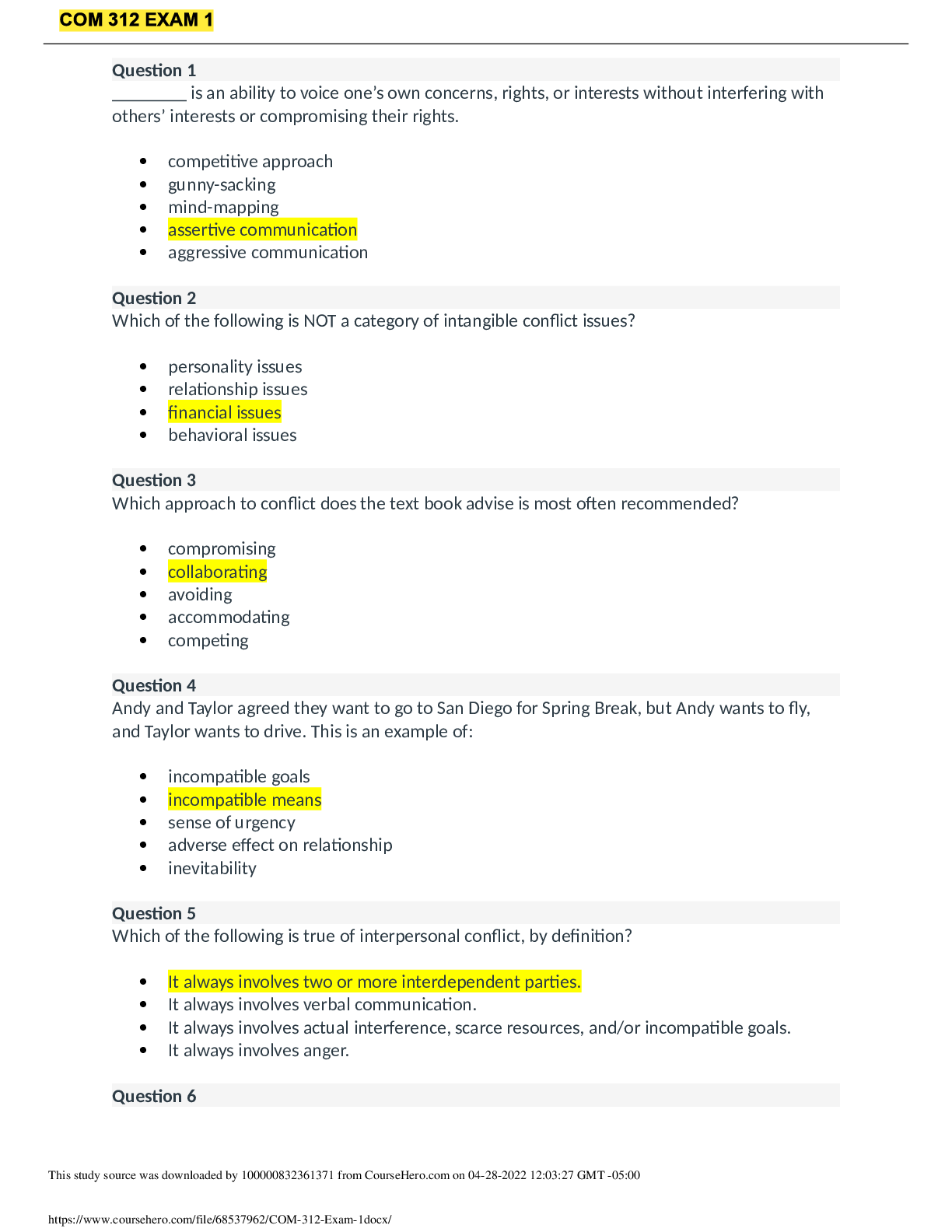
*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > MED SURG 2 EXAM 1 - Comprehensive review of Professor Martinez Medical Surgical Nursing II Exam Prim (All)
MED SURG 2 EXAM 1 - Comprehensive review of Professor Martinez Medical Surgical Nursing II Exam Primary Concepts of Adult Nursing II
Document Content and Description Below
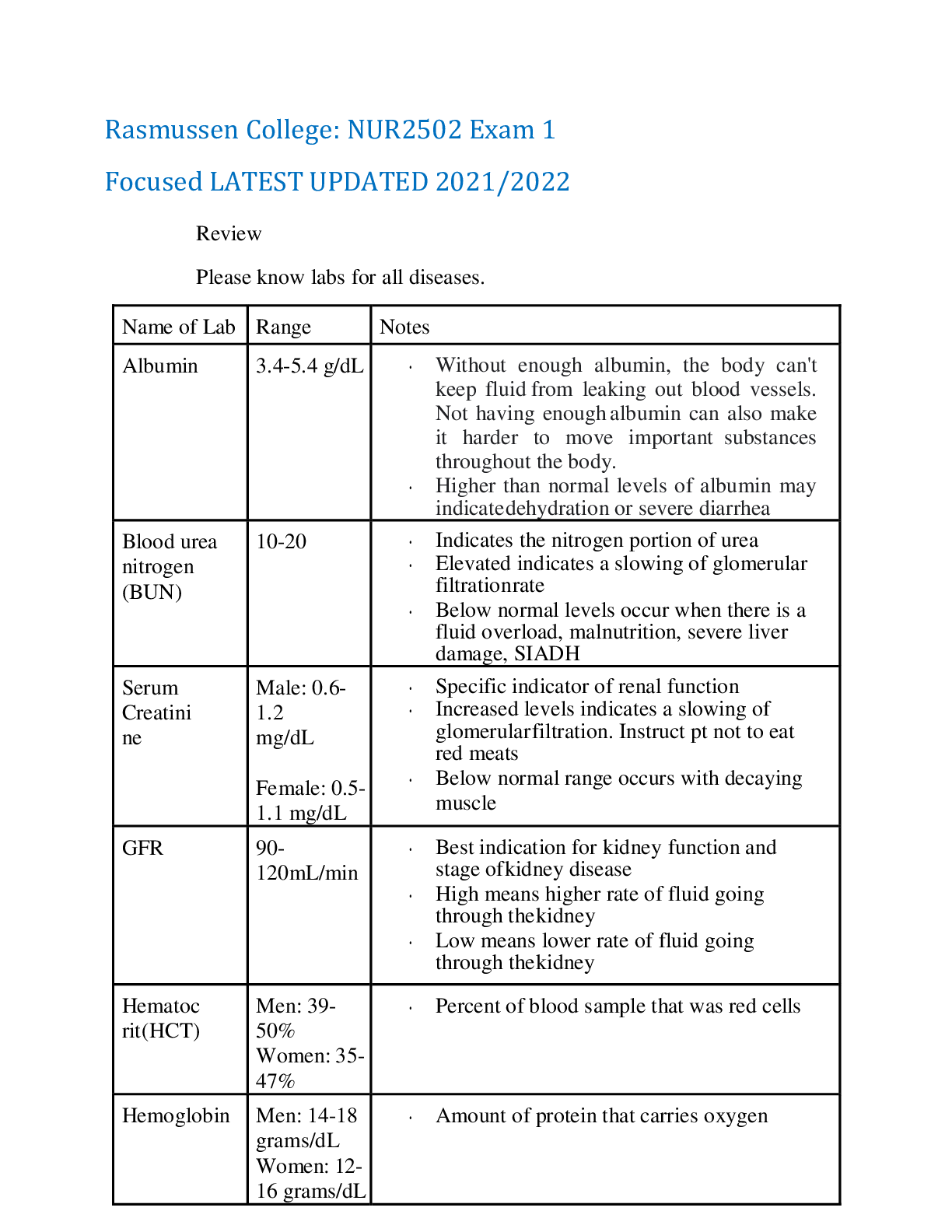
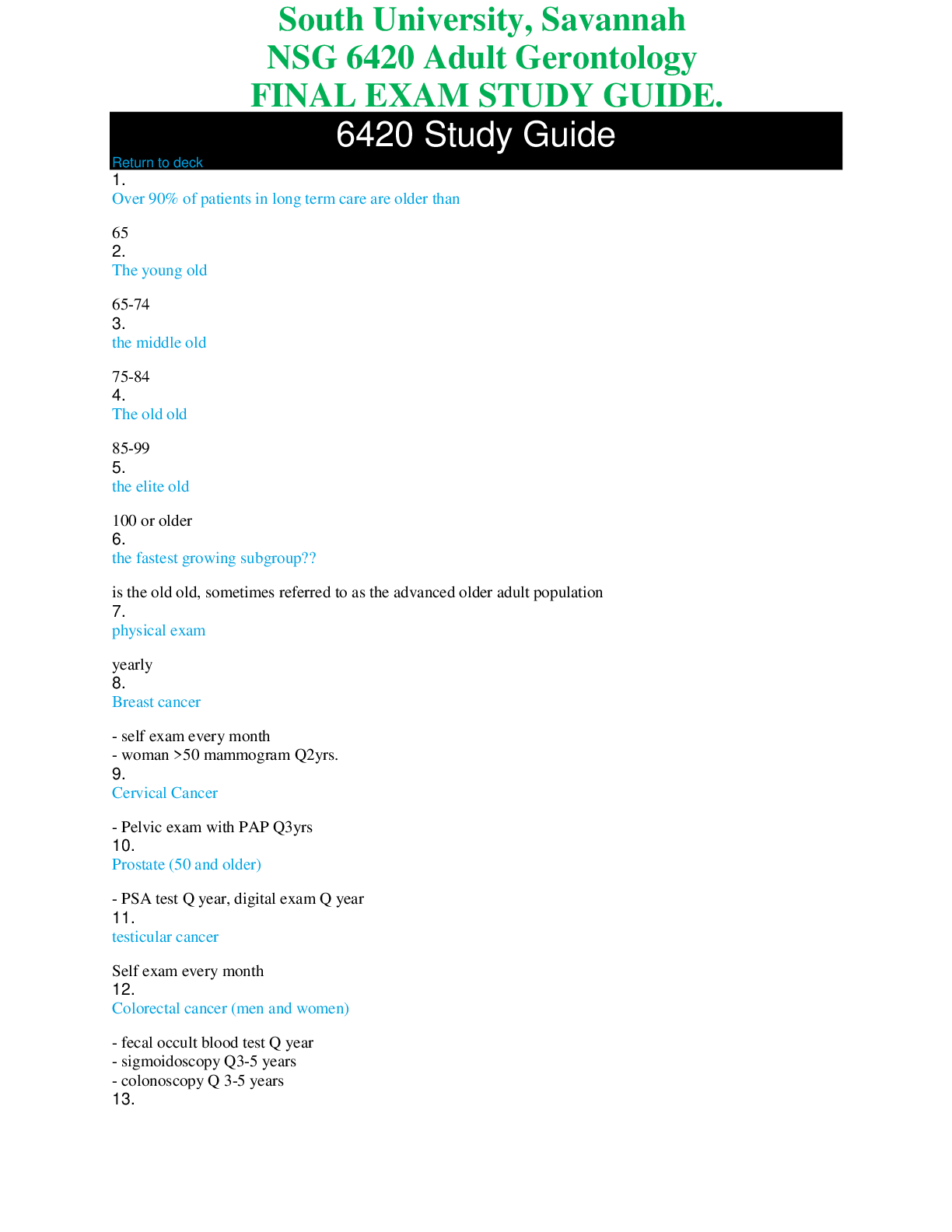
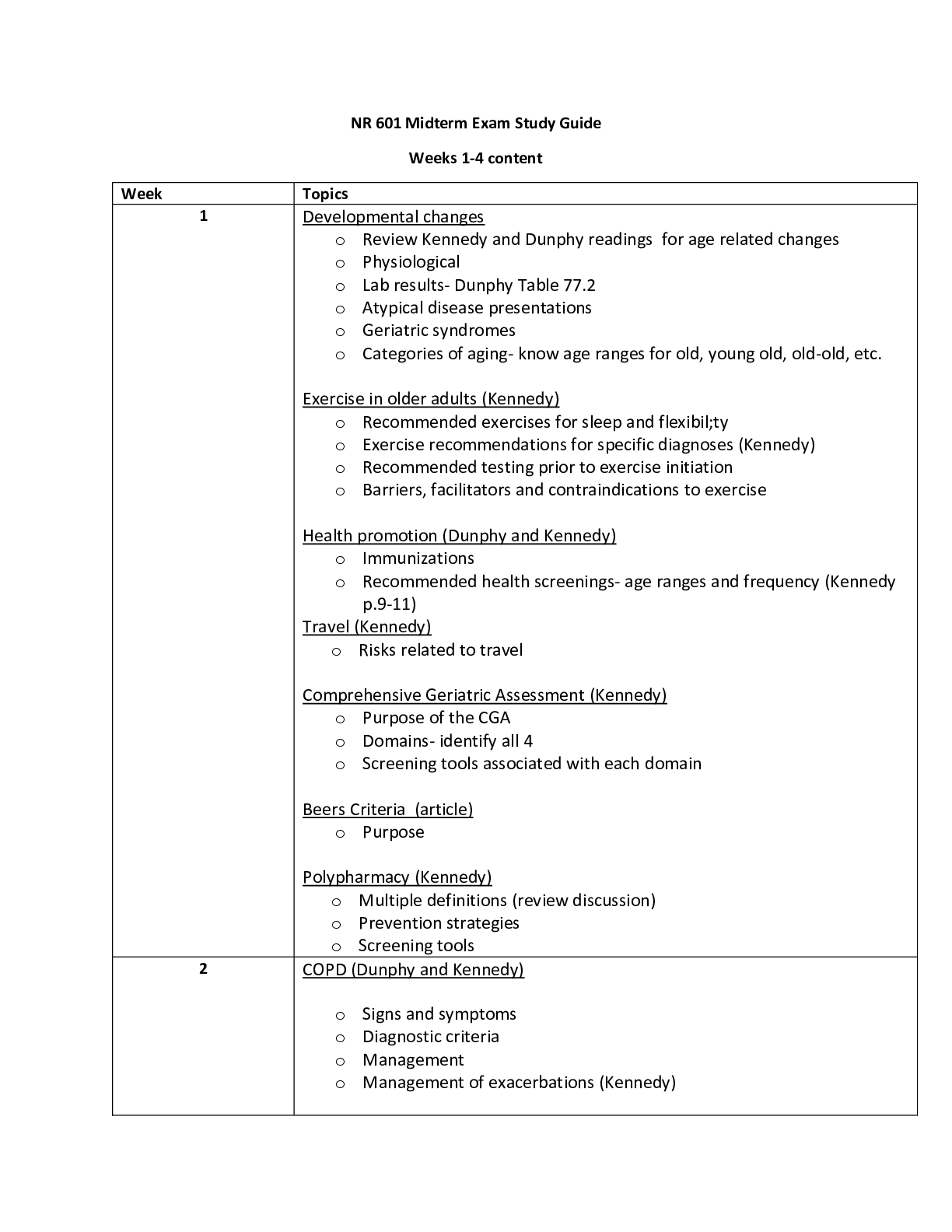
Ch. 25 – ASSESSMENT OF CARDIOVASCULAR FUNCTION Conduction System • Automaticity = ability to initiate an electrical impulse • Excitability = ability to respond to an electrical impulse • Co... nductivity = ability to transmit an electrical impulse from one cell to another Depolarization: Repolarization: return of cell to resting state caused by re-entry of potassium into cell while sodium exits CO = HR x SV Cardiac output = total amt. of blood ejected by one of the ventricles in L/min (in resting adult about 4-6 L/min) *post-menopausal women = higher risk of CAD b/c estrogen levels slowly disappear Chest pain – identify quantity (0-10), location, and quality. Radiation of pain? Medications – aspirin = common OTC med that improves outcomes in CAD pts Heart as a pump reduced pulse pressure, displaced PMI from 5th ICS mid- clavicular line, gallop sounds, murmurs Atrial/ventricular filling volumes JVD, peripheral edema, ascites, crackles, postural BP changes CARDIAC-SPECIFIC General appearance – changes to LOC, BMI > 30 Assessment of skin/extremities Postural blood pressure changes Normal heart sounds = S1, S2 (AV