*NURSING > ATI MEDICAL SURGICAL > (Davis’s success series.) Colgrove, Kathryn Cadenhead - Med-surg success _ a Q & A review applying (All)
(Davis’s success series.) Colgrove, Kathryn Cadenhead - Med-surg success _ a Q & A review applying critical thinking to test taking-F.A. Davis Company
Document Content and Description Below
Med-Surg Success A Q&A Review Applying Critical Thinking to Test Taking Third EdiTionDavis Edge NCLEX-RN® gives you the practice you need to confidently pass your boards. • Over 10,000 NCLEX-s... tyle questions to create practice quizzes on-the-go • Comprehensive Exam that simulates the NCLEX • Rationales for correct and incorrect answers • Anxiety-reducing test-taking tips SAVE 20% Use Promo Code: ORANGE5 START STUDYING TODAY! www.FADavis.com Study smarter with Davis Edge NCLEX-RN.® You’ll have 10,000+ questions at your fingertips to practice from your mobile device or laptop. Immediate feedback will highlight the content areas you are struggling in so that you know where to spend more time studying. Davis Edge allows you to create targeted practice quizzes to improve those areas—before you get to the NCLEX. Davis Edge is an incredible asset that is essential in preparing for an exam. - Michal W., Hill College Comprehensive, helpful, and a total life saver. – Lauren R., ECPI Promotion subject to change without notice. Offer valid for purchases from www.FADavis.com in the US only. STRESSED ABOUT THE NCLEX ? ®Med-Surg Success A Q&A Review Applying Critical Thinking to Test Taking Third EdiTion Kathryn Cadenhead Colgrove, RN, MSN, CNSF. A. Davis Company 1915 Arch Street Philadelphia, PA 19103 www.fadavis.com Copyright © 2017 by F.A. Davis Company Copyright © 2017 by F.A. Davis Company. All rights reserved. This book is protected by copyright. No part of it may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without written permission from the publisher. Printed in the United States of America Last digit indicates print number: 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Publisher, Nursing: Terri Wood Allen Content Project Manager: Julia L. Curcio Electronic Project Manager: Sandra A. Glennie Design and Illustrations Manager: Carolyn O’Brien As new scientific information becomes available through basic and clinical research, recommended treatments and drug therapies undergo changes. The author(s) and publisher have done everything possible to make this book accurate, up to date, and in accord with accepted standards at the time of publication. The author(s), editors, and publisher are not responsible for errors or omissions or for consequences from application of the book, and make no warranty, expressed or implied, in regard to the contents of the book. Any practice described in this book should be applied by the reader in accordance with professional standards of care used in regard to the unique circumstances that may apply in each situation. The reader is advised always to check product information (package inserts) for changes and new information regarding dose and contraindications before administering any drug. Caution is especially urged when using new or infrequently ordered drugs. Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data Names: Colgrove, Kathryn Cadenhead, author. Title: Med-surg success : a Q&A review applying critical thinking to test taking / Kathryn Cadenhead Colgrove. Description: Third edition. | Philadelphia, PA : F.A. Davis Company, [2017] | Includes bibliographical references and index. Identifiers: LCCN 2016019304 | ISBN 9780803644021 Subjects: | MESH: Nursing | Nursing Care | Test Taking Skills | Problem Solving | Examination Questions Classification: LCC RD99.25 | NLM WY 18.2 | DDC 617/.0231076--dc23 LC record available at https://lccn.loc.gov/2016019304 Authorization to photocopy items for internal or personal use, or the internal or personal use of specific clients, is granted by F. A. Davis Company for users registered with the Copyright Clearance Center (CCC) Transactional Reporting Service, provided that the fee of $.25 per copy is paid directly to CCC, 222 Rosewood Drive, Danvers, MA 01923. For those organizations that have been granted a photocopy license by CCC, a separate system of payment has been arranged. The fee code for users of the Transactional Reporting Service is: 8036-1169-2/04 0 + $.25.The authors dedicate this book to all nursing students who provide safe, competent, and “caring” nursing care which makes a difference in their clients’ lives. We hope this book helps these students to be successful in their nursing program, successful on their NCLEX-RN, and successful in the nursing profession. Our continued thanks to Bob Martone, who took a chance on us, and to Julia Curcio, who continues to support our endeavors in the publishing world. We would also like to thank Kara Evans for her editorial support during the production of the third edition. We hope the nursing students who use this book have as long, wonderful, and exciting a career as we have had in the nursing profession. I would like to dedicate this book to the memory of my mother, Mary Cadenhead, and grandmother, Elsie Rogers. They always said that I could accomplish anything I wanted to accomplish. I would also like to dedicate this book to my husband, Larry, children Laurie and Todd and Larry Jr. and Mai, and grandchildren Chris, Ashley, Justin C., Justin A., Connor, Sawyer, and Carson. Without their support and patience the book would not have been possible. Kathryn Colgrove This book is dedicated to the memory of my husband, Bill, and my parents, T/Sgt. Leo and Nancy Hargrove, who are the rocks on which my life is built. I would like to thank my sisters, Gail and Debbie, my nephew Benjamin, and Paula for their support and encouragement through the good times and the bad. My children, Teresa and Aaron, are the most important people in my life and I want to thank them for always believing in me. Ray Hargrove-Huttel (This was Ray’s dedication. Ray lost her battle with cancer on December 23, 2012. She is much loved and greatly missed. Kathy Colgrove)vii Reviewers Beth Batturs Martin, RN, MSN Director of Nursing and Healthcare Initiatives Anne Arundel Community College Arnold, Maryland Glenda Bondurant, MSN, RN Dean of Allied Health/Sciences Wilson Community College Wilson, North Carolina Johnnie A. Bratton, MSN, BSN, RN ADN Instructor Durham Technical Community College Durham, North Carolina Marsha Cannon, EdD, MSN, RN Associate Professor University of West Alabama Livingston, Alabama Barbara A. Caton, MSN, RN, CNE Assistant Professor Missouri State University – West Plains West Plains, Missouri Lorraine Smirle Collins, RN, MSN, CNOR Assistant Professor, Nursing Piedmont Virginia Community College Charlottesville, Virginia Pamela K. DeMoss, MSN, RN Assistant Professor University of Dubuque Dubuque, Iowa MaryAnn Edelman, RN, MS Professor, Department of Nursing Kingsborough Community College Brooklyn, New York Karen Elsea, MSN, RN Assistant Professor University of Indianapolis Indianapolis, Indiana Marie Everhart, MSN, RN, CNE Associate Professor Northampton Community College Bethlehem, Pennsylvania Christina Flint, RN, MSN, MBA Assistant Professor University of Indianapolis Indianapolis, Indiana Rebecca Fountain, RN, PhD Assistant Professor University of Texas at Tyler Tyler, Texas Charlene Beach Gagliardi, RN, BSN, MSN Assistant Professor Mount Saint Mary’s University Los Angeles, California Carol Girocco, RN, MSN, OCN Professor of Nursing Lone Star College – Montgomery Conroe, Texas Cheryl Harrington, MSN/MHA Assistant Professor of Nursing Morningside College Sioux City, Iowa Jackie Harris, MNSc, RN, CNE Assistant Professor of Nursing Harding University Carr College of Nursing Searcy, Arkansas Stephanie D. Huff, RN, DNP, FNP-BC Nursing Faculty Southern Union State Community College Opelika, Alabama Patricia A. Kelly, MSN, RN, APRN, FNP-BC Lecturer Southern Illinois University Edwardsville Edwardsville, Illinois Julie Kolker, MSN, BS, RN Associate Degree Nursing Instructor North Iowa Area Community College Mason City, Iowaviii RevieweRs Mary Jo Konkloski, MSN, RN, ANP Instructor Pomeroy College of Nursing at Crouse Hospital Syracuse, New York Karen Kulhanek, BSN, MEd, MSN Nursing Professor Kellogg Community College Battle Creek, Michigan Donna E. McCabe, DNP, APRN-BC, GNP Clinical Assistant Professor New York University College of Nursing New York, New York Ann Motycka, RN, MSN, CNE Professor Ivy Tech Community College Evansville, Indiana Michelle M. Murphy-Rozanski, PhD, MSN, RN, CRNP Senior Level Coordinator Temple University Health SystemNortheastern School of Nursing Philadelphia, Pennsylvania Lee Anne Nichols, PhD, RN Associate Professor University of Tulsa Tulsa, Oklahoma Laura C. Parker, MSN, RN, CCRN, CNE Associate Professor, Nursing County College of Morris Randolph, New Jersey Susan M. Perry, MS, RN Assistant Professor of Nursing SUNY Adirondack Queensbury, New York Gina Purdue, DNP, RN, CNE Associate Professor Eastern Kentucky University Richmond, Kentucky Lillian Rafeldt, RN, MA, CNE Professor of Nursing Three Rivers Community College Norwich, Connecticut Lori Riden, MSN, RN, CNE Nursing Professor Yavapai College Prescott, Arizona Brenda Sloan, RN, MA Assistant Professor Indiana Wesleyan University Marion, Indiana Cheryl Sorge, MA, BSN, RN Associate Professor, Tenured Indiana University-Purdue University Fort Wayne Fort Wayne, Indian Beryl Stetson, RNBC, MSN, CNE, LCCE, CLC Chairperson, Health Science Education Department Associate Professor, Nursing Raritan Valley Community College Branchburg, New Jersey Stephanie L. Turrise, PhD, RN, BC, APRN, CNE Assistant Professor University of North Carolina, Wilmington Wilmington, North Carolina Renée Wright, EdD, RN Assistant Professor York College Jamaica, New Yorkix Editors and Contributors to Past Editions Judy Callicoatt, RN, MS, CNS Associate Degree Nursing Instructor Trinity Valley Community College Kaufman, Texas Joan L. Consullo, RN, MS, CNRN Advanced Clinical Nurse, Neuroscience St. Luke’s Episcopal Hospital Houston, Texas Michelle L. Edwards, RN, MSN, ACNP, FNP Advanced Practice Nurse, Cardiology Acute Care Nurse Practitioner/Family Nurse Practitioner St. Luke’s Episcopal Hospital Houston, Texas Gail F. Graham, APRN, MS, NP-C Advanced Practice Nurse, Internal Medicine Adult Nurse Practitioner St. Luke’s Episcopal Hospital Houston, Texas Leslie Prater, RN, MS, CNS, CDE Clinical Diabetes Educator Associate Degree Nursing Instructor Trinity Valley Community College Kaufman, Texas Helen Reid, RN, PhD Dean, Health Occupations Trinity Valley Community College Kaufman, Texas Elester E. Stewart, RRT, RN, MSN, FNP Advanced Practice Nurse, Pulmonary Family Nurse Practitioner St. Luke’s Episcopal Hospital Houston, Texasxi 1 Test Taking ........................................................................................................................................ 