*NURSING > NCLEX-PN > NCLEX-PN Test Prep Questions and Answers with Explanations V5 PRACTICE EXAM 2 2020/2021 (STUDY MODE (All)
NCLEX-PN Test Prep Questions and Answers with Explanations V5 PRACTICE EXAM 2 2020/2021 (STUDY MODE)
Document Content and Description Below
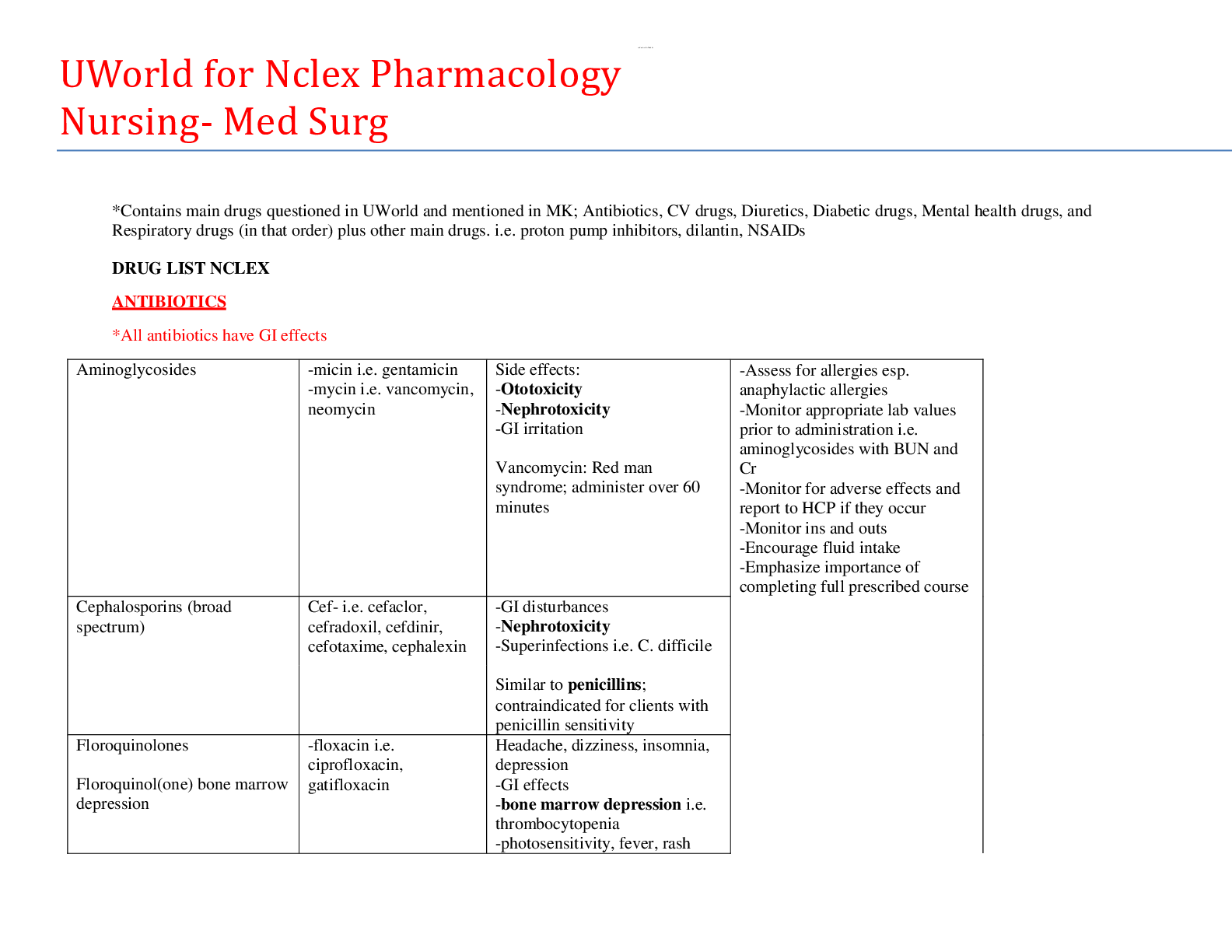
2020/2021 NCLEX-PN Test Prep Questions and Answers with Explanations V5 PRACTICE EXAM 2 (STUDY MODE) 1. Which post-operative assessment finding on a client with a femoral popliteal graft of the ... right leg would require immediate charge nurse notification? A. Edema of the right extremity and pain at the incision site B. A temperature of 99.6°F and redness of the incision C. Serous drainage noted at the surgical area D. A loss of posterior tibial and dorsalis pedis pulses on the right leg Answer D: A loss of pulses could indicate an occlusion in the graft, requiring surgical intervention. Answers A and C are expected post-operative occurrences with this surgical procedure, which makes them incorrect. Answer B is not classified as hyperthermia, so it is incorrect. 2. The nurse is caring for a client with nausea and vomiting. Laboratory results reveal a potassium level of 2.9mEq. Which ECG finding would the nurse expect to find due to the client’s potassium results? A. Depressed ST segments B. Elevated T waves C. Absent P waves D. Flattened QRSs Answer A: ECG changes associated with hypokalemia are peaked P waves, flat T waves, depressed ST segments, and prominent U waves. Answers B, C, and D are not associated with low potassium levels, so they are incorrect. 3. The nurse is preparing a patient for surgery on the lower abdomen. Which position would the nurse most likely place the client in for surgery on this area? A. Lithotomy B. Sims C. Prone D. Trendelenburg Answer D: The Trendelenburg position is used for surgeries on the lower abdomen and pelvis. This position helps to displace intestines into the upper abdomen and out of the surgical area. Answer A is reserved for vaginal, perineal, and some rectal surgeries. Answer B is used for renal surgery, and answer C is used for back surgery and some rectal surgeries. 4. The physician has prescribed a cleansing enema to a client scheduled for colon surgery. The nurse would place the client: A. Prone B. Supine C. Left Sims D. Dorsal recumbent Answer C: The left Sims position is the best position to use in this case because it follows the natural direction of the colon. Answer A places the client on the abdomen, and answers B and D position the client on the back, so they are all incorrect. 5. The nurse is caring for a client with chest trauma. Which finding would be most indicative of a tension pneumothorax? A. Frothy hemoptysis B. Trachea shift toward unaffected side of the chest C. Subcutaneous emphysema noted anterior chest D. Opening chest wound with a whistle sound emitting from the area Answer B: Trachea shift differentiates this clinical manifestation as a tension pneumothorax. When a person has a tension pneumothorax, air enters but cannot escape, causing a pressure build-up and a shifting of the great vessels, the heart, and the trachea to the unaffected side. Answer A correlates with a pulmonary contusion, so it is incorrect. Answers C and D are associated with a pneumothorax. This makes them nonspecific for tension pneumothorax and, thus, incorrect. 6. The nurse is reviewing a history on a new admission for surgery in the morning. Which long-term medication in the client’s history would be most important to report to the physician? A. Prednisone B. Lisinopril (Zestril) C. Docusate (Colace) D. Calcium carbonate (Oscal D) Answer A: Abrupt withdrawal of steroids can lead to collapse of the cardiovascular system; therefore, the physician should be notified for drug coverage. The medications in answers B, C, and D would not be as important as the maintenance of the steroids. Answer B is an ace-inhibitor used as an antihypertensive. Answer C is a stool softener, and answer D is a calcium and vitamin agent; thus, all are incorrect. 7. The nurse is explaining about the drug zafirlukast (Accolate) to a client with asthma. Which comment by the client would indicate ineffective teaching? A. “I should take this medication with meals.” B. “I need to report flulike symptoms to my doctor.” C. “My doctor might order liver tests while I’m on this drug.” D. “If I’m already having an asthma attack, this drug will not stop it.” Answer A: Accolate should be taken 1 hour before or 2 hours after eating to prevent slow absorption of the drug caused by taking it with meals; therefore, this statement is incorrect and requires further teaching by the nurse. Answers B, C, and D are all true statements regarding this drug and are correct statements made by the client. 8. A client is 4 hours post-operative left brain cerebral aneurysm clipping. Which assessment finding would cause the nurse the most concern? A. Temperature 99.4°F, heart rate 110, respiratory rate 24 B. Drowsiness, urinary output of 50mL in the past hour, 1cm blood drainage noted on surgical dressing C. BP 120/60, lethargic, right-sided weakness D. Alert and oriented, BP 168/96, heart rate 70 Answer C: The assessment finding that causes the most concern is the finding that could indicate a possible stroke. The right-sided weakness would mean there is a loss of muscular functioning on the side opposite the surgical procedure. Answers A, B, and D might indicate a need for reassessments but not a cause for immediate concern or intervention, so they are incorrect. 9. A client with pancreatic cancer has just been given a negative prognosis by the oncologist. The nurse hears the client state, “I don’t believe the doctor, and I think he has me confused with another patient.” This is an example of which of Kubler-Ross’ stages of dying? A. Denial B. Anger C. Depression D. Bargaining Answer A: Kubler Ross identified five stages of dying as the ways that people cope with death: denial, anger, bargaining, depression, and acceptance. Answer A is the first stage of denial that can be used as a buffer and a way to adapt. Other examples of statements made by the client in this stage are “This can’t be true” and “I want another opinion.” When dealing with these clients, the nurse needs to use open-ended statements, such as “Tell me more.” Answers B, C, and D are a few of the other stages of dying and, thus, are incorrect. 10. The nurse is discussing staff assignments. Which client assignment should be given to the nurse’s assistant? A. Emergency exploratory laparotomy with a colon resection the previous shift B. Client with a stroke scheduled for discharge to rehabilitation C. A client with terminal cancer in severe pain D. New admission with diverticulitis Answer B: The client with the stroke is the most stable client of the ones listed. The client in answer A would need extensive assessment. Answer C involves a client with a need for psychosocial support and nursing interventions. The client in answer D is a new admission with an infected diverticulum and would be less stable, with more unknowns. 11. A client is being discharged on warfarin (Coumadin) after hospitalization for atrial fibrillation. The nurse recognizes that which of the following foods would be restricted while the client is on this medication? A. Cabbage B. Apples C. Potatoes D. Macaroni Answer A: Vitamin K would decrease the effects of Coumadin; therefore the client should be taught to restrict green, leafy vegetables, such as broccoli, cabbage, turnip greens, and lettuce. Answers B, C, and D are food choices that are low in vitamin K, so they are incorrect. 