*NURSING > EXAM > NURSING : NUR1172 _Test 2 (TWO) – 50 Questions with answer and reasoning | Rasmussen College (Down (All)
NURSING : NUR1172 _Test 2 (TWO) – 50 Questions with answer and reasoning | Rasmussen College (Download To Score An A).
Document Content and Description Below
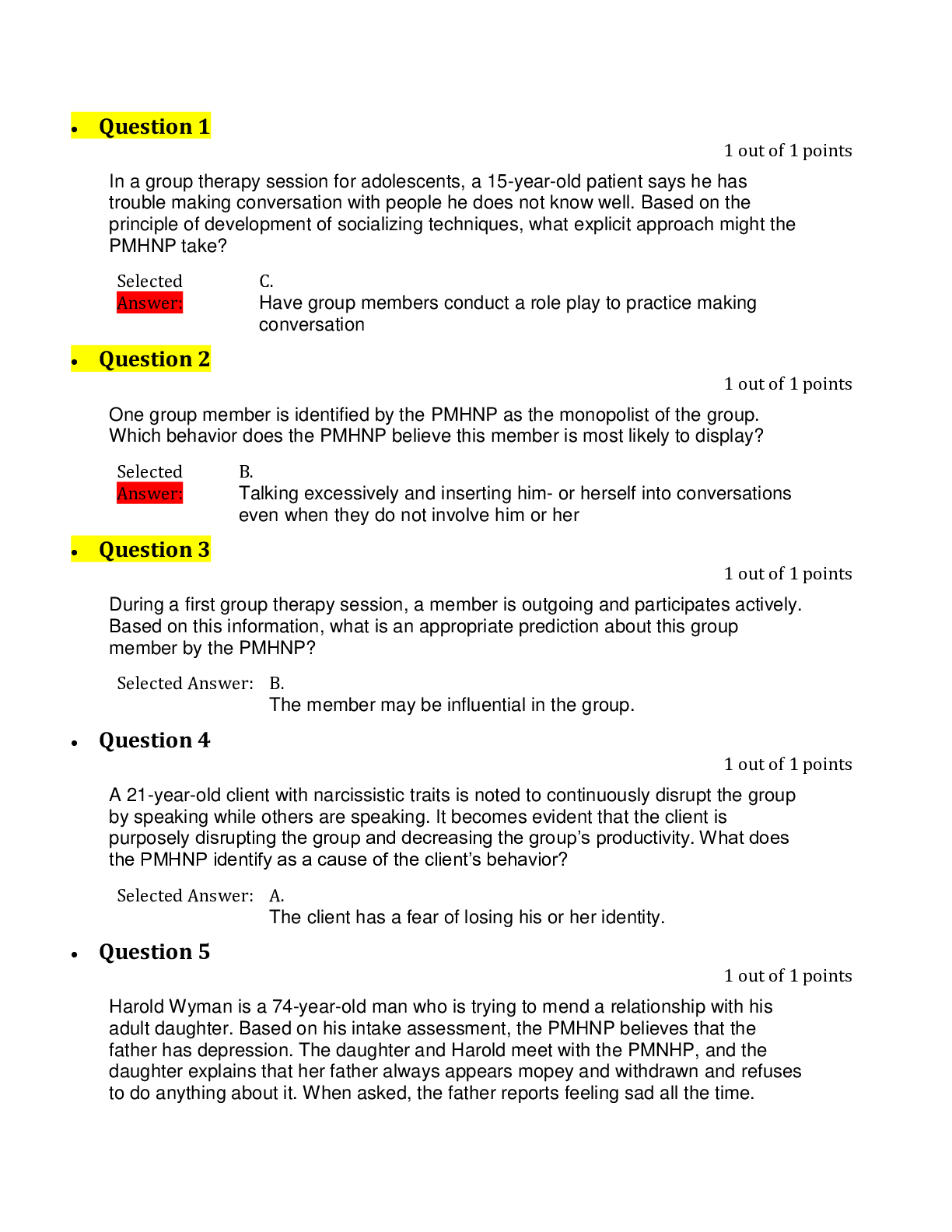
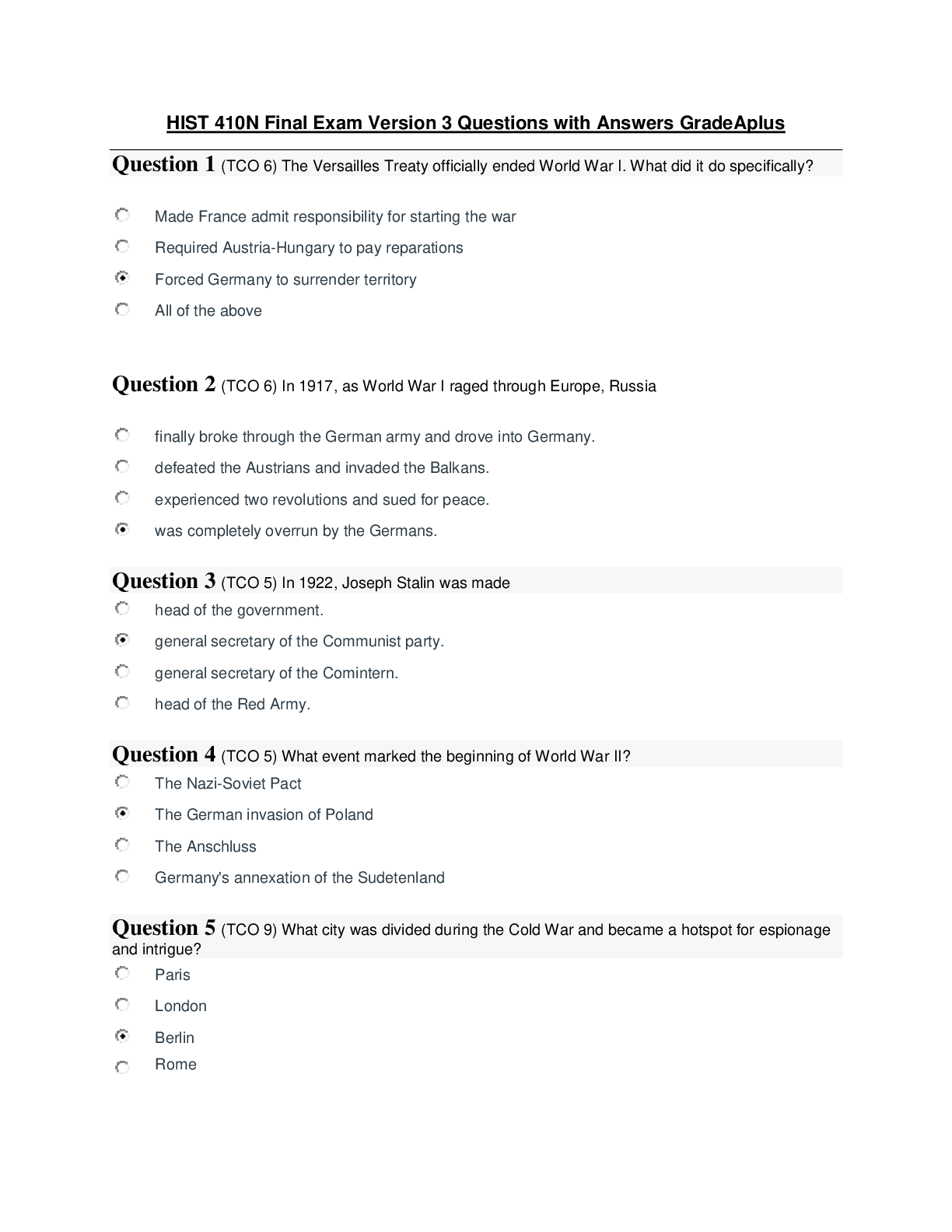
Test # 2 – Questions with answer and reasoning 1. The nurse educator is preparing an education module for the nursing staff on the dermis layer of skin. Which of these statements would be include... d in the module? The dermis: D. Contains Sensory Receptors Reasoning: The dermis consists mostly of collagen, has resilient elastic tissue that allows the skin to stretch, and contains nerves, sensory receptors, blood vessels, and lymphatics. It is not replaced every 4 weeks. 2. During an examination, the nurse finds that a patient has excessive dryness of the skin. The best term to describe this condition is: A. Xerosis Reasoning: Xerosis is the term used to describe skin that is excessively dry. Pruritus refers to itching, alopecia refers to hair loss, and seborrhea refers to oily skin. 3. A 75-year-old woman who has a history of diabetes and peripheral vascular disease has been trying to remove a corn on the bottom of her foot with a pair of scissors. The nurse will encourage her to stop trying to remove the corn with scissors because: A. The woman could be at increased risk for infection and lesions because of her chronic disease. Reasoning: A personal history of diabetes and peripheral vascular disease increases a person's risk for skin lesions in the feet or ankles. The patient needs to see a professional for assistance with corn removal. 4. During a skin assessment, the nurse notices that a Mexican-American patient has skin that is yellowish-brown; however, the skin on the hard and soft palate is pink and the patient's scleras are not yellow. From this finding, the nurse could probably rule out: B. Jaundice Reasoning: Jaundice is exhibited by a yellow color, which indicates rising amounts of bilirubin in the blood. It is first noticed in the junction of the hard and soft palate in the mouth and in the scleras. 5. A black patient is in the intensive care unit because of impending shock after an accident. The nurse would expect to find what characteristics in this patient's skin? C. Ashen, grey, or dull Reasoning: Pallor due to shock (decreased perfusion and vasoconstriction) in black-skinned people will cause the skin to appear ashen, gray, or dull. 6. An elderly woman is brought to the emergency department after being found lying on the kitchen floor 2 days, and she is extremely dehydrated. What would the nurse expect to see upon examination? B. Dry mucous membranes and cracked lips Reasoning: With dehydration, mucous membranes look dry and lips look parched and cracked. The other responses are not found in dehydration. 7. A 65-year-old man with emphysema and bronchitis has come to the clinic for a follow-up appointment. On assessment, the nurse might expect to see which assessment finding? D. Clubbing of the nails Reasoning: Clubbing of the nails occurs with congenital cyanotic heart disease, neoplastic, and pulmonary diseases. The other responses are assessment findings not associated with pulmonary diseases. 