*NURSING > EXAM > NR507 Final Exam_ Chamberlain College of Nursing. Verified Answers, Download to Score A. (All)
NR507 Final Exam_ Chamberlain College of Nursing. Verified Answers, Download to Score A.
Document Content and Description Below
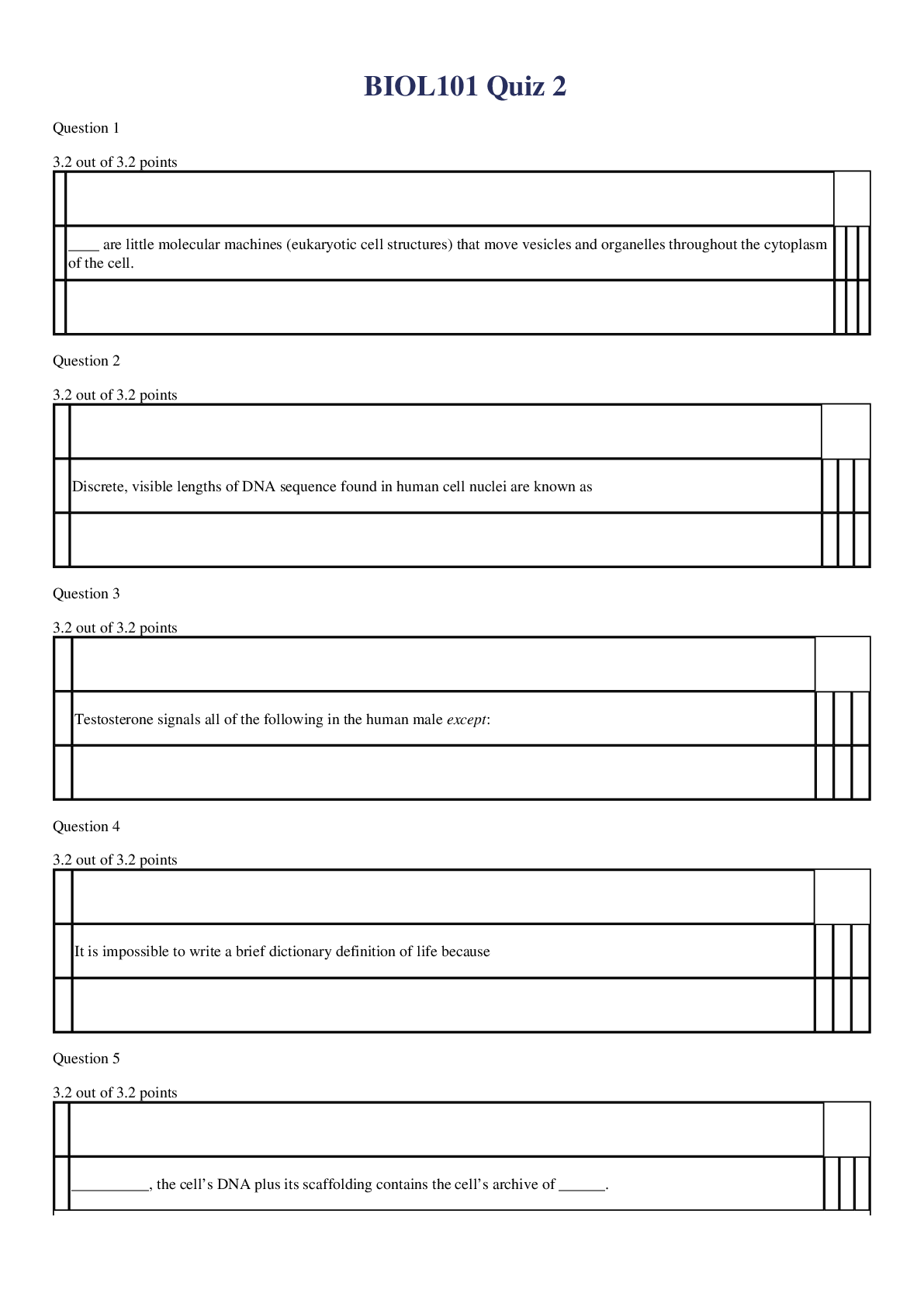
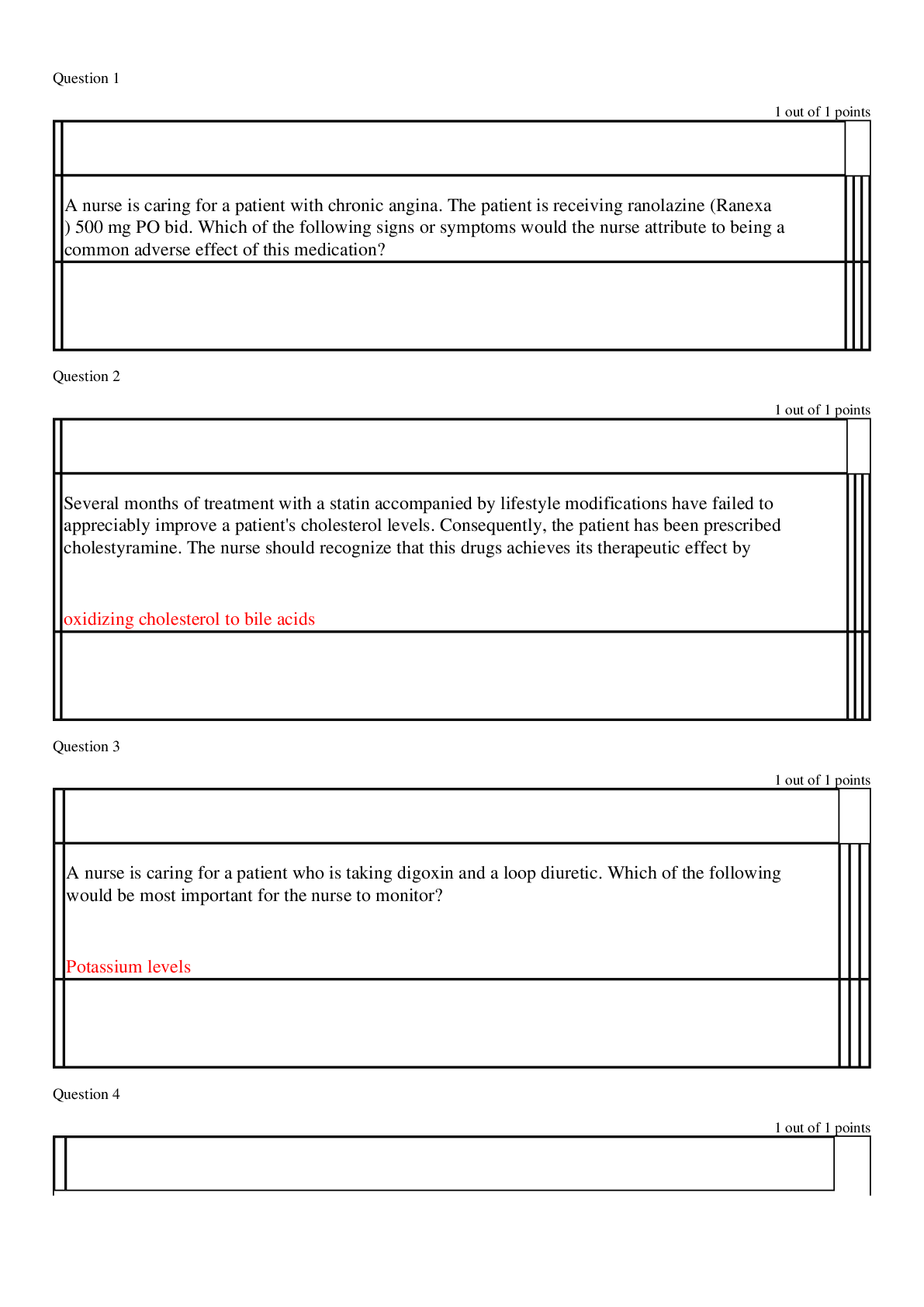
NR507 Final Exam Question 1 2 / 2 pts Tissue damage caused by the deposition of circulating immune complexes containing an antibody against the host DNA is the cause of which disease? Hemoly... tic anemia Pernicious anemia Systemic lupus erythematosus Myasthenia gravis Only the deposition of circulating immune complexes containing an antibody against the host DNA produce tissue damage in individuals with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Question 2 2 / 2 pts How does chest wall compliance in an infant differ from that of an adult? An adult’s chest wall compliance is lower than an infant’s. An adult’s chest wall compliance is higher than an infant’s. An adult’s chest wall compliance is the same as an infant’s. An adult’s chest wall compliance is dissimilar to that of an infant’s. Chest wall compliance is higher in infants than it is in adults, particularly in premature infants. Question 3 2 / 2 pts What term is used to describe a hernial protrusion of a saclike cyst that contains meninges, spinal fluid, and a portion of the spinal cord through a defect in a posterior arch of a vertebra? Encephalocele Meningocele Spina bifida occulta Myelomeningocele Myelomeningocele is a hernial protrusion of a saclike cyst containing meninges, spinal fluid, and a portion of the spinal cord with its nerves through a defect in the posterior arch of a vertebra. The remaining options are not appropriate terms to identity the described condition. Question 4 2 / 2 pts Continued therapy of pernicious anemia (PA) generally lasts how long? 6 to 8 weeks 8 to 12 months Until the iron level is normal The rest of one’s life Because PA cannot be cured, maintenance therapy is a life-long endeavor. Question 5 2 / 2 pts Cytokines are thought to cause fevers by stimulating the synthesis of which chemical mediator? Leukotriene Histamine Prostaglandin Bradykinin Cytokines seem to raise the thermoregulatory set point through stimulation of prostaglandin synthesis and turnover in thermoregulatory (brain) and nonthermoregulatory (peripheral) tissues. The other options do not accurately identify the appropriate chemical mediator. Question 6 2 / 2 pts The World Health Organization (WHO) defines grade 1 (overweight) as a BMI of: 18.5 to 24.9 25 to 29.9 30 to 39.9 40 to 50.9 A BMI of 25 to 29.9 kg/m2 is considered a grade 1 (overweight) classification. A BMI of 18.5 to 24.9 kg/m2 is considered normal range, whereas 30 to 39.9 kg/m2 is a grade 2 (severe overweight) classification, and a BMI higher than 40 kg/m2 is considered grade 3 (morbidly overweight). IncorrectQuestion 7 0 / 2 pts When diagnosed with hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN), why does the newborn develop hyperbilirubinemia after birth but not in utero? Excretion of unconjugated bilirubin through the placenta into the mother’s circulation is no longer possible. Hemoglobin does not break down into bilirubin in the intrauterine environment. The liver of the fetus is too immature to conjugate bilirubin from a lipid-soluble to water-soluble form. The destruction of erythrocytes producing bilirubin is greater after birth. Hyperbilirubinemia occurs in the neonate after birth because excretion of lipid-soluble unconjugated bilirubin through the placenta is no longer possible. This selection is the only option that accurately explains why HDN causes hyperbilirubinemia after birth but not in utero. Question 8 2 / 2 pts Which of the following describes how the body compensates for anemia? Increasing rate and depth of breathing Decreasing capillary vasoconstriction Hemoglobin holding more firmly onto oxygen Kidneys releasing more erythropoietin Tissue hypoxia creates additional demands and compensatory actions on the pulmonary and hematologic systems. The rate and depth of breathing increase in an attempt to increase the availability of oxygen. This selection