NURSING 1950 Mental Health Module 3 Exam Questions and Answers- SRTC
Document Content and Description Below
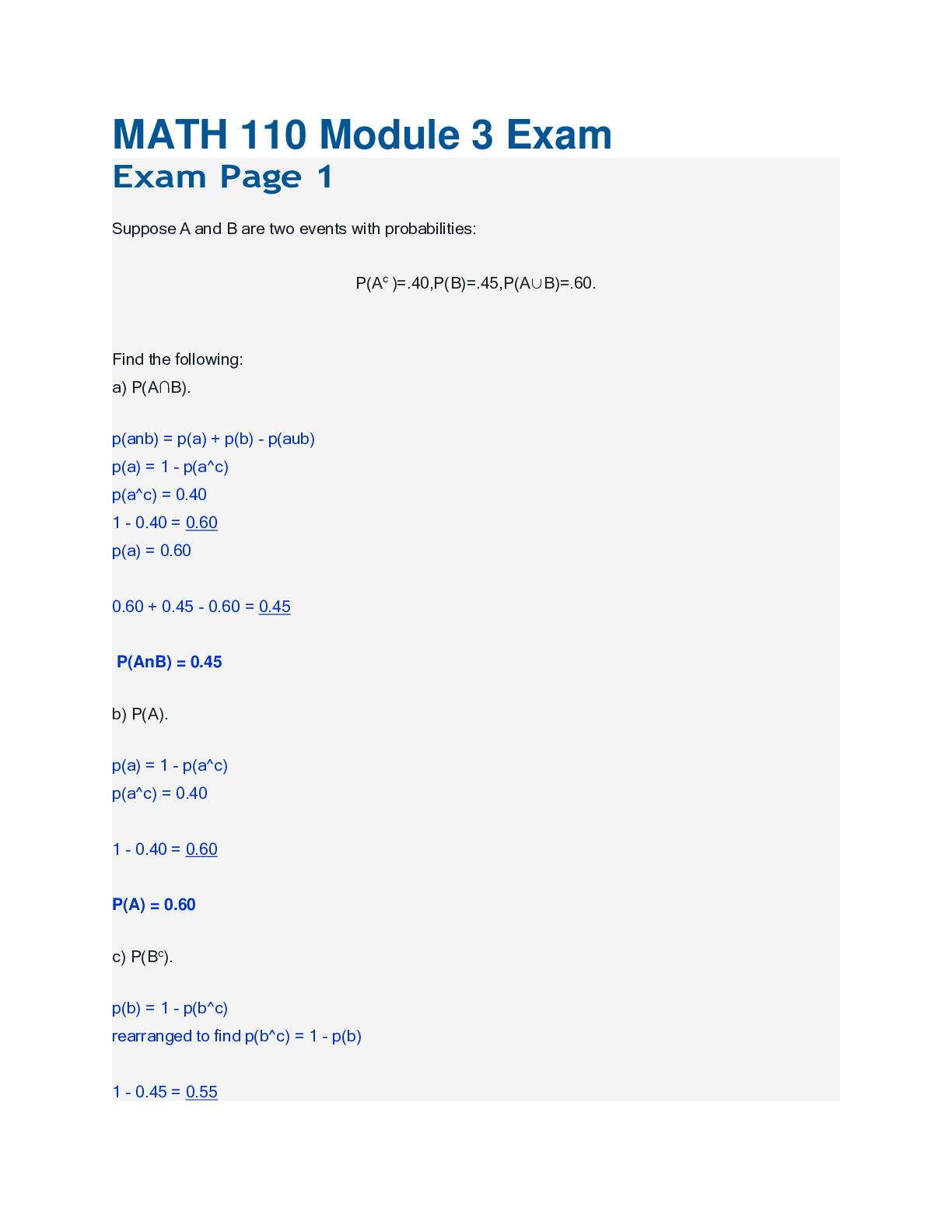
NURSING 1950 Mental Health Module 3 Exam Questions and Answers- SRTC 1. A patient became severely depressed when the last of the family's six children moved out of the home 4 months ago. The patient ... repeatedly says, "No one cares about me. I'm not worth anything." Which response by the nurse would be the most helpful? "I'll sit with you for 10 minutes now and 10 minutes after lunch to help you feel that I care about you." Spending time with the patient at intervals throughout the day shows acceptance by the nurse and will help the patient establish a relationship with the nurse. The therapeutic technique is "offering self." Setting definite times for the therapeutic contacts and keeping the appointments show predictability on the part of the nurse, an element that fosters trust building. 2. A patient became depressed after the last of the family's six children moved out of the home 4 months ago. Select the best initial outcome for the nursing diagnosis Situational low self-esteem related to feelings of abandonment. The patient will: verbalize realistic positive characteristics about self by (date). Low self-esteem is reflected by making consistently negative statements about self and self-worth. Replacing negative cognitions with more realistic appraisals of self is an appropriate intermediate outcome. 3. A patient diagnosed with major depression says, "No one cares about me anymore. I'm not worth anything." Today the patient is wearing a new shirt and has neat, clean hair. Which remark by the nurse supports building a positive self- esteem for this patient? "You're wearing a new shirt." Patients with depression usually see the negative side of things. The meaning of compliments may be altered to "I didn't look nice yesterday," or "They didn't like my other shirt." Neutral comments such as making an observation avoid negative interpretations. 4. An adult diagnosed with major depression was treated with medication and cognitive behavioral therapy. The patient now recognizes how passivity contributed to the depression. Which intervention should the nurse suggest? Social skills training Social skill training is helpful in treating and preventing the recurrence of depression. Training focuses on assertiveness and coping skills that lead to positive reinforcement from others and development of a patient's support system. 5. Priority interventions for a patient diagnosed with major depression and feelings of worthlessness should include: careful unobtrusive observation around the clock Approximately two-thirds of people with depression contemplate suicide. Patients with depression who exhibit feelings of worthlessness are at higher risk. Regular planned observations of the patient diagnosed with depression may prevent a suicide attempt on the unit. 6. When counseling patients diagnosed with major depression, an advanced practice nurse will address the negative thought patterns by using: cognitive behavioral therapy Cognitive behavioral therapy attempts to alter the patient's dysfunctional beliefs by focusing on positive outcomes rather than negative attributions. The patient is also taught the connection between thoughts and resultant feelings. Research shows that cognitive behavioral therapy involves the formation of new connections between nerve cells in the brain and that it is at least as effective as medication. 7. A patient says to the nurse, "My life doesn't have any happiness in it anymore. I once enjoyed holidays, but now they're just another day." The nurse documents this report as an example of: anhedonia Anhedonia is a common finding in many types of depression. It refers to feelings of a loss of pleasure in formerly pleasurable activities. 8. A patient diagnosed with major depression began taking a tricyclic antidepressant 1 week ago. Today the patient says, "I don't think I can keep taking these pills. They make me so dizzy, especially when I stand up." The nurse will: teach the patient strategies to manage postural hypotension Drowsiness, dizziness, and postural hypotension usually subside after the first few weeks of therapy with tricyclic antidepressants. Postural hypotension can be managed by teaching the patient to stay well hydrated and rise slowly. Knowing this information may convince the patient to continue the medication. 9. A patient diagnosed with depression is receiving imipramine (Tofranil) 200 mg qhs. Which assessment finding would prompt the nurse to collaborate with the health care provider regarding potentially hazardous side effects of this drug? Urinary retention All the side effects mentioned are the result of the anticholinergic effects of the drug. Only urinary retention and severe constipation warrant immediate medical attention. 10. A patient diagnosed with major depression tells the nurse, "Bad things that happen are always my fault." Which response by the nurse will best assist the patient to reframe this overgeneralization? "Let's look at one bad thing that happened to see if another explanation exists." assumption, the nurse can help the patient look at the premise more objectively and reframe it as a more accurate representation of fact. 11. A nurse worked with a patient diagnosed with major depression, severe withdrawal, and psychomotor retardation. After 3 weeks, the patient did not improve. The nurse is most at risk for feelings of: ineffectiveness and frustration Nurses may have expectations for self and patients that are not wholly realistic, especially regarding the patient's progress toward health. Unmet expectations result in feelings of ineffectiveness, anger, or frustration. 