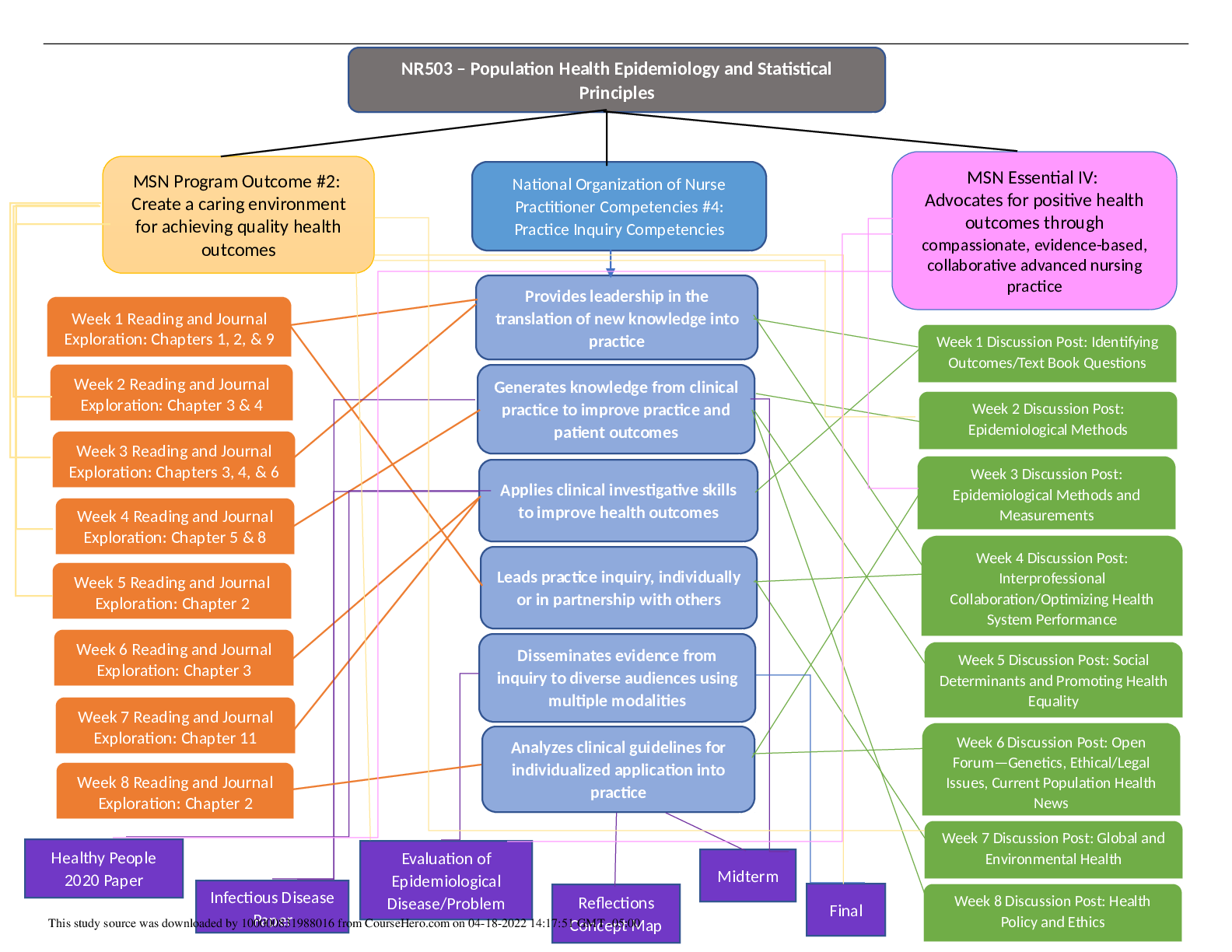
*NURSING > EXAM > CPNP-PC Exam Test Bank Questions & Answers, Answers Explained With Rationales, Graded 100% (All)
CPNP-PC Exam Test Bank Questions & Answers, Answers Explained With Rationales, Graded 100%
Document Content and Description Below
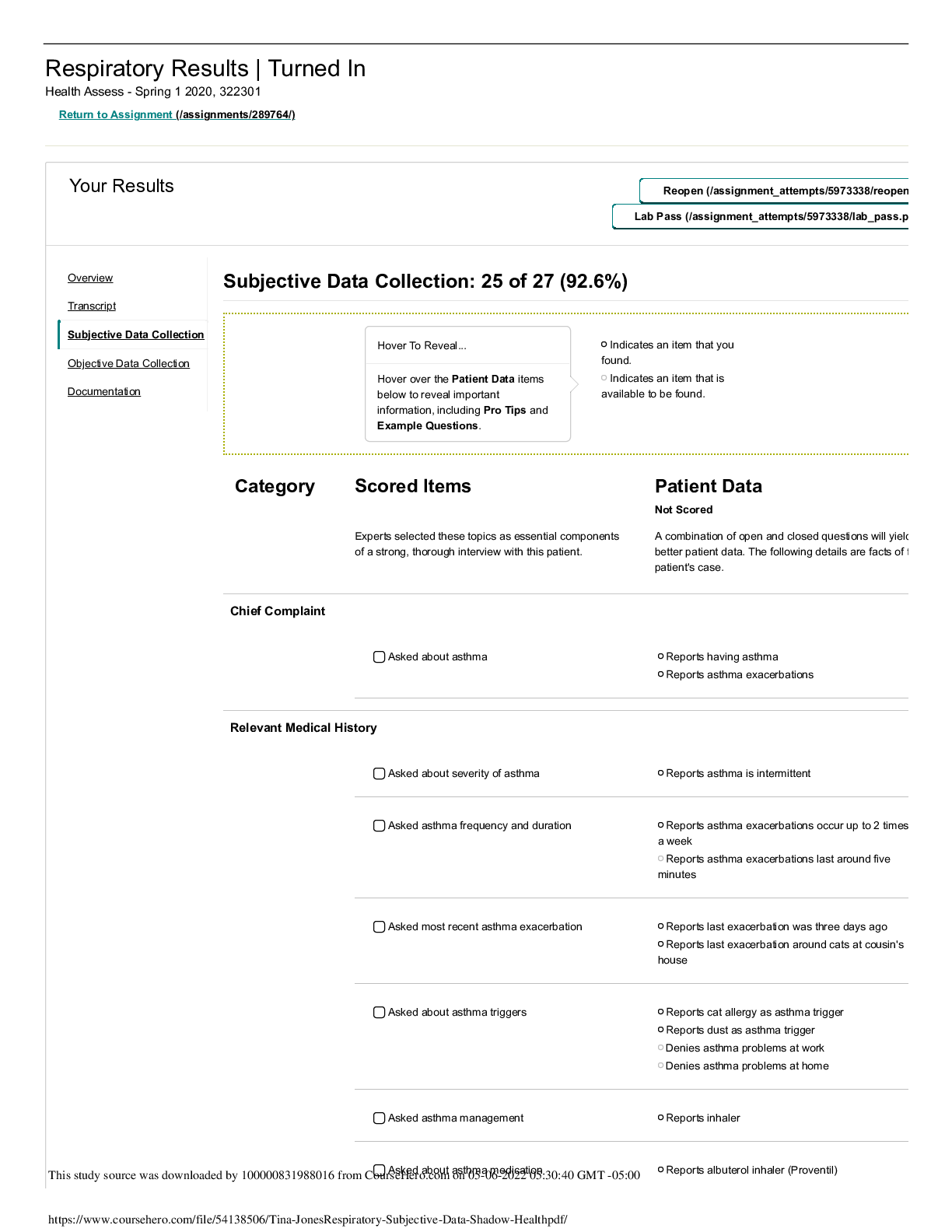
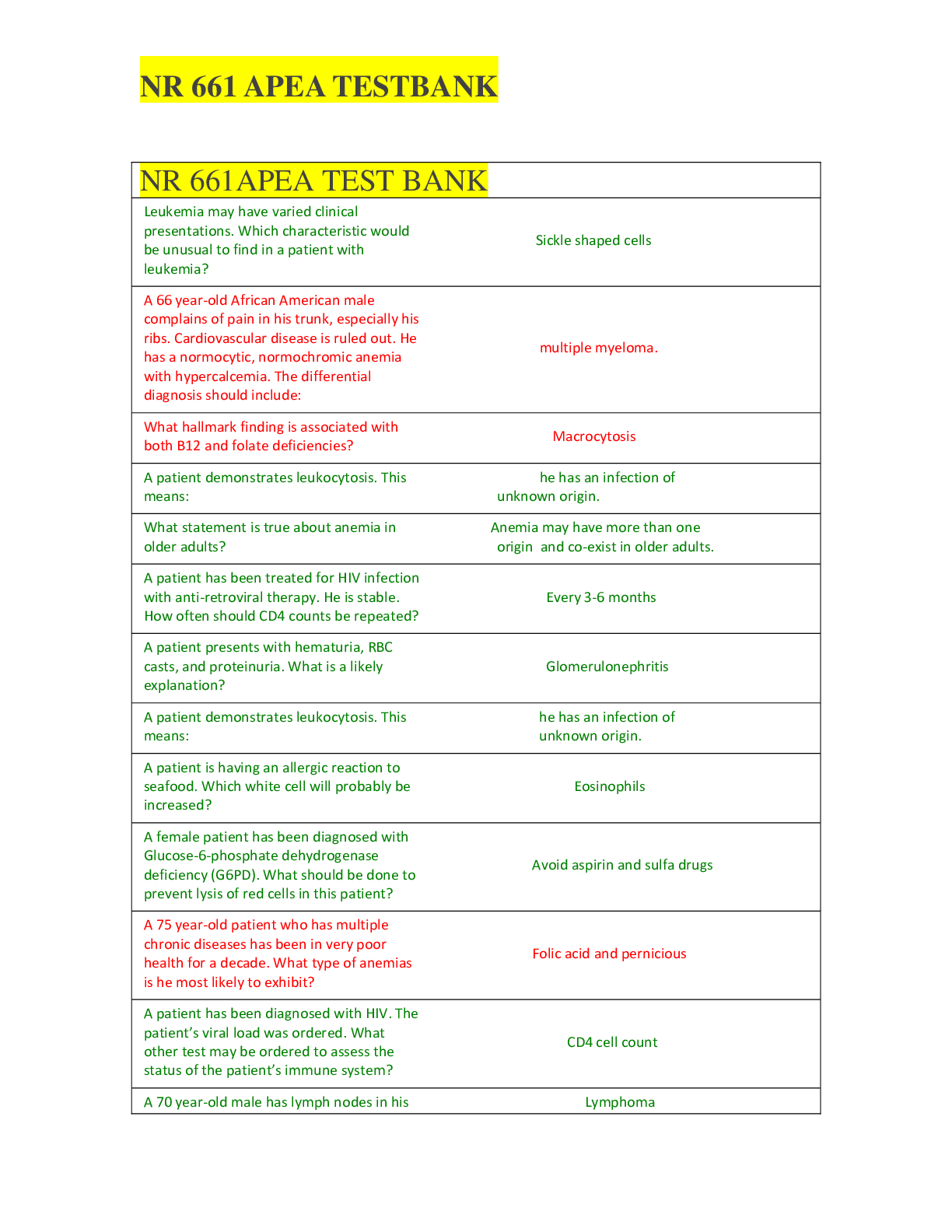
CPNP-PC Exam Test Bank Questions & Answers, Answers Explained With Rationales, Graded 100%-The mother of a 2 month old pt says that their family is relocating to Japan to pursue a long-term business o... pportunity. You know that the majority of Japan does not practice water fluoridation. You recommend that the mother incorporate fluoride supplementation of 0.25 mg/day into her child's diet, starting at what age? A. 3 months B. 6 months C. 1 year D. 3 years - B. 6 months (The AAP recommends that in areas w/little to no water fluoridation, children s/be started on fluoride supplementation @ 6 months, w/a daily dose of 0.25 mg. Supplementation is not required for the 1st 6 months of life, meaning 3 months of age is too early to introduce fluoride. By 1 year of age, the patient should already be receiving 0.25 mg/day. From 3-6 years of age, children should receive 0.50 mg/day of fluoride.) When treating a child prone to seizures an NP should primarily keep which childhood anatomical feature in mind? A. Smaller circulating blood volume B. Large tongue compared to the oropharynx C. A thin cranium D. Large head in comparison to body proportion - B. Large tongue compared to the oropharynx (Developmentally, the tongue of a child is often comparatively > than the oropharynx, which can protectively cause obstruction during a SZ & may lead to severe repercussions attributed to O2 loss. Children have a smaller circulating blood volume in absolute terms, but this is primarily a concern in cases of blood loss or bacterial infection no SZ. Children have thinner craniums, which would place them @ > risk of head injury if the skill is penetrated' this may present a concern during convulsions, but is < of a concern that the risk of obstruction. Lastly, a child's large head, in comparison to the child's body, accounts for a smaller body surface area when compared w/an adult, but this doesn't greatly influence potential complications from SZ) A newborn is born weighing 9lb. After 2 weeks, what would be the expected weight of the newborn? A. Eight lb B. Eight lb 5 oz C. Nine lb D. Nine lb 10 oz - C. Nine lb (The normal weight