1 INTRODUCTION ..................................................................................................................................... 1 GUIDELINES FOR USING THIS BOOK ........................................................................................... 1 PREPARING FOR LECTURE ............................................................................................................... 2 Sample Study Guide ........................................................................................................................ 2 PREPARING FOR AN EXAMINATION ............................................................................................... 3 Study ................................................................................................................................................... 3 Understanding What the Test Taker Does Not Know ............................................................... 3 The Night Before the Exam ........................................................................................................... 4 The Day of the Exam ....................................................................................................................... 4 Test-Taking Anxiety .......................................................................................................................... 4 TAKING THE EXAM ............................................................................................................................... 4 Test-Taking Hints for the Computerized NCLEX-RN Examination ........................................ 4 Understanding the Types of Nursing Questions ........................................................................ 5 THE RACE MODEL: THE APPLICATION OF CRITICAL THINKING TO MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS ............................................................................................. 6 CONCEPT-FOCUSED QUESTIONS .................................................................................................... 6 2 Neurological Disorders ............................................................................................................ 9 KEYWORDS/ABBREVIATIONS ............................................................................................................ 9 PRACTICE QUESTIONS ..................................................................................................................... 10 Cerebrovascular Accident (Stroke) ............................................................................................. 10 Head Injury ...................................................................................................................................... 11 Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) ............................................................................................................... 12 Seizures ............................................................................................................................................ 14 Brain Tumors ................................................................................................................................... 15 Meningitis ........................................................................................................................................ 16 Parkinson’s Disease ....................................................................................................................... 17 Substance Abuse ............................................................................................................................ 19 Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS or Lou Gehrig’s Disease) ............................................ 20 Encephalitis ..................................................................................................................................... 21 CONCEPTS ............................................................................................................................................ 22 PRACTICE QUESTIONS ANSWERS AND RATIONALES ............................................................ 26 Cerebrovascular Accident (Stroke) ............................................................................................. 26 Head Injury ...................................................................................................................................... 29 Spinal Cord Injury .......................................................................................................................... 32 Seizures ............................................................................................................................................ 34 Brain Tumors ................................................................................................................................... 37 Meningitis ........................................................................................................................................ 40 Parkinson’s Disease ....................................................................................................................... 43 Substance Abuse ............................................................................................................................ 45 Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS or Lou Gehrig’s Disease) ............................................ 48 Encephalitis ..................................................................................................................................... 50 CONCEPTS ............................................................................................................................................ 53 NEUROLOGICAL DISORDERS COMPREHENSIVE EXAMINATION ......................................... 57 NEUROLOGICAL DISORDERS COMPREHENSIVE EXAMINATION ANSWERS AND RATIONALES ....................................................................................................... 63 Table of Contentsxii Table of ConTenTs 3 Cardiac Disorders ...................................................................................................................... 71 KEYWORDS/ABBREVIATIONS .......................................................................................................... 71 PRACTICE QUESTIONS ..................................................................................................................... 72 Congestive Heart Failure .............................................................................................................. 72 Angina/Myocardial Infarction ....................................................................................................... 73 Coronary Artery Disease ................................................................................................................ 74 Valvular Heart Disease .................................................................................................................. 75 Dysrhythmias and Conduction Problems .................................................................................. 77 Inflammatory Cardiac Disorders ................................................................................................. 78 CONCEPTS ............................................................................................................................................ 79 PRACTICE QUESTIONS ANSWERS AND RATIONALES ............................................................ 82 Congestive Heart Failure .............................................................................................................. 82 Angina/Myocardial Infarction ....................................................................................................... 84 Coronary Artery Disease ................................................................................................................ 87 Valvular Heart Disease .................................................................................................................. 90 Dysrhythmias and Conduction Problems .................................................................................. 92 Inflammatory Cardiac Disorders ................................................................................................. 95 CONCEPTS ............................................................................................................................................ 98 CARDIAC DISORDERS COMPREHENSIVE EXAMINATION .................................................... 102 CARDIAC DISORDERS COMPREHENSIVE EXAMINATION ANSWERS AND RATIONALES ......................................................................................................................... 106 4 Peripheral Vascular Disorders ...................................................................................... 111 KEYWORDS/ABBREVIATIONS ....................................................................................................... 111 PRACTICE QUESTIONS .................................................................................................................. 112 Arterial Hypertension .................................................................................................................. 112 Arterial Occlusive Disease ......................................................................................................... 113 Atherosclerosis ............................................................................................................................. 114 Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm ..................................................................................................... 115 Deep Vein Thrombosis ............................................................................................................... 