*NURSING > MED-SURG EXAM > NUR 204 Exam 3 TestBank Questions and Answers GRADED A (All)
NUR 204 Exam 3 TestBank Questions and Answers GRADED A
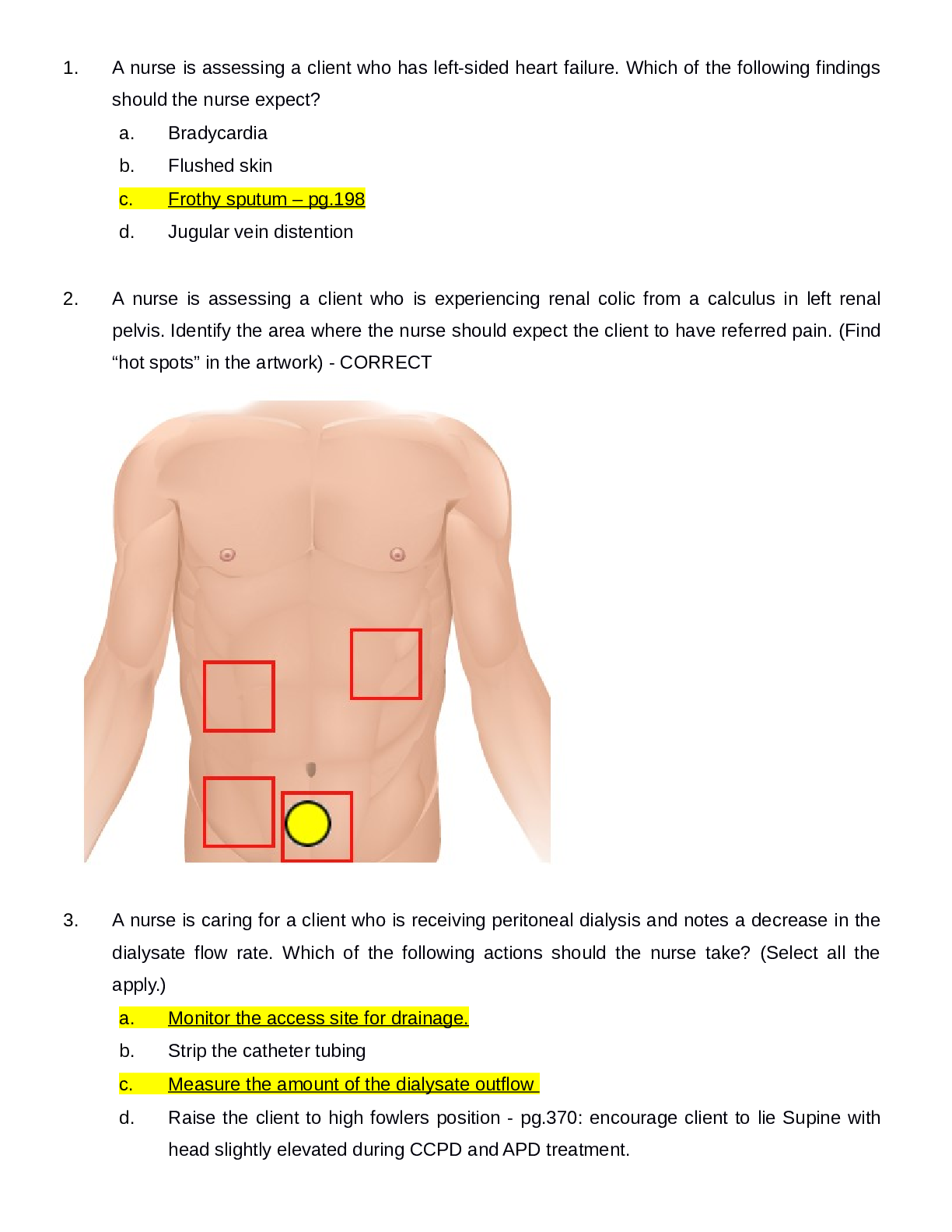
Document Content and Description Below
NUR 204 Exam 3 TestBank Questions and Answers The nurse is providing care to a pregnant woman in preterm labor. The patient is 32 weeks pregnant. Initially, the patient states, Ive gained 30 pounds... . That should be enough for the baby. Everything will be OK if I deliver now. After teaching the patient about fetal development, the nurse will know her teaching is effective if the patient makes which of the following statements? 1) The baby's lungs are well developed now, but he will be at increased risk for SIDS if I deliver early. 2) We should try to stop this labor now because the baby will be born with sleep apnea if I deliver this early. 3) If I deliver this early my baby is at risk for respiratory distress syndrome, a condition that can be life threatening. 4) Thanks for reassuring me; I was pretty sure there isnt much risk to the baby this far along in my pregnancy. RATIONALE: Premature infants (younger than 33 weeks gestation) are born before the alveolar surfactant system is fully developed. Therefore, they are at high risk for respiratory distress syndrome (RDS). RDS is characterized by widespread atelectasis (collapse of alveoli), usually related to a deficiency of surfactant that keeps air sacs open. The nurse is caring for a patient who is experiencing dyspnea. Which of the following positions would be most effective if incorporated into the patients care? 1) Supine 2) Head of bed elevated 80 3) Head of bed elevated 30 4) Lying on left side RATIONALE: Position affects ventilation. An upright or elevated position pulls abdominal organs down, thus allowing maximum diaphragm excursion and lung expansion. While a patient is receiving hygiene care, her chest tube becomes disconnected from the water-seal chest drainage system (CDU). Which action should the nurse take immediately? 1) Clamp the chest tube close to the insertion site. 2) Set up a new drainage system, and connect it to the chest tube. 3) Have the patient take and hold a deep breath while the nurse reconnects the tube to the CDU. 4) Place the disconnected end nearest the patient into a bottle of sterile water. Recollapse of the lung can occur because of loss of negative pressure within the system. This is commonly caused by air leaks, disconnections, or cracks in the bottles or chambers. If any of these occur, the nurse should immediately place the disconnected end nearest the patient into a bottle of sterile water or saline to a depth of 2 cm to serve as an emergency water seal until a new system can be connected. Do not clamp the chest tube because this can rapidly lead to a tension pneumothorax. A new drainage system should be set up to decrease the risk of infection, but the immediate action is to place the disconnected end into a bottle of sterile water. The nurse administers an antitussive/expectorant cough preparation to a patient with bronchitis. Which of the following responses indicates to the nurse that the medication is effective? 1) The amount of sputum the patient expectorates decreases with each dose administered. 2) Cough is completely suppressed, and she is able to sleep through the night. 3) Dry, unproductive cough is reduced, but her voluntary coughing is more productive. 4) Involuntary coughing produces large amounts of thick yellow sputum. ANS: 3 Antitussives are cough suppressants that reduce the frequency of an involuntary, dry, nonproductive cough. Antitussives are useful for adults when coughing is unproductive and frequent, leading to throat irritation or interrupted sleep. Expectorants help make coughing more productive. The goal of an antitussive/expectorant combination is to reduce the frequency of dry, unproductive coughing while making voluntary coughing more productive. The nurse is admitting to the medical-surgical unit an older adult woman with a diagnosis of pulmonary hypertension and right-sided heart failure. The patient is complaining of shortness of breath, and the nurse observes conversational dyspnea. What is the first action the nurse should take? 1) Review and implement the primary care providers prescriptions for treatments. 2) Perform a quick physical examination of breathing, circulation, and oxygenation. 3) Gather a thorough medical history, including current symptoms, from the family. 4) Administer oxygen to the patient through a nasal cannula. ANS: 2 The first action the nurse should take is to make a quick assessment of the adequacy of breathing, circulation, and oxygenation in order to determine the type of immediate intervention required. The nurses assessment should include simple questions about current symptoms. A more thorough medical history can be gathered once the patients oxygenation needs are addressed. Following a quick assessment, the nurse should then review and implement physicians orders. Administering oxygen is not appropriate without knowing what treatments the primary care provider has prescribed. You are caring for a young adult patient with an intracranial hemorrhage secondary to a closed head injury. During your assessment, you notice that the patients respirations follow a cycle progressively increasing in depth, then progressively decreasing in depth, followed by a period of apnea. Which of the following appropriately describes this respiratory pattern? 1) Biots breathing 2) Kussmauls respirations 3) Sleep apnea 4) Cheyne-Stokes respirations ANS: 4 This respiratory pattern is known as Cheyne-Stokes respirations. It is often associated with damage to the medullary respiratory center or high intracranial pressure due to brain injury. You are admitting a 54-year-old patient with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The physician prescribes O2 at 24% FIO2. What is the most appropriate oxygen delivery method for this patient? 1) Nonrebreather mask 2) Nasal cannula 3) Partial rebreather mask 4) Venturi mask ANS: 4 The Venturi mask is capable of delivering 24% to 50% FIO2. The cone-shaped adapter at the base of the mask allows a precise FIO2 to be delivered. This is very useful for patients with chronic lung disease. Rebreather masks are used when high concentrations of oxygen are required. A nasal cannula administers oxygen in liters per minute and does not allow administration of a precise FIO2. Which of the following provide the most reliable data about the effectiveness of airway suctioning? 1) The amount, color, consistency, and odor of secretions 2) The patients tolerance for the procedure 3) Breath sounds, vital signs, and pulse oximetry before and after suctioning 4) The number of suctioning passes required to clear secretions ANS: 3 Breath sounds, vital signs, and oxygen saturation levels before and after suctioning provide data about the effectiveness of suctioning. Information about the amount and appearance of secretions provides data about the likelihood of airway infection and/or inflammation. Data about the patients tolerance of suctioning provide information about the patients overall condition. The number of suctioning passes required to clear the secretions provides information about the amount of secretions present. What is the rationale for wrapping petroleum gauze around a chest tube insertion site? 1) Prevents air from leaking around the site 2) Prevents infection at the insertion site 3) Absorbs drainage from the insertion site 4) Protects the tube from becoming dislodged ANS: 1 Petroleum gauze creates a seal around the insertion site. Collapse of the lung can occur if there is a leak around the insertion site that causes loss of negative pressure within the system. Air leaks are one common cause of loss of negative pressure. You are caring for an adult patient with a tracheostomy who is being mechanically ventilated. His pulse oximetry reading is 85%, heart rate is 113, and respiratory rate is 30. The patient is very restless. His respirations are labored, and you hear gurgling sounds. You auscultate crackles and rhonchi in both lungs. What is the most appropriate action to take? 1) Call the respiratory therapist to check the ventilator settings. 2) Provide endotracheal suctioning. 3) Provide tracheostomy care. 4) Notify the physician of the patients signs of fluid overload. ANS: 2 Increased pulse and respiratory rates, decreased oxygen saturation, gurgling sounds during respiration, auscultation of adventitious breath sounds, and restlessness are signs that indicate the need for suctioning. Airways are suctioned to remove secretions and maintain patency. The patients symptoms should subside once the airway is cleared. Chest percussion and postural drainage would be an appropriate intervention for which of the following conditions? 1) Congestive heart failure 2) Pulmonary edema 3) Pneumonia 4) Pulmonary embolus ANS: 3 Chest physiotherapy moves secretions to the large, central airways for expectoration or suctioning. This treatment is not effective for conditions that do not involve the development of airway secretions, including congestive heart failure, pulmonary edema, and pulmonary embolus. Which of the following blood levels normally provides the primary stimulus for breathing? 1) pH 2) Oxygen 3) Bicarbonate 4) Carbon dioxide ANS: 4 Carbon dioxide (CO2) level provides the primary stimulus to breathe. High CO2 levels stimulate breathing to eliminate the excess CO2. A secondary, although important, drive to breathe is hypoxemia. Low blood O2 levels stimulate breathing to bring more oxygen into the lungs. A 62-year-old man with emphysema says, My doctor wants me to quit smoking. It's too late now, though; I already have lung problems. Which of the following would be the best response to his statement? 1) You should quit so your family does not get sick from exposure to secondhand smoke. 2) You will need to use oxygen, but remember it is a fire hazard to smoke with oxygen in your home. 3) Once you stop smoking, your body will begin to repair some of the damage to your lungs. 4) You should ask your primary care provider for a prescription for a nicotine patch to help you quit. ANS: 3 The nurses response should focus on correcting the patients misinformation rather than on convincing him to stop smoking. Once a person stops smoking, the body begins to repair the damage. During the first few days, the person will cough more as the cilia begin to clear the airways. Then the coughing subsides, and breathing becomes easier. Even long-time smokers can benefit from smoking cessation. The suggestions that the patients family will become ill and that oxygen is a fire hazard appear to be scare tactics, which can be seen as coercive, and would not be effective in motivating the patient to stop smoking. Although asking the primary care provider for a prescription may help the patient to stop smoking, it does not address his incorrect belief that it is too late for him to do so. The nurse administers intravenous morphine sulfate to a patient for pain control. She will need to monitor her patient for which of the following adverse effects? 1) Decreased heart rate 2) Muscle weakness 3) Decreased urine output 4) Respiratory depression ANS: 4 Opioids are potent respiratory depressants. Patients receiving opioids should be monitored for decreased rate and depth of respirations. When using sterile technique to perform tracheostomy care of a new tracheostomy, which of the following is correct? 1) You will need a single pair of sterile gloves. 2) Place the patient in semi-Fowlers position, if possible. 3) Clean the stoma under the faceplate with hydrogen peroxide. 4) Cut a slit in sterile 4 4 gauze halfway through to make a dressing. ANS: 2 Semi-Fowlers position promotes lung expansion and prevents back strain for the nurse. You will need two pairs of sterile gloves: one pair for dressing removal, and a clean pair for the rest of the procedure. You should clean the stoma under the faceplate with sterile saline. Never cut a 4 4 gauze for the dressing because lint and fibers from the cut edge could enter the trachea and cause respiratory distress. A patient has just had a chest tube inserted to dry-seal suction drainage. Which of the following is a correct nursing intervention for maintenance? 