8. A newborn infant has Down syndrome. During the skin assessment, the nurse notices a transient mottling in the trunk and extremities in response to the cooler examination room temperature. The infant's mother also notices the mottling and asks what it is. The nurse knows that this mottling is called: E. cutis marmorata Reasoning: Persistent or pronounced cutis marmorata occurs with Down syndrome or prematurity and is a transient mottling in the trunk and extremities in response to cooler room temperatures. A café au lait spot is a large round or oval patch of light-brown pigmentation. Carotenemia produces a yellow-orange color in light-skinned persons. Acrocyanosis is a bluish color around the lips, hands and fingernails, and feet and toenails. 9. The nurse is assessing for inflammation in a dark-skinned person. Which is the best technique? C. Palpate the skin for edema and increased warmth. Reasoning: Because you cannot see inflammation in dark-skinned persons, it is often necessary to palpate the skin for increased warmth, taut or tightly pulled surfaces that may be indicative of edema, and hardening of deep tissues or blood vessels. 10. A 52-year-old woman has a papule on her nose that has rounded, pearly borders and a central red ulcer. She said she first noticed it several months ago and that it has slowly grown larger. The nurse suspects which condition? B. Basil cell carcinoma Reasoning: Basal cell carcinoma usually starts as a skin-colored papule that develops rounded, pearly borders with a central red ulcer. It is the most common form of skin cancer, and it grows slowly. This description does not fit acne lesions 11. A father brings in his 2-month-old infant to the clinic because the infant has had diarrhea for the last 24 hours. He says that his baby has not been able to keep any formula down and that the diarrhea has been at least every 2 hours. The nurse suspects dehydration. The nurse should test skin mobility and turgor in this infant over the: D. Abdomen Reasoning: Test mobility and turgor over the abdomen in an infant. Poor turgor, or "tenting," indicates dehydration or malnutrition. The other areas are not appropriate sites for checking skin turgor in an infant. 12. The nurse notices that a patient's palpebral fissures are not symmetrical. On examination, the nurse may find that there has been damage to cranial nerve: C. VII Reasoning: Facial muscles are mediated by cranial nerve (CN) VII; asymmetry of palpebral fissures may be due to CN VII damage (Bell's palsy). 13. A patient says that she has recently noticed a lump in the front of her neck below her "Adam's apple" that seems to be getting bigger. During the assessment, the finding that leads the nurse to suspect that this may not be a cancerous thyroid nodule is that the lump (nodule): B. Is mobile and not hard Reasoning: Painless, rapidly growing nodules may be cancerous, especially the appearance of a single nodule in a young person. However, cancerous nodules tend to be hard and fixed to surrounding structures, not mobile. 14. The nurse needs to palpate the temporomandibular joint for crepitation. This joint is located just below the temporal artery and anterior to the: C. Tragus Reasoning: The temporomandibular joint is just below the temporal artery and anterior to the tragus. 