*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > NUR 2063:Essentials of Pathophysiology - Exam 1 review[studyguide latest 2021graded A+ (All)
NUR 2063:Essentials of Pathophysiology - Exam 1 review[studyguide latest 2021graded A+
Document Content and Description Below
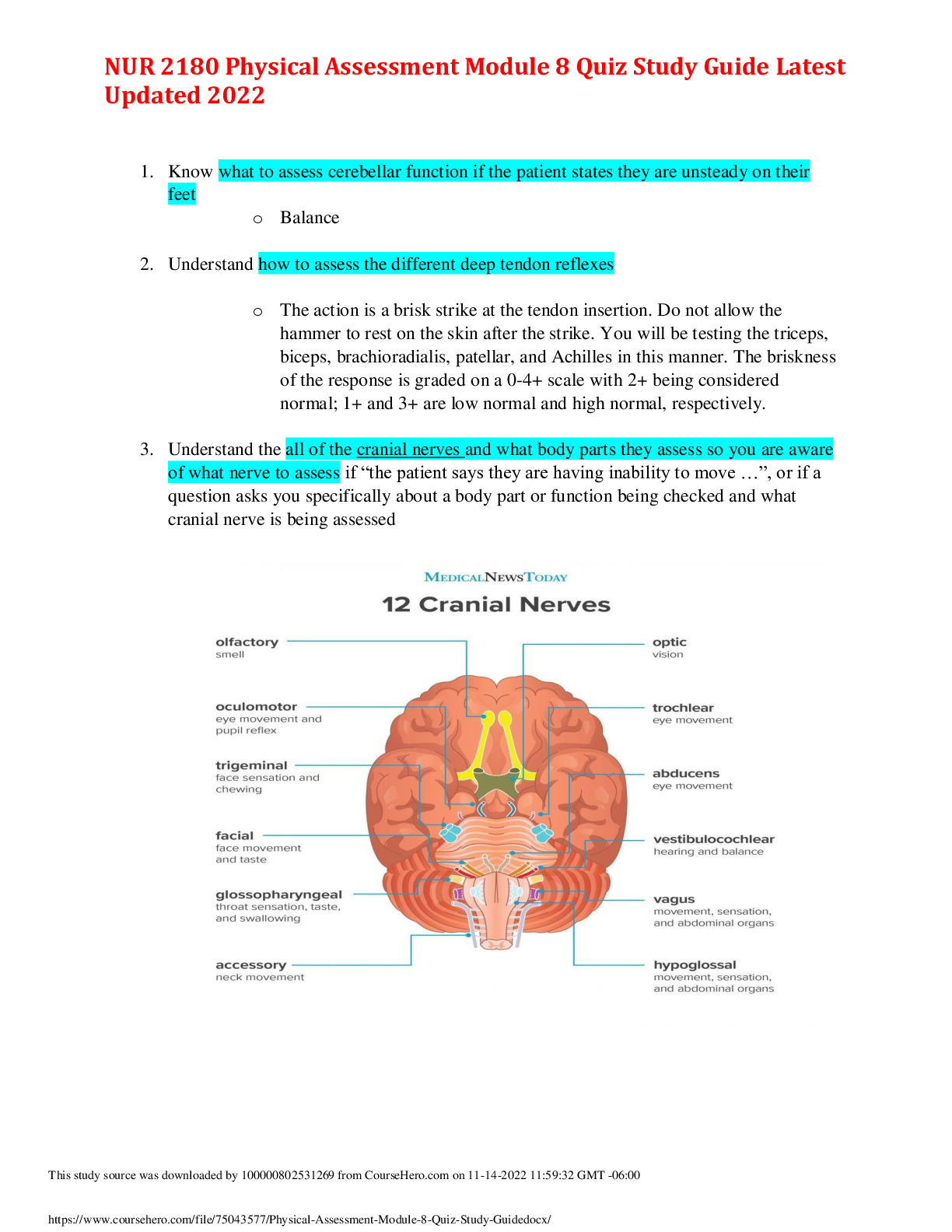
Essentials of Pathophysiology – Exam #1 Review Sheet Covers Modules 1, 2, and 3 – Chapters 1, 2, 3, 7, 8, 9, 10, 24, 51, 52, 53 1. Define pathophysiology. What does the study of pathophysiology ... include? PATHOPHYSIOLOGY: The study of all the abnormalities in physiologic function of living beings. o Derives from 2 disciplines: Patho meaning Dx of diseases through exam of organs, tissues, and cells. Physiology meaning Mechanical, physical, and biochemical functions. o There are FOUR parts of pathophysiology: 1- Etiology: causes/reasons of disease. This ID’s causal factors for Dz 2- Pathogenesis: Evolution of Dz from the initial stimulus to ultimate manifestations of the Dz. (GENESIS = CREATE) 2. Review terms such as signs, symptoms, acute, chronic, exacerbation, remission, convalescence, and sequela Signs: objective/observed manifestations o Ex: rash, change in temperature Symptoms: Subjective o Ex: pain, nausea Acute: short-lived. Chronic: lasts for months/years Exacerbation: increase in severity Remission: decrease in severity Remission: decrease in severity Convalescence: Stage of recovery Sequela: subsequent pathological condition resulting from an illness o Ex: renal failure 2/2 HTN o 3. What is epidemiology? Review the different levels of disease prevention such as primary, secondary, and tertiary as well as examples for each. Epidemiology is the study of study and analysis of the distribution, patterns and determinants of health and conditions in defined populations. o Primary level: altering susceptibility a. Ex: Immunizations o Secondary level” early detections/screenings a. Ex: Pap smears, breast exams, cancer screenings o Tertiary level: Rehabilitation (reduce disabilities) a. Ex: PT/OT after a stroke Florence Nightingale was the first practicing epidemiologist. 4. Review the difference between homeostasis and allostasis. Homeostasis: The process by which a state of internal, physiological equilibrium is maintained. o Ex: pH, concentration of ions in ECF, glucose levels, osmolality of ECF Allostasis: Steps the body takes to re-establish homeostasis. Adaptation to a changing internal and external environment o Ex: HR, body core temperature, BP 5. Review the three different stages of the General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS) including the alarm stage, adaptation/resistance, and exhaustion stage. What hormones are released during the alarm stage and what effects do they have on the body? Three stages of GAS: 1: Alarm Stage: Fight/Flight response. 