is the only option that accurately describes the compensation mechanism in such anemias. Question 9 2 / 2 pts An infant has a continuous machine-type murmur best heard at the left upper sternal border throughout systole and diastole, as well as a bounding pulse and a thrill on palpation. These clinical findings are consistent with which congenital heart defect? Atrial septal defect (ASD) Ventricular septal defect (VSD) Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) Atrioventricular canal (AVC) defect If pulmonary vascular resistance has fallen, then infants with PDA will characteristically have a continuous machine-type murmur best heard at the left upper sternal border throughout systole and diastole. If the PDA is significant, then the infant also will have bounding pulses, an active precordium, a thrill on palpation, and signs and symptoms of pulmonary overcirculation. The presentations of the other congenital heart defects are not consistent with the described the symptoms. Question 10 2 / 2 pts Research has shown a link between cancer and which sexually transmitted disease? Syphilis Gonorrhea Human papillomavirus Pelvic inflammatory disease Human papillomavirus (HPV) is the most common sexually transmitted virus in the United States. High-risk, or oncogenic, HPVs can cause cancer. A persistence of infection with high-risk HPV is a prerequisite for the development of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) lesions and invasive cervical cancers. No research supports such a link between the remaining options and cancer. Question 11 2 / 2 pts When renin is released, it is capable of which action? Inactivation of autoregulation Direct activation of angiotensin II Direct release of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) Formation of angiotensin I When renin is released, it cleaves an α-globulin (angiotensinogen produced by liver hepatocytes) in the plasma to form angiotensin I. Question 12 2 / 2 pts What characteristic do atopic individuals have that make them genetically predisposed to develop allergies? Greater quantities of histamine More histamine receptors Greater quantities of IgE A deficiency in epinephrine Atopic individuals tend to produce higher quantities of IgE and to have more crystalline fragment (Fc) receptors for IgE on their mast cells. The other options do not cause this reaction. Question 13 2 / 2 pts What is the primary cause of the symptoms of polycythemia vera? Decreased erythrocyte count Destruction of erythrocytes Increased blood viscosity Neurologic involvement As polycythemia vera progresses, many of the symptoms are related to the increased blood cellularity and viscosity. No other option is the primary cause of the symptoms of polycythemia vera. Question 14 2 / 2 pts Pressure in the left ventricle must exceed pressure in which structure before the left ventricle can eject blood? Superior vena cava Aorta Inferior vena cava Pulmonary veins Pressure in the ventricle must exceed aortic pressure before blood can be pumped out during systole. The aorta is the only structure in which pressure must be less than the amount of blood in the left ventricle for ejection to occur. Question 15 2 / 2 pts Children with phenylketonuria (PKU) are unable to synthesize: Essential amino acid, phenylalanine, to tyrosine Renin, erythropoietin, and antidiuretic hormone Aldosterone, cortisol, and androgens Neurotransmitters gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and acetylcholine PKU is an inborn error of metabolism characterized by the inability of the body to convert the essential amino acid, phenylalanine, to tyrosine. PKU does not affect synthesis of the other options. Question 16 2 / 2 pts What is the chance with each pregnancy that a child born to two parents with the sickle trait will have sickle cell disease (SCD)? 