12. Which assessment finding in a client with emphysema indicates to the nurse that the respiratory problem is chronic? A. Wheezing on exhalation B. Productive cough C. Clubbing of fingers D. Cyanosis Answer C: The clinical manifestation of clubbing of the fingers takes time. This indicates that the condition is chronic and not acute, making answer C the correct answer. Answers A, B, and D are all nonspecific for chronicity, so they are incorrect. 13. A client who has just undergone a laparoscopic tubal ligation complains of “free air pain.” What would be the nurse’s best action? A. Ambulate the client B. Instruct the client to breathe deeply and cough C. Maintain the client on bed rest with her legs elevated D. Insert an NG tube to low wall suction Answer A: Ambulating the client should help to pass the air. The air is used during the surgical procedure to assist in performance of the surgery. Answers B and C would not help, so they are incorrect. Answer D is not necessary or appropriate at this time. 14. The nurse is planning shift duties. Which is the least appropriate task for the nursing assistant? A. Assisting a COPD client admitted 2 days ago to get up in the chair B. Feeding a client with bronchitis who has an old paralysis on the right side C. Accompanying a discharged emphysema client to the transportation area D. Assessing an emphysema client complaining of difficulty breathing Answer D: Assessment is not within the role of a nurse’s assistant, which makes this the least appropriate of the tasks listed. Answers A, B, and C are all appropriate tasks for an assistant, so they are incorrect. 15. Which nursing order would the nurse anticipate for a client with pancreatitis? A. Force fluids to 3,000mL/24 hours B. Insert a nasogastric tube and connect it to low intermittent suction C. Place the client in reverse Trendelenburg position D. Place the client in enteric isolation Answer B: An NG is inserted to decrease the secretion of pancreatic juices and assist in pain relief. Answer A is incorrect because these clients are held NPO. Clients are placed in semi-Fowler’s position, which makes answer C incorrect. Answer D is not appropriate because the wastes are not contaminated. 16. Assessment findings for the client admitted with a stroke reveal an absence of the gag reflex. The nurse suspects injury to which cranial nerve? A. XII (hypoglossal) B. X (vagus) C. IX (glossopharyngeal) D. VII (facial) Answer B: To test for vagus nerve problems, the nurse uses a tongue blade and depresses the back of the throat to elicit a gag reflex. Other ways to test for damage to the vagus nerve are by having the client say “Ah” while observing for uniform rising of the uvula and the soft palate. The absence of this reflex could indicate damage to the X cranial nerve. Answers A, C, and D are not tested in this manner, so they are incorrect. 17. The nurse at a clinic is present when the healthcare provider (HCP) notifies a client of the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. What medication does the nurse anticipate the provider prescribing? A. Hydrocodone/acetaminophen (Loritab) B. Meloxicam (Mobic) C. Hydromorphone hydrochloride (Dilaudid) D. Alprazolam (Xanax) Answer B: Mobic has anti-inflammatory effects and is useful for arthritis. Answers A and C are opiods and can cause dependency. They are not effective for arthritis. Answer D is an anti-anxiety agent not given for arthritis. 18. A client with gallstones and obstructive jaundice is experiencing severe itching. The physician has prescribed cholestyramine (Questran). The client asks, “How does this drug work?” What is the nurse’s best response? A. “It blocks histamine, reducing the allergic response.” B. “It inhibits the enzyme responsible for bile excretion.” C. “It decreases the amount of bile in the gallbladder.” D. “It binds with bile acids and is excreted in bowel movements with stool.” Answer D: Questran works by binding the bile acids in the GI tract and eliminating them, decreasing the itching associated with jaundice. Answers A, B, and C are not how Questran works to decrease itching. 19. A client with ulcerative colitis requires an illeostomy. The nurse would instruct the client to do which of the following measures as an essential part of caring for the stoma? A. Perform massage of the stoma three times a day B. Include high-fiber foods, especially nuts, in the diet C. Limit fluid intake to prevent loose stools D. Cleanse the peristomal skin meticulously Answer D: Careful cleansing is necessary to prevent skin breakdown and skin irritation. Answer A is not an intervention used for illeostomies. Clients should avoid high fiber and gas-producing foods, as in answer B. Answer C is incorrect because these clients are not on fluid restriction. 20. Diphenoxylate hydrochloride and atropine sulfate (Lomotil) is prescribed for the client with ulcerative colitis. The nurse realizes that the medication is having a therapeutic effect when which of the following is noted? A. There is an absence of peristalasis. B. The number of diarrhea stools decreases. C. Cramping in the abdomen has increased. D. Abdominal girth size increases. Answer B: Lomotil’s desired effect is to decrease GI motility and the number of diarrhea stools. Answers A and D do not occur with the use of Lomotil. The drug should decrease cramping instead of increasing it, as in answer C. 21. The physician is about to remove a chest tube. Which client instruction is appropriate? A. Take a deep breath, exhale, and bear down B. Hold the breath for 2 minutes and exhale slowly C. Exhale upon actual removal of the tube D. Continually breath deeply in and out during removal Answer A: This procedure prevents air entrance while the chest tube is being removed. Answer B is incorrect because it requires a lack of ventilation for too long of a period and exhalation is not allowed. Answers C and D allow air to enter the thoracic cavity during removal, so they are incorrect. 22. A client with severe anxiety has been prescribed haloperidol (Haldol). What clinical manifestation suggests that the client is experiencing side effects from this medication? A. Cough B. Tremors C. Diarrhea D. Pitting edema Answer B: Tremors are an extrapyramidal side effect that can occur when taking Haldol. Answers A, C, and D are not side or adverse effects of Haldol. 23. A client with a femur fracture is exhibiting shortness of breath, pain upon deep breathing, and a cough that produces blood-tinged sputum. The nurse would determine that these clinical manifestations are indicative of which of the following? A. Congestive heart failure B. Pulmonary embolus C. Adult respiratory distress syndrome D. Tension pneumothorax Answer B: Hemoptysis is a hallmark symptom of a pulmonary embolus. This client’s fracture history and other clinical manifestation leads to this conclusion. The clinical manifestations as a group do not correlate with the diagnoses in answers A, C, and D. 24. A client with Alzheimer’s disease has been prescribed donepezil (Aricept). Which information should the nurse include when explaining about Aricept? A. “Take the medication with meals.” B. “The medicine can cause dizziness, so rise slowly.” C. “If a dose is skipped, take two the next time.” D. “The pill can cause an increase in heart rate.” Answer B: A side effect of Aricept is dizziness; therefore, the client should be reminded to move slowly on rising from a lying or sitting position. Answer A is incorrect because it should be taken at bedtime, with no regard to food. Increasing the number of pills can increase the side effects, so answer C is incorrect. Another effect of the drug is bradycardia, making answer D incorrect. 