12. A patient diagnosed with depression begins selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressant therapy. The nurse should provide information to the patient and family about: reporting increased suicidal thoughts Some evidence indicates that suicidal ideation may worsen at the beginning of antidepressant therapy; thus, close monitoring is necessary. 13. A nurse taught a patient about a tyramine-restricted diet. Which menu selection would the nurse approve? Mashed potatoes, ground beef patty, corn, green beans, apple pie The correct answer describes a meal that contains little tyramine. Vegetables and fruits contain little or no tyramine. Fresh ground beef and apple pie are safe. 14. What is the focus of priority nursing interventions for the period immediately after electroconvulsive therapy treatment? Supporting physiological stability During the immediate post-treatment period, the patient is recovering from general anesthesia; hence, the priority need is to establish and support physiological stability. 15. A nurse provided medication education for a patient diagnosed with major depression who began a new prescription for phenelzine (Nardil). Which behavior indicates effective learning? The patient: confers with a pharmacist when selecting over-the-counter medications Over-the-counter medicines may contain vasopressor agents or tyramine, a substance that must be avoided when the patient takes MAOI antidepressants. Medications for colds, allergies, or congestion or any preparation that contains ephedrine or phenylpropanolamine may precipitate a hypertensive crisis. 16. Major depression resulted after a patient's employment was terminated. The patient now says to the nurse, "I'm not worth the time you spend with me. I am the most useless person in the world." Which nursing diagnosis applies? Situational low self-esteem The patient's statements express feelings of worthlessness and most clearly relate to the nursing diagnosis of situational low self-esteem. 17. A patient diagnosed with major depression does not interact with others except when addressed, and then only in monosyllables. The nurse wants to show nonjudgmental acceptance and support for the patient. Which communication technique will be effective? Make observations Making observations about neutral topics such as the environment draws the patient into the reality around him or her but places no burdensome expectations for answers on the patient. Acceptance and support are shown by the nurse's presence. 18. A patient being treated for depression has taken 300 mg amitriptyline (Elavil) daily for a year. The patient calls the case manager at the clinic and says, "I stopped taking my antidepressant 2 days ago. Now I am having cold sweats, nausea, a rapid heartbeat, and nightmares." The nurse will advise the patient to: "Take a dose of your antidepressant now and come to the clinic to see the health care provider." The patient has symptoms associated with abrupt withdrawal of the tricyclic antidepressant. Taking a dose of the drug will ameliorate the symptoms. Seeing the health care provider will allow the patient to discuss the advisability of going off the medication and to be given a gradual withdrawal schedule if discontinuation is the decision. 19. Which documentation for a patient diagnosed with major depression indicates the treatment plan was effective? Slept 6 hours uninterrupted. Sang with activity group. Anticipates seeing grandchild. Sleeping 6 hours, participating with a group, and anticipating an event are all positive events. 20. A patient was diagnosed with seasonal affective disorder (SAD). During which month would this patient's symptoms be most acute? January The days are short in January, so the patient would have the least exposure to sunlight. Seasonal affective disorder is associated with disturbances in circadian rhythm. 21. A patient diagnosed with depression repeatedly tells staff, "I have cancer. It's my punishment for being a bad person." Diagnostic tests reveal no cancer. Select the priority nursing diagnosis. Risk for suicide A patient diagnosed with depression who feels so worthless as to believe cancer is deserved is at risk for suicide. 22. A patient diagnosed with major depression refuses solid foods. In order to meet nutritional needs, which beverage will the nurse offer to this patient? Milk Milk is the only beverage listed that provides protein, fat, and carbohydrates. In addition, milk is fortified with vitamins. 23. During a psychiatric assessment, the nurse observes a patient's facial expression is without emotion. The patient says, "Life feels so hopeless to me. I've been feeling sad for several months." How will the nurse document the patient's affect and mood? Affect flat; mood depressed Mood refers to a person's self-reported emotional feeling state. Affect is the emotional feeling state that is outwardly observable by others. 24. A disheveled patient with severe depression and psychomotor retardation has not showered for several days. The nurse will: firmly and neutrally assist the patient with showering When patients are unable to perform self-care activities, staff must assist them rather than ignore the issue. Better grooming increases self-esteem. 25. A patient diagnosed with major depression began taking escitalopram (Lexapro) 5 days ago. The patient now says, "This medicine isn't working." The nurse's best intervention would be to: explain the time lag before antidepressants relieve symptoms Escitalopram is an SSRI antidepressant. One to three weeks of treatment is usually necessary before symptom relief occurs. This information is important to share with patients. 