15. A patient has come in for an examination and states, "I have this spot in front of my ear lobe here on my cheek that seems to be getting bigger and is tender. What do you think it is?" The nurse notes swelling below the angle of the jaw and suspects that it could be an inflammation of his: B. Parotid Gland Reasoning: Swelling with the parotid gland occurs below the angle of the jaw and is most visible when the head is extended. Painful inflammation occurs with mumps, and swelling also occurs with abscesses or tumors. Swelling occurs anterior to the lower ear lobe. 16. The nurse suspects that a patient has hyperthyroidism and laboratory data indicate that the patient's T4 and T3 hormone levels are elevated. Which of these findings would the nurse most likely find on examination? A. Tachycardia Reasoning: Thyroxine and tri-iodothyronine are thyroid hormones that stimulate the rate of cellular metabolism, resulting in tachycardia. With an enlarged thyroid as in hyperthyroidism, the nurse might expect to find diffuse enlargement (goiter) or a nodular lump, but not an atrophied gland. Dyspnea and constipation are not findings associated with hyperthyroidism. 17. During an assessment of an infant, the nurse notes that the fontanels are depressed and sunken. The nurse suspects which condition? B. Dehydration Reasoning: Depressed and sunken fontanels occur with dehydration or malnutrition. Mental retardation and rickets have no effect on fontanels. Increased intracranial pressure would cause tense or bulging, and possibly pulsating fontanels. 18. The nurse is performing an assessment on a 7-year-old child who has symptoms of chronic watery eyes, sneezing, and clear nasal drainage. The nurse notices the presence of a transverse line across the bridge of the nose, dark blue shadows below the eyes, and a double crease on the lower eyelids. These findings are characteristic of: A. Allergies Reasoning: Chronic allergies often develop chronic facial characteristics. These include blue shadows below the eyes, a double or single crease on the lower eyelids, open-mouth breathing, and a transverse line on the nose. 19. During an examination, the nurse finds that a patient's left temporal artery is tortuous and feels hardened and tender compared with the right temporal artery. The nurse suspects which condition? C. Temporal arteritis Reasoning: The artery looks more tortuous and feels hardened and tender with temporal arteritis. These assessment findings are not consistent with the other responses. 20. When examining the eye, the nurse notices that the patient's eyelid margins approximate completely. The nurse recognizes that this assessment finding: A. is expected Reasoning: The palpebral fissure is the elliptical open space between the eyelids, and, when closed, the lid margins approximate completely, which is a normal finding. 21. During ocular examinations, the nurse keeps in mind that movement of the extraocular muscles is: D. stimulated by cranial nerves III, IV, and VI. Reasoning: Movement of the extraocular muscles is stimulated by three cranial nerves: III, IV, and VI. 22. A patient is unable to read even the largest letters on the Snellen chart. The nurse should take which action next? D. Shorten the distance between the patient and the chart until it is seen and record that distance. Reasoning: If the person is unable to see even the largest letters, then the nurse should shorten the distance to the chart until it is seen and should record that distance (e.g., "10/200"). If visual acuity is even lower, then the nurse should assess whether the person can count fingers when they are spread in front of the eyes or can distinguish light perception from a penlight. If vision is poorer than 20/30, then a referral to an ophthalmologist or optometrist is necessary, but first the nurse must assess the visual acuity. 