117 Peripheral Venous Disease ........................................................................................................ 118 CONCEPTS ......................................................................................................................................... 119 PRACTICE QUESTIONS ANSWERS AND RATIONALES ......................................................... 122 Arterial Hypertension .................................................................................................................. 122 Arterial Occlusive Disease ......................................................................................................... 124 Atherosclerosis ............................................................................................................................. 127 Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm ..................................................................................................... 129 Deep Vein Thrombosis ............................................................................................................... 132 Peripheral Venous Disease ........................................................................................................ 134 CONCEPTS ......................................................................................................................................... 137 PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISORDERS COMPREHENSIVE EXAMINATION ...................... 141 PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISORDERS COMPREHENSIVE EXAMINATION ANSWERS AND RATIONALES .................................................................................................... 145 5 Hematological Disorders ................................................................................................... 149 KEYWORDS/ABBREVIATIONS ....................................................................................................... 149 PRACTICE QUESTIONS .................................................................................................................. 150 Leukemia ....................................................................................................................................... 150 Lymphoma ..................................................................................................................................... 151 Anemia ........................................................................................................................................... 152 Bleeding Disorders ...................................................................................................................... 153 Blood Transfusions ...................................................................................................................... 154 Sickle Cell Anemia ...................................................................................................................... 156 CONCEPTS ......................................................................................................................................... 157 PRACTICE QUESTIONS ANSWERS AND RATIONALES ......................................................... 159 Leukemia ....................................................................................................................................... 159 Lymphoma ..................................................................................................................................... 161Table of ConTenTs xiii Anemia ........................................................................................................................................... 164 Bleeding Disorders ...................................................................................................................... 167 Blood Transfusions ...................................................................................................................... 169 Sickle Cell Anemia ...................................................................................................................... 173 CONCEPTS ......................................................................................................................................... 176 HEMATOLOGICAL DISORDERS COMPREHENSIVE EXAMINATION .................................... 179 HEMATOLOGICAL DISORDERS COMPREHENSIVE EXAMINATION ANSWERS AND RATIONALES .................................................................................................... 183 6 Respiratory Disorders .......................................................................................................... 189 KEYWORDS/ABBREVIATIONS ....................................................................................................... 189 PRACTICE QUESTIONS .................................................................................................................. 190 Upper Respiratory Infection (URI) .......................................................................................... 190 Lower Respiratory Infection ...................................................................................................... 191 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) ................................................................. 192 Reactive Airway Disease (Asthma) .......................................................................................... 194 Lung Cancer ................................................................................................................................. 195 Cancer of the Larynx .................................................................................................................. 198 Pulmonary Embolus .................................................................................................................... 199 Chest Trauma ............................................................................................................................... 200 Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome .................................................................................... 201 CONCEPTS ......................................................................................................................................... 203 PRACTICE QUESTIONS ANSWERS AND RATIONALES ......................................................... 206 Upper Respiratory Infection ...................................................................................................... 206 Lower Respiratory Infection ...................................................................................................... 208 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) ................................................................. 211 Reactive Airway Disease (Asthma) .......................................................................................... 214 Lung Cancer ................................................................................................................................. 216 Cancer of the Larynx .................................................................................................................. 219 Pulmonary Embolus .................................................................................................................... 222 Chest Trauma ............................................................................................................................... 224 Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) ..................................................................... 227 RESPIRATORY DISORDERS COMPREHENSIVE EXAMINATION .......................................... 233 RESPIRATORY DISORDERS COMPREHENSIVE EXAMINATION ANSWERS AND RATIONALES .................................................................................................... 239 7 Gastrointestinal Disorders ............................................................................................... 249 KEYWORDS/ABBREVIATIONS ....................................................................................................... 249 PRACTICE QUESTIONS .................................................................................................................. 250 Gastroesophageal Reflux (GERD) ............................................................................................ 250 Inflammatory Bowel Disease .................................................................................................... 251 Peptic Ulcer Disease .................................................................................................................. 252 Colorectal Disease ....................................................................................................................... 253 Diverticulosis/Diverticulitis ........................................................................................................ 254 Gallbladder Disorders ................................................................................................................. 255 Liver Failure .................................................................................................................................. 256 Hepatitis ........................................................................................................................................ 258 Gastroenteritis .............................................................................................................................. 259 Abdominal Surgery ...................................................................................................................... 260 Eating Disorders .......................................................................................................................... 261 Constipation/Diarrhea Disorders .............................................................................................. 262 CONCEPTS ......................................................................................................................................... 263 PRACTICE QUESTIONS ANSWERS AND RATIONALES ......................................................... 265 Gastroesophageal Reflux (GERD) ............................................................................................ 265 Inflammatory Bowel Disease .................................................................................................... 