game progression of an infant indicates that, @ 1-2 weeks mark, the weight will be approx the same as birth. The infant will typically lose 10% of the BW in the days after birth, weighing a little over 8 lb, & then gain that weight back w/in 7-14 days. By 5 months, will double, & by 1 year triple, by 2 years quadruple.) The Denver II assessment test commonly measures a child for all of the following except: A. Personal-social development B. Language C. Fine motor development D. Intelligence - D. Intelligence (Although the Denver II assessment test measures several aspects of child development, it is NOT an intelligence test. It measures language, personal-social dev, fine motor, & gross motor dev.) Kasey, age 7 months, is bought to the clinic by her concerned parents. They have been talking to other parents in their parenting group & need reassurance that Kasey is keeping up developmentally. As you observe Kasey, you notice that she responds to her name, consistently babbles, crawls around on the floor, & is able to pick up objects. Which of the following additional milestones would also be expected in a child her age? A. Supports weight on feet B. Holds head steady C. Equal coordination of hands D. Plays independently - A. Supports weight on feet (A child exhibiting the milestones of a 6-9 month old, as evidenced by crawling, babbling, picking up objects, & responding to her name, is likely to be able to support her weight on her feet. The ability to hold her head steady by 2-5 months; play independently & exhibit equal coordination in her hands by 10-12 months.) Isaac age 6 months, has been brought to your practice by his parents for a routine check-up. As you enter the interview phase, you would know all of these methods would be well-suited for the interview except: A. Carefully phrasing potential health & safety concerns to respect the cultural practices of Isaac's parents B. Breaking from the assessment regularly to ensure the parents have accurately expressed their concerns C. Phrasing your questions in an open-ended fashion to ensure a nonjudgemental approach D. Using play to keep the patient engaged, regularly putting the assessment on hold to ensure a proper response - C. Phrasing your questions in an open-ended fashion to ensure a nonjudgemental approach (Although a non-judgmental approach s/be utilized @ all times, questions s/be directed & purposeful, not open-ended, to ensure key details of the patient's hx are not missed. Other proper techniques to utilize