23. A 60-year-old man is at the clinic for an eye examination. The nurse suspects that he has ptosis of one eye. How should the nurse check for this? C. Observe the distance between the palpebral fissures Reasoning: Ptosis is drooping of the upper eyelid that would be apparent by observing the distance between the upper and lower eyelids. The confrontation test measures peripheral vision. Measuring near vision or the corneal light test does not check for ptosis. 24. The nurse is performing an eye assessment on an 80-year-old patient. Which of these findings is considered abnormal? B. Unequal pupillary constriction in response to light Reasoning: Pupils are small in old age, and the pupillary light reflex may be slowed, but pupillary constriction should be symmetric. The assessment findings in the other responses are considered normal in older persons. 25. The mother of a 2-year-old is concerned because her son has had three ear infections in the past year. What would be an appropriate response by the nurse? E. "Your son's eustachian tube is shorter and wider than yours because of his age, which allows for infections to develop more easily." Reasoning: The infant's eustachian tube is relatively shorter and wider, and its position is more horizontal than the adult's, so it is easier for pathogens from the nasopharynx to migrate through to the middle ear. 26. While discussing the history of a 6-month-old infant, the mother tells the nurse that she took a great deal of aspirin while she was pregnant. What question would the nurse want to include in the history? A. "Does your baby seem to startle with loud noise?" Reasoning: Children at risk for hearing deficit include those exposed in utero to a variety of conditions, such as maternal rubella, or to maternal ototoxic drugs. 27. The nurse is assessing a 16-year-old patient with head injuries from a recent motor vehicle accident. Which of the following statements indicates the most important reason for assessing for any drainage from the canal? B. Bloody or clear watery drainage can indicate a basal skull fracture. Reasoning: Frank blood or clear watery drainage (cerebrospinal leak) after trauma suggests a basal skull fracture and warrants immediate referral. 28. Which of the following is a risk factor for ear infections in young children? D. Passive cigarette smoke Reasoning: Passive or second hand smoke is a risk factor for ear infections. 29. During an otoscopic examination, the nurse notes an area of black and white dots on the tympanic membrane and ear canal wall. What does this finding suggest? D. Yeast or fungal infection Reasoning: A colony of black or white dots on the drum or canal wall suggests a yeast or fungal infection (otomycosis). 30. The nurse is auscultating the lungs of a patient who had been sleeping and notes short, popping, crackling sounds that stop after a few breaths. The nurse recognizes that these breath sounds are: A. atalectatic crackles, and not pathologic Reasoning: One type of adventitious sound, atelectatic crackles, is not pathologic. They are short, popping, crackling sounds that sound like fine crackles but do not last beyond a few breaths. When sections of alveoli are not fully aerated (as in people who are asleep or in the elderly), they deflate slightly and accumulate secretions. Crackles are heard when these sections are expanded by a few deep breaths. Atelectatic crackles are heard only in the periphery, usually in dependent portions of the lungs, and disappear after the first few breaths or after a cough. 