20% 25% 33% 50% A 25% chance exists with each pregnancy that a child born to two parents with sickle cell trait will have SCD. Genetic counseling enables people with SCD or with the sickle cell trait to make informed decisions about transmitting this genetic disorder to their offspring. Question 17 2 / 2 pts Carcinoma refers to abnormal cell proliferation originating from which tissue origin? Blood vessels Epithelial cells Connective tissue Glandular tissue Only cancers arising from epithelial cells are called carcinomas. Question 18 2 / 2 pts Chvostek and Trousseau signs indicate which electrolyte imbalance? Hypokalemia Hyperkalemia Hypocalcemia Hypercalcemia Two clinical signs of hypocalcemia are the Chvostek sign and Trousseau sign. These clinical signs are not indicative of any of the other options. Question 19 2 / 2 pts The ability of the pathogen to invade and multiply in the host is referred to as: Infectivity Toxigenicity Pathogenicity Virulence Infectivity is the ability of the pathogen to invade and multiply in the host. The other options do not accurately denote the pathogen’s ability to invade and multiply in the host. Question 20 2 / 2 pts An infant has a crescendo-decrescendo systolic ejection murmur located between the second and third intercostal spaces along the left sternal border. A wide fixed splitting of the second heart sound is also found. These clinical findings are consistent with which congenital heart defect? Atrial septal defect (ASD) Ventricular septal defect (VSD) Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) Atrioventricular canal (AVC) defect Because most children with ASD are asymptomatic, diagnosis is usually made during a routine physical examination by the auscultation of a crescendo-decrescendo systolic ejection murmur that reflects increased blood flow through the pulmonary valve. The location of the murmur is between the second and third intercostal spaces along the left sternal border. A wide fixed splitting of the second heart sound is also characteristic of ASD, reflecting volume overload to the right ventricle and causing prolonged ejection time and a delay of pulmonic valve closure. The presentations of other congenital heart defects are not consistent with the described symptoms. Question 21 2 / 2 pts Which cancer originates from connective tissue? Osteogenic sarcoma Basal cell carcinoma Multiple myeloma Adenocarcinoma Cancers arising from connective tissue usually have the suffix -sarcoma. The remaining options are not cancers that originate in the connective tissue and, in addition, are lacking the common suffix. Question 22 2 / 2 pts Which substance is used to correct the chronic anemia associated with chronic renal failure? Iron Erythropoietin Cobalamin (vitamin B12) Folate One of the most significant advances in the study of hematopoietic growth factors has been the development of erythropoietin for individuals with chronic renal failure. The other options are not associated with the treatment of chronic anemia. Question 23 2 / 2 pts Which of the following are formed elements of the blood that are not cells but are disk-shaped cytoplasmic fragments essential for blood clotting? Monocytes Platelets Macrophages Erythrocytes Platelets (thrombocytes) are not true cells but are disk-shaped cytoplasmic fragments that are essential for blood coagulation and control of bleeding. This description is not accurate for any of the other options. Question 24 2 / 2 pts What is the term for a herniation or protrusion of brain and meninges through a defect in the skull? Encephalocele Meningocele Arachnoidocele Cephacephalocele Encephalocele refers to a herniation or protrusion of brain and meninges through a defect in the skull, resulting in a saclike structure. The other terms are not used to describe an encephalocele. Question 25 2 / 2 pts A hypersensitivity reaction that produces an allergic response is called: Hemolytic shock Anaphylaxis Necrotizing vasculitis Systemic erythematosus Examples of systemic anaphylaxis are allergic reactions to beestings, peanuts, and fish. The other options are not accurate examples of hypersensitivity. Question 26 2 / 2 pts Which characteristic is true of type II (white fast-motor) muscle fibers? Slow contraction speed Fast conduction velocities Profuse capillary supply Oxidative metabolism Type II fibers, also called white fast-motor fibers, are innervated by relatively large type II alpha motor neurons with fast conduction velocities. This selection is the only correct option provided. Question 