*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > DeVry University. NR 228 STUDY GUIDE. LATEST 2020/21. A+ RATED (All)
DeVry University. NR 228 STUDY GUIDE. LATEST 2020/21. A+ RATED
Document Content and Description Below
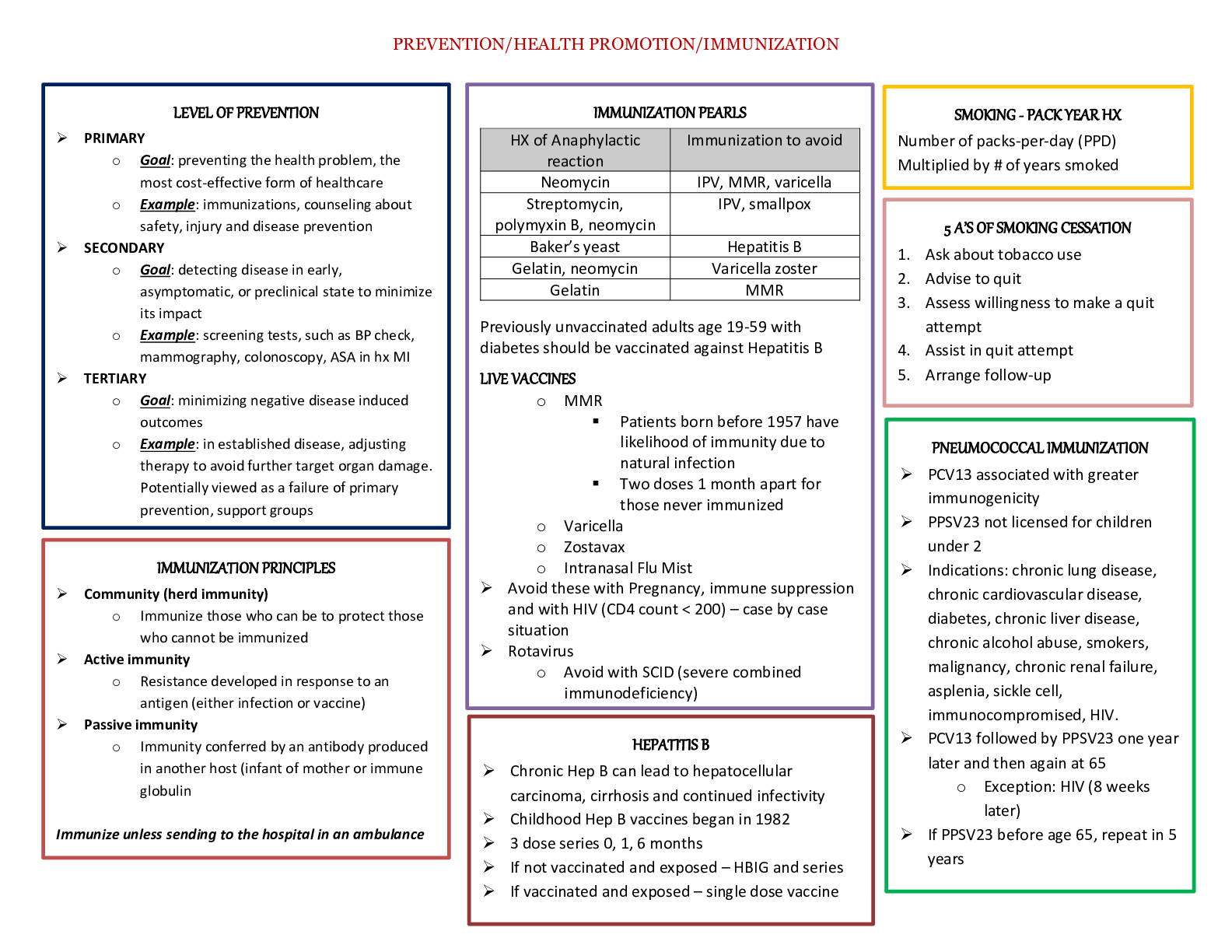
DeVry University. NR 228 STUDY GUIDE. LATEST 2020/21. A+ RATED.STUDY GUIDE NR 228 Chapter 1 Define health and wellness Heath is a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being ... and not merely the absence of disease and infirmity. Physical health: The efficiency of the body to function appropriately, to maintain immunity to disease, and to meet daily energy requirements - Intellectual health: The use of intellectual abilities to learn and to adapt to changes in one's environment Emotional health: The capacity to easily express or suppress emotions appropriately Social health: The ability to interact with people in an acceptable manner and sustain relationships with family members, friends, and colleagues Spiritual health: The cultural beliefs that give purpose to human existence, found through faith in the teachings of organized religions, in an understanding of nature or science, or in an acceptance of the humanistic view of life Environmental health: The external factors that affect our health and well-being, including the physical context within which one lives and works as affected by determinants of ethnicity, education, income, and occupation; and extending to the larger environment of safeguarding natural resources to reduce exposure to preventable hazards. Wellness is an active process of becoming aware of and making choices toward a more successful existence. Wellness is a lifestyle choice – example – you have the choice to be well or not to be well. Describe health promotion o Consist of strategies used to raise the level of health of the individuals, families, groups and communities. Nurses function on a health promotion model. Physician function on a sick model. Environment plays a role in health and wellness. For example: Knowledge: Learning new information about the benefits or risks of health-related behaviors Techniques: Applying new knowledge to everyday activities; developing ways to modify current lifestyles Community supports: Availability of environmental or regulatory measures to support new health-promoting behaviors within a social context The major survey that focuses on nutritional and health status of Americans: o Is the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) - focuses on data from the dietary intake, medical history, biochemical evaluation, physical examinations, and measurements of American population groups. 2 day study to track and see how we shop and what we eat. o The dietary intake portion of the NHANES is called What We Eat in America (WWEIA). o Conducted as a collaboration between the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), USDHHS, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), National Center for Health Statistics. State the purpose of Healthy People 2020 Healthy people 2020: Mission Healthy People 2020 strives to: • Identify nationwide health-improvement priorities. • Increase public awareness and understanding of the determinants of health, disease, and disability and the opportunities for progress. • Provide measurable objectives and goals that are applicable at the national, state, and local levels. • Engage multiple sectors to take actions to strengthen policies and improve practices that are driven by the best available evidence and knowledge. • Identify critical research, evaluation, and data-collection needs. Overarching