25. A client who had an abdominal aortic aneurysm repair is having delayed healing of the wound. Which laboratory test result would most closely correlate to this problem? A. Decreased albumin B. Decreased creatinine C. Increased calcium D. Increased sodium Answer A: Protein is a necessary component of wound healing. An inadequate amount of protein would correlate with the client’s wound not healing properly. Answers B, C, and D do not directly relate to wound healing, so they are incorrect. 26. A client with diagnosed diabetes visits the clinic complaining of shakiness and tingling sensations. Which of the following questions is most important for the LPN/LVN to ask? A. When did you last eat? B. Did you bring your medication with you? C. What was your blood glucose and when was it checked? D. Is there anyone available to drive you home today? Answer C: The client is exhibiting symptoms of hypoglycemia. The LPN needs to gather information related to the client’s diagnosis. The questions in A, B, and D are appropriate. But the priority would be to find out the problem and treat it. 27. Which exam is most reliable in diagnosing peptic ulcer disease? A. Upper-gastrointestinal x-ray B. Gastric analysis C. Endoscopy D. Barium studies Answer C: Although all of the tests listed can be used to diagnose an ulcer, an endoscopic exam is the only way to obtain accurate visual evidence. Answers A, B, and D are not as accurate or reliable, which makes them incorrect. 28. A client recovering from a thyroidectomy tells the nurse, “I feel numbness and my face is twitching.” What is the nurse’s best initial action? A. Offer mouth care B. Loosen the neck dressing C. Notify the physician D. Document the finding as the only action Answer C: The parathyroid gland can be inadvertently removed or injured with thyroid removal. This can cause hypocalcemia and symptoms of tetany, which requires notifying the physician. Answers A and B are ineffective ways to treat or obtain treatment for hypocalcemia. Answer D would allow the condition to progress, so it is incorrect. 29. A client is to undergo insertion of an esophageal gastric balloon tube. Which instruction would the nurse include in teaching about the purpose of the device? A. “The device applies pressure to the veins in the esophagus and stomach.” B. “It is used to prevent the accumulation of ascites.” C. “It will prevent bleeding of arteries in the esophagus.” D. “The doctor will use the tube to inject sclerosing solution into esophageal varices.” Answer A: An esophageal gastric balloon tube is inserted for bleeding esophageal varices by placing direct pressure and stopping the bleeding. It cannot be used to prevent fluid build-up in the peritoneal cavity, as in answer B. The bleeding is a venous backup of blood, not an arterial one, so answer C is incorrect. Sclerotherapy is done by endoscopic procedure, so answer D is incorrect. 30. A client is admitted to the chemical dependency unit for evaluation of alcoholism. Which question is part of an alcoholism-assessment tool called the CAGE questionnaire? A. How often do you have a drink containing alcohol? B. Have people annoyed you by criticizing your drinking? C. Have you or someone else ever been injured as a result of your drinking? D. How many drinks containing alcohol do you have on a typical day when you are drinking? Answer B: One of the questions on the CAGE assessment asks whether criticism of one’s drinking is annoying. Other questions included in this assessment tool are “Have you ever felt you should cut down on your drinking?”, “Have you felt guilty about your drinking?”, and “Have you ever had a drink first thing in the morning to steady your nerves or get rid of a hangover?.” The answers in A, C, and D are part of the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT), so they are incorrect. 31. A client has an order to remove the nasogastric tube. Which is the correct nursing action to remove the tube? A. Apply sterile gloves and untape the tube from the client’s face B. Pull the tube out 2 inches, pause for 2 minutes, and repeat until the entire tube is removed C. Instill 30mL of normal saline before removing the tube D. Pull the tube out steadily and smoothly while keeping it pinched Answer D: The nurse should also ask the client to hold his breath to prevent aspiration, which is the correct procedure for discontinuing an NG tube. Clean gloves should be used for this procedure, making answer A incorrect. The tube should be removed continuously without pause, so answer B is incorrect. An amount of 30mL of air—not normal saline—can be inserted before removal, so answer C is incorrect. 32. The nurse is preparing a client with cirrhosis for a paracentesis. How will the nurse position the client for this procedure? A. Trendelenburg B. Lying on the right side C. Lying on the left side D. Sitting position Answer D: Placing the client in the sitting position for a paracentesis is recommended. The side-lying and head-down positions in answers A, B, and C are not recommended for a paracentesis. 33. A client has a vagal nerve stimulator in place to prevent seizures. Which would indicate that the device is working properly? A. The client’s voice changes when operating. B. Hiccups occur with each stimulation. C. The client can feel vibrations in the area of the vagal nerve stimulator when operational. D. The client’s radial pulse obliterates when the stimulator is activated. Answer A: A vagal nerve stimulator is inserted surgically to treat seizure activity. If the device is working properly, the client will notice a voice change when the device is active. Answers B, C, and D don’t occur with the operation of the device, which makes them incorrect. 34. The nurse working on a surgical unit would identify which client as having the highest risk for pulmonary complications after surgery? A. A 24-year-old with open reduction internal fixation of the ulnar B. A 45-year-old with an open cholecystectomy C. A 36-year-old after a hysterectomy D. A 50-year-old after a lumbar laminectomy Answer B: The risk factors for pulmonary complications increase with abdominal surgery for clients over age 40, and for those with prolonged periods in bed. Answer B includes two risk factors, an age of more than 40 years and abdominal surgery in an area under the diaphragm. Answers A and C have one risk factor each, which makes them incorrect. Answer D involves a risk factor for deep vein thrombosis, so it is incorrect. 35. A client arrives after a house fire. What clinical manifestation is most indicative of possible carbon monoxide poisoning? A. Pulse oximetry reading of 80% B. Expiratory stridor and nasal flaring C. Cherry-red color to the mucous membranes D. Presence of carbonaceous particles in the sputum Answer C: The hallmark symptom of carbon monoxide poisoning is the cherry-red color. The answers in A, B, and D are not specific to carbon monoxide poisoning. 