267 Peptic Ulcer Disease .................................................................................................................. 269 Colorectal Disease ....................................................................................................................... 272xiv Table of ConTenTs Diverticulosis/Diverticulitis ........................................................................................................ 275 Gallbladder Disorders ................................................................................................................. 277 Liver Failure .................................................................................................................................. 280 Hepatitis ........................................................................................................................................ 282 Gastroenteritis .............................................................................................................................. 285 Abdominal Surgery ...................................................................................................................... 287 Eating Disorders .......................................................................................................................... 290 Constipation/Diarrhea Disorders .............................................................................................. 292 GASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS COMPREHENSIVE EXAMINATION .............................. 298 GASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS COMPREHENSIVE EXAMINATION ANSWERS AND RATIONALES .................................................................................................... 304 8 Endocrine Disorders ............................................................................................................. 313 KEYWORDS/ABBREVIATIONS ....................................................................................................... 313 PRACTICE QUESTIONS .................................................................................................................. 314 Diabetes Mellitus ........................................................................................................................ 314 Pancreatitis ................................................................................................................................... 316 Cancer of the Pancreas .............................................................................................................. 317 Adrenal Disorders ........................................................................................................................ 319 Pituitary Disorders ....................................................................................................................... 320 Thyroid Disorders ........................................................................................................................ 321 CONCEPTS ......................................................................................................................................... 322 PRACTICE QUESTIONS ANSWERS AND RATIONALES ......................................................... 325 Diabetes Mellitus ........................................................................................................................ 325 Pancreatitis ................................................................................................................................... 330 Cancer of the Pancreas .............................................................................................................. 332 Adrenal Disorders ........................................................................................................................ 335 Pituitary Disorders ....................................................................................................................... 337 Thyroid Disorders ........................................................................................................................ 339 CONCEPTS ......................................................................................................................................... 343 ENDOCRINE DISORDERS COMPREHENSIVE EXAMINATION ............................................. 346 ENDOCRINE DISORDERS COMPREHENSIVE EXAMINATION ANSWERS AND RATIONALES .................................................................................................... 350 9 Genitourinary Disorders ..................................................................................................... 355 KEYWORDS/ABBREVIATIONS ....................................................................................................... 355 PRACTICE QUESTIONS .................................................................................................................. 356 Acute Renal Failure (ARF) ........................................................................................................ 356 Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) ................................................................................................. 357 Fluid and Electrolyte Disorders ................................................................................................ 358 Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) .................................................................................................... 359 Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy .................................................................................................. 361 Renal Calculi ................................................................................................................................ 362 Cancer of the Bladder ................................................................................................................ 363 CONCEPTS ......................................................................................................................................... 365 PRACTICE QUESTIONS ANSWERS AND RATIONALES ......................................................... 368 Acute Renal Failure (ARF) ........................................................................................................ 368 Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) ................................................................................................. 370 Fluid and Electrolyte Disorders ................................................................................................ 373 Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) .................................................................................................... 376 Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy .................................................................................................. 378 Renal Calculi ................................................................................................................................ 380 Cancer of the Bladder ................................................................................................................ 383 CONCEPTS ......................................................................................................................................... 386 GENITOURINARY DISORDERS COMPREHENSIVE EXAMINATION .................................... 389 GENITOURINARY DISORDERS COMPREHENSIVE EXAMINATION ANSWERS AND RATIONALES .................................................................................................... 392Table of ConTenTs xv 10 Reproductive Disorders ..................................................................................................... 397 KEYWORDS/ABBREVIATIONS ....................................................................................................... 397 PRACTICE QUESTIONS .................................................................................................................. 398 Breast Disorders .......................................................................................................................... 398 Pelvic Floor Relaxation Disorders ............................................................................................ 399 Uterine Disorders ........................................................................................................................ 400 Ovarian Disorders ........................................................................................................................ 401 Prostate Disorders ....................................................................................................................... 403 Testicular Disorders .................................................................................................................... 404 Sexually Transmitted Diseases ................................................................................................. 405 CONCEPTS ......................................................................................................................................... 406 PRACTICE QUESTIONS ANSWERS AND RATIONALES ......................................................... 409 Breast Disorders .......................................................................................................................... 409 Pelvic Floor Relaxation Disorders ............................................................................................ 412 Uterine Disorders ........................................................................................................................ 414 Ovarian Disorders ........................................................................................................................ 416 Prostate Disorders ....................................................................................................................... 419 Testicular Disorders .................................................................................................................... 422 Sexually Transmitted Diseases ................................................................................................. 424 CONCEPTS ......................................................................................................................................... 