closure, semilunar closure) Abnormal heart sounds = S3, S4 Brain (b-type) natriuretic peptide (BNP) = neuro-hormone that helps regulate BP and fluid volume DX EVALUATION ELECTROCARDIOOGRAPHY (EKG) • CONTINUOUS EKG MONITORING o Standard of care for pts @ high risk for dysrhythmias CARDIAC STRESS TESTING o Normally: cardiac arteries dilate to four times their usual diameter in response to increased metabolic demands for oxygen and nutrients o Stress test determines the following CARDIAC EVALUATIONS Transthoracic echocardiography Transesophageal echocardiography CARDIAC CATH COMPLICATIONS Anaphylaxis (iodine) Hemodynamic Monitoring Central Venous Pressure (CVP) Measures filling pressure in right atrium/ventricle at end of diastole (PRELOAD) Phlebostatic level = reference point for the atrium when the patient is in a supine position – helps with measuring of the BP most accurately HYPERTENSION Essential HTN = BP must be greater than 140/90 on 2 separate occasions in order to DX Looking for proteinuria (common can also happen with pregnant women) BUN creatinine clearance Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers (ARB) Hypertensive Crisis Classification Hypertensive Emergency ► Clinical dysfunction of target organ Hypertensive Urgency ► Elevated BP but no evidence of progressive target organ damage ► HA, epistaxis, anxiety ► PO agents with goal of normalizing BP in 24-48 hours THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM (ECG) EKG/ECG is a graph tracing of the electrical activity of the heart Not the mechanical activity! Information obtainable from an EKG rhythm strip analysis: Normal