36. A client is admitted after a motor vehicle accident. The nurse suspects that the client is in the compensatory stage of shock due to which clinical manifestations? A. Blood pressure 120/70, confusion, heart rate 120 B. Crackles on chest auscultation, mottled skin, lethargy C. Skin color jaundice, urine output less than 30mL the past hour, heart rate 170 D. Rapid, shallow respirations; unconscious; petechiae anterior chest Answer A: When a person is in the compensatory stage of shock, the BP remains within normal limits. Increased heart rate occurs that allows cardiac output to be maintained. The client also exhibits confusion and cold and clammy skin. Answer B correlates with the progressive stage of shock, so it is incorrect. Answers C and D both indicate that the client is past compensation, so they are incorrect. 37. Which medication should the nurse have available in case a client has an anaphylactic reaction to penicillin G benzathine (Bicillin)? A. Epinephrine B. Diazepam (Valium) C. Sodium bicarbonate D. Phentolamine mesylate (Regitine) Answer A: Epinephrine, antihistamines, and resuscitation equipment should be available in case of a reaction to penicillin. Epinephrine is used for allergic reactions. Answer B is an antianxiety agent, and answer D is used for high blood pressure. The anti-ulcer agent in answer C is not used for allergic reactions. 38. A client is admitted with benign prostatic hypertrophy. Which clinical manifestation should the nurse expect? A. Frequent urge to void B. Foul-smelling urine C. Copious urine output D. Pain on urination Answer A: The person with benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH) has clinical manifestations that are caused by the obstruction. Symptoms of BPH include frequency of urination, difficulty in starting the urine flow, and a frequent urge to void. If the client develops a urinary tract infection, the urine might smell, but it is not directly related to the BPH, so answer B is incorrect. Urinary retention also occurs, making answer C incorrect. Pain with urination is not a symptom of BPH, so answer D is incorrect. 39. Which clinical manifestation during a bone marrow transplant alerts the nurse to the possibility of an adverse reaction? A. Fever B. Red urine C. Hypertension D. Shortness of breath Answer D: Shortness of breath signifies an adverse reaction to the transplant procedure. Answers A and C can occur with the transplant process but do not signify an adverse reaction. Answer B is a normal finding with the bone marrow transplant. 40. Which area in dark-skinned individuals would be the most likely to show a skin cancerous lesion? A. Chest B. Arms C. Face D. Palms Answer D: The palms of the hands and soles of the feet are areas in darkskinned clients where skin cancer is more likely to develop because of the decreased pigmentation found in these areas. Answers A, B, and C are areas where high pigmentation occurs and, therefore, are less likely to show signs of cancer. 41. A client with a gastrointestinal bleed has an NG tube to low continuous wall suction. To assess bowel sounds, the nurse should perform which of the following procedures? A. Insert 10mL of air in NG tube and listen over the abdomen with a stethoscope B. Clamp the tube while listening to the abdomen with a stethoscope C. Irrigate the tube with 30mL of NS while auscultating the abdomen D. Turn the suction on high and auscultate over the naval area Answer B: It is important to clamp the tube while auscultating because the sound from the suction interferes with the auscultation process. Answer A is one measure used to determine whether NG is in the stomach, but not to assess bowel sounds. Answers C and D are not the correct procedure for assessment of bowel sounds, so they are incorrect. 42. A burn client’s care plan reveals an expected outcome of no localized or systemic infection. Which assessment by the nurse supports this outcome? A. Wound culture results show minimal bacteria B. Cloudy, foul-smelling urine output C. White blood cell count of 14,000 D. Temperature of 101°F Answer A: A culture result that shows minimal bacteria is a favorable outcome. Answers B, C, and D are abnormal and negative outcomes, so they are incorrect. 43. The nurse is preparing to administer promethazine hydrochloride (Phenergan). This drug should produce which therapeutic effect? A. Marked diuresis B. Decreased nausea C. Constriction of the pupils D. Increased seizure threshold Answer B: Phenergan is used for prevention and treatment of nausea and vomiting, sedation, adjunct to pain and anesthesia medications, and allergic reactions. Answers A, C, and D are not desired effects of the drug Phenergan, which makes them incorrect. 44. Which antibiotic is safest to administer to a client who is allergic to penicillin? A. Cefazolin (Ancef) B. Amoxicillin (Amoxil) C. Erythromycin (Erythrocin) D. Ceftriazone (Rocephin) Answer C: Erythromycin is the only drug listed that is not penicillin based. Answers A, B, and D are in the same family as penicillin, so they are not as safe to administer, which makes them incorrect. 45. The nurse notes the following laboratory test results on a 24-hour postburn client. Which abnormality should be of particular concern? A. Potassium 7.5mEq/L B. Sodium 131mEq/L C. Arterial pH 7.34 D. Hematocrit 52% Answer A: Normal potassium is 3.5–5.0. Severe life-threatening complications can occur with hyperkalemia, requiring the physician to be notified of any abnormality. Answers B, C, and D are normal results, which makes them incorrect. 46. Which technique is correct for administration of ear drops to a 3-yearold? A. Hold the child’s head up and extended B. Place the head in chin tuck position C. Pull the pinna down and back D. Irrigate the ear before medication administration Answer C: Pulling the pinna down and back is correct for administering ear drops to a child because the child’s ear canal is short and straight. The pinna is pulled up and back for adults. Answers A and B are improper technique and would make it harder for the drops to be administered. Answer D would be incorrect because this is not a necessary part of administering ear drops, even though irrigation might be done at times to cleanse the ear for assessment. 47. The nurse is caring for a client with scalding burns across the face, neck, entire anterior chest, and entire right arm. Using the rule of nines, what is the estimated percentage of body burned? A. 18% B. 23% C. 32% D. 36% Answer C: The rule of nines is a way to estimate the percentage of body surface area burned (see the following figure). The calculation would be 4.5% for the face and neck, 9% for the entire arm, and 18% for the entire anterior chest, which would be 31.5%, or approximately 32%. Answers A, B, and D are not correctly calculated sums of the burned areas. 48. The nurse caring for a client in shock recognizes that the glomerular filtration rate of the kidneys will remain intact if the client’s mean arterial pressure remains above which minimal value? A. 80 B. 70 C. 60 D. 50 Answer A: Acute renal failure can occur when the MAP drops below 80. The mean arterial pressures in answers B, C, and D are too low to allow proper functioning of the kidney, which makes these answers incorrect. 