427 REPRODUCTIVE DISORDERS COMPREHENSIVE EXAMINATION ...................................... 430 REPRODUCTIVE DISORDERS COMPREHENSIVE EXAMINATION ANSWERS AND RATIONALES .................................................................................................... 434 11 Musculoskeletal Disorders .............................................................................................. 439 KEYWORDS/ABBREVIATIONS ....................................................................................................... 439 PRACTICE QUESTIONS .................................................................................................................. 440 Degenerative/Herniated Disk Disease ..................................................................................... 440 Osteoarthritis ................................................................................................................................ 441 Osteoporosis ................................................................................................................................. 442 Amputation ................................................................................................................................... 443 Fractures ....................................................................................................................................... 444 Joint Replacements .................................................................................................................... 446 CONCEPTS ......................................................................................................................................... 447 PRACTICE QUESTIONS ANSWERS AND RATIONALES ......................................................... 450 Degenerative/Herniated Disk Disease ..................................................................................... 450 Osteoarthritis ................................................................................................................................ 452 Osteoporosis ................................................................................................................................. 454 Amputation ................................................................................................................................... 457 Fractures ....................................................................................................................................... 459 Joint Replacements .................................................................................................................... 461 CONCEPTS ......................................................................................................................................... 464 MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS COMPREHENSIVE EXAMINATION ............................. 467 MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS COMPREHENSIVE EXAMINATION ANSWERS AND RATIONALES .................................................................................................... 470 12 Integumentary Disorders .................................................................................................. 475 KEYWORDS/ABBREVIATIONS ....................................................................................................... 475 PRACTICE QUESTIONS .................................................................................................................. 475 Burns .............................................................................................................................................. 475 Pressure Ulcers ............................................................................................................................ 477 Skin Cancer .................................................................................................................................. 478 Bacterial Skin Infection ............................................................................................................. 479 Viral Skin Infection ..................................................................................................................... 481 Fungal/Parasitic Skin Infection ................................................................................................ 482 CONCEPTS ......................................................................................................................................... 484 PRACTICE QUESTIONS ANSWERS AND RATIONALES ......................................................... 486xvi Table of ConTenTs Burns .............................................................................................................................................. 486 Pressure Ulcers ............................................................................................................................ 488 Skin Cancer .................................................................................................................................. 491 Bacterial Skin Infection ............................................................................................................. 493 Viral Skin Infection ..................................................................................................................... 496 Fungal/Parasitic Skin Infection ................................................................................................ 499 CONCEPTS ......................................................................................................................................... 501 INTEGUMENTARY DISORDERS COMPREHENSIVE EXAMINATION ................................... 504 INTEGUMENTARY DISORDERS COMPREHENSIVE EXAMINATION ANSWERS AND RATIONALES .................................................................................................... 507 13 Immune System Disorders .............................................................................................. 513 KEYWORDS/ABBREVIATIONS ....................................................................................................... 513 PRACTICE QUESTIONS .................................................................................................................. 514 Multiple Sclerosis ........................................................................................................................ 514 Guillain-Barré Syndrome ........................................................................................................... 515 Myasthenia Gravis ....................................................................................................................... 516 Systemic Lupus Erythematosus ............................................................................................... 518 Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome ................................................................................. 519 Allergies and Allergic Reactions .............................................................................................. 521 Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) ......................................................................................................... 522 CONCEPTS ......................................................................................................................................... 523 PRACTICE QUESTIONS ANSWERS AND RATIONALES ......................................................... 526 Multiple Sclerosis ........................................................................................................................ 526 Guillain-Barré Syndrome ........................................................................................................... 528 Myasthenia Gravis ....................................................................................................................... 531 Systemic Lupus Erythematosus ............................................................................................... 533 Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome ................................................................................. 536 Allergies and Allergic Reactions .............................................................................................. 538 Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) ......................................................................................................... 541 CONCEPTS ......................................................................................................................................... 544 IMMUNE SYSTEM DISORDERS COMPREHENSIVE EXAMINATION ................................... 547 IMMUNE SYSTEM DISORDERS COMPREHENSIVE EXAMINATION ANSWERS AND RATIONALES .................................................................................................... 551 14 Sensory Deficits ....................................................................................................................... 557 KEYWORDS/ABBREVIATIONS ....................................................................................................... 557 PRACTICE QUESTIONS .................................................................................................................. 558 Eye Disorders ................................................................................................................................ 558 Ear Disorders ................................................................................................................................ 559 CONCEPTS ......................................................................................................................................... 560 PRACTICE QUESTIONS ANSWERS AND RATIONALES ......................................................... 562 Eye Disorders ................................................................................................................................ 562 Ear Disorders ................................................................................................................................ 564 CONCEPTS ......................................................................................................................................... 567 SENSORY DEFICITS COMPREHENSIVE EXAMINATION ........................................................ 