1) Keep the head of the bed flat for 6 hours. 2) Immobilize the patients arm on the affected side. 3) Keep the drainage system lower than the insertion site. 4) Drain condensation into the humidifier when it collects in the tubing. ANS: 3 The drainage system must be below the insertion site to prevent fluid flowing back into the pleural cavity and compromising the patients respiratory status. Maintain patient in semirecumbent position (head of bed elevated 30 to 45 degrees), not flat. This is extremely important to promote lung expansion, reduce gastric reflux, and prevent ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP), if the person is being mechanically ventilated. Patients being mechanically ventilated are at high risk for developing VAP, which is associated with high mortality rates. Mouth rinses and mouthwashes are a part of the recommended routine for preventing VAP. They also provide comfort and preserve integrity of the mucous membranes. Encourage the patient to move the arm on the affected side; if he cannot, perform passive range-of-motion. You should check the ventilator tubing frequently for condensation, and drain the fluid into a collection device or waste receptacle because condensation in the ventilator tubing can cause resistance to airflow. Moreover, the patient can aspirate it if it backflows down into the endotracheal tube. The fluid should not be drained into the humidifier because the patients secretions may have contaminated it. The nurse is counseling a 17-year-old girl on smoking cessation. The nurse should include which of the following helpful tips in her education? Choose all that apply. 1) Keep healthy snacks or gum available to chew instead of smoking a cigarette. 2) Don't tell your friends and family you are trying to quit, until you feel confident that you'll be successful. 3) Plan a time to quit when you will not have many other demands or stressors in your life. 4) Reward yourself with an activity you enjoy when you quit smoking. ANS: 1, 3, 4 People who are trying to quit smoking often are more successful when they are accountable to other people who are encouraging and supportive. Having something to chew (e.g., carrot sticks, gum, nuts, or seeds) can distract from the desire to smoke a cigarette. Setting a date to stop smoking and choosing a time of low stress are two strategies that help people be more successful with smoking cessation. Self-reward for meeting goals is a form of positive reinforcement. A patient has a history of COPD. His pulse oximetry reading is 97%. What other findings would indicate adequate tissue and organ oxygenation? Choose all that apply. 1) Normal urine output 2) Strong peripheral pulses 3) Clear breath sounds bilaterally 4) Normal muscle strength ANS: 1, 2, 4 To determine adequacy of tissue oxygenation, assess respiration, circulation, and tissue/organ function. Good peripheral circulation is characterized by strong peripheral pulses. Impaired tissue oxygenation to the kidneys would result in abnormal kidney function (e.g., poor urine output). Hypoxic limb tissue would result in abnormal muscle functioning (e.g., muscle weakness and pain with exercise). Adequacy of tissue oxygenation cannot be determined by assessing pulmonary ventilation alone; circulation must also be assessed. The nurse is teaching a patient about her chest drainage system. Which of the following should the nurse include in the teaching? Choose all that apply. 1) Perform frequent coughing and deep-breathing exercises. 2) Sit up in a chair but do not walk while the drainage system is in place. 3) Get out of bed without assistance as much as possible. 4) Immediately notify the nurse if she experiences increased shortness of breath. ANS: 1, 4 Patients should regularly perform coughing and deep-breathing exercises to promote lung reexpansion. Also to promote lung reexpansion, the nurse should encourage the patient to be as active as her condition permits, rather than telling her not to walk. Chest drainage systems are bulky, but patients with disposable systems can still get out of bed and ambulate. However, the patient will need assistance from one or two staff members to protect and monitor the system and to monitor her responses to activity; she should not get out of bed on her own. If a patient with a chest drainage system becomes acutely short of breath, the patient should immediately notify the nurse so the nurse can check for occlusion of the system, which can result in a tension pneumothorax. When providing safety education to the mother of a toddler, you would inform the mother that, based on the childs developmental stage, he is at high risk for which of the following factors that influence oxygenation? Choose all that apply. 1) Frequent, serious respiratory infections 2) Airway obstruction from aspiration of small objects 3) Drowning in small amounts of water around the home 4) Development of asthma ANS: 2, 3 As a toddlers respiratory and immune systems mature, the risk for frequent and serious infections is less than in infanthood. Most children recover from upper respiratory infections without difficulty. Toddlers airways are relatively short and small and may be easily obstructed, and they often put objects in their mouth as part of exploring their environment, thus increasing their risk for aspiration and airway obstruction. In addition, toddlers are at high risk for drowning in very small amounts of water around the home (e.g., in a bucket of water or toilet bowl). The risk for developing asthma is not significantly influenced by the childs developmental stage. Obesity is associated with higher risk for which of the following conditions that affect the pulmonary and cardiovascular systems? Choose all that apply. 1) Reduced alveolar-capillary gas exchange 2) Lower respiratory tract infections 3) Sleep apnea 4) Hypertension ANS: 2, 3, 4 Obesity causes multiple health problems, many of which affect the lungs, heart, and circulation. Large abdominal fat stores press upward on the diaphragm, preventing full chest expansion and leading to hypoventilation and dyspnea on exertion. The risk for respiratory infection increases because lower lung segments are poorly ventilated, and secretions are not removed effectively. When an obese person lies down, chest expansion is limited even more. Excess neck girth and fat stores in the upper airway often lead to obstructive sleep apnea. Obesity also increases the risk of developing atherosclerosis and hypertension. Obesity does not cause reduced alveolar-capillary gas exchange. Which of the following is/are accurate about nasotracheal suctioning? Choose all that apply. 1) Apply suction for no longer than 10-15 sec during a single pass. 2) Apply suction while inserting and removing the catheter. 3) Reapply oxygen between suctioning passes for ventilator patients. 4) Gently rotate the suction catheter as you remove it. ANS: 1, 4 Limiting suctioning to 10 seconds or less and reapplying oxygen between suctioning passes prevent hypoxia. Suction should be applied only while withdrawing the catheter, using a continuous rotating motion to prevent trauma to the airway. Endotracheal suctioning is used when the patient is being mechanically ventilated, and most ventilator patients have in-line suctioning, so there is no need to reapply oxygen. Which of the following factors influence normal lung volumes and capacities? Choose all that apply. 1) Age 2) Race 3) Body size 4) Activity level ANS: 1, 3, 4 Normal lung volumes and capacities vary with body size, age, and exercise level. Volumes and capacities are higher in men, in large people, and in athletes. Race does not influence normal lung volumes and capacities. Of the following interventions, which is/are likely to reduce the risk of postoperative atelectasis? Choose all that apply. 1) Administer bronchodilators. 2) Apply low-flow oxygen. 3) Encourage coughing and deep breathing. 4) Administer pain medication. ANS: 3, 4 Pain alters the rate and depth of respirations. Often, patients in pain breathe shallowly, which puts them at risk for atelectasis. Regularly assess all patients for pain. Once you have medicated the patient, reassess breath sounds, and encourage the patient to cough and breathe deeply. This will help to open air sacs and mobilize secretions in the airways. ____________________ is the movement of air into and out of the lungs through the act of breathing. ____________________ refers to the exchange of gases (oxygen and carbon dioxide) in the lungs. ANS: Ventilation; Respiration Pulmonary ventilation (breathing) is the movement of air into and out of the lungs. Oxygenation of the blood, and ultimately of organs and tissues, depends on adequate ventilation. Respiration refers to gas exchangethat is, the oxygenation of blood and elimination of carbon dioxide in the lungs. Although the plural form respirations is used to mean breaths when taking vital signs, this is a misnomer: You cannot measure gas exchange by counting breaths per minute. Prolonged use of high oxygen concentrations reduces ____________________ production, which leads to alveolar collapse and reduced lung elasticity. ANS: surfactant Oxygen toxicity can develop when oxygen concentrations of more than 50% are administered for longer than 48 to 72 hours. The amount of air moved into and out of the lungs with each normal breath is known as the ____________________. Normally, this volume is around ____________________ mL. ANS: tidal volume; 500 A patient diagnosed with hypertension is taking an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor. When planning care, which of the following outcomes would be appropriate for the patient? 1) BP will be lower than 135/85 mm Hg on all occasions. 2) BP will be normal after 2 to 3 weeks on medication. 3) Patient will not experience dizziness on rising. 4) Urine output will increase to at least 50 mL/hr ANS: 1 Goals must be clearly stated so that it is easy to evaluate if they have been met. BP . . . lower than 135/85 mm Hg . . . is clearly stated and easily evaluated. In contrast, BP will be normal . . . does not clearly state the desired endpoint. Freedom from dizziness on rising is probably not achievable because ACE inhibitors are vasodilating agents, which may cause vessel dilation and hypotension, especially when the patient arises from a seated or lying position. Patients should be warned of this effect. The expected/desired effect of the ACE inhibitor is to lower the blood pressure; the urine output is minimally relevant in determining that outcome, if at all. You are preparing the nursing care plan for a middle-aged patient admitted to the intensive care unit for an acute myocardial infarction (heart attack). His symptoms include tachycardia, palpitations, anxiety, jugular vein distention, and fatigue. Which of the following nursing diagnoses is most appropriate? 1) Decreased Cardiac Output 2) Impaired Tissue Perfusion 3) Impaired Cardiac Contractility 4) Impaired Activity Tolerance ANS: 1 The patients symptoms reflect altered cardiac preload, a component of cardiac output. Acute myocardial infarction is often associated with decreased cardiac output as a result of altered cardiac pumping ability. Although the other nursing diagnoses might be associated with Decreased Cardiac Output, these diagnoses cannot be determined from the symptoms presented. Additionally, Impaired Cardiac Contractility is not a NANDA-I nursing diagnosis. You are to connect a patient to a cardiac monitor. Which of the following actions should you take to ensure an accurate electrocardiogram tracing? 1) Select electrode placement sites over bony prominences. 2) Apply the electrodes immediately after cleansing the skin, before the alcohol evaporates. 3) Before applying the electrodes, rub the placement sites with gauze until the skin reddens. 