27 2 / 2 pts What type of fracture occurs at a site of a preexisting bone abnormality and is a result of a force that would not normally cause a fracture? Idiopathic Incomplete Pathologic Greenstick Only a pathologic fracture is a break at the site of a preexisting abnormality, usually by force that would not fracture a normal bone. Question 28 2 / 2 pts What part of the brain provides the emotional response to pain? Limbic system Parietal lobe Thalamus Hypothalamus The limbic and reticular tracts are involved in alerting the body to danger, initiating arousal of the organism, and emotionally processing the perceived afferent signals, not just as stimuli, but also as pain. The remaining options do not fulfill this objective. Question 29 2 / 2 pts The portion of the pituitary that secretes oxytocin is: Posterior Inferior Anterior Superior Only the posterior pituitary secretes oxytocin. Question 30 2 / 2 pts Which dyskinesia involves involuntary movements of the face, trunk, and extremities? Paroxysmal Tardive Hyperkinesia Cardive Tardive dyskinesia is the involuntary movement of the face, trunk, and extremities. The other terms do not describe involuntary movements of the face, trunk, and extremities. Question 31 2 / 2 pts Which term is also used to refer to paradoxic sleep? Non-REM Light REM Delta wave REM sleep is also known as paradoxic sleep because the electroencephalographic (EEG) pattern is similar to the normal awake pattern. None of the other terms are used to identify paradoxic sleep. Question 32 2 / 2 pts Which clinical manifestations would be expected for a child who has complete trisomy of the twenty-first chromosome? Widely spaced nipples, reduced carrying angle at the elbow, and sparse body hair An IQ of 25 to 70, low nasal bridge, protruding tongue, and flat, low-set ears High-pitched voice, tall stature, gynecomastia, and an IQ of 60 to 90 Circumoral cyanosis, edema of the feet, short stature, and mental slowness Individuals with this disease are mentally retarded, with IQs usually ranging from 25 to 70. The facial appearance is distinctive and exhibits a low nasal bridge, epicanthal folds (which produce a superficially Asian appearance), protruding tongue, and flat, low-set ears. The correct option is the only one that accurately describes the clinical manifestations of the complete trisomy of the twenty-first chromosome. IncorrectQuestion 33 0 / 2 pts Where is oxytocin synthesized? Hypothalamus Paraventricular nuclei Anterior pituitary Posterior pituitary ADH and oxytocin are synthesized in hypothalamic neurons but are stored and secreted by the posterior pituitary. The other options do not synthesize oxytocin. IncorrectQuestion 34 0 / 2 pts What is the most common opportunistic infection associated with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)? Non-Hodgkin lymphoma Kaposi sarcoma Toxoplasmosis Cytomegalovirus Toxoplasmosis is the most common opportunistic infection and occurs in approximately one third of individuals with AIDS. Cytomegalovirus encephalitis is common in those with AIDS but is often not diagnosed while the person is alive. Other neoplasms associated with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) include systemic non-Hodgkin lymphoma and metastatic Kaposi sarcoma. Question 35 2 / 2 pts Atrial fibrillation, rheumatic heart disease, and valvular prosthetics are risk factors for which type of stroke? Hemorrhagic Thrombotic Embolic Lacunar High-risk sources for the onset of embolic stroke are atrial fibrillation (15% to 25% of strokes), left ventricular aneurysm or thrombus, left atrial thrombus, recent myocardial infarction, rheumatic valvular disease, mechanical prosthetic valve, nonbacterial thrombotic endocarditis, bacterial endocarditis, patent foramen ovale, and primary intracardiac tumors. These are not risk factors for the other options provided. Question 36 2 / 2 pts How many days does it take for the entire epithelial population of the small intestines to be replaced? 