26. A nurse is caring for a patient with low self-esteem. Which nonverbal communication should the nurse anticipate from this patient? Eyes pointed downward Nonverbal communication is usually considered more powerful than verbal communication. Downward casted eyes suggest feelings of worthlessness or hopelessness. 27. A patient diagnosed with major depression received six electroconvulsive therapy sessions and aggressive doses of antidepressant medication. The patient owns a small business and was counseled not to make major decisions for a month. Select the correct rationale for this counseling. Temporary memory impairments and confusion may occur with electroconvulsive therapy. Recent memory impairment and/or confusion is often present during and for a short time after electroconvulsive therapy. An inappropriate business decision might be made because of forgotten important details. 28. A nurse instructs a patient taking a medication that inhibits the action of monoamine oxidase (MAO) to avoid certain foods and drugs because of the risk of: hypertensive crisis Patients taking MAO-inhibiting drugs must be on a tyramine-free diet to prevent hypertensive crisis. In the presence of MAOIs, tyramine is not destroyed by the liver and in high levels produces intense vasoconstriction, resulting in elevated blood pressure. 29. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TCM) is scheduled for a patient diagnosed with major depression. Which comment by the patient indicates teaching about the procedure was effective? "I might be a little dizzy or have a mild headache after each procedure." Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TCM) treatments take about 30 minutes. Treatments are usually 5 days a week. Patients are awake and alert during the procedure. After the procedure, patients may experience a headache and lightheadedness. 30. The admission note indicates a patient diagnosed with major depression has anergia and anhedonia. For which measures should the nurse plan? (Select all that apply) - Instilling a sense of hopefulness - Assisting with self-care activities - Accommodating psychomotor retardation Anergia refers to a lack of energy. Anhedonia refers to the inability to find pleasure or meaning in life; thus, planning should include measures to accommodate psychomotor retardation, assist with activities of daily living, and instill hopefulness. 31. A student nurse caring for a patient diagnosed with depression reads in the patient's medical record, "This patient shows vegetative signs of depression." Which nursing diagnoses most clearly relate to the vegetative signs? Select all that apply. - Imbalanced nutrition: less than body requirements - Sexual dysfunction - Self-care deficit - Insomnia Vegetative signs of depression are alterations in body processes necessary to support life and growth, such as eating, sleeping, elimination, and sexual activity. These diagnoses are more closely related to vegetative signs than diagnoses associated with feelings about self. 32. A patient diagnosed with major depression shows vegetative signs of depression. Which nursing actions should be implemented? Select all that apply. - Offer laxatives if needed. - Monitor food and fluid intake. - Provide a quiet sleep environment. The correct options promote a normal elimination pattern. Although excessive intake of stimulants such as caffeine may make the patient feel jittery and anxious, small amounts may provide useful stimulation. 33. A patient being treated with paroxetine (Paxil) 50 mg po daily for depression reports to the clinic nurse, "I took a few extra tablets earlier today and now I feel bad." Which assessments are most critical? Select all that apply. - Vital signs - Presence of abdominal pain and diarrhea - Hyperactivity or feelings of restlessness The patient is taking the maximum dose of this SSRI and has ingested an additional unknown amount of the drug. Central serotonin syndrome must be considered. Symptoms include abdominal pain, diarrhea, tachycardia, elevated blood pressure, hyperpyrexia, increased motor activity, and muscle spasms. Central serotonin syndrome may progress to a full medical emergency if not treated early. 34. A nurse wants to teach alternative coping strategies to a patient experiencing severe anxiety. Which action should the nurse perform first? Lower the patient's current anxiety. A patient experiencing severe anxiety has a markedly narrowed perceptual field and difficulty attending to events in the environment. 35. A patient experiencing moderate anxiety says, "I feel undone." An appropriate response for the nurse would be: "I'm not sure I understand. Give me an example." Increased anxiety results in scattered thoughts and an inability to articulate clearly. 36. A patient fearfully runs from chair to chair crying, "They're coming! They're coming!" The patient does not follow the staff's directions or respond to verbal interventions. The initial nursing intervention of highest priority is to: provide for the patient's safety Safety is of highest priority because the patient experiencing panic is at high risk for self-injury related to increased non-goal-directed motor activity, distorted perceptions, and disordered thoughts. 