569 SENSORY DEFICITS COMPREHENSIVE EXAMINATION ANSWERS AND RATIONALES ......................................................................................................................... 572 15 Emergency Nursing .............................................................................................................. 577 KEYWORDS/ABBREVIATIONS ....................................................................................................... 577 PRACTICE QUESTIONS .................................................................................................................. 578 Shock ............................................................................................................................................. 578 Bioterrorism .................................................................................................................................. 579 Codes .............................................................................................................................................. 580 Disasters/Triage ............................................................................................................................ 581 Poisoning ....................................................................................................................................... 582 Violence, Physical Abuse, and Neglect .................................................................................. 584Table of ConTenTs xvii CONCEPTS ......................................................................................................................................... 585 PRACTICE QUESTIONS ANSWERS AND RATIONALES ......................................................... 588 Shock ............................................................................................................................................. 588 Bioterrorism .................................................................................................................................. 591 Codes .............................................................................................................................................. 594 Disasters/Triage ............................................................................................................................ 596 Poisoning ....................................................................................................................................... 599 Violence, Physical Abuse, and Neglect .................................................................................. 602 CONCEPTS ......................................................................................................................................... 605 EMERGENCY NURSING COMPREHENSIVE EXAMINATION ................................................. 607 EMERGENCY NURSING COMPREHENSIVE EXAMINATION ANSWERS AND RATIONALES ......................................................................................................................... 610 16 Perioperative Care .................................................................................................................. 615 KEYWORDS/ABBREVIATIONS ....................................................................................................... 615 PRACTICE QUESTIONS .................................................................................................................. 616 Preoperative .................................................................................................................................. 616 Intraoperative ............................................................................................................................... 617 Postoperative ................................................................................................................................ 618 Acute Pain .................................................................................................................................... 619 CONCEPTS ......................................................................................................................................... 620 PRACTICE QUESTIONS ANSWERS AND RATIONALES ......................................................... 623 Preoperative .................................................................................................................................. 623 Intraoperative ............................................................................................................................... 625 Postoperative ................................................................................................................................ 628 Acute Pain .................................................................................................................................... 630 CONCEPTS ......................................................................................................................................... 633 PERIOPERATIVE CARE COMPREHENSIVE EXAMINATION ................................................... 635 PERIOPERATIVE CARE COMPREHENSIVE EXAMINATION ANSWERS AND RATIONALES ......................................................................................................................... 638 17 Cultural and Spiritual Nursing and Alternative Health Care .............. 643 KEYWORDS/ABBREVIATIONS ....................................................................................................... 643 PRACTICE QUESTIONS .................................................................................................................. 644 CONCEPTS ......................................................................................................................................... 647 PRACTICE QUESTIONS ANSWERS AND RATIONALES ......................................................... 649 CONCEPTS ANSWERS AND RATIONALES ................................................................................ 655 CULTURAL NURSING AND ALTERNATIVE HEALTH CARE COMPREHENSIVE EXAMINATION ............................................................................................ 658 CULTURAL NURSING AND ALTERNATIVE HEALTH CARE COMPREHENSIVE EXAMINATION ANSWERS AND RATIONALES ....................................................................... 661 18 End-of-Life Issues .................................................................................................................. 667 ABBREVIATIONS ............................................................................................................................... 667 PRACTICE QUESTIONS .................................................................................................................. 668 Advance Directives ...................................................................................................................... 668 Death and Dying .......................................................................................................................... 669 Chronic Pain ................................................................................................................................. 670 Ethical/Legal Issues .................................................................................................................... 672 Organ/Tissue Donation ................................................................................................................ 673 CONCEPTS ......................................................................................................................................... 675 PRACTICE QUESTIONS ANSWERS AND RATIONALES ......................................................... 676 Advance Directives ...................................................................................................................... 676 Death and Dying .......................................................................................................................... 678 Chronic Pain ................................................................................................................................. 681 Ethical/Legal Issues .................................................................................................................... 684 Organ/Tissue Donation ................................................................................................................ 687xviii Table of ConTenTs CONCEPTS ANSWERS AND RATIONALES ................................................................................ 690 END-OF-LIFE ISSUES COMPREHENSIVE EXAMINATION .................................................... 692 END-OF-LIFE ISSUES COMPREHENSIVE EXAMINATION ANSWERS AND RATIONALES ......................................................................................................................... 696 19 Pharmacology ............................................................................................................................ 701 KEYWORDS/ABBREVIATIONS ....................................................................................................... 701 TEST-TAKING HINTS FOR PHARMACOLOGY QUESTIONS ................................................... 702 Drug Cards .................................................................................................................................... 702 Sample Drug Cards.........................................................................................................704 Example #1: Digoxin .................................................................................................................. 705 Example #2: Furosemide .......................................................................................................... 705 MEDICATIONS ADMINISTRATION IN A MEDICAL-SURGICAL SETTING COMPREHENSIVE EXAMINATION ............................................................................................ 706 MEDICATIONS ADMINISTRATION IN A MEDICAL-SURGICAL SETTING COMPREHENSIVE EXAMINATION ANSWERS AND RATIONALES ................................... 717 20 Comprehensive Final Examination ........................................................................... 733 COMPREHENSIVE FINAL EXAMINATION .................................................................................. 733 COMPREHENSIVE FINAL EXAMINATION ANSWERS AND RATIONALES ......................... 