number of pages
22
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 12, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
40