37. A patient fearfully runs from chair to chair crying, "They're coming! They're coming!" The patient does not follow the staff's directions or respond to verbal interventions. Which nursing diagnosis has the highest priority? Risk for injury A patient experiencing panic-level anxiety is at high risk for injury related to increased non-goal-directed motor activity, distorted perceptions, and disordered thoughts. 38. A patient checks and rechecks electrical cords related to an obsessive thought that the house may burn down. The nurse and patient explore the likelihood of an actual fire. The patient states this event is not likely. This counseling demonstrates principles of: cognitive restructuring Cognitive restructuring involves the patient in testing automatic thoughts and drawing new conclusions. 39. A patient undergoing diagnostic tests says, "Nothing is wrong with me except a stubborn chest cold." The spouse reports the patient smokes, coughs daily, lost 15 pounds, and is easily fatigued. Which defense mechanism is the patient using? Denial Denial is an unconscious blocking of threatening or painful information or feelings. 40. A patient with an abdominal mass is scheduled for a biopsy. The patient has difficulty understanding the nurse's comments and asks, "What do you mean? What are they going to do?" Assessment findings include tremulous voice, respirations 28, and pulse 110. What is the patient's level of anxiety? Moderate Moderate anxiety causes the individual to grasp less information and reduces problem-solving ability to a less-than-optimal level. 41. A patient preparing for surgery has moderate anxiety and is unable to understand preoperative information. Which nursing intervention is most appropriate? Present the information again in a calm manner using simple language. Giving information in a calm, simple manner will help the patient grasp the important facts. 42. A patient is experiencing moderate anxiety. The nurse encourages the patient to talk about feelings and concerns. What is the rationale for this intervention? Concerns stated aloud become less overwhelming and help problem solving begin. 43. A nurse assesses a patient with a tentative diagnosis of generalized anxiety disorder. Which question would be most appropriate for the nurse to ask? "Do you find it difficult to control your worrying?" Patients with generalized anxiety disorder frequently engage in excessive worrying. 44. A patient in the emergency department shows disorganized behavior and incoherence after a friend suggested a homosexual encounter. In which room should the nurse place the patient? An interview room furnished with a desk and two chairs Individuals experiencing severe to panic-level anxiety require a safe environment that is quiet, non-stimulating, structured, and simple. 45. A person has minor physical injuries after an auto accident. The person is unable to focus and says, "I feel like something awful is going to happen." This person has nausea, dizziness, tachycardia, and hyperventilation. What is the person's level of anxiety? Severe The person whose anxiety is severe is unable to solve problems and may have a poor grasp of what is happening in the environment. 46. Two staff nurses applied for a charge nurse position. After the promotion was announced, the nurse who was not promoted said, "The nurse manager had a headache the day I was interviewed." Which defense mechanism is evident? Projection Projection is the hallmark of blaming, scapegoating, prejudicial thinking, and stigmatizing others. 47. A patient tells a nurse, "My new friend is the most perfect person one could imagine: kind, considerate, and good-looking. I can't find a single flaw." This patient is demonstrating: Idealization Idealization is an unconscious process that occurs when the individual attributes exaggerated positive qualities to another. 48. A patient experiences a sudden episode of severe anxiety. Of these medications in the patient's medical record, which is most appropriate to give as a prn anxiolytic? lorazepam (Ativan) Lorazepam is a benzodiazepine used to treat anxiety. It may be given as a prn medication. 49. Two staff nurses applied for promotion to nurse manager. The nurse not promoted initially had feelings of loss but then became supportive of the new manager by helping make the transition smooth and encouraging others. Which term best describes the nurse's response? Altruism Altruism is the mechanism by which an individual deals with emotional conflict by meeting the needs of others and receiving gratification vicariously or from the responses of others. 50. A person who feels unattractive repeatedly says, "Although I'm not beautiful, I am smart." This is an example of: Compensation Compensation is an unconscious process that allows us to make up for deficits in one area by excelling in another area to raise self-esteem. 51. A person speaking about a rival for a significant other's affection says in an emotional, syrupy voice, "What a lovely person. That's someone I simply adore." The individual is demonstrating: reaction formation Reaction formation is an unconscious mechanism that keeps unacceptable feelings out of awareness by using the opposite behavior. 52. An individual experiences sexual dysfunction and blames it on a partner by calling the person unattractive and unromantic. Which defense mechanism is evident? Rationalization Rationalization involves unconsciously making excuses for one's behavior, inadequacies, or feelings. 53. A student says, "Before taking a test, I feel very alert and a little restless." The nurse can correctly assess the student's experience as: mild anxiety Mild anxiety is rarely obstructive to the task at hand. It may be helpful to the patient because it promotes study and increases awareness of the nuances of questions. 