4) Ensure that the gel on the back of the electrodes is dry. ANS: 3 Electrodes should be placed over soft tissues or close to bone in order to obtain accurate waveforms. Sites over bony prominences, thick muscles, and skinfolds can produce artifact; therefore, they should not be used. Alcohol removes skin oils that may prevent the electrodes from adhering. However, the alcohol should be allowed to dry before the electrodes are placed. Rubbing the skin with gauze or a washcloth removes dead skin cells and promotes better electrical contact. A dry electrode will not conduct electrical activity; gel should not be dry. Chronic stress may lead directly to cardiovascular disease because of the repeated release of which of the following? 1) Histamine 2) Catecholamines 3) Cortisol 4) Protease ANS: 2 The stress response stimulates release of catecholamines from the sympathetic nervous system. This results in increased heart rate and contractility, vasoconstriction, and increased tendency of blood to clot. Cortisol is also released in the stress response, but it is more indirectly related to development of cardiovascular disease through altered glucose, fat, and protein metabolism. The nurse is teaching a pregnant woman about the increased oxygen demand that develops during pregnancy. The nurse knows the patient comprehends the teaching when she makes the following statement: 1) I may need to drink more fluids in order to make more oxygen. 2) I may need to take an iron supplement so that I am not anemic. 3) I will need a multivitamin supplement for several months. 4) I will need to eat more fruits and vegetables. ANS: 2 During pregnancy, oxygen demand increases dramatically. To compensate, the mothers blood volume increases by 30%. The woman requires additional iron to produce this blood as well as to meet fetal requirements. Failure to meet these iron demands can result in maternal anemia, reducing tissue oxygenation of the mother. Which part of the ECG tracing represents ventricular repolarization? 1) P wave 2) QRS complex 3) T wave 4) U wave ANS: 2 The QRS complex represents ventricular depolarization and leads to ventricular contraction. The P wave represents the firing of the SA node and conduction of the impulse through the atria. In the healthy heart, this leads to atrial contraction. The T wave represents the return of the ventricles to an electrical resting state so they can be stimulated again (ventricular repolarization). The atria also repolarize, but they do so during the time of ventricular depolarization; thus, they are obscured by the QRS complex and cannot be seen on the ECG complex. The U wave is not always seen on the ECG but may be detected with electrolyte imbalance, such as hypokalemia or hypercalcemia. U waves sometimes occur in response to certain medication (e.g., digitalis, epinephrine). Inverted U wave may occur with ischemia to the cardiac muscle. Three days ago a patient had cardiac surgery to bypass three occlusions of his coronary arteries. Veins for the bypass were harvested from his right leg. He informs the nurse that his leg is warm and tender in his right calf. The nurse notes a 3-cm periwound erythema and swelling at the distal end of the incision. Staples are intact along the incision, and there is no drainage. Vital signs are stable. The nurse would suspect that the patient has what kind of complication? 1) Deep vein thrombosis 2) Dehiscence of the wound 3) Internal bleeding 4) Infection at the incisional site ANS: 1 Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a clot in the veins that are deep under the muscles of the leg. DVT can occur after surgery, after lengthy bedrest, or after trauma. Symptoms include pain, warmth, redness, and swelling of the leg. Dorsiflexion of the foot (pulling toes forward) and Pratts sign (squeezing calf to trigger pain) have not been found to be reliable in diagnosing DVT. Dehiscence is the rupture of a suture line, whereas evisceration is the protrusion of internal organs through the rupture. Internal bleeding is a wound-healing complication associated with hematoma formation, pain, hypotension, and tachycardia. Infection is a complication of wound healing that causes warmth, pain, inflammation of the affected area, and changes in vital signs (i.e., elevated pulse and temperature). Nursing interventions to reduce the risk of clot formation in the legs include which of the following activities? Choose all that apply. 1) Keep the patients hips and knees flexed while the patient is in bed. 2) Apply compression devices (e.g., sequential compression devices). 3) Turn the patient frequently or encourage frequent position changes. 4) Promote adequate hydration by encouraging oral intake. ANS: 2, 3, 4 Antiembolism stockings and SCDs are frequently used in perioperative patients to promote venous return and prevent clot formation. Turn patients frequently; teach patients to change positions frequently. This prevents vessel injury from prolonged pressure in one position. Promote adequate hydration to keep the blood from becoming viscous (thick). Viscous blood clots more readily. Which of the following medications would you expect to be included in the treatment of a patient with congestive heart failure? Choose all that apply. 1) Nitrates 2) Beta-adrenergic agents 3) Diuretics 4) Anticoagulants ANS: 2, 3 Beta-adrenergic agents block stimulation of beta receptors in the heart, lungs, and blood vessels and decrease heart rate, slow conduction through the AV node, and decrease myocardial oxygen demand by reducing myocardial contractility. Diuretics increase removal of sodium and water from the body through increased urine output. Diuretics reduce the volume of circulating blood and prevent accumulation of fluid in the pulmonary circulation. As the nurse caring for a patient who has suffered a myocardial infarction that has damaged the sinoatrial (SA) node, you should plan to monitor for which of the following potential complications? Choose all that apply. 1) Decreased heart rate 2) Increased heart rate 3) Decreased cardiac output 4) Decreased strength of ventricular contractions ANS: 1, 3 Normally, the SA node is the primary pacemaker for the heart and initiates a rate of 60 to 100 beats per minute. If the SA node fails, the atrioventricular node can take over as the pacemaker, but it generally triggers a slower heart rate. Cardiac output will decrease as a result of the decrease in heart rate. Damage to the SA node interferes with the electrical activity of the heart but does not directly affect the pumping action of the heart. Which outcome statement is related to Decreased Cardiac Output? Choose all that apply. 1) No dyspnea or shortness of breath with exertion 2) Normal skin color 3) Respiratory rate less than 16 breaths/min 4) Brisk capillary refill ANS: 1, 2, 4 Individualized goals/outcome statements depend on nursing diagnoses you identify for the patient. However, for a patient with compromised cardiac output, you might plan goals, such as no shortness of breath with exertion, brisk capillary refill in nailbeds, and normal skin color with no pallor. Respiratory rate of less than 16 breaths/min is hypoventilation and can lead to poor oxygenation and tissue acidosis. (See Chapter 39 for more information about acidbase balance.) Your client is a healthy, older adult who has come to the health clinic because she reports not feeling like herself. When you are gathering data in your clients health history, she tells you that she is feeling more fatigue when walking up stairs and doing her normal household activities. What normal physiologic changes in the cardiovascular system occur with aging? Choose all that apply. 1) Cardiac contractile strength is reduced. 2) Heart valves become more rigid. 3) Peripheral vessels lose elasticity. 4) Heart responds to increased oxygen demands. ANS: 1, 2, 3 Cardiac efficiency gradually declines as the heart muscle loses contractile strength and heart valves become thicker and more rigid. The peripheral vessels become less elastic, which creates more resistance to ejection of blood from the heart. As a result of these changes, the heart becomes less able to respond to increased oxygen demands, and it needs longer recovery times after responding. True or False Nicotine increases the risk for thrombus (blood clot) formation. ANS: T Nicotine increases the risk for thrombus formation because of its constricting effects on blood vessel walls. True or False A troponin level is a laboratory test performed to determine how well the cells, tissues, and organs are supplied with oxygen. ANS: F Troponin is a serum evaluation used to detect myocardial infarction (MI). Levels of these contractile proteins remain elevated for up to 7 days after MI. Organ function indirectly evaluates the extent to which oxygen demands have been met in the cells, organs, and tissues. True or False Heat causes vasodilation, which decreases cardiac output and oxygenation. ANS: F Heat causes vasodilation, which increases cardiac output and oxygenation. Which body fluid lies in the spaces between the body cells? 1) Interstitial 2) Intracellular 3) Intravascular 4) Transcellular ANS: 1 Extracellular fluid lies outside the cells. It is composed of three types of fluid: interstitial, intravascular, and transcellular. Interstitial fluid lies in the spaces between the body cells. Intracellular fluid is contained within the cells. Intravascular fluid is the plasma within the blood. Transcellular fluid includes specialized fluids, such as cerebrospinal, pleural, peritoneal, and synovial; and digestive juices. Chloride, bicarbonate, phosphate, and sulfate are examples of what type of charged particles and why? 1) Cations, because they carry a positive charge 2) Cations, because they carry a negative charge 3) Anions, because they carry a positive charge 4) Anions, because they carry a negative charge ANS: 4 Anions are electrolytes that carry a negative charge; they include chloride, bicarbonate, phosphate, and sulfate. Electrolytes that carry a positive charge are called cations. Cations include sodium, potassium, calcium, and magnesium. A patient is brought to the emergency department (ED) by paramedics after a person standing on the sidewalk saw him fall on a crowded street. He has a history of alcoholism and is frequently brought to the ED. The nurse finds the patient to be disoriented; he has periods of being calm mixed with episodes of being disruptive and loud. His vital signs are the following: BP 138/84 mm Hg; pulse 135 beats/min, regular and strong; respiratory rate 22 breaths/min; temperature 37.1C (98.1F). What electrolyte imbalance might the nurse suspect? 1) Hypomagnesemia 2) Hypocalcemia 3) Hyperkalemia 4) Hypernatremia ANS: 1 Hypomagnesemia is a frequent consequence of alcoholism. Signs and symptoms include disorientation, mood changes, and tachycardia. Hypocalcemia, a low calcium level, is associated with muscle spasms and tetany. Hyperkalemia, a high potassium level, manifests as weakness, fatigue, and cardiac dysrhythmias. Hypernatremia, a high sodium level, produces extreme thirst and agitation. The passive process by which molecules of a solute move through a cell membrane from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration is called which of the following? 1) Osmosis 2) Filtration 3) Hydrostatic pressure 4) Diffusion ANS: 4 Diffusion is a passive process by which molecules move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. Osmosis is the movement of water across a membrane from an area of a less-concentrated solution to an area of more-concentrated solution. Filtration is the movement of water and smaller particles from an area of high pressure to low pressure. Hydrostatic pressure is the force created by fluid within a closed system. A client is admitted to the emergency department (ED) in respiratory distress. The results of his arterial blood gases are the following: pH = 7.30; PCO2 = 40; HCO3 = 19 mEq/L; PO2 = 80. The nurse interprets the findings as which of the following? 