31. The direction of blood flow through the heart is best described by which of the following? B. Right atrium—right ventricle—pulmonary artery—lungs—pulmonary vein—left atrium—left ventricle Reasoning: Returning blood from the body empties into the right atrium and flows into the right ventricle and then goes to the lungs through the pulmonary artery. The lungs oxygenate the blood and it is then returned to the left atrium by the pulmonary vein. It goes from there to the left ventricle and then out to the body through the aorta. 32. The component of the conduction system referred to as the pacemaker of the heart is the: B. Sinoatrial (SA) node Reasoning: Specialized cells in the SA node near the superior vena cava initiate an electrical impulse. (Because the SA node has an intrinsic rhythm, it is the "pacemaker.") 33. In assessing the carotid arteries of an older patient with cardiovascular disease, the nurse would: B. listen with the bell of the stethoscope to assess for bruits. Reasoning: If cardiovascular disease is suspected, auscultate each carotid artery for the presence of a bruit. Avoid compressing the artery because this could create an artificial bruit and it could compromise circulation if the carotid artery is already narrowed by atherosclerosis. 34. While counting the apical pulse on a 16-year-old patient, the nurse notes an irregular rhythm. His rate speeds up on inspiration and slows on expiration. What would be the nurse's response? C. No further response is needed because this is normal. Reasoning: The rhythm should be regular, although sinus arrhythmia occurs normally in young adults and children. With sinus arrhythmia, the rhythm varies with the person's breathing, increasing at the peak of inspiration, and slowing with expiration. 35. During the precordial assessment on an 8-month pregnant patient, the nurse palpates the apical impulse at the fourth left intercostal space lateral to the midclavicular line. This would indicate C. displacement of the heart from elevation of the diaphragm. Reasoning: Palpation of the apical impulse is higher and lateral compared with the normal position because the enlarging uterus elevates the diaphragm and displaces the heart up and to the left and rotates it on its long axis. 36. The mother of a 10-month-old tells the nurse that she has noticed that her son becomes blue when he is crying and that the frequency of this is increasing. He is also not crawling yet. During the examination the nurse palpates a thrill at the left lower sternal border and auscultates a loud systolic murmur in the same area. What would be the most likely cause of these findings? A. Tetralogy of Fallot Reasoning: Tetralogy of Fallot subjective findings include (1) severe cyanosis, not in the first months of life but developing as the infant grows, and right ventricle outflow (i.e., pulmonic) stenosis gets worse; (2) cyanosis with crying and exertion at first, then at rest; (3) slowed development. Objective findings include (1) thrill palpable at left lower sternal border; (2) S1 normal, S2 has A2 loud and P2 diminished or absent;(3) murmur is systolic, loud, crescendo-decrescendo. 