Goals: • Attain high-quality, longer lives free of preventable disease, disability, injury, and premature death. • Achieve health equity, eliminate disparities, and improve the health of all groups. • Create social and physical environments that promote good health for all. • Promote quality of life, healthy development, and healthy behaviors across all life stages. Disease prevention: test Primary prevention consists of activities to avert the initial development of a disease or poor health. Example: education - protection against the effects of a disease agent, as with vaccination. It can also include changes to behaviors such as cigarette smoking or diet. Secondary prevention involves early detection to halt or reduce the effects of a disease or illness. Example: screenings - detecting a disease in its earliest stages, before symptoms appear, and intervening to slow or stop its progression: "catch it early." Other examples - is the Pap test to screen for cancer of the cervix, or a PSA blood test for prostate cancer; other instances include teaching people about the early signs of disease that they should watch for, and what type of treatment to seek. Screening for breast cancers. Tertiary prevention occurs after a disorder develops. Example: chemo for cancers have s/e such as N/V, loss of appetite - reduce complication and disability. Tertiary prevention frequently involves diet therapy. Examples include eliminating offending allergens from an asthmatic patient's environment and routinely screening for and managing early renal, eye, and foot problems in a diabetic patient. NOTE: Tertiary prevention manages an existing disease, with the goal to restore a patient to highest function, minimize the negative consequences of the disease, and prevent disease-related complications. Maintain and promote better nutritional standards. Health Literacy: is the ability to acquire and comprehend basic health concepts, such as nutrition, and apply them to one's own health decisions. Examples: Grade school, College, University - Formal education is purposefully planned for implementation in a school setting. Non- formal: examples: hospitals, clinics, and community centers. Teaching and educating groups, individual by a nurse. You should educate your patient at a 5th grade level – always educate your patients at the level they are at. Informal – examples - watching television, reading newspapers and magazines, browsing the Internet, and conversing with other people. CDC Identify the 6 (six) nutrient categories and lest their function. Test Based on a 2,000 calorie diet Note: energy released from foods is measured in Kcal. Nutrients provide energy, regulating body processes and aid in the growth and repair of body tissues Carbs: 4 Kcal Protein: 4 Kcal Lipids: 9 kcal Alcohol: 7 Kcal Kcal definition: a calorie is the amt of heat it takes to raise the temp of a gram of water 1 degrees. 1. Carbs: providing energy, major source of fuel. Simple carbs: fruits, milk, all sweeteners including white/brown sugars, honey, high fructose corn syrup. Complex carbs – cereals, grains, pasta, fruits, vegetables – all except fiber which are broken down into glucose which is a simple carb (Glucose provides the most efficient form of energy for muscles and the brain and body, carbs, lipids and proteins provide energy). Fiber prevent [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 11 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 19, 2021
Number of pages
11
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 19, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
37























.png)