1) Respiratory acidosis with normal oxygen levels 2) Respiratory alkalosis with hypoxia 3) Metabolic acidosis with normal oxygen levels 4) Metabolic alkalosis with hypoxia ANS: 3 The pH is acidotic. The HCO3 of 19 mEq/L is low and has moved in the same direction as the pH, indicating a metabolic disorder. The PCO2 is within normal range with no signs of compensation. The PO2 level is normal. A patient is admitted to the emergency department (ED) in respiratory distress. The results of his first arterial blood gases were: pH = 7.30; PCO2 = 40; HCO3 = 19 mEq/L; PO2 = 80. The nurse evaluates the patients treatment plan by examining repeat arterial blood gases (ABGs). The results are: pH = 7.38; PCO2 = 32; HCO3 = 19 mEq/L. The nurse concludes which of the following? 1) Respiratory acidosis; the treatment plan is ineffective. 2) Metabolic alkalosis; the treatment plan is effective. 3) Partial compensation; the treatment plan is ineffective. 4) Full compensation; the treatment plan is effective. ANS: 4 Full compensation has occurred as the PCO2 has returned the pH to the normal range. This change indicates that the treatment plan is effective. Partial compensation would be indicated by changes in the PCO2, but the pH would still be outside the normal range. The ABG is now complete compensation metabolic acidosis. When a patient has metabolic acidosis, which body system influences the acid-base imbalance to produce the compensatory changes in the arterial blood gases? 1) Respiratory system 2) Renal system 3) Vascular system 4) Neurological system ANS: 1 In a metabolic problem, the respiratory system compensates. In a respiratory problem, the renal system must compensate. The respiratory system compensates early in the disorder, but it may take up to 3 days for the renal system to compensate fully. A patients arterial blood gas results are as follows: pH = 7.30; PCO2 = 40; HCO3 = 19 mEq/L; PO2 = 80. An appropriate nursing diagnosis for the patient is which of the following? 1) Impaired Gas Exchange 2) Metabolic Acidosis 3) Risk for Impaired Gas Exchange 4) Risk for Acid-Base Imbalance ANS: 1 An appropriate diagnosis is Impaired Gas Exchange. The arterial blood gas (ABG) results provide the defining characteristics for Impaired Gas Exchange. The ABG results demonstrate metabolic acidosis; however, this is not a nursing diagnosis. The patient has an actual problem; therefore, the risk for nursing diagnoses are incorrect. Additionally, there is no nursing diagnosis of AcidBase Imbalance or Risk for AcidBase Imbalance. The nurse is caring for a patient with a medical diagnosis of hypernatremia. The following prescriptions are written in the clients electronic health record. Which one should the nurse question? 1) Administer an IV of D5W at 125 mL/hr. 2) Strict I&O monitoring. 3) Restrict oral intake to 900 mL every 24 hr. 4) Monitor serum electrolytes every 4 hr. ANS: 3 Restricting the oral intake of a patient with hypernatremia (Na+ greater than 145 mEq/L) would lead to further elevation in the serum sodium level. Infusing D5W IV fluid is appropriate, as this solution does not contain sodium. Hydrating the patient with D5W would reduce the serum sodium level. Strict I&O monitoring and laboratory evaluation of electrolytes every 4 hr would ensure that the patient is safely rehydrated. Which process requires energy to maintain the unique composition of extracellular and intracellular compartments? 1) Diffusion 2) Osmosis 3) Filtration 4) Active transport ANS: 4 Active transport occurs when molecules move across cell membranes from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. Active transport requires energy expenditure for the movement to occur against a concentration gradient. In the presence of ATP, the sodium potassium pump actively moves sodium from the cell into the extracellular fluid. Active transport is vital for maintaining the unique composition of both the extracellular and intracellular compartments. Diffusion, osmosis, and filtration are passive processes The nurse records a patients hourly urine output from an indwelling catheter as follows: 0700: 36 mL 0800: 45 mL 0900: 85 mL 1000: 62 mL 1100: 50 mL 1200: 48 mL 1300: 94 mL 1400: 78 mL 1500: 60 mL The nurse can conclude that the patients urine output should be described as which of the following? 1) Low 2) Within normal limits 3) High 4) Inconclusive ANS: 2 Urine accounts for the greatest amount of fluid loss. Normal urine output for an average-sized adult is approximately 1,500 mL in 24 hr. Urine output varies according to intake and activity but should remain at least 30 to 50 mL per hour. The patients urine output is within the normal range. This patient has an indwelling catheter, which will result in continual flow of urine. Which of the following is the principal site for regulation of fluid and electrolyte balance? 1) Cardiac system 2) Vascular system 3) Pulmonary system 4) Renal system ANS: 4 A balance of fluid and electrolytes is essential to maintain homeostasis. Excesses or deficits can lead to severe disorders. The kidneys are the principal regulator of fluid and electrolyte balance and are the primary source of fluid output. Specific hormones (e.g., ADH, aldosterone) cause the kidneys to regulate the bodys fluid and electrolyte balance. The heart and vascular system are involved in fluid balance but not in electrolyte balance and not as dramatically in fluid balance as are the kidneysthat is, they do not actually regulate electrolytes. The pulmonary system plays a major role in regulation of acidbase balance. Which electrolyte is the primary regulator of fluid volume? 1) Potassium 2) Calcium 3) Sodium 4) Magnesium ANS: 3 Sodium is the major cation in the extracellular fluid (ECF). Its primary function is to regulate fluid volume. When sodium is reabsorbed in the kidney, water and potassium are also reabsorbed, thereby maintaining ECF volume. Potassium is a key electrolyte in cellular metabolism. Calcium is responsible for bone health and neuromuscular and cardiac functions. It is also an essential factor in blood clotting. Magnesium is a mineral used in more than 300 biochemical reactions in the body. A patient has been vomiting for 2 days and has not been able to eat or drink anything during this time. She has not urinated for 12 hours. Physical examination reveals the following: T = 99.6F (37.6C) orally; P = 110 beats/min weak and thready; BP = 80/52 mm Hg. Her skin and mucous membranes are dry, and there is decreased skin turgor. The patient states that she feels very weak. Which of the following is an appropriate nursing diagnosis for this patient? 1) Impaired Gas Exchange related to ineffective breathing 2) Excess Fluid Volume related to limited fluid output 3) Deficient Fluid Volume related to abnormal fluid loss 4) Electrolyte Imbalance related to decreased oral intake ANS: 3 Vomiting has made this patient hypovolemic; therefore, she has deficient fluid volume. There is no information to indicate that she has respiratory problems or Impaired Gas Exchange. Her symptoms are not consistent with Excess Fluid Volume. Electrolyte Imbalance is not a nursing diagnosis. Which of the following is the most appropriate goal for a patient with the nursing diagnosis of Deficient Fluid Volume? 1) Electrolyte balance restored, as evidenced by improved levels of alertness and cognitive orientation 2) Electrolyte balance restored, as evidenced by sodium returning to normal range 3) Patient demonstrates effective coughing and deep breathing techniques. 4) Maintains fluid balance, as evidenced by moist mucous membranes and urinating every 4 hours ANS: 4 Moist mucous membranes and urinating every 4 hours would demonstrate restoration of fluid balance. Electrolyte imbalance does not necessarily occur with Deficient Fluid Volume; if electrolyte imbalance were present, the nursing diagnosis would be different. There is no evidence that this patient has a respiratory problem, so coughing and deep breathing are irrelevant. Which laboratory results on a clients health record should alert the nurse to a potential problem? 1) Na+ = 137 mEq/L 2) K+ = 5.2 mEq/L 3) Ca2+ = 9.2 mg/dL 4) Mg2+ = 1.8 mg/dL ANS: 2 A potassium level of 5.2 mEq/L indicates hyperkalemia. The other results are all within normal ranges. A patients vital signs prior to a blood transfusion were: T = 97.6F (36.4C); P = 72 beats/min; R = 22 breaths/min; and BP = 132/76 mm Hg. Twenty minutes after the transfusion was begun, the patient began complaining of feeling itchy and hot. The nurse discovered a rash on the patients trunk. Vital signs were: T = 100.8F (38.2C); P = 82 beats/min; R = 24 breaths/min; BP = 146/88 mm Hg. Based on these findings, what is the priority intervention? 1) Administer an antihistamine (anti-allergenic) medication. 2) Flush the blood tubing with D5W immediately. 3) Prepare for emergency resuscitation. 4) Stop the blood transfusion immediately. ANS: 4 The nurse should suspect a transfusion reaction. When a transfusion reaction is suspected, the infusion should be stopped immediately. The blood bag and tubing must be sent to the laboratory for analysis. A new IV line of normal saline should be hung. Diphenhydramine (an antihistamine) may be ordered once the physician has been notified of the patients condition. There is no information indicating that the patient is in danger of cardiovascular collapse or requires resuscitation. A patient is receiving an IV infusion of lactated Ringers solution and 40 mEq of KCl at 100 mL/hr. When assessing the IV site, the nurse notes swelling, erythema, and warmth. There is a palpable cord along the vein, and the infusion is sluggish. The patient is complaining of pain at the site. The nurse would recognize these findings to be consistent with which of the following? 1) Infiltration 2) Extravasation 3) Hematoma 4) Phlebitis ANS: 4 Phlebitis is an inflammation of the vein. It may be caused by the infusion of solutions that are irritating to the vein. Patients receiving IV solutions with potassium chloride are at a higher risk for phlebitis, as it is irritating to the vein. The symptom of a palpable cord along the vein distinguishes this as phlebitis. Infiltration presents as erythema, pain, and swelling. However, there is no palpable cord with inflammation. Extravasation is infiltration of a vesicant substance into the tissues. Differentiating symptoms include blanching and coolness of the surrounding skin; the formation of blisters and subsequent tissue sloughing and necrosis are later signs. A hematoma is a localized mass of blood outside the blood vessel. This is generally seen when a vein is nicked during an unsuccessful insertion of an IV line or when an IV line is discontinued without pressure applied over the site. The nurse assesses that her patients intravenous solution has infiltrated into the tissues. What action should she take first? 1) Aspirate, then inject 0.5 mL normal saline. 2) Restart the IV line in a different vein. 3) Stop the infusion immediately. 4) Notify the primary care provider. ANS: 3 The nurse should first stop the infusion to avoid further tissue trauma. Because the IV has infiltrated, you must assume that the nurse has already checked the patency of the line by aspirating. There is no point in injecting saline because doing so puts even more fluid in the tissues. Injecting fluid to try to clear a clot from the catheter is not recommended because of the possibility of causing an embolism. Once the infusion is stopped, the nurse must assess whether the patient needs additional IV therapy. If so, a new IV line must be restarted above the site of infiltration or in the opposite arm. The nurse may need to inform the primary care provider if she is unable to find a new IV site or if she believes the patient no longer needs an IV. The physician has ordered a complete blood count for a 6-year-old child. When the nurse enters the room, she finds the child sobbing uncontrollably. His mother tells him to shut up and act your age. How should the nurse proceed? 1) Request that the mother leave the room immediately. 2) Request the help of a coworker to hold the child down. 3) Inform the child that this wont hurt a bit. 4) Calmly approach the child and tell him what is going to happen. ANS: 4 Having blood drawn may be uncomfortable and frightening for a 6-year-old child. A calm approach can alleviate some of the fear. Explain to the childs mother that the boys behavior is normal. Informing the child that the blood draw will not hurt is wrong and will make him distrustful of future interventions. The nurse may need the help of a coworker, but she should first try a calm approach. A healthcare provider prescribes 250 mL of 0.9% sodium chloride to be infused over 2 hours. A microdrip infusion set is being used. What is the drip rate (drops/min) that the nurse should monitor? 