744 Glossary of English Words Commonly Encountered on Nursing Examinations ................................................................................................. 761 Appendix A: Normal Laboratory Values ............................................................... 765 Appendix B: Sample Nursing Concept Care Map ....................................... 767 Illustration Credits ................................................................................................................. 771 Index ................................................................................................................................................. 7731 Test Taking INTRODUCTION This book is part of a series of books published by the F.A. Davis Company designed to assist the student nurse to be successful in nursing school. This book focuses on critical thinking in regard to test taking. There are the usual test questions found in review books, but the test taker will also find test-taking hints in 19 of 20 chapters. Table 1-1 indicates the breakdown of the content found on the NCLEX-RN. This book has attempted to follow this blueprint. The 2016–2019 NCLEX-RN blueprint includes additional types of alternative test questions. The end of each chapter includes these new graphic types of test questions. The most important aspect of taking any examination is to become knowledgeable about the subject matter the test will cover. There is no substitute for studying the material. Book one of this series—Fundamentals Success: A Q & A Review Applying Critical Thinking to Test Taking, 4th edition, by Patricia M. Nugent and Barbara A. Vitale—defines critical thinking and the RACE model for applying critical thinking to test-taking skills, and the specific topics in that volume will not be repeated in this book. This book will also assist the test taker to apply critical-thinking skills directly to the questions found on nursing examinations. 1 GUIDELINES FOR USING THIS BOOK This book is designed to assist the nursing student when preparing for and taking medicalsurgical examinations as well as the graduate nurse who is preparing to take the national licensure examination. The book is divided into chapters according to body systems and includes chapters on pharmacology, end-of-life issues, emergency nursing, and alternative therapy; a 100-question final examination; and the DavisPlus site containing 150 additional questions. Chapters 2 through 18 are further divided into disease processes to more easily help the test taker identify specific content. A comprehensive final including other content areas as well as disease processes is included at the end of each chapter. In the Answers and Rationales sections of the chapters, an explanation for the correct answer as well as the incorrect distracters is provided. In Chapters 2 through 18, a Test-Taking Hint is provided for every question in the content area. Each question is coded according to Bloom’s Taxonomy for categorizing levels of abstraction required for the test taker to arrive at the correct answer. As specified by the National Council of State Boards of Nursing (NCSBN) testing information, the questions are coded by Content, Integrated Nursing Process, Client Needs, Cognitive Level (Bloom’s Taxonomy), and Concept. There are no test-taking hints provided for the comprehensive final examinations or the questions on DavisPlus. In Chapter 19, the pharmacology chapter, the test-taking hints are discussed in the beginning of the chapter.2 Med-Surg SucceSS PREPARING FOR LECTURE In preparation for attending class on a specific topic, the student should have read the assignment and prepared notes to take to class. Any information the student does not understand should be highlighted in order to clarify the information if the instructor does not cover it in class or if, after the lecture, the student still does not understand the concept. A piece of paper, or study guide, divided into categories of information should be sufficient for most disease processes. If the student is unable to limit the information to one page, the student is probably not being discriminatory when reading. The idea is not to rewrite the textbook but rather to glean from the textbook the important, need-to-know information. Sample Study Guide Medical Diagnosis: Definition: DIAGNOSTIC TESTS: SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS: NURSING INTERVENTIONS: (List normal values) (Include teaching) PROCEDURES AND NURSING IMPLICATIONS: MEDICAL INTERVENTIONS: Complete the study guide in one color of pen but take a different color or a pencil to class along with a highlighter and the study guide. Whatever the instructor emphasizes during the lecture on the study guide should be highlighted. Whatever information the instructor emphasizes in the lecture that the student did not include on the study guide should be Table 1-1 Client Needs Categories and Percentage of Items Client Needs Percentage of Items SAFE AND EFFECTIVE CARE ENVIRONMENT • Management of Care 17–23% • Safety and Infection Control 9–15% • Health Promotion and Maintenance 6–12% • Psychosocial Integrity 6–12% PHYSIOLOGICAL INTEGRITY • Basic Care and Comfort 6–12% • Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies 12–18% • Reduction of Risk Potential 9–15% • Physiological Adaption 11–17% The National Council of State Boards of Nursing, Inc., Chicago, IL, with permission.chapter 1 teSt taking 3 written in the different color pen or pencil. The student should reread the information in the textbook that was included in lecture but was not included on the study guide. When studying for the examination, the student can identify the information obtained from the textbook and the information obtained in class. The information on the study guide that is highlighted represents information that the student thought was important from reading the textbook and the instructor emphasized during the lecture. This is important, need-to-know information for the examination. Please note, however, the instructor may not emphasize laboratory tests and values but still expects the student to realize the importance of this information. The completed study guides can be carried with the student in a folder and reviewed during children’s sports practices, when waiting for an appointment, or at any time the student finds a minute that is spent idly. This is making the most of limited time. The study guides should also be carried to clinical assignments to use when caring for clients in the hospital. Students who prepare before attending class will find the lecture easier to understand and, as a result, those students will score higher on examinations. Being prepared allows the student to listen to the instructor and not sit in class trying to write every word from the overhead presentation. The student should recognize the importance of the instructor’s hints during the lecture. The instructor may emphasize information by highlighting areas on overhead slides, repeating information, or emphasizing a particular fact, which usually means the instructor thinks the information is very important. Important information usually finds its way onto tests at some point. PREPARING FOR AN EXAMINATION Study The student should plan to study three (3) hours for every one (1) hour of class. For example, a course that is three (3) hours of credit requires nine (9) hours of study each week. Cramming immediately before the test usually indicates the student is at risk for being unsuccessful on the examination. The information acquired during cramming is not learned and will be quickly forgotten. Nursing examinations include material required by the registered nurse when caring for clients at the bedside. The knowledge required to care for clients builds on ALL previous knowledge as well as information newly acquired. Understanding What the Test Taker Does Not Know The first time many students realize they do not understand the information is during the examination, when it is too late. Nursing examinations contain high-level application questions requiring the test taker not only to have memorized information but also to be able to interpret the data and make a judgment as to the correct course of action. Test takers must recognize their own areas of weakness before seeing an examination for the first time. This book is designed to assist test takers to identify their areas of weakness before the examination. Two (2) to three (3) days before the examination, the student should compose a practice test and take the examination. If a topic of study proves to be an area of strength, as evidenced by selecting the correct answer to the question, then the student should proceed to study other areas identified as weaknesses. Missing the question identifies a weakness. If the test taker does not understand the rationale for the correct answer, the test taker should read the appropriate textbook and try to understand the rationale for the correct answer. The test taker should be cautious about reading rationales for the incorrect distracters. During the examination, the test taker may remember reading the information but could become confused about whether the information applied to the correct answer or to the incorrect distracter.4 Med-Surg SucceSS The Night Before the Exam The night before the examination, the student should quit studying by 6:00 to 7:00 p.m. The student should do something fun or relaxing up until bedtime and get a good night’s rest before taking the examination. Studying until bedtime or in an all-night cram session leaves the student tired and sleepy during the examination, which is just when the mind should be at its top performance. The Day of the Exam The student should eat a meal before an examination; a source of carbohydrate for energy along with a protein source makes a good meal. Skipping a meal before the examination leaves the brain without nourishment. A bagel with peanut butter and milk is an excellent meal; it provides a source of protein and sustained release of carbohydrates. Do not eat donuts or drink soft drinks. The energy from these is quickly available but will not last throughout the time required for an examination. Excessive fluid intake may cause the need to urinate during the examination and make it hard for the test taker to concentrate. Test-Taking Anxiety If the student has test-taking