54. A student says, "Before taking a test, I feel very alert and a little restless." Which nursing intervention is most appropriate to assist the student? Explain that the symptoms result from mild anxiety and discuss the helpful aspects. Teaching about symptoms of anxiety, their relation to precipitating stressors, and, in this case, the positive effects of anxiety will serve to reassure the patient. 55. A cruel and abusive person often uses rationalization to explain the behavior. Which comment demonstrates use of this defense mechanism? "That person should not have provoked me." Rationalization consists of justifying one's unacceptable behavior by developing explanations that satisfy the teller and attempt to satisfy the listener. 56. A patient experiencing panic suddenly began running and shouting, "I'm going to explode!" Select the nurse's best action. Tell the patient, "Stop running and take a deep breath. I will help you." Safety needs of the patient and other patients are a priority. Comments to the patient should be simple, neutral, and give direction to help the patient regain control. 57. A person who has been unable to leave home for more than a week because of severe anxiety says, "I know it does not make sense, but I just can't bring myself to leave my apartment alone." Which nursing intervention is appropriate? Teach the person to use positive self-talk techniques. Positive self-talk, a form of cognitive restructuring, replaces negative thoughts such as "I can't leave my apartment" with positive thoughts such as "I can control my anxiety." 58. A nurse assesses an individual who commonly experiences anxiety. Which comment by this person indicates the possibility of obsessive-compulsive disorder? "I check where my car keys are eight times." Recurring doubt (obsessive thinking) and the need to check (compulsive behavior) suggest obsessive-compulsive disorder. 59. When alprazolam (Xanax) is prescribed for a patient who experiences acute anxiety, health teaching should include instructions to: avoid alcoholic beverages Drinking alcohol or taking other anxiolytics along with the prescribed benzodiazepine should be avoided because depressant effects of both drugs will be potentiated. 60. The nurse assesses a patient who complains of loneliness and episodes of anxiety. Which statement by the patient is mostly likely if this patient also has agoraphobia? "Being afraid to go out seems ridiculous, but I can't go out the door." Individuals who are agoraphobic generally acknowledge that the behavior is not constructive and that they do not really like it. 61. A patient diagnosed with obsessive-compulsive disorder has this nursing diagnosis: Anxiety related to as evidenced by inability to control compulsive cleaning. Which phrase correctly completes the etiological portion of the diagnosis? persistent thoughts about bacteria, germs, and dirt Many compulsive rituals accompany obsessive thoughts. The patient uses these rituals for anxiety relief. 62. A patient performs ritualistic hand washing. Which action should the nurse implement to help the patient develop more effective coping? Encourage the patient to participate in social activities. Because obsessive-compulsive patients become overly involved in the rituals, promotion of involvement with other people and activities is necessary to improve coping. 63. For a patient experiencing panic, which nursing intervention should be implemented first? Provide calm, brief, directive communication. Calm, brief, directive verbal interaction can help the patient gain control of overwhelming feelings and impulses related to anxiety. 64. A child was placed in a foster home after being removed from abusive parents. The child is apprehensive and overreacts to environmental stimuli. The foster parents ask the nurse how to help the child. Which interventions should the nurse suggest? Select all that apply. - Use a calm manner and low voice. - Maintain simplicity in the environment. - Explain and reinforce reality to avoid distortions. 65. A nurse plans health teaching for a patient with generalized anxiety disorder who begins a new prescription for lorazepam (Ativan). What information should be included? Select all that apply. - Caution in use of machinery - The importance of caffeine restriction - Avoidance of alcohol and other sedatives 66. Which assessment questions would be most appropriate for the nurse to ask a patient with possible obsessive-compulsive disorder? Select all that apply. - "Are there others in your family who must do things in a certain way to feel comfortable?" - "Is it difficult to keep certain thoughts out of your awareness?" - "Do you do certain things over and over again?" 67. The nurse assesses an adult who is socially withdrawn and hoards. Which nursing diagnoses most likely apply to this individual? Select all that apply. - Ineffective home maintenance - Chronic low self-esteem - Risk for injury 68. A nurse works with a patient diagnosed with posttraumatic stress disorder who has frequent flashbacks as well as persistent symptoms of arousal. Which intervention should be included in the plan of care? Explain that the physical symptoms are related to the psychological state. Persons with posttraumatic stress disorder often experience somatic symptoms or sympathetic nervous system arousal that can be confusing and distressing. Explaining that these are the bodys responses to psychological trauma helps the patient understand how such symptoms are part of the illness and something that will respond to treatment. This decreases powerlessness over the symptoms and helps instill a sense of hope. It also helps the patient to understand how relaxation, breathing exercises, and imagery can be helpful in symptom reduction. The goal of treatment for posttraumatic stress disorder is to come to terms with the event so treatment efforts would not include repression of memories or numbing. 