1) 60 2) 75 3) 125 4) 250 ANS: 3 Calculate the drip rate by multiplying the number of milliliters to be infused per hour (hourly rate) by the drop factor in drops/mL, divided by 60 minutes. An infusion of 250 mL in 2 hours results in an hourly rate of 125 mL/hr. 125 (mL/hr) 60 (drops/mL) = 125 drops/min 60 min The nurse examines the electrocardiogram (ECG) tracing of a client and notes tall T waves. What electrolyte imbalance should the nurse suspect? 1) Hypokalemia 2) Hypophosphatemia 3) Hyperkalemia 4) Hypercalcemia ANS: 3 Potassium levels affect the heart. A tall, peaked T wave on an ECG is associated with hyperkalemia. A flat T wave is associated with hypokalemia. Phosphorous levels do not trigger ECG changes. The nurse gathers the following data: BP = 150/94 mm Hg; neck veins distended; P = 104 beats/min; pulse bounding; respiratory rate = 20 breaths/min; T = 37C (98.6F). What disorder should the nurse suspect? 1) Hypovolemia 2) Hypercalcemia 3) Hyperkalemia 4) Hypervolemia ANS: 4 Hypervolemia results from retention of sodium and water. Blood pressure rises, the pulse is bounding, and neck veins become distended due to increased intravascular volume. A patient has a continuous IV infusion at 60 mL/hr. The right hand IV has infiltrated and the nurse has started a new IV on the left forearm. Which of the following interventions should the nurse also perform? 1) Elevate the patients left forearm. 2) Schedule daily dressing changes to the new IV site. 3) Change the administration set. 4) Place the patient in Fowlers position. ANS: 3 Reusing an IV set from a previous site increases the risk of contamination. IV dressings are usually changed every 72 to 96 hours when the IV site is rotated. There is no reason to elevate the patients left forearm or to place him in Fowlers position. When performing a central venous catheter dressing change, which of the following steps is/are correct? 1) Wear sterile gloves while removing and discarding the soiled dressing. 2) Apply pressure on the catheter-hub junction when removing the soiled dressing. 3) Place a sterile transparent dressing over the site and the catheter-hub junction. 4) Have the patient wear a mask or turn his head away from the site. ANS: 4 Aseptic technique should be used with approaching the insertion site. Therefore, both nurse and patient should wear a mask. If the patient cannot wear a mask, have him turn his head away from the insertion site during the procedure. Sterile gloves should be worn when placing the new sterile dressing; however, procedure gloves are used to remove the soiled dressing. The nurse should stabilize the catheter while removing the soiled dressing but not apply pressure to the catheter-hub junction. The transparent dressing should cover the hub of the catheter, but not the catheter-hub junction; this makes it too difficult to remove without disturbing the integrity of the IV line or the site. In a healthy adult, which of the following regulate(s) body fluids? Choose all that apply. 1) Hormone levels 2) Fluid intake 3) Oxygen saturation 4) Kidney function ANS: 1, 2, 4 A balance between fluid intake and output is essential to maintain homeostasis. Excesses or deficits of intake can lead to severe disorders. The kidneys are the principal regulator of fluid and electrolyte balance and are the primary source of fluid output. Specific hormones (e.g., ADH, aldosterone) cause the kidneys to regulate the bodys fluid and electrolyte balance. Oxygen saturation does not regulate fluids. It measures the saturation of oxygen on hemoglobin and is influenced by the partial pressure of oxygen, alveolararterial gradient lung disease, and the amount and type of hemoglobin (such as sickle cell anemia). A patient has been admitted to the nursing unit with a diagnosis of chronic renal failure. She will be dialyzed for the first time the following morning. Which of the following are appropriate nursing interventions for the patient? Choose all that apply. 1) Encourage oral fluid intake as desired. 2) Place the patient on strict I&O. 3) Weigh the patient before and after dialysis. 4) Maintain a total fluid restriction of 1,000 mL as prescribed. ANS: 2, 3, 4 Fluids are restricted in patients with chronic renal failure because of decreased renal function. Therefore, encouraging oral fluids would not be appropriate. Appropriate nursing interventions for this patient include monitoring the intake and output, weighing the patient before and after dialysis, following a strict renal diet, and monitoring laboratory values. Identify the mechanism(s) involved in acid-base balance. Choose all that apply. 1) Respiratory mechanisms 2) Active transport mechanisms 3) Renal mechanisms 4) Buffer systems ANS: 1, 3, 4 Acidbase balance is regulated by respiratory mechanisms, renal mechanisms, and buffer systems. Acidbase regulation can be monitored by examining arterial blood gases, especially blood pH. Buffer systems prevent wide swings in pH by absorbing or releasing free hydrogen ions. The lungs (respiratory mechanisms) control the carbonic acid supply via carbon dioxide. Conditions that cause retention of carbon dioxide, such as chronic obstruction pulmonary disease, lower the pH, whereas tachypneic conditions, such as hyperventilation syndrome, blow off carbon dioxide and increase the pH. The kidneys (renal mechanisms) regulate the concentration of plasma bicarbonate. By reabsorbing or excreting bicarbonate, the kidneys affect acidbase balance. Active transport involves the movement of fluids and electrolytes in the body. Identify the appropriate intervention(s) for a patient with hypovolemia. Choose all that apply. 1) Teach deep-breathing techniques. 2) Monitor I&O daily. 3) Encourage fluid intake. 4) Monitor electrolyte balance. ANS: 2, 3, 4 Hypovolemia occurs when more fluid is lost than is taken into the body. Monitoring I&O provides information to evaluate the status of the problem. Encouraging fluid intake helps to correct the problem. It is good to monitor electrolytes because electrolyte imbalance can occur with hypovolemia (although it may not occur at first). Deep-breathing techniques do not address fluid balance; there is no evidence that the patient has a respiratory disorder. A patients blood group is B. The nurse knows the patient can receive blood only from donors with what group(s) of blood? Choose all that apply. 1) A 2) B 3) O 4) AB ANS: 2, 3 Persons with blood group B can receive blood only from the blood groups B and O. Those with blood group AB may receive AB, A, B, and O blood. Blood group A persons may receive blood from A and O donors. Persons with blood group O may receive blood only from O donors. Blood group AB persons are considered universal recipients, and blood group O persons are considered universal donors. A nurse is caring for a patient with a peripheral IV line located in the right forearm. The patient informs the nurse that the IV site is burning. Upon assessment the nurse determines that the IV solution has infiltrated. What site(s) is/are appropriate to consider when restarting the IV line? Choose all that apply. 1) Left hand 2) Right wrist 3) Right antecubital area 4) Right saphenous vein ANS: 1, 3 When restarting an IV line after an infiltration, you must restart above the site of infiltration. As a result, the right antecubital area is correct. The opposite extremity (e.g., left hand) may also be used. The right saphenous vein is incorrect because that vein is located in the leg. The leg should be used as a last resort for an IV site. The primary care provider should be notified if a leg is being considered as an IV site. A patient has been diagnosed with hypovolemia. Which order(s) for hydration should the nurse question? Choose all prescriptions that should be questioned. 1) 0.9% (normal) saline at 100 mL/hr 2) Lactated Ringers solution at 100 mL/hr 3) Total parenteral nutrition solution at 100 mL/hr 4) D5W solution at 100 mL/hr ANS: 3, 4 Hypovolemia occurs when there is a proportional loss of water and electrolytes from the ECF. Lactated Ringers and 0.9% (normal) saline are isotonic fluids that remain inside the intravascular space, thus increasing volume. The D5W is a hypotonic solution that would pull body water from the intravascular compartment into the interstitial fluid compartment. Total parenteral nutrition is a hypertonic fluid used to provide nutrition for the patient who cannot meet caloric needs by eating or enteral nutrition. When assisting with bedside central venous catheter (CVC) placement, which nursing intervention is appropriate? Choose all that apply. 1) Don sterile gloves and mask (and possibly gown). 2) Scrub the insertion site with antibacterial soap for 1 min. 3) Verify that informed consent has been obtained. 4) Place the patient in low Fowlers position. ANS: 1, 3 Maximum barrier sterile technique is used for CVC insertion (sterile gloves, mask, and gown), although some agency policies do not include sterile gown for the nurse. This is an invasive procedure, so informed consent is required. The nurse should confirm that this has been obtained. The scrub is not done with antibacterial soap. The scrub is done with chlorhexidinealcohol solution or, alternatively, first with 70% alcohol and then with povidone detergent. The patient is placed in Trendelenburg position with a rolled towel between the shoulders for best site access. ____________________ are substances that develop an electrical charge when dissolved in water. ANS: Electrolytes A(n) ____________________ is any compound that contains hydrogen ions that can be released. ANS: acid A(n) ____________________ is a compound that combines with (accepts) hydrogen ions in a solution. ANS:base What is the most significant change in kidney function that occurs with aging? 1) Decreased glomerular filtration rate 2) Proliferation of micro blood vessels to renal cortex 3) Formation of urate crystals 4) Increased renal mass ANS: 1 Glomerular filtration rate is the amount of filtrate formed by the kidneys in 1 minute. Renal blood flow progressively decreases with aging primarily because of reduced blood supply through the micro blood vessels of the kidney. A decrease in glomerular filtration is the most important functional deficit caused by aging. Urate crystals are somewhat common in the newborn period. They might indicate that the infant is dehydrated. In older people, they result from too much uric acid in the blood, although this is not related to aging. Renal mass (weight) decreases over time, starting around age 30 to 40. While performing a physical assessment, the student nurse tells her instructor that she cannot palpate her patients bladder. Which statement by the instructor is best? You should: 1) Try to palpate it again; it takes practice but you will locate it. 2) Palpate the patients bladder only when it is distended by urine. 3) Document this abnormal finding on the patients chart. 4) Immediately notify the nurse assigned to the care of your patient. ANS: 2 The bladder is not palpable unless it is distended by urine. It is not difficult to palpate the bladder when distended. The nurse should document her finding, but it is not an abnormal finding. It is not necessary to notify the nurse assigned to the patient. Which urine specific gravity would be expected in a patient admitted with dehydration? 1) 1.002 2) 1.010 3) 1.025 4) 1.030 ANS: 4 Normal urine specific gravity ranges from 1.010 to 1.025. Specific gravity less than 1.010 indicates fluid volume excess, such as when the patient has fluid overload (too much IV fluid) or when the kidneys fail to concentrate urine. Specific gravity greater than 1.025 is a sign of deficient fluid volume that occurs, for example, as a result of blood loss or dehydration. Which medication class will the primary care provider most likely prescribe to increase urine output in the patient admitted with congestive heart failure? 