49. Which assessment data on a child with hydrocephalus would be the most objective? A. Anorexia B. Vomiting C. Head measurement D. Temperature Answer C: An increase in head growth is used as a diagnostic gauge for hydrocephalus. Answers A and B can also occur with hydrocephalus, but they are not as specific or diagnostic as head circumference, so they are incorrect. Answer D is not related to hydrocephalus, so it is incorrect. 50. The nurse recognizes which of the following types of leukemia as being more common in an older adult? A. Acute myelocytic leukemia B. Acute lymphocytic leukemia C. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia D. Chronic granulocytic leukemia Answer C: Two-thirds of the clients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia are older than 60 years of age at diagnosis. Answers A, B, and D do not occur more often in the elderly, so they are incorrect. 51. A client has pneumonia. Which assessment finding best indicates that the client’s respiratory efforts are currently adequate? A. The client is able to talk. B. The client is alert and oriented. C. The client’s O2 saturation is 97%. D. The client’s chest movements are uninhibited. Answer C: The oxygen saturation is the best indicator of respiratory status because it is more objective. Answers A, B, and D are subjective and nonspecific, so they are incorrect. 52. The nurse is discussing with parents the recommended activities for children with asthma. Which sports activity would the nurse include in the discussion? A. Soccer B. Swimming C. Football D. Track Answer B: Because of the moisturized air inhaled with swimming, it is an ideal sport for children with respiratory conditions, so this is correct. Answers A, C, and D could trigger an attack with asthma and would not be recommended. 53. Which of the following would the nurse perform when giving medication via an NG tube? A. Ascertain tube patency and placement. B. Position the client dorsal recumbent. C. Reconnect the tube to suction immediately after administration of the drug. D. Administer the drug as rapidly as possible to prevent clogging the tube. Answer A: Making sure that the tube is in the right location is an important first step. Clients should be positioned with the head elevated, the medication should be administered slowly, and the NG tube should be clamped for 20-30 minutes after medication administration; therefore, answers B, C, and D are incorrect. 54. An infant in the nursery is 48 hours old and has not passed meconium. The nurse suspects which of the following? A. Coarctation of the aorta B. Tetralogy of fallot C. Hyperbilirubinemia D. Cystic fibrosis Answer D: A newborn who has not passed meconium in the first 24 hours could have cystic fibrosis. This is due to the thick secretions preventing passage of the meconium, resulting in obstruction of the bowel. Answers A and B are both cardiovascular problems that are not associated with meconium passage, so these are incorrect. Answer C is not associated with meconium and is evidenced by a yellow skin tone and an elevated serum bilirubin level. 55. Which of the following laboratory results would cause the most concern in the immunosuppressed client? A. A sodium level of 50mg/dL B. A blood glucose of 110mg/dL C. A platelet count of 100,000/cu mm D. A white cell count of 5,000/cu mm Answer A: Normal sodium is 135–145mEq, so this is a low blood level that should be reported. Answers B, C, and D are normal or near-normal readings. 56. The nurse has an order to administer meperidine (Demerol) 75 mg IM for pain. The drug available is Demerol 100mg in 2 mLs. How many mL(S) will the nurse administer? A. 1.0 mL B. 1.3 mL C. 1.5 mL D. 1.7 mL Answer C: The correct calculation is 1.5 mL, which is calculated as follows: 75 mg?= 2mL/100mg= 150/100= 1.5 mL Answers A, B, and D are incorrect calculations, so they are wrong. 57. A client is diagnosed with left subclavian artery obstruction. What additional findings would the nurse expect? A. Memory loss and disorientation B. Numbness in the face, mouth, and tongue C. Radial pulse differences over 10bpm D. Frontal headache with associated nausea or emesis Answer C: Obstruction of the subclavian artery would show a decrease in radial heart rate on the side of the obstruction. Answers A, B, and D are related to neurological problems or deficits, which makes them incorrect. 58. The nurse is giving information to a client at high risk for the development of skin cancer. Which instruction should be included? A. “You should see the doctor every 6 months.” B. “Sunbathing should be done between the hours of noon and 3 p.m.” C. “If you have a mole, it should be removed and biopsied.” D. “You should wear sunscreen when going outside.” Answer D: Everyone should wear sunscreen when going outside, to protect them from the ultraviolet exposure. Answer A is not necessary. Answer C is incorrect because only moles that are suspicious require removal and biopsy. Answer B is the period of day when the sun rays are most detrimental to the skin. 59. A client who is complaining of nausea, has an order for hydroxyzine hydrochloride (Vistaril) 75mg every 3–4 hours IM p.r.n. for nausea. The vial contains 100mg per 2mL. How many milliliters will the nurse administer? A. 0.8mL B. 1.5mL C. 2.0mL D. 2.5mL Answer B: The desired dose is 75mg. The dose on hand is 100mg in 2mL, making the correct dose 1.5mL. The answers in A, C, and D are incorrect calculations. 60. The nurse is caring for a client who is experiencing pruritis. Which would be the most appropriate nursing intervention? A. Suggest the client take warm showers B.I.D. B. Add baby oil to the client’s bath water C. Apply powder to the client’s skin D. Suggest a hot water rinse after bathing Answer B: Adding baby oil to the client’s bathwater could assist in soothing the itching. Answers A, C, and D would increase dryness and worsen the skin itching. 61. A nurse is caring for a client with a diagnosis of prostate cancer. Which laboratory result does the nurse note that specifically correlates with this diagnosis? A. Creatinine 0.9 mg/dL B. Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) 26.4 mg/dL C. Prostate specific antigen (PSA) 10.0 ng/mL D. Hemoglobin (HGB) 16 gms Answer C: A patient with prostate cancer usually has an elevated PSA count. The normal PSA level is less than 4 ng/mL. The answers in A and D are both normal, so they are incorrect. Answer B is an elevated level, but not related to the prostate cancer, so it is a wrong option. 62. The nurse is giving instructions on the removal of ticks at a Girl Scout meeting. Which information is proper procedure for tick removal? A. “Use tweezers to remove the tick, disinfecting the area after removal.” B. “Apply nail polish to the tick, then remove it with your gloved fingers.” C. “Soak alcohol on a piece of cloth, smothering the tick, and pull it out with the cloth.” D. “Apply a lighted match to the tick and wipe it off.” Answer A: The recommended procedure is to use tweezers to remove the tick, using a slow steady force, and to disinfect the area before and after doing so. Answers B, C, and D are not the correct procedure to safely remove a tick. 63. The nurse recognizes that which of the following protective equipment is most appropriate to wear when suctioning a client with a tracheostomy? A. Gown, goggles, and gloves B. Gown only C. Gloves only D. Gown and shoe covers Answer A: Standard precautions require that goggles, a gown, and gloves be worn when there is a danger of contamination by splashing. Answers B and C are not adequate for the suctioning procedure. A gown is not an adequate precaution and shoe covers are not required, making answer D incorrect. 