during an interview include ensuring cultural sensitivity, ensuring accurate perception of the parents' concerns, using lay to enhance the patient's comfort, & pausing to allow adequate time for a response.) Which of the following does not commonly impact temperature stability & regulation in a child? A. Increased subcutaneous tissue w/increased evaporative heat loss B. Decreased body surface area to mass ratio C. Thinner skin D. Increased energy expenditure - A. Increased subcutaneous tissue w/increased evaporative heat loss (Temp stability in children is commonly impacted by their limited, no increased, SQ tissue w/evaporative heat loss, as well as a smaller BSA to mass ratio, thinner skin, & increased energy expenditure. D/t the fact that more energy is needed to facilitate proper growth, less energy is available for thermoregulation. These factors are important b/c they put children @ an increased risk of hypothermia.) You ask Samuel, a toddler, to point to one body part & he points directly to his elbow. Samuel's mother states that he just started correctly pointing to body parts last week. If Samuel is properly reaching expected developmental milestones, he would most likely be: A. About 13 months old B. About 18 months old C. About 20 months old D. About 2 years old - B. About 18 months old (A properly developing toddler would be expected to point to his body parts @ 15-18 months old. A 13 month old can typically walk & understand a few words, but would not be expected to point to body parts. A 20 month old & a 2 year old would already be expected to be able to properly indicate parts of their body.) Holly, age 4, is at a WCE. During the visit, her weight is recorded as being 40 lb. Assuming expected growth parameters, how much will Holly most likely weigh in 2 years? A. 60 lb B. 52 lb C. 45 lb D. 42 lb - B. 52 lb (School age children typically gain around 5-7 lbs annually. Therefore 40 + 10 = 50 & 40 + 12 = 52 so closest answer is B - 52 lbs.) All of the following accurately reflect the typical WCE except: A. After age 4 years, a child should have a WCE yearly B. Children on ADHD medication should see a physician or NP q6m C. WCE are arranged around immunizations schedules, which are the key purpose of the visit D. If the parents are experienced, their newborn does not commonly need to have a check-up until 1-2 weeks after birth - C. WCE are arranged around immunizations schedules, which are the key purpose of the visit (WCE commonly include PE to assess the