69. Four teenagers died in an automobile accident. One week later, which behavior by the parents of these teenagers most clearly demonstrates resilience? The parents who: create a scholarship fund at their child's high school Resilience refers to positive adaptation or the ability to maintain or regain mental health despite adversity. Loss of a child is among the highest-risk situations for maladaptive grieving. The parents who create a scholarship fund are openly expressing their feelings and memorializing their child. 70. After the sudden death of his wife, a man says, "I can't live without her...she was my whole life." Select the nurse's most therapeutic reply. "Her death is a terrible loss for you." Adjustment disorders may be associated with grief. A statement that validates a bereaved persons loss is more helpful than false reassurances and clichés. It signifies understanding. 71. A woman just received notification that her husband died. She approaches the nurse who cared for him during his last hours and says angrily, "If you had given him your undivided attention, he would still be alive." How should the nurse analyze this behavior? Anger is an expected emotion in an adjustment disorder Symptoms of adjustment disorder run the gamut of all forms of distress including guilt, depression, and anger. Anger may protect the bereaved from facing the devastating reality of loss. 72. A wife received news that her husband died of heart failure and called her family to come to the hospital. She angrily tells the nurse who cared for him, "He would still be alive if you had given him your undivided attention." Select the nurse's best intervention. Say to the wife, "I understand you are feeling upset. I will stay with you until your family comes." The nurse builds trust and shows compassion in the face of adjustment disorders. Therapeutic responses provide comfort. The nurse should show patience and tact while offering sympathy and warmth. 73. A child drowned while swimming in a local lake 2 years ago. Which behavior indicates the child's parents have adapted to their loss? The parents: throw flowers on the lake at each anniversary date of the accident Resilience refers to positive adaptation or the ability to maintain or regain mental health despite adversity. Loss of a child is among the highest-risk situations for an adjustment disorder and maladaptive grieving. The parents who throw flowers on the lake on each anniversary date of the accident are openly expressing their feelings. 74. A store clerk was killed during a robbery 2 weeks ago. His widow, who has a long history of schizoaffective disorder, cries spontaneously when talking about his death. Select the nurse's most therapeutic response. "The unexpected death of your husband is very painful. I'm glad you are able to talk about your feelings." The patient is expressing feelings related to the loss, and this is an expected and healthy behavior. This patient is at risk for a maladaptive response because of the history of a serious mental illness, but the nurses priority intervention is to form a therapeutic alliance and support the patients expression of feelings. 75. Which scenario demonstrates a dissociative fugue? After being caught in an extramarital affair, a man disappeared but then reappeared months later with no memory of what occurred while he was missing. The patient in a dissociative fugue state relocates and lacks recall of his life before the fugue began. Often fugue states follow traumatic experiences and sometimes involve assuming a new identity. Such persons at some point find themselves in their new surroundings, unable to recall who they are or how they got there. A feeling of detachment from ones body or from the external reality is an indication of depersonalization disorder. 76. The nurse who is counseling a patient with dissociative identity disorder should understand that the assessment of highest priority is: risk for self-harm Assessments that relate to patient safety take priority. Patients with dissociative disorders may be at risk for suicide or self-mutilation, so the nurse must be alert for indicators of risk for self-injury. 77. A patient states, "I feel detached and weird all the time. It is as though I am looking at life through a cloudy window. Everything seems unreal. It really messes up things at work and school." This scenario is most suggestive of which health problem? Depersonalization disorder Depersonalization disorder involves a persistent or recurrent experience of feeling detached from and outside oneself. Although reality testing is intact, the experience causes significant impairment in social or occupational functioning and distress to the individual. 