anxiety, then it is advisable for the student to arrive at the testing site 45 minutes before the examination. Find a seat for the examination and place books there to reserve the desk. The student should walk for 15 minutes at a fast pace away from the testing site and at the end of the 15 minutes the student should turn and walk back. This exercise literally walks anxiety away. If other test takers getting up and leaving the room bothers the test taker, the test taker should try to get a desk away from the group, in front of the room or facing a wall. Most schools allow students to wear hunter’s ear plugs during a test if noise bothers the student. Most NCLEX-RN test sites will provide ear plugs if the graduate requests them. TAKING THE EXAM During the examination, if the test taker finds a question that contains totally unknown information and the test taker is taking a pencil-and-paper test, the test taker should circle the question and skip it. Another question may help to answer the skipped question. Delaying moving on and worrying over a question will place the next few questions in jeopardy. The mind will not let go of the worry, and the test taker may miss important information in the subsequent questions. During the NCLEX-RN computerized test, the test taker should take some deep breaths and then select an answer. The computer does not allow the test taker to return to a question. Test takers who become anxious during an examination should stop, put their hands in their lap, shut their eyes, and take a minimum of five (5) deep breaths before resuming the examination. The test taker must become aware of personal body signals that indicate increasing stress levels. Some people get gastrointestinal symptoms and others feel a tightening of muscles. Test-Taking Hints for the Computerized NCLEX-RN Examination A computer administers the NCLEX-RN examination. Here are some test-taking hints that specifically apply to examination by computer. • The test is composed of 75 to 265 questions. The computer determines with a 95% certainty that the test taker’s ability is above the passing standard before the examination will conclude. The minimum number of questions the test taker will receive is 75 questions.chapter 1 teSt taking 5 • The examination comprises multiple-choice questions and may include several types of alternate questions: • Fill-in-the-blank questions, which test math abilities. • “Select all that apply” questions, which require the test taker to select more than one distracter as the correct answer. In a “Select All” question, a minimum of two answers will be correct and in some questions all of the options may be correct. This is a new revision of the NCLEX-RN examination. Previously, there had to be at least one incorrect option. Click-and-drag questions, which require the test taker to identify a specific area of the body as the correct answer. • An audio component, which requires the test taker to identify body sounds. Examples of most of these types of questions are included in this book. In an attempt to illustrate the click-and-drag questions, this book has pictures with lines to delineate A, B, C, and D. A fifth type of question which prioritizes the answers 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 in order of when the nurse would implement the intervention is also included in this book. Finally, the audio questions can be found on the F.A. Davis Web site. • Test takers should not be overly concerned if they possess rudimentary computer skills. The test taker must use the mouse to select the correct answer. Every question asks for a confirmation before being submitted as the answer. • Other than typing pertinent personal information, the test taker must be able to type numbers and use the drop-down computer calculator. The test taker can request an erase slate to calculate math problems by hand. • The test taker should practice taking tests on the computer before taking the NCLEX-RN examination. Many textbooks contain computer disks with test questions, and there are many online review opportunities. • The test taker should refer to the Web site for the National Council of State Boards of Nursing (http://www.ncsbn.org) for additional information on the NCLEX-RN examination. Understanding the Types of Nursing Questions coMponentS of a Multiple-choice QueStion A multiple-choice question is called an item. Each item has two parts. The stem is the part that contains the information that identifies the topic and its parameters and then asks a question. The second part consists of one or more possible responses, which are called options. One of the options is the correct answer and the others are the wrong answers, called distracters. The client diagnosed with angina complains of chest pain while ambulating in the hall. Which intervention should the nurse implement first? Stem a. Have the client sit down. Correct answer Options b. Monitor the pulse oximeter reading. c. Administer sublingual nitroglycerin. Distracters d. Apply oxygen via nasal cannula. cognitive levelS of nurSing QueStionS Questions on nursing examinations reflect a variety of thinking processes that nurses use when caring for clients. These thinking processes are part of the cognitive domain, and they progress from the simple to the complex, from the concrete to the abstract, and from the6 Med-Surg SucceSS tangible to the intangible. There are four types of thinking processes represented by nursing questions: • Knowledge Questions—The emphasis is on recalling remembered information. • Comprehension Questions—The emphasis is on understanding the meaning and intent of remembered information. • Application Questions—The emphasis is on remembering understood information and utilizing the information in new situations. • Analysis Questions—The emphasis is on comparing and contrasting a variety of elements of information. THE RACE MODEL: THE APPLICATION OF CRITICAL THINKING TO MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS Answering a test question is like participating in a race. Of course, the test taker wants to come in first and be the winner. However, the thing to remember about a race is that success is not based just on speed but also on strategy and tactics. The same is true about nursing examinations. Although speed may be a variable that must be considered when taking a timed test, so that the amount of time spent on each question is factored into the test strategy, the emphasis on RACE is the use of critical-thinking techniques to answer multiple-choice questions. The RACE Model presented next is a critical-thinking strategy to use when answering nursing multiple-choice questions. If the test taker follows the RACE model every time when examining a test question, its use will become second nature. This methodical approach will improve the test taker’s abilities to critically analyze a test question and improve chances of selecting the correct answer. The RACE Model has four steps to answering a test question. The best way to remember the four steps is to refer to the acronym RACE. R—Recognize what information is in the stem. • Recognize the key words in the stem. • Recognize who the client is in the stem. • Recognize what the topic is about. A—Ask what is the question asking? • Ask what are the key words in the stem that indicate the need for a response? • Ask what is the question asking the nurse to implement? C—Critically analyze the options in relation to the question asked in the stem. • Critically scrutinize each option in relation to the information in the stem. • Critically identify a rationale for each option. • Critically compare and contrast the options in relation to the information in the stem and their relationships to one another. E—Eliminate as many options as possible. • Eliminate one option at a time. The text Fundamentals Success: A Q & A Review Applying Critical Thinking to Test Taking, 4th edition, by Patricia M. Nugent and Barbara A. Vitale, includes an in-depth discussion exploring the RACE Model in relation to the thinking processes as represented in multiple-choice nursing questions. CONCEPT-FOCUSED QUESTIONS A number of states and nursing programs within the states have chosen to use a Concept-based curriculum approach to nursing education. Oregon, North Carolina, and Texas are among these states. This is a change from the disease-based model of nursing education that followed a disease-based approach. Over the years of curriculum development in nursing, the number of topics has expanded under the disease-based curriculum to become burdensome and unwieldychapter 1 teSt taking 7 for students and faculty. These schools have transitioned to teaching “concepts” of client needs, utilizing specific exemplars of commonly occurring disease processes to represent the concept to students. This is not a new idea but rather a return to a previous method of nursing curriculum. For example, if the curriculum being taught is Oxygenation, it would be taught using the exemplars of pneumonia or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Under the concept, there are similarities of nursing assessment guidelines and nursing interventions. Assessing the client’s lung fields, elevating the head of the bed for maximum lung expansion, and administering oxygen are applicable for both exemplars and also for asthma, respiratory distress, myasthenia gravis with respiratory involvement, and others that require these same interventions. The exemplars require the nurse to determine what makes this Oxygenation problem different from a client with myasthenia. The concept problem focus is designed to encourage critical thinking and problem solving. This book includes questions at the end of most chapters that focus on the larger concept with the use of exemplars [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 801 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jun 03, 2021
Number of pages
801
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jun 03, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
43

 Kathryn Colgrove, Ray Huttel, Colgrove - Med-Surg Success_ A Course Review Applying Critical Thinking to Test Taking, Second Edition (Davis's Q&A Series)-F.png)
 (2500+ Q & A).png)
 Latest 2021.png)







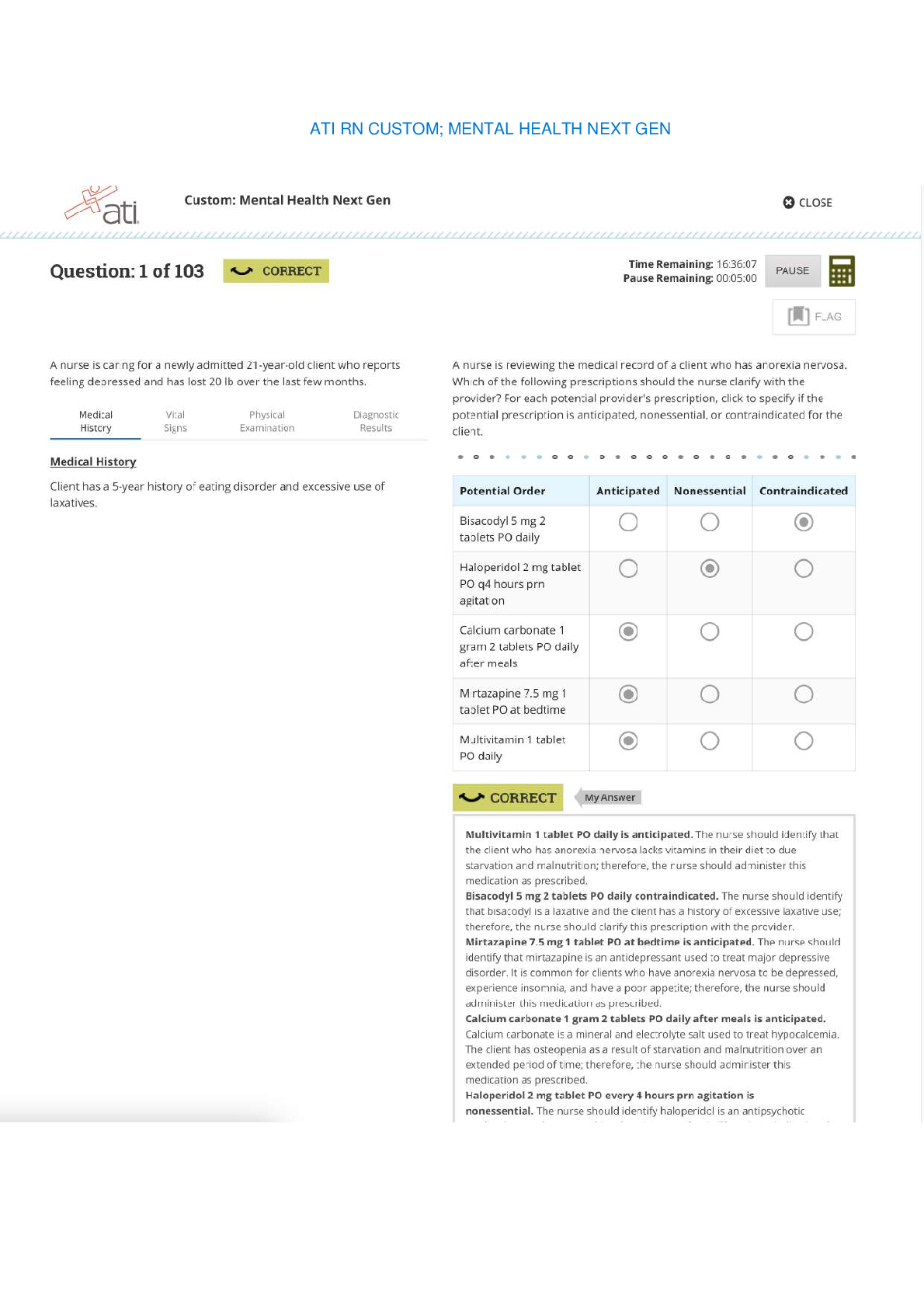
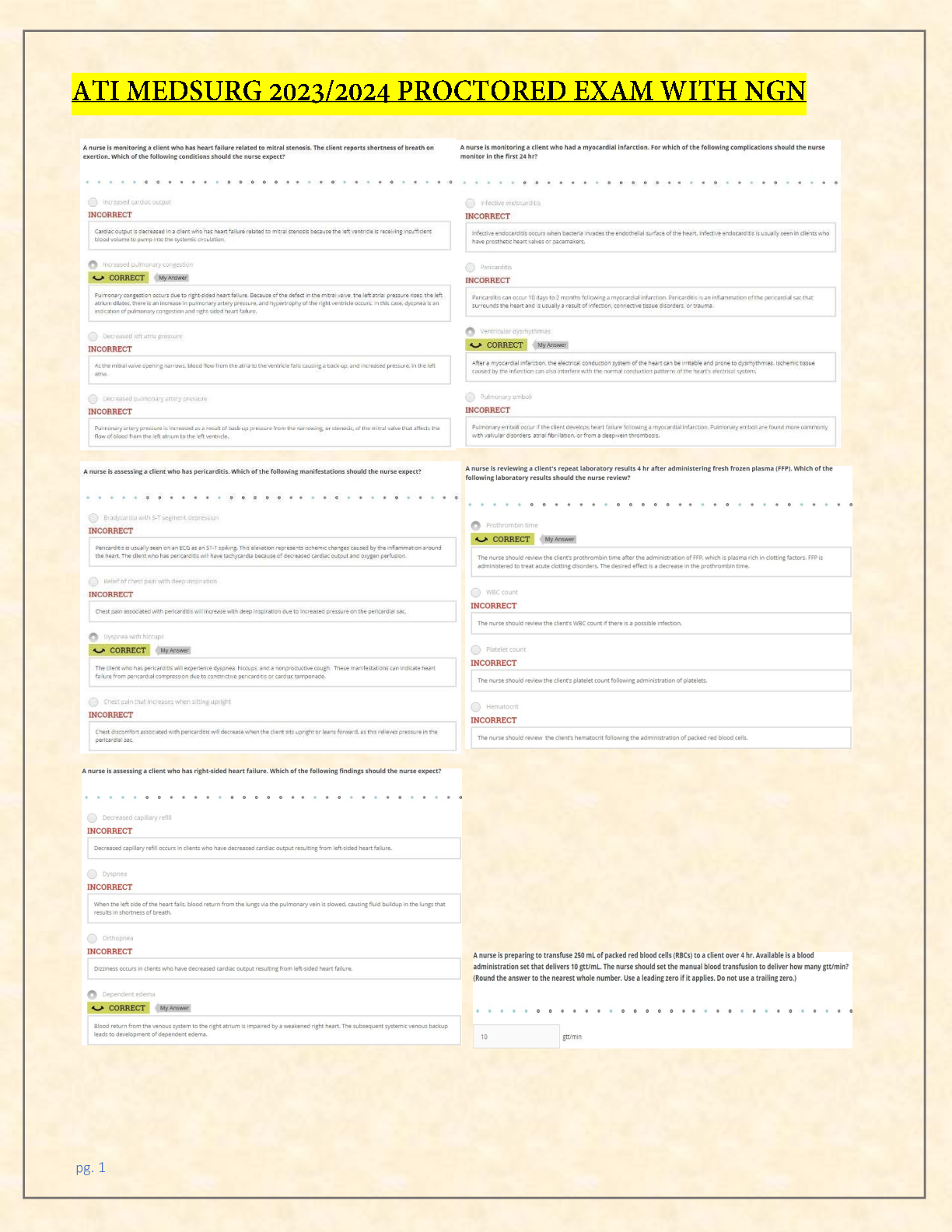
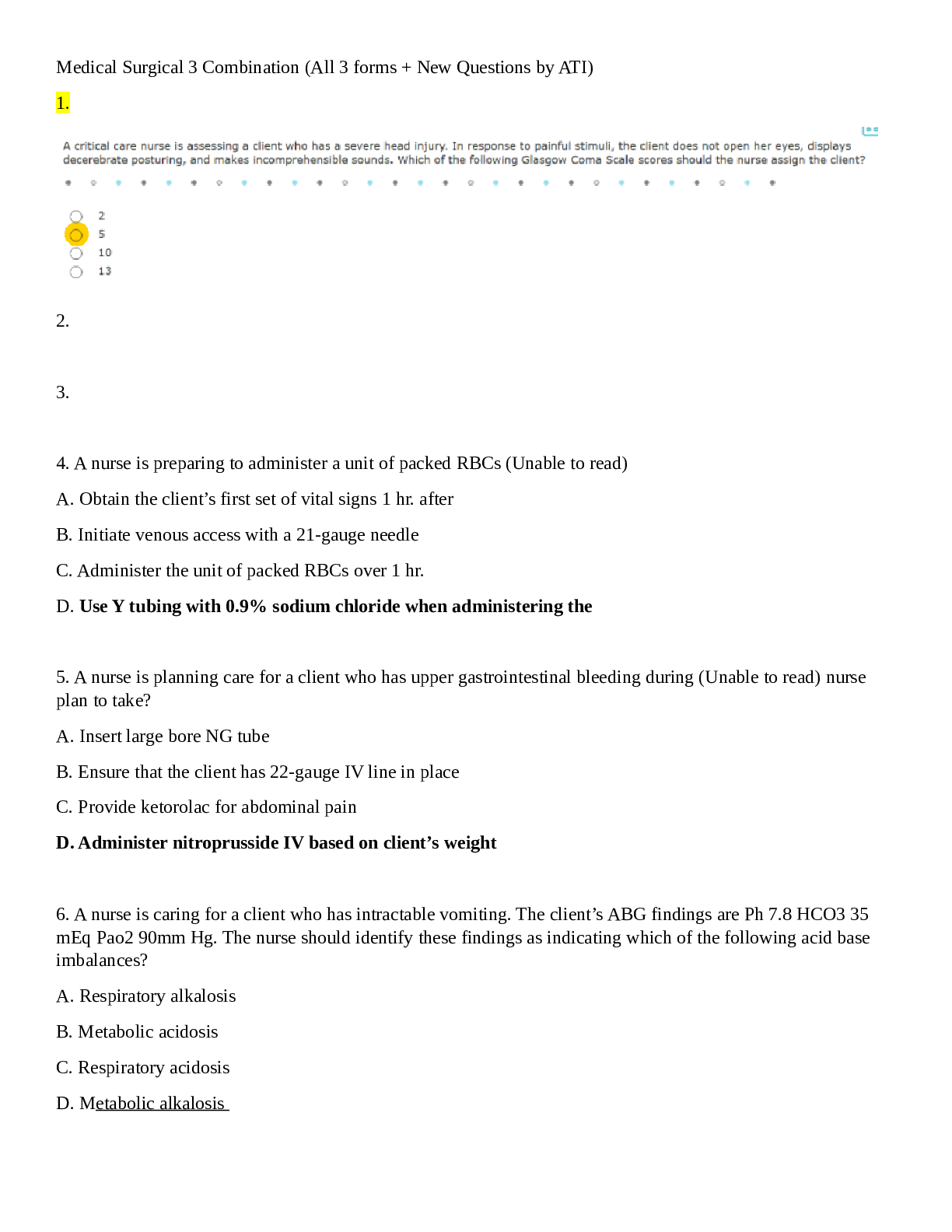
 – Chamberlain College of Nursing.png)