64. Which statement made by a client’s son signifies abnormal grieving by the client? A. “Mother still has episodes of crying, and it’s been 6 months since Daddy died.” B. “Mother seems to have forgotten the bad things that Daddy did in his lifetime.” C. “She really had a hard time after Daddy’s funeral. She said that she had a sense of longing.” D. “Mother has not been saddened at all by Daddy’s death. She acts like nothing has happened.” Answer D: Abnormal grieving occurs when someone acts as if nothing has happened. Answers A, B, and C are normal parts of the grieving process, so they are incorrect. 65. Which statement made by the client would alert the nurse to a possible fluid and electrolyte imbalance in an 80-year-old client being admitted to a nursing home? A. “My skin is always so dry.” B. “I often use a laxative for constipation.” C. “I have always liked to drink a lot of water.” D. “I sometimes have a problem with dribbling urine.” Answer B: The misuse and overuse of laxatives can cause serious fluid and electrolyte imbalances in the elderly, so this is the correct choice. Answers A and D can be normal occurrences associated with the physiological changes of aging. Answer C is an incorrect response because the client states that increased fluid intake is not a new occurrence. 66. The nurse is reviewing laboratory results. Serum sodium of 156mEq/L is noted. What changes would the nurse expect the client to exhibit? A. Hyporeflexia B. Manic behavior C. Depression D. Muscle cramps Answer B: The normal sodium is 135–145mEq/L. When hypernatremia occurs, the client can exhibit manic and hyperactivity behaviors. Other symptoms of increased sodium include restlessness, twitching, seizures, and hyperreflexia. Answers A, and C are not symptoms of high sodium levels, so they are incorrect. Answer D is associated with low sodium levels. 67. A nurse would expect a client admitted with congestive heart failure to be treated with which drug? A. Furosemide (Lasix) B. Pentoxifyline (Trental) C. Warfarin (Coumadin) D. Metaxalone (Skelaxin) Answer A: Clients with congestive heart failure are usually treated with a diuretic, such as Lasix and Digoxin. Answer B is a hematologic, and answer C is an anticoagulant. Skelaxin, in answer D, is a muscle relaxer. These drugs are not used to decrease fluid or improve cardiac output necessary for the treatment of congestive heart failure, so they are incorrect. 68. The nurse is assessing the chart of a client admitted for surgery when an order is noted to administer Atropine 2mg IM as a pre-operative medication to a 40-year-old client. What initial nursing action is most appropriate? A. Clarifying the order with the physician B. Administering the medication deep IM C. Checking the chart for client allergies D. Performing the mathematical calculation to determine dosage due Answer A: The usual dosage of atropine as a preoperative medication is 0.4– 0.6mg. The ordered dosage is too high, so the order requires clarification. Answer B is incorrect because of the ordered dosage. Answers C and D will be required, but not before getting a correct dosage order. 69. A client is admitted to the emergency room with a complaint of chest pain. The physician suspects a myocardial infarction and orders heparin and nitroglycerin. Which home medication, taken just before admission, would the nurse report to the ER physician immediately? A. Acetaminophen (Tylenol) B. Sildenafil (Viagra) C. Chlordiazeproxide/clidnium (Librax) D. Escitalopram (Lexapro) Answer B: Nitroglycerin is contraindicated with the use of Viagra. The medications in B, C, and D have no adverse effects when administered with heparin or nitroglycerin, so they are incorrect. 70. A client is to undergo a bone marrow aspiration. The nurse plans to include which statement in the client preparation? A. “You will be sitting on the side of the bed during the procedure.” B. “Portions of the procedure will cause pain or discomfort.” C. “You will be given some medication to cause amnesia of the test.” D. “You will not be able to drink fluids for 24 hours before the study.” Answer B: There will be a sensation of pulling during the aspiration. This feeling is painful. Answer A is incorrect because the position is inappropriate for bone marrow aspiration. Answer D is not a required preprocedure diet change. Although the client might receive a local anesthetic and/or pain medication, amnesic medications such as Versed are not usually administered, so answer C is incorrect. 71. A client is scheduled for surgical repair of an abdominal aortic aneurysm. Which assessment is most crucial during the preoperative period? A. Assessment of the client’s level of anxiety B. Evaluation of the client’s exercise tolerance C. Identification of peripheral pulses D. Assessment of bowel sounds and activity Answer C: It is most important to identify the pulses preoperatively to have a baseline for post-operative evaluation. Answers A, B, and D are not priorities for the client preoperatively. 72. Which of the following dysrhythmias is most likely to occur during suctioning? A. Bradycardia B. Tachycardia C. Ventricular ectopic beats D. Sick sinus syndrome Answer A: Excessive vagal stimulation causes bradycardia because of parasympathetic stimulation. Answers B, C, and D are not arrhythmias associated with suctioning, so they are incorrect. 73. The nurse is reiterating discharge instructions for a client being discharged after an esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) and a confirmed gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Which statement by the client indicates that further instructions are necessary? A. “I should avoid the following in my diet: fatty foods, alcohol, peppermint, caffeine, and chocolate.” B. “I should maintain a desirable body weight.” C. “I need to lie flat after meals to delay gastric emptying.” D. “I need to avoid eating or drinking 2-3 hours before bedtime.” Answer C: The client should keep the head of the bed elevated after meals. The answers in options A, B, and D are all correct instructions for clients with GERD, which indicates correct understanding. 74. The LPN/LVN is caring for a client with Clostidium difficile (C difficile). Which of the following observations indicates to the nurse that the client’s condition is improving? A. Increased watery stools B. Malaise C. Anorexia D. Moist mucous membranes Answer D: Dehydration is associated with C difficile due to the diarrhea and temperature elevation. Moist mucous membranes would indicate adequate hydration showing an improved patient outcome. Answers A, B, and C are manifestations of the condition and do not indicate an improvement, so they are incorrect. 