1) Thiazide diuretic 2) Loop diuretic 3) MAO inhibitor 4) Anticholinergic ANS: 2 A loop diuretic [e.g., Furosemide (Lasix)] increases urine elimination. It works by limiting the reabsorption of water in the renal tubules and is used to reduce congestion in the cardiopulmonary circulation. A thiazide diuretic is used to treat high blood pressure by reducing the amount of sodium and water in the blood vessels. An MAO inhibitor [e.g., phenelzine (Nardil)] is an antidepressant that is used after other medications have proven unsuccessful in lifting symptoms of serious depression. Anticholinergics [e.g., ipratropium (Atrovent)] relax smooth muscle in the airways. Also known as antispasmodics, they reduce airway constriction experienced by those with asthma, for example. The nurse identifies the nursing diagnosis Urinary Incontinence (Total) in an older adult patient admitted after a stroke. Urinary Incontinence places the patient at risk for which complication? 1) Skin breakdown 2) Urinary tract infection 3) Bowel incontinence 4) Renal calculi ANS: 1 Urine contains ammonia, which may cause excoriation with prolonged contact with the skin. Bowel incontinence, not urinary incontinence, increases the patients risk for urinary tract infection. Immobility and high consumption of calcium-containing foods increase the risk for renal calculi. The nurse is caring for a patient who underwent a bowel resection 2 hours ago. His urine output for the past 2 hours totals 50 mL. Which action should the nurse take? 1) Do nothing; this is normal postoperative urine output. 2) Increase the infusion rate of the patients IV fluids. 3) Notify the provider about the patients oliguria. 4) Administer the patients routine diuretic dose early. ANS: 3 50 mL in 2 hours is not normal output. The kidneys typically produce 60 mL of urine per hour. Therefore, the nurse should notify the provider when the patient shows diminished urine output (oliguria). Patients who undergo abdominal surgery commonly require increased infusions of IV fluid during the immediate postoperative period. The nurse cannot provide increased IV fluids without a providers order. The nurse should not administer any medications before the scheduled time without a prescription. The provider may hold the patients scheduled dose of diuretic if he determines that the patient is experiencing deficient fluid volume. The nurse measures the urine output of a patient who requires a bedpan to void. Which action should the nurse take first? Put on gloves and: 1) Have the patient void directly into the bedpan. 2) Pour the urine into a graduated container. 3) Read the volume with the container on a flat surface at eye level. 4) Observe the color and clarity of the urine in the bedpan. ANS: 1 First, the nurse should put on gloves and have the patient void directly into the bedpan. Next, she should pour the urine into a graduated container, place the measuring device on a flat surface, and read the amount at eye level. She should observe the urine for color, clarity, and odor. Then, if no specimen is required, she should discard the urine in the toilet and clean the container and bedpan. Finally, she should record the amount of urine voided on the patients intake and output record. The nurse instructs a woman about providing a clean-catch urine specimen. Which of the following statements indicates that the patient correctly understands the procedure? 1) I will be sure to urinate into the hat you placed on the toilet seat. 2) I will wipe my genital area from front to back before I collect the specimen midstream. 3) I will need to lie still while you put in a urinary catheter to obtain the specimen. 4) I will collect my urine each time I urinate for the next 24 hours. ANS: 2 To obtain a clean-catch urine specimen, the nurse should instruct the patient to cleanse the genital area from front to back and collect the specimen midstream. This follows the principle of going from clean to dirty. The nurse should have the ambulatory patient void into a hat (container for collecting the urine of an ambulatory patient) when monitoring urinary output, but not when obtaining a clean-catch urine specimen. A urinary catheter is required for a sterile urine specimen, not a clean-catch specimen. A 24-hour urine collection may be necessary to evaluate some disorders, but a clean-catch specimen is a one-time collection. What position should the patient assume before the nurse inserts an indwelling urinary catheter? 1) Modified Trendelenburg 2) Prone 3) Dorsal recumbent 4) Semi-Fowlers ANS: 3 The nurse should have the patient lie supine with knees flexed, feet flat on the bed (dorsal recumbent position). If the patient is unable to assume this position, the nurse should help the patient to a side-lying position. Modified Trendelenburg position is used for central venous catheter insertion. Prone position is sometimes used to improve oxygenation in patients with adult respiratory distress syndrome. Semi-Fowlers position is used to prevent aspiration in those receiving enteral feedings. A patient complains that she passes urine whenever she sneezes or coughs. How should the nurse document this complaint in the patients healthcare record? 1) Transient incontinence 2) Overflow incontinence 3) Urge incontinence 4) Stress incontinence ANS: 4 Stress incontinence is an involuntary loss of urine that occurs with increased intra-abdominal pressure. Activities that typically produce the symptom include sneezing, coughing, laughing, lifting, and exercise. Transient incontinence is a short-term incontinence that is expected to resolve spontaneously. It is typically caused by urinary tract infection or medications, such as diuretics. Overflow incontinence is the loss of urine when the bladder becomes distended; it is commonly associated with fecal impaction, enlarged prostate, and neurological conditions. Urge incontinence is the involuntary loss of urine associated with a strong urge to void. Which outcome is appropriate for the patient who underwent urinary diversion surgery and creation of an ileal conduit for invasive bladder cancer? 1) Patient will resume his normal urination pattern by (target date). 2) Patient will perform urostomy self-care by (target date). 3) Patient will perform self-catheterization by (target date). 4) Patients urine will remain clear with sufficient volume. ANS: 2 The most appropriate outcome for this patient is the patient will perform urostomy self-care by a specific date. The patient with an ileal conduit is unable to resume a normal urination pattern; urine, along with mucus, drains continuously from the stoma site, so the urine will not be clear. Also, the phrase sufficient volume is too vague for an outcome statement. The patient with a continent urostomy inserts a catheter into the stoma to drain urine. Which intervention should the nurse take first to promote micturition in a patient who is having difficulty voiding? 1) Insert an indwelling urinary catheter. 2) Notify the provider immediately. 3) Insert an intermittent, straight catheter. 4) Pour warm water over the patients perineum. ANS: 4 The nurse should perform independent nursing measures, such as pouring warm water over the patients perineum before notifying the provider. If nursing measures fail, the nurse should notify the provider. The provider may order an indwelling urinary catheter or a straight catheter to relieve the patients urinary retention. The student nurse asks the provider if she will prescribe an indwelling urinary catheter for a hospitalized patient who is incontinent. The provider explains that catheters should be utilized only when absolutely necessary because: 1) They are the leading cause of nosocomial infection. 2) They are too expensive for routine use. 3) They contain latex, increasing the risk for allergies. 4) Insertion is painful for most patients. ANS: 1 Indwelling urinary catheters should not be routinely used for hospitalized patients with incontinence because they are the leading cause of healthcare-acquired infection (nosocomial). The cost of an indwelling urinary catheter should not deter its use if necessary. Latex-free catheters are available for patients with or at risk for latex allergy. Insertion may be somewhat uncomfortable, but it should not be painful. A patient who sustained a spinal cord injury will perform intermittent self-catheterization after discharge. After discharge teaching, which statement by the patient would indicate correct understanding of the procedure? 1) I will need to replace the catheter weekly. 2) I can use clean, rather than sterile, technique at home. 3) I will remember to inflate the catheter balloon after insertion. 4) I will dispose of the catheter after use and get a new one each time. ANS: 2 The nurse should inform the patient that clean technique can be used after discharge. The patient should wash his hands before the procedure, then wash the reusable catheter in soap and water, and rinse and store it in a clean, dry place. It is not necessary for the patient to use a new catheter for each catheterization. The patient should use a straight catheter; therefore, a balloon is not inflated after insertion. Straight catheters are removed immediately after use. The nurse notes that a patients indwelling urinary catheter tubing contains sediment and crusting at the meatus. Which action should the nurse take? 1) Notify the provider immediately. 2) Flush the catheter tubing with saline solution. 3) Replace the indwelling urinary catheter. 4) Encourage fluids that increase urine acidity. ANS: 3 The catheter needs to be changed when sediment collects in the tubing or catheter and crusting at the meatus occurs. It is not necessary to notify the provider immediately. The nurse should not flush the catheter tubing. The patient should be encouraged to consume fluids that increase urine acidity to prevent urinary tract infection; however, it will not help clear the catheter tubing of sediment. The surgeon orders hourly urine output measurement for a patient after abdominal surgery. The patients urine output has been greater than 60 mL/hour for the past 2 hours. Suddenly the patients urine output drops to almost nothing. What should the nurse do first? 1) Irrigate the catheter with 30 mL of sterile solution. 2) Replace the patients indwelling urinary catheter. 3) Infuse 500 mL of normal saline solution IV over 1 hour. 4) Notify the surgeon immediately. ANS: 1 If the patients urinary output suddenly ceases, the nurse should irrigate the urinary catheter to assess whether the catheter is blocked. If no blockage is detected, the nurse should notify the surgeon. The surgeon may request that the catheter be changed if irrigation does not help or if the tubing is not kinked. However, the nurse should not change a catheter in the immediate postoperative period without consulting with the surgeon. The surgeon may prescribe an IV fluid bolus if the patient is suspected to have a deficient fluid volume. A patient is admitted with high BUN and creatinine levels, low blood pH, and elevated serum potassium level. Based on these laboratory findings the nurse suspects which diagnosis? 1) Cystitis 2) Renal calculi 3) Enuresis 4) Renal failure ANS: 4 Elevated BUN, creatinine, and serum potassium levels and low blood pH are signs of renal failure. Cystitis is an infection of the bladder and would not result in abnormal renal function. Renal calculi typically produce blood in the urine but do not lead to marked renal dysfunction and failure. Enuresis is involuntary urination, particularly common in children, and does not produce renal dysfunction. The cause of enuresis is often emotional, developmental, or trauma related. A mother tells the nurse at an annual well-child checkup that her 6-year-old son occasionally wets himself. Which response by the nurse is appropriate? 1) Explain that occasional wetting is normal in children of this age. 2) Tell the mother to restrict her child's activities to avoid wetting. 