37. When the nurse is auscultating the carotid artery for bruits, which of the following reflects correct technique? C. Lightly apply the bell of the stethoscope over the carotid artery; have the patient take a breath, exhale, and hold it briefly while the nurse listens. Reasoning: Lightly apply the bell of the stethoscope over the carotid artery at three levels; have the patient take a breath, exhale, and hold it briefly while you listen. Holding the breath on inhalation will also tense the levator scapulae muscles, which makes it hard to hear the carotids. Examine only one carotid artery at a time to avoid compromising arterial blood flow to the brain. Avoid pressure over the carotid sinus, which may lead to decreased heart rate, decreased blood pressure, and cerebral ischemia with syncope. 38. The nurse is preparing for a class on risk factors for hypertension and reviews recent statistics. Which racial group has the highest prevalence of hypertension in the world? A. Blacks Reasoning: According to the American Heart Association, the prevalence of heart disease and stroke is higher among black adults than in other racial groups. 39. A 67-year-old patient states that he recently began to have pain in his left calf when climbing the 10 stairs to his apartment. This pain is relieved by sitting for about 2 minutes; then he is able to resume his activities. The nurse interprets that this patient is most likely experiencing: A. Claudication Reasoning: Intermittent claudication feels like a "cramp" and is usually relieved by rest within 2 minutes. The other responses are not correct. 40. When assessing a patient the nurse notes that the left femoral pulse as diminished, 1+/4+. What should the nurse do next? B. Auscultate the site for a bruit. Reasoning: If a pulse is weak or diminished at the femoral site, the nurse should auscultate for a bruit. Presence of a bruit, or turbulent blood flow, indicates partial occlusion. The other responses are not correct. 41. A patient has been diagnosed with venous stasis. Which of the following would the nurse most likely observe? D. A brownish discoloration to the skin of the lower leg Reasoning: A brown discoloration occurs with chronic venous stasis as a result of hemosiderin deposits (a byproduct of red blood cell degradation). Pallor, cyanosis, atrophic skin, and unilateral coolness are all signs associated with arterial problems. 42. When auscultating over a patient's femoral arteries the nurse notes the presence of a bruit on the left side. The nurse knows that: D. bruits occur with turbulent blood flow, indicating partial occlusion. Reasoning: bruits occur with turbulent blood flow, indicating partial occlusion. 43. A patient has hard, non-pitting edema of the left lower leg and ankle. The nurse knows that: A. non-pitting, hard edema occurs with lymphatic obstruction. Reasoning: Unilateral edema occurs with occlusion of a deep vein and with unilateral lymphatic obstruction. With these factors, it is nonpitting and feels hard to the touch. 