physical well-being of a child; preventive care (immunizations).. communication w/the parents, developmental tracking, & personal family issues are all equally important aspects of the WCE. If no complications they should have a WCE yearly after age 4, if taking ADHD meds then they s/be seen q6m, after birth, it is recommended that the newborn be seen in 2-4 days unless the parents are experienced.) Most stage-based theories of development focus primarily on: a. The continuity of development b. The discontinuity of development c. Persistence of inherent personality characteristics d. The influence of context on development - b. The discontinuity of development (These theories address deviations from developmental progress norms.) The common practice of using "time-outs" w/young children is a direct application of: a. Operant conditioning b. Classical conditioning c. Separation-individuation d. Maturational reinforcement - a. Operant conditioning (Time-out is a practice of behavioral modification as promulgated by B. F. Skinner's model of operant conditioning w/a negative consequence for an unacceptable behavior.) Good communication among families, schools, & primary care providers is an example of which ecological concept? a. Microsystem b. Mesosystem c. Exosystem d. Macrosystem - b. Mesosystem (A mesosystem is the link or relationship between the various settings (microsystems) w/in which a child exists (i.e., home, school, day care, etc.).) Which of the following findings would most likely be associated w/asymmetric intrauterine growth retardation? a. Weight, length, & head circumference ranging from 3rd - 5th percentile b. Heavy maternal smoking throughout pregnancy c. Weight at 3rd percentile & length at 25th d. Gestational diabetes - c. Weight at 3rd percentile & length at 25th (The weight & length are at significantly different percentiles; if the IUGR were symmetrical, these would be at the same percentile.) Early reflexive responses that are not r/t survival include all but: a. Babinski b. Moro c. Swimming d. Rooting - d. Rooting (Rooting (i.e., moving the head to locate the nipple) is a key survival reflex.) The most likely weight of a 1-year-old child whose weight @ birth was 6 pounds would be: a. 19-20 pounds b. 13-14 pounds c. 25-26 pounds d. Impossible to estimate - a. 19-20 pounds (An infant's weight should approximately triple by the age of 1 year.) One of the major psychosocial tasks of infancy is: a. Development of secure attachment b. Separation-individuation