78. The unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) says to the nurse, "That patient with amnesia looks fine, but when I talk to her, she seems vague. What should I be doing for her?" Select the nurse's best reply. "Use short, simple sentences and keep the environment calm and protective." Disruptions in ability to perform activities of daily living, confusion, and anxiety are often apparent in patients with amnesia. Offering simple directions to promote activities of daily living and reduce confusion helps increase feelings of safety and security. A calm, secure, predictable, protective environment is also helpful when a person is dealing with a great deal of uncertainty. Recollection of memories should proceed at its own pace, and the patient should only gradually be given information about her past. 79. A patient diagnosed with depersonalization disorder tells the nurse, "It's starting again. I feel as though I'm going to float away." Which intervention would be most appropriate at this point? Engage the patient in a physical activity such as exercise. Helping the patient apply a grounding technique, such as exercise, assists the patient to interrupt the dissociative process. 80. A person runs from a crowded nightclub after a pyrotechnics show causes the building to catch fire. Which division of the autonomic nervous system will be stimulated in response to this experience? Sympathetic nervous system The autonomic nervous system is comprised of the sympathetic (fight or flight response) and parasympathetic nervous system (relaxation response). In times of stress, the sympathetic nervous system is stimulated. A person would experience stress associated with the experience of being in danger. 81. The gas pedal on a person's car stuck on a busy interstate highway, causing the car to accelerate rapidly. For 20 minutes, the car was very difficult to control. Afterward, this person's cortisol regulation was compromised. Which assessment finding would the nurse expect associated with the dysregulation of cortisol? Flashbacks Cortisol is a hormone released in response to stress. Severe dissociation or mindflight occurs for those who have suffered significant trauma. The episodic failure of dissociation causes intrusive symptoms such as flashbacks, thus dysregulating cortisol. The cortisol level may go up or down, so diuresis and/or weight gain may or may not occur. 82. A soldier returns to the United States from active duty in a combat zone in Afghanistan. The soldier is diagnosed with posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). The nurse's highest priority is to screen this soldier for: depression Comorbidities for adults with PTSD include depression, anxiety disorders, sleep disorders, and dissociative disorders. 83. Two weeks ago, a soldier returned to the U.S. from active duty in a combat zone in Afghanistan. The soldier was diagnosed with posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Which comment by the soldier requires the nurse's immediate attention? "I saw my best friend get killed by a roadside bomb. I don't understand why it wasn't me." The correct response indicates the soldier is thinking about death and feeling survivors guilt. These emotions may accompany suicidal ideation, which warrants the nurses follow-up assessment. Suicide is a high risk among military personnel diagnosed with posttraumatic stress disorder. 84. A soldier returned home from active duty in a combat zone in Afghanistan and was diagnosed with posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). The soldier says, "If there's a loud noise at night, I get under my bed because I think we're getting bombed." What type of experience has the soldier described? Flashback Flashbacks are dissociative reactions in which an individual feels or acts as if the traumatic event were recurring. Illusions are misinterpretations of stimuli, and although the experience is similar, it is better termed a flashback because of the diagnosis of PTSD. 85. A soldier returned 3 months ago from Afghanistan and was diagnosed with posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Which social event would be most disturbing for this soldier? Fireworks display on July 4th The exploding noises associated with fireworks are likely to provoke exaggerated responses for this soldier. 86. A soldier served in combat zones in Iraq during 2010 and was deployed to Afghanistan in 2013. When is it most important for the nurse to screen for signs and symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD)? Screening should be on-going PTSD can have a very long lag time, months to years. Screening should be on- going. 87. A soldier in a combat zone tells the nurse, "I saw a child get blown up over a year ago, and I still keep seeing bits of flesh everywhere. I see something red, and the visions race back to my mind." Which phenomenon associated with posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is the soldier describing? Reexperiencing Spontaneous or cued recurrent, involuntary, and intrusive distressing memories of the traumatic events are often associated with PTSD. The soldier has described intrusive thoughts and visions associated with reexperiencing the traumatic event. 88. A soldier who served in a combat zone returned to the U.S. The soldier's spouse complains to the nurse, "We had planned to start a family, but now he won't talk about it. He won't even look at children." The spouse is describing which symptom associated with posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD)? Avoidance Physiological reactions to reminders of the event that include persistent avoidance of stimuli associated with the trauma results in the individuals avoiding talking about the event or avoiding activities, people, or places that arouse memories of the trauma. Avoidance is exemplified by a sense of foreshortened future and estrangement. 