44. During an assessment, a patient tells the nurse that her fingers often change color when she goes out in cold weather. She describes these episodes as her fingers first turning white, then blue, then red with a burning, throbbing pain. The nurse suspects that she is experiencing: B. Raynaud's syndrome. Reasoning: The condition with episodes of abrupt, progressive tricolor change of the fingers in response to cold, vibration, or stress is known as Raynaud's syndrome. 45. While examining a patient, the nurse observes abdominal pulsations between the xiphoid and umbilicus. The nurse would suspect that these are: C. normal abdominal aortic pulsations. Reasoning: Normally, one may see the pulsations from the aorta beneath the skin in the epigastric area, particularly in thin persons with good muscle wall relaxation. 46. A patient has hypoactive bowel sounds. The nurse knows that a potential cause of hypoactive bowel sounds is: B. peritonitis. Reasoning: Diminished or absent bowel sounds signal decreased motility from inflammation as seen with peritonitis, with paralytic ileus after abdominal surgery, or with late bowel obstruction. 47. The nurse notes that a patient has had a black, tarry stool and recalls that a possible cause would be: C. gastrointestinal bleeding. Reasoning: Black stools may be tarry as a result of occult blood (melena) from gastrointestinal bleeding. Red blood in stools occurs with localized bleeding around the anus. 48. A patient is recovering from several hours of orthopedic surgery. During an assessment of the patient's lower legs, the nurse will monitor for signs of acute venous symptoms. Signs of acute venous symptoms include: Select all that apply. A- Intense, sharp pain, with the deep muscle tender to touch, D- Onset is sudden, E.- Calf is warm, red, and swollen Reasoning: Signs and symptoms of acute venous problems include pain in the calf that has a sudden onset and that is intense and sharp with tenderness in the deep muscle when touched. The calf is warm, red, and swollen. Options B, C, and F are symptoms of chronic venous problems. 49. A patient has been admitted with chronic arterial symptoms. During the assessment, the nurse should expect which findings? Select all that apply. A-The patient has a history of diabetes and cigarette smoking, B-The patient's skin is pale and cool,E-The patient states that the pain gets worse when walking. Reasoning: Patients with chronic arterial symptoms often have a history of smoking and diabetes (among other risk factors). The pain has a gradual onset, with exertion, and is relieved with rest or dangling. The skin appears cool and pale. The other responses reflect chronic venous problems. 50. A 55-year-old man is in the clinic for a yearly check-up. He is worried because his father died of prostate cancer. The nurse knows that which tests should be done at this time? Select all that apply. A- Blood test for prostate-specific antigen, D- Digital rectal examination Reasoning: Prostate cancer is typically detected by testing the blood for prostate-specific antigen (PSA) or by a digital rectal exam (DRE). It is recommended that both PSA and DRE be offered to men yearly, beginning at age 50 years. If the PSA is elevated, then further lab work or a transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) and biopsy may be recommended. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 9 pages
Instant download
 (1).png)
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 08, 2021
Number of pages
9
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 08, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
30






.png)