3) Suggest time out to reinforce the importance of staying dry. 4) Inform the mother that medication is commonly used to control wetting. ANS: 1 The nurse should explain that occasional wetting is normal in children during the early school years. The mother should handle the situation calmly and avoid punishing the child. Medications are occasionally prescribed for nocturnal enuresis when the child is older and not sleeping at home, but not for occasional daytime wetting. Which task can the nurse safely delegate to the nursing assistive personnel? 1) Palpating the bladder of a patient who is unable to void 2) Administering a continuous bladder irrigation 3) Providing indwelling urinary catheter care 4) Obtaining the patients history and physical assessment ANS: 3 The nurse can safely delegate indwelling urinary catheter care to nursing assistive personnel who are adequately trained to do so. Palpating the bladder, administering continuous bladder irrigation, and obtaining the patients history and physical assessment involve the critical thinking skills of a professional nurse. Which action should the nurse take when beginning bladder training using scheduled voiding? 1) Offer the patient a bedpan every 2 hours while she is awake. 2) Increase the voiding interval by 30 to 60 minutes each week. 3) Frequently ask the patient if she has the urge to void. 4) Increase the frequency between voiding even if urine leakage occurs. ANS: 1 The nurse should offer the patient the bedpan or assist the patient to the bathroom every 2 hours while she is awake. You would encourage the patient to get up once during the night to void, but awakening the patient every 2 hours would lead to fatigue. If the patient adheres to the schedule, the voiding interval should be increased by 15 to 30 minutes each week. Simply asking the patient about the urge to void does not help to manage bladder emptying. A patient is prescribed furosemide (Lasix), a loop diuretic, for treatment of congestive heart failure. The patient is at risk for which electrolyte imbalance associated with use of this drug? 1) Hypocalcemia 2) Hypokalemia 3) Hypomagnesemia 4) Hypophosphatemia ANS: 2 Furosemide is a loop diuretic, which causes potassium to pass into the urine. This drug increases the risk for hypokalemia (low potassium); it does not cause hypocalcemia (low calcium in the blood), hypomagnesemia (low blood magnesium), or hypophosphatemia (low blood phosphorous). Which daily urine output is within normal limits for a newborn weighing 8 pounds? 1) 288 mL 2) 180 mL 3) 36 mL 4) 18 mL ANS: 2 A newborn weighing 8 pounds (3.6 kg) should produce 15 to 60 mL of urine per kilogram per day. If the newborn produces 50 mL/kg/day and weighs 3.6 kg, he will produce a total of 180 mL in 24 hours. The other options are not within normal limits and require further assessment. The nurse is teaching an older female patient how to manage urge incontinence at home. What is the first-line approach to reducing involuntary leakage of urine? 1) Insertion of a pessary 2) Intermittent self-catheterization 3) Bladder training 4) Anticholinergic medication ANS: 3 The goal of bladder training is to enable the patient to hold increasingly greater volumes of urine in the bladder and to increase the interval between voiding. This involves patient teaching, scheduled voiding, and self-monitoring using a voiding diary. In addition to teaching the mechanisms of urination, teach distraction and relaxation strategies to help inhibit the urge to void. Other techniques include deep breathing and guided imagery. A pessary is an incontinence device that is inserted into the vagina to reduce organ prolapse or pressure on the bladder. Clean, intermittent self-catheterization is a good option for managing incontinence that is resistant to conservative measure, such as bladder training, Kegel exercises, lifestyle modification, and medication. Anticholinergic medication can be highly effective for improving urinary incontinence. However, more conservative measures, such as timed voiding and Kegel exercises, are recommended first. What is the best technique for obtaining a sterile urine specimen from an indwelling urinary catheter? 1) Use antiseptic wipes to cleanse the meatus prior to obtaining the sample. 2) Briefly disconnect the catheter from the drainage tube to obtain the sample. 3) Withdraw urine through the port using a needleless access device. 4) Obtain the urine specimen directly from the collection bag. ANS: 3 To obtain a specimen from an indwelling catheter, insert the needleless access device with a 20- or 30-mL syringe into the specimen port, and aspirate to withdraw the amount of urine you need. Wiping the meatus with an antiseptic material helps to minimize contamination for a clean-catch voided specimen, not a sample collected from a closed system such as an indwelling catheter system. Never disconnect the catheter from the drainage tube to obtain a sample. Interrupting the system creates a portal of entry for pathogens, thereby increasing the risk of contamination. Do not take the specimen from the collection bag because that urine may be several hours old. Which of the following is/are an appropriate goal(s) for a patient with urinary incontinence? Choose all that apply. 1) Increase the intake of citrus fruits. 2) Maintain daily oral fluids to 8 to 10 servings per day. 3) Limit daily caffeine intake to less than 100 mg. 4) Engage in high-impact, aerobic exercise. ANS: 2, 3 The nurse should encourage lifestyle changes such as limiting caffeine intake to fewer than 100 mg per day; limiting intake of alcohol, artificial sweeteners, spicy foods, and citrus fruit; and maintaining daily oral fluid intake to 8 to 10 servings per day. High-impact exercise can be associated with stress incontinence for those with weakened pelvic muscles that support the bladder and urethra. True or False Nurses should obtain information about urinary control from all female patients. ANS: T All women, especially older women and those who have experienced childbirth, should be screened for different types of urinary incontinence. When changing a diaper, the nurse observes that a 2-day-old infant has passed a green-black, tarry stool. What should the nurse do? 1) Notify the provider immediately. 2) Do nothing; this is normal. 3) Give the baby sterile water until the mothers milk comes in. 4) Apply a skin barrier cream to the buttocks to prevent irritation. ANS: 2 The nurse should do nothing; this is normal. During the first few days of life, a term newborn passes green-black, tarry stools known as meconium. Stools transition to a yellow-green color over the next few days. After that, the appearance of stools depends upon the feedings the newborn receives. Sterile water does nothing to alter this progression. Meconium stools are more irritating to the buttocks than other stools because they are so sticky and the skin usually must be rubbed to cleanse it. However, meconium leads to skin breakdown like a watery stool does. Considering normal developmental and physical maturation in children, for which age would a goal of Achieves bowel control by the end of this month be most realistic? 1) 18 months 2) 3 years 3) 4 years 4) 5 years ANS: 2 Between ages 2 and 3 years, a child can typically control defecation, thereby making toilet training possible. Nevertheless, some children, especially boys, may not achieve consistent bowel control until somewhat later. The nurse educates a patient about the primary risk factors for irritable bowel syndrome. Which behavior by the patient would be evidence of learning? The patient: 1) Reduces her intake of gluten-containing products. 2) Does not consume foods that contain lactose. 3) Consumes only two servings of caffeinated beverages per day. 4) Takes measures to reduce her stress level. ANS: 4 Stress is a primary factor in the development of irritable bowel syndrome. Other risk factors include caffeine consumption and lactose intolerance; however, they are not primary risk factors. Celiac disease is associated with gluten intake. Which of the following goals is appropriate for a patient with a nursing diagnosis of Constipation? The patient increases the intake of: 1) Milk and cheese. 2) Bread and pasta. 3) Fruits and vegetables. 4) Lean meats. ANS: 3 The nurse should encourage the patient to increase his intake of foods rich in fiber because they promote peristalsis and defecation, thereby relieving constipation. Low-fiber foods, such as bread, pasta, and other simple carbohydrates, as well as milk, cheese, and lean meat, slow peristalsis. A patient is diagnosed with an intestinal infection after traveling abroad. The nurse should encourage the intake of which food to promote healing? 1) Yogurt 2) Pasta 3) Oatmeal 4) Broccoli ANS: 1 Although the patient may have diarrhea, the goal is not to stop the diarrhea, but to eliminate the pathogens from the digestive tract. The active bacteria in yogurt stimulate peristalsis and promote healing of intestinal infections. Pasta is a low-fiber food that slows peristalsis. It does not promote healing of intestinal infections. Oatmeal stimulates peristalsis, but it does not promote healing of intestinal infections. Broccoli stimulates gas production; it is ineffective against intestinal infections. A nurse is teaching wellness to a womens group. The nurse should explain the importance of consuming at least how much fluid to promote healthy bowel function (assume these are 8-ounce servings)? 1) 3 to 4 servings a day 2) 5 to 6 servings a day 3) 7 to 8 servings a day 4) 9 to 10 servings a day ANS: 3 A minimum of 7 to 8 servings of fluid should be consumed each day to promote healthy bowel function. A patient with a skin infection is prescribed cephalexin (an antibiotic) 500 mg orally q 12 hours. The patient complains that the last time he took this medication, he had frequent episodes of loose stools. Which recommendation should the nurse make to the patient? 1) Stop taking the drug immediately if diarrhea develops. 2) Take an antidiarrheal agent, such as diphenoxylate. 3) Consume yogurt daily while taking the antibiotic. 4) Increase your intake of fiber until the diarrhea stops. ANS: 3 Antibiotics such as cephalexin, given to combat infection, decrease the normal flora in the colon that cause diarrhea. Bacterial populations can be maintained by encouraging the patient to consume yogurt daily while taking the drugs. Diarrhea is a common adverse effect of antibiotics; stopping the drug is not necessary. The patient should not be encouraged to take an antidiarrheal agent at this time. Increasing the intake of fiber combats constipation, not diarrhea. Which collaborative interventions will help prevent paralytic ileus in a patient who underwent right hemicolectomy for colon cancer? 1) Administer morphine 4 mg IV every 2 hours for pain. 2) Administer IV fluids at 125 mL/hr. 3) Insert an indwelling urinary catheter to monitor I&O. 4) Keep the patient NPO until bowel sounds return. ANS: 4 Patients who require bowel surgery typically remain NPO until peristalsis returns, helping to prevent paralytic ileus, a complication that can occur after the bowel is surgically manipulated. Administering morphine promotes comfort but may increase the risk of ileus. Administering IV fluids prevents dehydration but does not directly prevent ileus. Inserting an indwelling urinary catheter prevents urine retention and facilitates monitoring postoperative urine output. The nurse in a long-term care facility is teaching a group of residents about increasing dietary fiber. Which foods should she explain are high in fiber? 1) White bread, pasta, and white rice 2) Oranges, raisins, and strawberries 3) Whole milk, eggs, and bacon 4) Peaches, orange juice, and bananas ANS: 2 Oranges, raisins, and strawberries are high in fiber. White bread, pasta, and white rice are carbohydrates. Whole milk, eggs, and bacon are high in cholesterol. Peaches, orange juice, and bananas are sources of potassium. The nurse is assessing a patient who underwent bowel resection 2 days ago. As she auscultates the patients abdomen, she notes low-pitched, infrequent bowel sounds. How should she document this finding? 