75. The LPN/LVN is describing a 24-hour urine collection to a client. Which of the following explanations is most accurate? A. Void and save the urine at the start of the collection period to begin the process B. Wash the perineal area with soap and water before each void C. Collect the urine in a sterilized container or receptacle D. Empty the bladder at the end of the collection period and save this urine Answer D: Proper procedure is to empty the bladder and save the urine at the end of the collection period. Clients should void and discard the urine at the beginning of the collection period, so answer A is incorrect. Answer B is utilized when collecting a midstream (clean catch) specimen, so it is incorrect. The urine doesn’t have to be collected in a sterile container; therefore, C is incorrect. 76. A client who has had thoracic surgery has been instructed in arm and shoulder exercises. The nurse recognizes which of the following as the primary reason for these exercises? A. Restore movement B. Prevent edema of the scapula C. Provide psychological stress relief D. Prevent respiratory complications Answer A: The reasons for these exercises are to restore movement, prevent stiffening of the shoulder area, and improve the client’s muscle power. Answer B is not prevented by the exercises utilized. Although the answers in C and D might have a positive outcome from performing these exercises, they are not the primary reason the exercises are done. 77. For the drugs oseltamivir (Tamiflu) and zanamivir (Relenza) to be the most effective in eliminating the influenza virus, they should be administered within which time period? A. 2 days of the client becoming ill B. 7 days of the client becoming ill C. 10 days of exposure to influenza D. 14 days of exposure to influenza Answer A: The best effect of the medications occurs if given within 2–3 days of illness with the influenza virus. Answers B, C, and D are not within the allotted time period for the drugs to be effective in eliminating the influenza virus. 78. A 22-year-old female is being discharged after an admission for bipolar disorder. Discharge medications include valproate (Depakote). Which statement by the client would cause the nurse concern because of the prescription? A. “I am trying to get pregnant.” B. “My career as a secretary is just beginning.” C. “I usually exercise 4 times a week.” D. “I am on a well-balanced diet.” Answer A: Depakote can cause neural tube defects in pregnant women, so the client should be on birth control or should not take this drug. A client’s career, exercise level, and diet will not affect the dose or prescription for this drug, so answers B, C, and D are incorrect. 79. A tuberculin test has been administered to an elderly client in preparation for nursing home placement. Which of these skin reactions at the site of the test could indicate a positive result? A. Induration B. Ulceration C. Rash D. Redness Answer A: The hardening or induration could indicate a positive test result. A reaction of 0–4mm is not significant. A larger-size induration could indicate exposure to tuberculosis. Answers B, C, and D without induration are nonsignificant, so they are incorrect. 80. The nurse is discussing discharge plans with a 30-year-old client who has sickle cell disease. Assessment findings include spleenomegaly. What information obtained in the discussion would cause the most concern? The client: A. Eats fast food daily for lunch B. Drinks a beer occasionally C. Sometimes feels fatigued D. Works as a furniture mover Answer D: A client with an enlarged spleen has an increased risk for rupture; therefore, heavy lifting would be contraindicated. Answers A, B, and C would not be a cause for a concern because of the enlarged spleen. 81. The influenza vaccine is contraindicated in clients with allergies to which of the following? A. Eggs B. Shellfish C. Iodine D. Pork Answer A: The vaccine is made from eggs, so clients with allergies to eggs should not receive the vaccine. Shellfish and iodine are associated with the dye used for intravenous pyelograms, so answers B and C are incorrect. An allergy to pork, as in answer D, does not indicate a need to avoid the influenza virus. 82. The nurse is caring for a client who is of the Islam religious group. Which food selection would be inappropriate to offer to this client? A. Jell-O B. Chicken C. Milk D. Broccoli Answer A: People of the Islam religion are prohibited from eating foods with gelatin. They also must avoid pork, alcohol products and beverages, and animal shortening. Answers B, C, and D would all be appropriate because they can be included in the diet of people of the Islam religion. 83. The nurse identifies which of the following as a side effect of the influenza vaccine? A. Febrile reaction B. Hypothermia C. Dyspnea D. Generalized rash Answer A: The client, especially a child, could experience a febrile reaction. This makes hypothermia or a decreased temperature, as in answer B, incorrect. Another side effect is soreness at the injection site. A generalized rash and difficulty breathing are not side effects of the vaccine; therefore, answers C and D are incorrect. 84. Which breakfast selection by a client with osteopenia indicates that the client understands the dietary management of the disease? A. Scrambled eggs, toast, and coffee B. Bran muffin with margarine C. Granola bar and half of a grapefruit D. Bagel with jam and skim milk Answer D: The highest amount of calcium is in this answer. The client also needs to know that calcium in combination with high fiber and caffeine decreases the absorption; therefore, answers A, B, and C are incorrect. 85. A client is admitted with cholethiasis and has obstructive jaundice. Which clinical manifestations does the LPN/LVN expect to observe? A. Clear straw urine B. White sclera C. Clay colored stool D. Red nailbeds Answer C: The obstruction decreases the elimination of bile causing the collection of bilirubin in the blood instead of it being removed by the urinary and Gastrointestinal system. This leads to a lack of normal color of the stool and urine. Answers A, B, and D do not occur with obstructive jaundice so they are incorrect. 86. The nurse is assessing a client with gastroenteritis for hypovolemia. Which laboratory result would help the nurse in confirming a volume deficit? A. Hematocrit 55% B. Potassium 5.0mEq/L C. Urine specific gravity 1.016 D. BUN 18mg/dL Answer A: Hematocrit levels can be elevated with hypovolemia caused by fluid loss. Answers B, C, and D are all normal levels. Potassium (normal 3.5– 5.3mEq/L) levels would be decreased with hypovolemia; BUN (normal 5– 20mg/dL) and specific gravity (1.016–1.022) levels would be elevated with hypovolemia. 87. A client has an order for Codeine 60 mg IM. An available vial contains Codeine 30 mg/mL. What volume of drug would the nurse administer? A. 0.5mL B. 1.0mL C. 1.5mL D. 2.0mL Answer D: The dose to administer is 2mL, which is calculated as follows: 60 mg?= 1 mL/30 mg=60/30 = 2.0 mL Answers A, B, and C are incorrect calculations. 88. The nurse is assessing elderly clients at a nursing home. Which of the following findings would not be considered a normal part of the aging process? A. Complaints of a dry mouth B. Loss of 1 inch of height in the last year C. Stiffened joints D. Rales bilaterally on chest auscultation Answer D: Rales would indicate lung congestion and the need for follow-up. Answers A, B, and C are normal health-related changes with aging. 