c. Symbiosis d. Regulation - a. Development of secure attachment (The development of an infant-caregiver bond is key to the prevention of long-term psychological effects associated w/deprivation and/or failure to develop secure, stable bonds.) Which developmental theory best explains the multifactorial etiology of failure to thrive? a. Organismic-maturational theory b. Social learning theory c. Transactional theory d. Psychoanalytic theory - c. Transactional theory (Transactional theory explains risks and protective factors associated w/resilience & vulnerability. It may explain some of the environmental factors associated w/FTT.) Most healthy infants are able to reach, grasp, & hold on to a rattle or other small toy by about: a. 2 months b. 6 months c. 8 months d. 10 months - b. 6 months (These are gross developmental norms associated w/the 6 mo child.) The pincer grasp is a fine motor skill that involves the ability to pick up a small object such as a raisin or piece of cereal w/the thumb & forefinger & that usually is mastered around: a. 4 months b. 6 months c. 9 months d. 16 months - c. 9 months (This is a developmental norm for a child of 9 months.) You would be concerned about the language development of a child who: a. Repeats simple phrases at 32 months b. Stutters when excited or tired at the age of 7 years c. Has a vocabulary of 10 words at 12 months d. Pronounces words that are not understandable at 24 months - b. Stutters when excited or tired at the age of 7 years (Stuttering associated w/fatigue or excitement is not unusual in a preschooler but may indicate a more pervasive problem in a 7-year-old.) The most common temperament profile is: a. Easy b. Difficult c. Slow-to-warm-up d. Intermediate - a. Easy (p. 36 Approximately 40% of children are described as having an easy (rhythmic, approachable, adaptive) temperament.) The underlying emotion of an insecurely attached (avoidant) relationship is: a. Ambivalence b. Deprivation c. Anger d. Conditional love - c. Anger (Attachment is the bond that develops throughout the first year of life; underlying anger characterizes avoidance or an insecure bond.) [Show More]
Last updated: 6 days ago
Preview 5 out of 118 pages
Loading document previews ...
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$16.50
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jun 25, 2024
Number of pages
118
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jun 25, 2024
Downloads
0
Views
9


















.png)