1) Hyperactive bowel sounds 2) Abdominal bruit sounds 3) Normal bowel sounds 4) Hypoactive bowel sounds ANS: 4 Hypoactive bowel sounds are low-pitched, infrequent, and quiet. An abdominal bruit is a hollow, blowing sound found over an artery, such as the iliac artery. Normal bowel sounds are high pitched with approximately 5 to 35 gurgles occurring every minute. Hyperactive bowel sounds are very high pitched and more frequent than normal bowel sounds. The healthcare team suspects that a patient has an intestinal infection. Which action should the nurse take to help confirm the diagnosis? 1) Prepare the patient for an abdominal flat plate. 2) Collect a stool specimen that contains 20 to 30 mL of liquid stool. 3) Administer a laxative to prepare the patient for a colonoscopy. 4) Test the patients stool using a fecal occult test. ANS: 2 To confirm the diagnosis of an infection, the nurse should collect a liquid stool specimen that contains 20 to 30 mL of liquid stool. An abdominal flat plate and a fecal occult blood test cannot confirm the diagnosis. Colonoscopy is not necessary to obtain a specimen to confirm the diagnosis. The nurse is instructing a patient about performing home testing for fecal occult blood. The nurse can conclude that learning occurs if the patient says, For 3 days prior to testing, I should avoid eating: 1) Beef. 2) Milk. 3) Eggs. 4) Oatmeal. ANS: 1 The nurse should instruct the patient to avoid red meat, chicken, fish, horseradish, and certain raw fruits and vegetables for 3 days prior to fecal occult blood testing. The nurse is instructing a patient about performing home testing for fecal occult blood. The nurse should explain that ingestion of which substance may cause a false-negative fecal occult blood test? 1) Vitamin D 2) Iron 3) Vitamin C 4) Thiamine ANS: 3 Ingestion of vitamin C can produce a false-negative fecal occult blood test; ingestion of vitamin D, iron, and thiamine does not. Iron can lead to a false-positive result. Which action should the nurse take to assess a 2-year-old child for pinworms? 1) Press clear cellophane tape against the anal opening at night to obtain a specimen. 2) Collect a freshly passed stool from a diaper using a wooden specimen blade. 3) Place a smear of stool on a slide and add two drops of reagent. 4) Prepare the patient for a flat plate (x-ray) of the abdomen. ANS: 1 To assess for pinworms, the nurse should press cellophane tape against the childs anal opening during the night or as soon as he awakens. Remove the tape immediately, and place it on a slide. Perineal swabs may also be necessary for microscopic study. Collecting a fresh stool specimen from a diaper describes the method for an infant or toddler. Placing a smear of stool on a slide and adding a reagent describes fecal occult blood testing. An abdominal flat plate is not a method of assessing for pinworms. The nurse must irrigate the colostomy of a patient who is unable to move independently. How should the nurse position the patient for this procedure? 1) Semi-Fowlers position 2) Left side-lying position 3) Supine with the head of the bed lowered flat 4) Supine with the head of bed raised to 30 degrees ANS: 2 The nurse should position an immobile patient in a left side-lying position to irrigate his colostomy. Semi-Fowlers, supine with the bed lowered flat, and the supine position with the head of bed elevated to 30 are not appropriate positions for colostomy irrigation. A mother of a school-age child seeks healthcare because her child has had diarrhea after being ill with a viral infection. The patient states that after vomiting for 24 hours, his appetite has returned. Which recommendation should the nurse make to this mother? 1) Consume a diet consisting of bananas, white rice, applesauce, and toast. 2) Drink large quantities of water regularly to prevent dehydration. 3) Take loperamide (an antidiarrheal) as needed to control diarrhea. 4) Increase the consumption of raw fruits and vegetables. ANS: 1 The nurse should encourage the patient with diarrhea who has an appetite to consume a diet that consists of bananas, white rice, applesauce, and toast. These foods are easy to digest, provide calories for energy, and help provide a source of calcium. The patient should sip liquids frequently to prevent dehydration; large quantities might worsen diarrhea. Medication, such as loperamide (Imodium), is usually reserved for chronic diarrhea. Raw fruits and vegetables may worsen diarrhea. Which is a key treatment intervention for the patient admitted with diverticulitis? 1) Antacid 2) Antidiarrheal agent 3) Antibiotic therapy 4) NSAIDs ANS: 3 A key treatment for diverticulitis (an infected diverticulum) is antibiotic therapy; if antibiotic therapy is ineffective, surgery may be necessary. Antacids, antidiarrheal agents, and NSAIDs are not indicated for treatment of diverticulitis. The nurse assesses a patients abdomen 4 days after abdominal surgery and notes that bowel sounds are absent. This finding most likely suggest which postoperative complication? 1) Paralytic ileus 2) Small bowel obstruction 3) Diarrhea 4) Constipation ANS: 1 Absent bowel sounds on the fourth postoperative day suggests paralytic ileus, a complication associated with abdominal surgery. A small bowel obstruction and diarrhea produce hyperactive bowel sounds. Constipation might be associated with hypoactive bowel sounds. A patient with a colostomy complains to the nurse, I am noticing really bad odors coming from my pouch. To help control odor, which foods should the nurse advise him to consume? 1) White rice and toast 2) Tomatoes and dried fruit 3) Asparagus and melons 4) Yogurt and parsley ANS: 4 Yogurt, cranberry juice, parsley, and buttermilk may help control odor. White rice and toast (also bananas and applesauce) help control diarrhea. Asparagus, peas, melons, and fish are known to cause odor. Tomatoes, pears, and dried fruit are high-fiber foods that might cause blockage in a patient with an ostomy. A patient with severe hemorrhoids is incontinent of liquid stool. Which of the following interventions is contraindicated? 1) Apply an indwelling fecal drainage device. 2) Apply an external fecal collection device. 3) Place an incontinence garment on the patient. 4) Place a waterproof pad under the patients buttocks. ANS: 1 An indwelling fecal drainage device is contraindicated for children; for more than 30 consecutive days of use; and for patients who have severe hemorrhoids, recent bowel, rectal, or anal surgery or injury; rectal or anal tumors; or stricture or stenosis. External devices are not typically used for patients who are ambulatory, agitated, or active in bed because the device may be dislodged, causing skin breakdown. External devices cannot be used effectively when the patient has Impaired Skin Integrity because they will not seal tightly. Absorbent products are not contraindicated for this patient unless Impaired Skin Integrity occurs. Even with absorbent products or an external collection device, the nurse should place a waterproof pad under the patient to protect the bed linens. A patient has a colostomy in the descending (sigmoid) colon and wants to control bowel evacuation and possibly stop wearing an ostomy pouch. To help achieve this goal, nurse should teach the patient to: 1) Call the primary care provider if the stoma becomes pale, dusky, or black. 2) Limit the intake of gas-forming foods such as cabbage, onions, and fish. 3) Irrigate the stoma to produce a bowel movement on a schedule. 4) Avoid returning to the use of an ostomy appliance if he becomes ill. ANS: 3 Patients with an ostomy in the descending or sigmoid colon may use colostomy irrigation as a means to control and schedule bowel evacuation and possibly eliminate the need to wear an ostomy pouch. Limiting the intake of gas-forming foods is a good idea from a social perspective; however, it does not help achieve the goal of having regular bowel movements and thus, eliminating the need to wear a pouch. When illness occurs, it may be difficult to control the output, so the patient can use an ostomy appliance. This will not make it more difficult to schedule the bowel movements after the illness passes. Which factor(s) place(s) the patient at risk for constipation? Choose all that apply. 1) Sedentary lifestyle 2) High-dose calcium therapy 3) Lactose intolerance 4) Consuming spicy foods ANS: 1, 2 Physical activity stimulates peristalsis and bowel elimination. Therefore, those with a sedentary lifestyle commonly experience constipation. High-dose calcium therapy also predisposes a patient to constipation. Lactose intolerance and consuming spicy foods are associated with a nursing diagnosis of Diarrhea, not Constipation. A patient who has been immobile since sustaining injuries in a motor vehicle accident complains of constipation. The nurse encourages him to consume eight to ten 8-ounce servings of fluid daily. Which fluid(s) should the patient avoid because of the diuretic effect? Choose all that apply. 1) Cranberry juice 2) Water 3) Coffee 4) Ginger ale 5) Tea ANS: 3, 5 Coffee, tea, and caffeine-containing sodas should be avoided because caffeine promotes diuresis, placing the patient at further risk for constipation. Water is the preferred fluid; however, fruit juices and decaffeinated sodas are also acceptable. The nurse must administer an enema to an adult patient with constipation. Which of the following would be a safe and effective distance for the nurse to insert the tubing into the patients rectum? Choose all that apply. 1) 2 in (5.1 cm) 2) 3 in (7.6 cm) 3) 4 in (10.2 cm) 4) 5 in (12.7 cm) ANS: 2, 3 When administering an enema, the nurse should insert the tubing about 3 to 4 inches into the patients rectum. Two inches would not be effective because it would not place the fluid high enough in the rectum. Five inches is too much. When performing an abdominal assessment, what sequence of assessment techniques should the nurse use? Label the steps from A to D, with A being the first step to perform. A. Auscultation B. Palpation C. Percussion D. Inspection ANS: D, A, C, B When performing an abdominal assessment, the nurse should follow the sequence: inspection, auscultation, percussion, and palpation. Percussion and palpation may stimulate peristalsis, so the techniques with the least contact should be done first. The nurse is collecting a stool specimen. Arrange the following steps in the order in which the nurse should perform them. Label the steps from A to D, with A being the first step to perform. A. Have the patient defecate into a special container placed under the toilet seat. B. Put on gloves and place the specimen in a specimen container. C. Ask the patient to void to empty the bladder. D. Place a label on the specimen container. ANS: C, A, B, D The nurse should ask the patient to void and then have him defecate into a special container placed under the toilet seat. Next, the nurse should put on gloves and, using a tongue blade, place the specimen into the container. Finally, she should label the specimen and send it to the laboratory for analysis. When administering an enema, list the following steps in the order in which they should be performed. Label the steps from A to F, with A being the first step to perform. A. Document the results of the procedure. B. Assess the patient for cramping. C. Insert the tubing about 3 to 4 inches into the rectum. D. Lubricate the tip of the enema tubing generously. E. Raise the container to the correct height and instill the solution at a slow rate. F. Encourage the patient to hold the solution for 3 to 15 minutes, depending on the type of enema. ANS: D, C, E, B, F, A You must lubricate the tip before inserting the tubing. You would then insert the tubing and begin instilling the solution before assessing for cramping that the instillation might produce. Only after the solution is instilled would you ask the patient to hold the solution. The last action is to document the results of the procedure, after the procedure is finish [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 50 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 14, 2021
Number of pages
50
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 14, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
94


.png)