30 to 45 15 to 25 7 to 15 4 to 7 The entire epithelial population is replaced approximately every 4 to 7 days. Question 37 2 / 2 pts What term describes the loss of the comprehension or production of language? Agnosia Aphasia Akinesia Dysphasia Aphasia is the loss of the comprehension or production of language. The remaining options are not terms used to describe this loss of function. Question 38 2 / 2 pts Open-angle glaucoma occurs because of: Decreased production of aqueous humor Increased production of vitreous humor Obstructed outflow of aqueous humor Excessive destruction of vitreous humor Open-angle glaucoma occurs because of an obstruction of the outflow of aqueous humor at trabecular meshwork or Schlemm canal. The remaining options fail to accurately describe the cause of open-angle glaucoma. Question 39 2 / 2 pts What is the most common malignant bone tumor diagnosed during childhood? Chondrosarcoma Fibrosarcoma Ewing Sarcoma Osteosarcoma Of the options available, osteosarcoma is the most common bone tumor that occurs during childhood; it originates from bone-producing mesenchymal cells. Question 40 2 / 2 pts What is the cause of familial hypercholesterolemia (FH)? Diet high in saturated fats Increased production of cholesterol by the liver Reduction in the number of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptors on cell surfaces Abnormal function of lipoprotein receptors circulating in the blood A reduction in the number of functional LDL receptors on cell surfaces causes FH. Lacking the normal number of LDL receptors, cellular cholesterol uptake is reduced and circulating cholesterol levels increase (see Box 5-3). The other options are not the basis for developing familial FH. Question 41 2 / 2 pts Which risk factor for hypertension is influenced by genetic factors and lifestyle? Sodium intake Physical inactivity Psychosocial stress Obesity The most important environmental risk factors for hypertension are increased sodium intake, decreased physical activity, psychosocial stress, and obesity. However, obesity is, itself, influenced by genes and the environment. Question 42 2 / 2 pts Which substance is a water-soluble protein hormone? Thyroxine Aldosterone Follicle-stimulating hormone Insulin Peptide or protein hormones, such as insulin, pituitary, hypothalamic, and parathyroid, are water soluble and circulate in free (unbound) forms. All the remaining options are fat-soluble hormones. Question 43 2 / 2 pts When does the male body begin to produce sperm? Before birth Shortly after birth At puberty When erection is possible Erections begin in utero and continue throughout life, but ejaculation does not occur until sperm production begins at puberty. Question 44 2 / 2 pts Saliva contains which immunoglobulin (Ig)? IgA IgE IgG IgM Saliva contains only IgA, which helps prevent infection. Question 45 2 / 2 pts Which serum laboratory test is elevated in all forms of osteogenesis imperfecta? Phosphorus Calcium Alkaline phosphatase Total protein Of the available options, serum alkaline phosphatase is elevated in all forms of the disease. Question 46 2 / 2 pts What causes the crystallization within the synovial fluid of the joint affected by gouty arthritis? Reduced excretion of purines Overproduction of uric acid Increase in the glycosaminoglycan levels Overproduction of proteoglycans When the uric acid reaches a certain concentration in fluids, it crystallizes, forming insoluble precipitates that are deposited in connective tissues throughout the body. Crystallization in synovial fluid causes acute, painful inflammation of the joint, a condition known as gouty arthritis. This selection is the only option that accurately identifies the cause of crystallization in synovial fluid associated with gouty arthritis. Question 47 2 / 2 pts Acute glomerulonephritis (AGN) may be accompanied by a positive throat or skin culture for which bacteria? Staphylococcus aureus Streptococcus Pseudomonas aeruginosa Haemophilus AGN may be accompanied by a positive throat or skin culture for Streptococcus. AGN is not associated with any of the other options. Question 48 2 / 2 pts Considering the mediating factors of premenstrual syndrome (PMS), which medication may be used either continually or only during the menstrual period as a treatment for the condition? NSAIDs Estrogen SSRIs Progesterone A selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI) (an antidepressant) relieves symptoms in approximately 60% to 90% of women and may be continually administered or only prescribed during the premenstrual period. Oral contraceptive pills that contain estrogen and progesterone also can be continuously used for up to 3 months to decrease the frequency of menstrual periods, PMS, and premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD). Nonsteriodal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) would not be continually administered. Question 49 2 / 2 pts What is the second most commonly recognized genetic cause of mental retardation? Down syndrome Fragile X syndrome Klinefelter syndrome Turner syndrome The fragile X syndrome is the second most common genetic cause of mental retardation (after Down syndrome). The correct option is not observed with enough frequency to be recognized as the second most common cause of mental retardation. Question 50 2 / 2 pts Insulin transports which electrolyte in the cell? Potassium Calcium Sodium Phosphorus Insulin facilitates the intracellular transport of potassium, phosphate, and magnesium. Insulin does not facilitate the transport of the other electrolytes. Question 51 2 / 2 pts Which hormone stimulates gonads to produce both male and female hormones? Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) Luteinizing hormone (LH) Estrogen Extrahypothalamic factors cause the hypothalamus to secrete GnRH, which stimulates the anterior pituitary to secrete gonadotropins—FSH and LH. These hormones, in turn, stimulate the gonads (ovaries or testes) to secrete female or male sex hormones. Question 52 2 / 2 pts The secretion of adrenocorticotropic-stimulating hormone (ACTH) will result in the increased level of which hormone? Thyroxine Insulin Cortisol. Antidiuretic hormone Psychologic and physiologic stress (e.g., hypoxia, hypoglycemia, hyperthermia, exercise) increases ACTH secretion, leading to increased cortisol levels. Only cortisol describes the appropriate feedback loop. Question 53 2 / 2 pts Antipsychotic drugs block which neurotransmitter receptor? Norepinephrine Gamma-aminobutyric acid Serotonin Dopamine The dopamine hypothesis initially suggested that abnormal elevation in dopaminergic transmission contributes to the onset of schizophrenia. This hypothesis was based on pharmacologic studies showing that antipsychotic drugs are potent blockers of brain dopamine receptors; therefore the other options are incorrect. Question 54 2 / 2 pts In 95% of children of delayed puberty, the problem is caused by: Disruption in the hypothalamus Disruption of the pituitary Deficit in estrogen or testosterone Physiologic hormonal delays In 95% of children with delayed puberty, the delay is physiologic; that is, hormonal levels are normal and the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis is intact, but maturation is slowly happening. This option is the only answer that accurately describes the most common cause of delayed puberty. Question 55 2 / 2 pts Which clinical manifestations are associated with fibromyalgia? Hot, tender, and edematous muscle groups bilaterally Fasciculations of the upper and lower extremity muscles Exercise intolerance and painful muscle cramps Sensitivity at tender points and profound fatigue Widespread joint and muscle pain, fatigue, and tender points are characteristics of fibromyalgia, a chronic musculoskeletal syndrome. Increased sensitivity to touch (i.e., tender points), the absence of systemic or localized inflammation, and fatigue and sleep disturbances are common. Fatigue is profound. The remaining options include symptoms not generally associated with fibromyalgia. Question 56 2 / 2 pts What happens to the vagina’s lining at puberty? It becomes thinner. It becomes thicker. It assumes a neutral pH. It undergoes atrophy. Before puberty, vaginal pH is approximately 7 (neutral) and the vaginal epithelium is thin. At puberty, the pH becomes more acidic (4 to 5) and the squamous epithelial lining thickens. Cell atrophy is not associated with puberty. Question 57 2 / 2 pts What is the first sign of puberty in girls? Breast enlargement Growth of pubic hair Menstruation