sinus rhythm = occurs when the electrical impulse starts at a regular rate and rhythm and in the SA node and travels trhough the normal conduction pathway. Premature Ventricular Complexes (PVCs) It’s the same as PAC but this one eventually be life threatening • Causes: o Can occur in healthy patients (intake of caffeine, alcohol, nicotine AV Nodal Reentry Tachycardia (SVT) • Impulse that is conducted to an area in the AV node that causes impulse to be rerouted back into area over and over again @ very fast rate (SA node lost control) CH. 27 MGMT OF PTS W. CORONARY VASCULAR DISORDERS • Atherosclerosis = abnormal accumulation of lipid deposits + fibrous tissue within arterial walls and CAD RISK FACTORS: Non-modifiable family HX, increasing age, gender (men develop CAD earlier age than women), race (African Americans develop CAD > whites) Unstable angina = symptoms increase in frequency + severity; may NOT be relieved by rest or nitro (pts w/ unstable require medical intervention*)…can occur at rest --> ACS Interventions Q* - patients with suspected MI should immediately receive: DX: 12-lead ECG and lab tests (cardiac biomarkers) are performed to clarify if unstable angina, NSTEMI, or STEMI CH. 18 ADRENERGIC DRUGS SNS + PNS = Autonomic Nervous System o Alpha2 receptors – • Beta-adrenergic receptors: all located on post-synaptic effector cells MOA: When any of the adrenergic drugs is given, it bathes the synaptic cleft and once there, has the opportunity to induce a response. This can be accomplished in one of the three ways: • Respiratory - Treatment of asthma and bronchitis • Topical Nasal Decongestants - Treatment of nasal congestion Indications: Adrenergic Agonists • Cardiovascular - Used to support the heart during cardiac failure or shock • Ophthalmic – Temporary relief of conjunctival congestion • Overactive Bladder – The beta-3 agonist, mirabegron (Myrbetriq) relaxes the detrusor muscle • Beta-Adrenergic o CNS Mild tremors, headache, nervousness, dizziness ASSESSMENT: • Assess for allergies, asthma, and HX of HTN, cardiac dysrhythmias, & other CV disease. Vasoactive Adrenergic Drugs (pressors, inotropes) – cardioselective sympathomimetics • IV drug only; given by continuous infusion epinephrine (Adrenalin) • Endogenous vasoactive catecholamine • Stimulates alpha-adrenergic receptor phenylephrine (Neo-Synephrine) • Works almost exclusively on the alpha-adrenergic receptors IMPLEMENTATION: • Intravenous administration CH. 19 ADRENERGIC-BLOCKING DRUGS Adrenergic antagonists – (Sympatholytics) opposite effects of adrenergic drugs; inhibit the stimulation of the SNS by acting on different receptor types • Drug Effects: adrenergic blockade of these alpha-1 receptors leads to effects such as: • Most commonly used to treat the extravasation of vasoconstricting drugs such as norepinephrine, epinephrine, and dopamine BETA BLOCKERS • Block stimulation of beta-receptors in the SNS CONTRAINDICATIONS: • Drug allergies All beta blockers have a black box warning stating that the medication should not be stopped abruptly but tapered over 1-2 weeks. Some of the most serious undesirable effects can be caused by acute withdrawal exacerbation of underlying angina, precipitation of an MI, or rebound HTN! • Other