2: Resistance/Adaptation: Activity of nervous/endocrine systems to return to homeostasis 3: Exhaustion: If stressor is not removed the body cannot return to homeostasis. The body will go into allostatic overload and organs tissues give out. o Ex: renal failure 2/2 HTN 6. Review the differences between the sympathetic vs the parasympathetic nervous systems. What happens to the body during “fight-or-flight” response? Stressor Excites receptors Hypothalamus relases CRH + ACH This activates the SNS Providing a surge of energy Adrenal Medulla releases catecholamines (epinepherine and Norepinepherine) Increased cardiac output, increased respirations, enhanced blood coag. increased BP, dialated pupils, increadd BG (energy), GI/GU supressed. Adrenal Medulla releases cortisol due to ACTH. Corticosteroids stabilize vascular reactivitiy, inhibit glucose uptake, suppress protein sysnthesis *inhibit release of CRH+ACH fron the hypothalamus 7. Review the functions of the various organelles of the cell such as the nucleus, mitochondria, ribosome, lysosome, endoplasmic reticulum, peroxisome, golgi apparatus Nucleus Control center or “brain” of the cell DNA and genes stored here Production of messenger RNA Contains the instructions needed to build nearly all the body’s proteins Most cells contain only one nucleus Some cells like liver and skeletal muscle cells contain more Red blood cells contain no nucleus Mitochondria - “Power house” of the cell Provide energy to the cell in the form of ATP More metabolically active cells have more mitochondria Mitochondria are enclosed by two membranes Outer membrane Inner membrane has folds called cristae Mitochondria are a unique organelle because they contain their own set of DNA Ribosomes Site of protein production - RNA produced in nucleus sent to ribosomes RNA Protein = Translation Found either floating in the cytoplasm (free) or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum (bound) Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Series of folded membranes that move proteins around the cell Continuous with nuclear membrane of nucleus Rough ER – ribosomes attached to ER Site of protein synthesis Production of integral proteins and phospholipids found in cellular membranes Smooth ER – ribosomes not attached to smooth ER Functions include: Detoxification Lipid metabolism Synthesis of hormones Calcium storage Golgi Bodies (Golgi Apparatus) Organelle made up of stacked, flattened membranes Sorts and packages proteins produced in ER Protein “packaging plant” – cell post office Move materials within cell and out of the cell Lysosomes Lysosomes are spherical membranous organelles containing digestive enzymes Lysis = breakdown Digests particles taken in by endocytosis Including bacteria, viruses, and toxins Degrades worn-out or nonfunctional organelles and tissues Peroxisomes membranous sacs containing a variety of powerful enzymes such as oxidase and catalase Oxidases use molecular oxygen (O2) to detoxify harmful substances such as alcohol and f formaldehyde Neutralize dangerous free radicals into hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) Free radicals - highly reactive chemicals with unpaired electrons that can damage biological molecules Catalase breaks down hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) into H2O and O2 Numerous peroxisomes found in liver and kidney cells [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 18 pages
Instant download

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 30, 2021
Number of pages
18
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 30, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
37






.png)