Vaginal discharge Of the options available, the first sign of puberty in girls is usually thelarche or breast development. Question 58 2 / 2 pts Which term is used to identify the temporary displacement of two bones causing the bone surfaces to partially lose contact? Dislocation Subluxation Malunion Nonunion Dislocation is the temporary displacement of a bone from its normal position in a joint. If the contact between the two surfaces is only partially lost, then the injury is referred to as a subluxation. This selection is the only option that identifies the temporary displacement of two bones, causing the bone surfaces to partially lose contact. Question 59 2 / 2 pts What is the basic structural unit in compact bone? Small channels called canaliculi Osteocytes within the lacunae Tiny spaces within the lacunae Haversian system The basic structural unit in compact bone is the haversian system (see Figure 43-4). This selection is the only option that accurately identifies the basic structure of compact bone. Question 60 2 / 2 pts What anchors articular cartilage to the underlying bone? Sharpey fibers Collagen fibers Glycoproteins Elastin fibers Collagen fibers are important components of the cartilage matrix because they anchor the cartilage securely to underlying bone. This statement is not true of the other options. Question 61 2 / 2 pts Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) is released to stimulate thyroid hormone (TH) and is inhibited when plasma levels of TH are adequate. This is an example of: Positive feedback Negative feedback Neural regulation Physiologic regulation Feedback systems provide precise monitoring and control of the cellular environment. Negative feedback occurs because the changing chemical, neural, or endocrine response to a stimulus negates the initiating change that triggered the release of the hormone. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) from the hypothalamus stimulates TSH secretion from the anterior pituitary. Secretion of TSH stimulates the synthesis and secretion of THs. Increasing levels of T4 and triiodothyronine (T3) then generate negative feedback on the pituitary and hypothalamus to inhibit TRH and TSH synthesis. The described example is not accurately identified by any of the other options. Question 62 2 / 2 pts Clinical manifestations that include irregular or heavy bleeding, the passage of large clots, and the depletion of iron stores support which diagnosis? Premenstrual syndrome Dysfunctional uterine bleeding Polycystic ovary syndrome Primary dysmenorrhea Unpredictable and variable bleeding, in terms of amount and duration, characterize dysfunctional uterine bleeding. Especially during perimenopause, dysfunctional bleeding also may involve flooding and the passage of large clots, which often indicate excessive blood loss. Excessive bleeding can lead to iron-deficiency anemia. This option is the only answer that demonstrates the clinical manifestations described. Question 63 2 / 2 pts The absence of which major hormone is a determinant of sexual differentiation (wolffian system) in utero? Estrogen Progesterone Growth hormone Testosterone In the absence of testosterone, a loss of the wolffian system occurs and the two gonads develop into ovaries at 6 to 8 weeks’ gestation. Between 6 and 7 weeks’ gestation, the male embryo differentiates under the influence of TDF. The presence of estrogen is a determinating factor. None of the other options function as a major determinant to sexual differentiation in utero. Question 64 2 / 2 pts Obesity acts as an important risk factor for type 2 diabetes mellitus by: Reducing the amount of insulin the pancreas produces Increasing the resistance to insulin by cells Obstructing the outflow of insulin from the pancreas Stimulating the liver to increase glucose production People with type 2 diabetes mellitus suffer from insulin resistance (i.e., their cells have difficulty using insulin). The other options are not associated with the effect of obesity regarding insulin production. Question 65 2 / 2 pts Which hormone is involved in the regulation of serum calcium levels? Parathyroid hormone (PTH) Thyroxine (T4) Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) Triiodothyronine (T3) The parathyroid glands produce PTH, a regulator of serum calcium; therefore the other options are incorrect. Question 66 2 / 2 pts An insufficient dietary intake of which vitamin can lead to rickets in children? C B12 B6 D Rickets results from either insufficient vitamin D, insensitivity to vitamin D, wasting of vitamin D by the kidney, or inability to absorb vitamin D and calcium in the gut. Vitamin D is the only vitamin associated with rickets. Question 67 2 / 2 pts What is the function of the mucus secreted by the Bartholin glands? Enhancement of the motility of sperm Lubrication of the urinary meatus and vestibule Maintenance of an acid-base balance to discourage proliferation of pathogenic bacteria Enhancement of the size of the penis during intercourse In response to sexual stimulation, the Bartholin glands secrete mucus that serves only to lubricate the inner labial surfaces, as well as to enhance the viability and motility of sperm. Question 68 2 / 2 pts Which hormone triggers uterine contractions? Thyroxine Oxytocin Growth hormone Insulin Oxytocin is responsible for the contraction of the uterus and milk ejection in lactating women and may affect sperm motility in men. The remaining options are not capable of triggering uterine contractions. Question 69 2 / 2 pts Which bones are affected in Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease? Heads of the femur Distal femurs Heads of the humerus Distal tibias A recurrent interruption of the blood supply to only the femoral heads presumably produces Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease, which is a self-limited disease of the hip. Question 70 2 / 2 pts An individual’s genetic makeup is referred to as his or her: Phenotype Genotype Heterozygous locus Homozygous locus An individual’s genotype is his or her genetic makeup. The correct option is the only one that accurately defines a person’s genetic makeup. Question 71 2 / 2 pts What term is used to identify the calcium crystals that are associated with chronic gout? Stones Spurs Tophi Nodes With time, crystal deposition in subcutaneous tissues causes the formation of small white nodules, or tophi, that are visible through the skin. Crystal aggregates deposited in the kidneys can form urate renal stones and lead to renal failure. None of the other options are associated with the calcium crystals resulting from chronic gout. Question 72 2 / 2 pts Which gastric cells secrete hydrochloric acid and intrinsic factor? Parietal Chief G H Of the available options, only the parietal cells (oxyntic cells) secrete hydrochloric acid and intrinsic factor. Question 73 2 / 2 pts A criterion for a diagnosis of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is a period of excessive worrying that lasts for at least how many months? 3 6 9 12 GAD is diagnosed when an individual spends at least 6 months worrying excessively and exhibits at least three of the six symptoms. Although 3 months is not sufficient time, the remaining options are excessive. Question 74 2 / 2 pts A major characteristic of type 1 diabetes mellitus is that there is: Partial insulin secretion An autoimmune cause factor Insulin resistance Obesity as a common risk factor A strong association between type 1 diabetes and the presence of several human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class II alleles indicate that type 1 diabetes mellitus is an autoimmune disease. The remaining options are associated with type 2 diabetes. Question 75 2 / 2 pts Dilation of the ipsilateral pupil, following uncal herniation, is the result of pressure on which cranial nerve (CN)? Optic (CN I) Abducens (CN VI) Oculomotor (CN III) Trochlear (CN IV) The oculomotor CN (III) is involved in this manifestation of pupil dilation. None of the other options would result in pupil dilation when subjected to pressure. [Show More]
Last updated: 8 months ago
Preview 1 out of 36 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 13, 2020
Number of pages
36
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 13, 2020
Downloads
1
Views
74
















 – CHAMBERLAIN COLLEGE OF NURSING.png)