89. A client at the clinic reports to the nurse, “I have trouble seeing signs at a distance, but no trouble seeing things close up.” The nurse identifies the correct term for this vision problem as: A. Myopia B. Emmetropia C. Hyperopia D. Astigmatism Answer A: Myopia is nearsightedness due to the cornea being too steep or the eye being too long. This causes light to come into focus in front of the retina, resulting in blurred distant vision. Answer B is normal vision. Farsightedness is blurred near and often distant vision, as in answer C. Astigmatism occurs when light rays focus in multiple points, causing blurred vision not related to near or far vision; thus, answer D is incorrect. 90. A client has signs of increased intracranial pressure. Which one of the following is an early indicator of increased intracranial pressure? A. Widening pulse pressure B. Decrease in the pulse rate C. Dilated, fixed pupils D. Decrease in level of consciousness Answer D: The nurse observes sluggishness and lethargy as early indications of increased ICP in a client. A change in vital signs and papillary changes, as in answers A, B, and C, are late signs of increased ICP. 91. Which statement by a client who is taking topiramate (Topamax) indicates that the client has understood the nurse’s instruction? A. “I will take the medicine before going to bed.” B. “I will drink 8 to 10 ten-ounce glasses of water a day.” C. “I will eat plenty of fresh fruits.” D. “I must take the medicine with a meal or snack.” Answer B: There is an increased risk for kidney stones with topiramate (Topamax) use, so fluids are an important part of problem prevention. The drug is not required to be taken with meals or at bedtime, so answers A and D are incorrect. Answer C is not required with the use of this medication. 92. A client with AIDS is admitted to the unit. A family member asks the nurse, “How much longer will it be?” Which response by the nurse is most appropriate? A. “This must be a terrible situation for you.” B. “I don’t know. I’ll call the doctor.” C. “I cannot say exactly. What are your concerns at this time?” D. “Don’t worry, it will be very soon.” Answer C: The nurse responds appropriately by answering the question honestly and attempting to assess for more information that will allow the person to ventilate feelings. Answer A is an appropriate response but is not as appropriate as C. Answers B and D are nontherapeutic communication techniques. 93. The LPN/LVN is working on a team that includes an RN and a nursing assistant. The LPN/LVN should be assigned which of the following clients? A. A client with terminal pancreatic cancer in severe pain B. A client with peripheral vascular disease requiring a dressing change C. A client with alzheimers disease requiring ambulatory assistance D. A client with trauma who had a chest tube inserted 1 hour ago Answer B: The LPN should be assigned the client requiring a dressing change. This client is the one most correlated to the LPN’s scope of practice. The clients described in answer options A and D are more appropriate to the RN. The nursing assistant should care for the client needing ambulatory assistance as described in answer C because this relates to the nurses assistants standards and practices. 94. The nurse is caring for a client with a basilar skull fracture. Fluid is assessed leaking from the ear. What is the nurse’s first action? A. Irrigate the ear canal gently B. Notify the physician C. Test the drainage for glucose D. Apply an occlusive dressing Answer C: Testing the drainage for glucose could indicate the presence of cerebrospinal fluid, making this the best initial action. The next action would be to notify the physician, as in answer B. Answers A and D would be contraindicated, so they are incorrect. 95. The nurse has inserted an NG tube for enteral feedings. Which assessment result is the best indication that an NG tube is properly placed in the stomach? A. Aspiration of tan-colored mucus B. Green aspirate with a pH of 3 C. A swish auscultated with the injection of air D. Bubbling in a cup of NS when the end of the tube is placed in the cup Answer B: The aspirate of gastric content should be green, brown, clear, or colorless, with a gastric pH between 1 and 5. Answer A would most likely be from the lungs, so it is incorrect. Answers C and D are not as accurate as color and pH for confirming gastric location, so they are incorrect. 96. Which one of the following assessment findings is within normal expectations for a post-operative craniotomy client? A. A decrease in responsiveness the third post-op day B. Sluggish pupil reaction the first 24–48 hours C. Dressing changes 3–4 times a day for the first 3 days D. Temperature range of 98.8°F–99.6°F the first 2–3 days Answer D: A slight elevation in temperature would be expected from surgical intervention and would not be a cause for concern. Answers A, B, and C could indicate a progressing complication, so they are incorrect. 97. A client with alcoholism has been instructed to increase his intake of thiamine. Which food is highest in thiamine? A. Roast beef B. Broiled fish C. Baked chicken D. Sliced pork Answer D: Pork has more thiamine than beef, fish, or chicken, which makes answers A, B, and C incorrect. 98. A client is immobile. Which nursing intervention would best improve tissue perfusion to prevent skin problems? A. Assessing the skin daily B. Massaging any erythematous areas on the skin C. Changing incontinence pads as soon as they become soiled D. Performing range-of-motion exercises, and turning and repositioning the client Answer D: Activity, exercise, and repositioning the client will increase circulation and improve tissue perfusion. Answer A will help to identify problem areas but will not improve the perfusion of the tissue. Answer B should be avoided because it could increase the damage if trauma was present. Answer C should be done to prevent irritation of the skin, but this action does not improve perfusion. 99. The nurse is discussing nutritional needs with the dietician at the nursing home. Which diet selection indicates a proper diet for healing of a decubitus ulcer? A. Tossed salad, milk, and a slice of caramel cake B. Vegetable soup and crackers, and a glass of tea C. Baked chicken breast, broccoli, wheat roll, and an orange D. Hamburger, French fries, and corn on the cob Answer C: These clients need a balanced nutritional diet with protein and vitamin C, making it the most balanced meal plan. Answers A and B both lack protein, which is very important in maintaining a positive nitrogen balance. Answer D has protein but is lacking in vitamins. 100. A client is admitted to the chemical dependency unit due to cocaine addiction. The client states, “I don’t know why you are all so worried. I am in control. I don’t have a problem.” Which defense mechanism is being utilized? A. Rationalization B. Projection C. Dissociation D. Denial Answer D: The statement reflects the use of denial as a means of coping with the illness. Answers A, B, and C are defense mechanisms not reflected by the statement. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 4 pages
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 12, 2021
Number of pages
4
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 12, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
61





 Practice Test (Total Questions 725).png)

 Questions and Answers with Explanations.png)



.png)