beta blockers • Antacids • Anticholinergics • Digoxin Beta blockers also delay recovery from hypoglycemia in patients with type 1 diabetes TOXICITY atropine may be given IV for management of bradycardia Nonselective beta blockers – Adverse effects: “Beta blocker monitor for side effects b/c you can constrict too much so keep monitoring the blood pressure, always check the BP before administering the medication. Can cause CHF on the patient CHF- weight gainIf you gain weight 2lb in 24hrs its not good can administer diuretics” atenolol (Tenormin) propranolol (Inderal) = prototypical nonselective beta-1 and beta-2 blocking drug NURSING PROCESS ASSESSMENT • Assess for allergies and history of COPD, hypotension, cardiac dysrhythmias, bradycardia, HF, or other cardiovascular problems patients with pre-existing bradycardia, decreased cardiac contractility, HF, and/or decreased conduction with heart block CANNOT TAKE BETA-1 BLOCKERS ** -patients with a HX of asthma, emphysema, bronchitis, or any condition with increased airway resistance or bronchoconstriction CANNOT TAKE BETA-2 BLOCKERS ** • If any of the meds are given IV ECG monitoring recommended PATIENT TEACHING • Encourage to take medications as prescribed • Should never stop these drugs abruptly • Alpha blockers Change positions slowly to prevent or minimize postural hypotension [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 63 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 23, 2020
Number of pages
63
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 23, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
71




















.png)