89. A soldier returned home last year after deployment to a war zone. The soldier's spouse complains, "We were going to start a family, but now he won't talk about it. He will not look at children. I wonder if we're going to make it as a couple." Select the nurse's best response. "Posttraumatic stress disorder often strains relationships. Here are some community resources for help and support." Posttraumatic stress disorder precipitates changes that often lead to divorce. Its important to provide support to both the veteran and spouse. 90. Which assessment finding best supports dissociative fugue? The patient states: "I cannot recall why I'm living in this town." The patient in a fugue state frequently relocates and assumes a new identity while not recalling previous identity or places previously inhabited. 91. After major reconstructive surgery, a patient's wounds dehisced. Extensive wound care was required for 6 months, causing the patient to miss work and social activities. Which pathophysiology would be expected for this patient? Dysfunction of the: hippocampus The scenario presents chronic and potentially debilitating stress. If arousal continues unabated, neuronal changes occur that alter the neural circuitry of the prefrontal cortex, reducing the size the hippocampus so that memory is impaired. 92. Relaxation techniques help patients who have experienced major traumas because they: engage the parasympathetic nervous system In response to trauma, the sympathetic arousal symptoms of rapid heart rate and rapid respiration prepare the person for flight or fight responses. Afterward, the dorsal vagal response damps down the sympathetic nervous system. This is a parasympathetic response with the heart rate and respiration slowing down and decreasing the blood pressure. Relaxation techniques promote activity of the parasympathetic nervous system. 93. Select the correct etiology to complete this nursing diagnosis for a patient with dissociative identity disorder. Disturbed personal identity related to: cognitive distortions associated with unresolved childhood abuse issues Nearly all patients with dissociative identity disorder have a history of childhood abuse or trauma. 94. A young adult says, "I was sexually abused by my older brother. During those assaults, I went somewhere else in my mind. I don't remember the details. Now, I often feel numb or unreal in romantic relationships, so I just avoid them." Which disorders should the nurse suspect based on this history? Select all that apply. - Acute stress disorder - Depersonalization disorder -Posttraumatic stress disorder Acute stress disorder, depersonalization disorder, and posttraumatic stress disorder can involve dissociative elements, such as numbing, feeling unreal, and being amnesic for traumatic events. All three disorders are also responses to acute stress or trauma, which has occurred here. 95. A 10-year-old child was placed in a foster home after being removed from parental contact because of abuse. The child has apprehension, tremulousness, and impaired concentration. The foster parent also reports the child has an upset stomach, urinates frequently, and does not understand what has happened. What helpful measures should the nurse suggest to the foster parents? The nurse should recommend: (select all that apply) - conveying empathy and acknowledging the child's distress. - explaining and reinforcing reality to avoid distortions. - using a calm manner and low, comforting voice. -staying with the child until the anxiety decreases. The childs symptoms and behavior suggest that he is exhibiting posttraumatic stress disorder. Interventions appropriate for this level of anxiety include using a calm, reassuring tone, acknowledging the childs distress, repeating content as needed when there is impaired cognitive processing and memory, providing opportunities for comforting and normalizing play and physical activities, correcting any distortion of reality, and staying with the child to increase his sense of security 96. The nurse interviewing a patient with suspected posttraumatic stress disorder should be alert to findings indicating the patient: (select all that apply) - avoids people and places that arouse painful memories. - experiences flashbacks or reexperiences the trauma. - experiences symptoms suggestive of a heart attack. - demonstrates hypervigilance or distrusts others. - feels detached, estranged, or empty inside. These assessment findings are consistent with the symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder. Ritualistic behaviors are expected in obsessive-compulsive disorder. 97. Which experiences are most likely to precipitate posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD)? Select all that apply. - An adolescent was kidnapped and held for 2 years in the home of a sexual predator. - A passenger was in a bus that overturned on a sharp curve and tumbled down an embankment. - An adult was trapped for 3 hours at an angle in an elevator after a portion of the supporting cable breaks. PTSD usually occurs after a traumatic event that is outside the range of usual experience. Examples are childhood physical abuse, torture/kidnap, military combat, sexual assault, and natural disasters, such as floods, tornados, earthquakes, tsunamis; human disasters, such as a bus or elevator accident; or crime-related events, such being taken hostage. The common element in these experiences is the individuals extraordinary helplessness or powerlessness in the face of such stressors. 98. Which assessment data would help the health care team distinguish symptoms of conversion (functional neurological) disorder from symptoms of illness anxiety disorder (hypochondriasis)? patients style of presentation 99. Which prescription medication would the nurse expect to be prescribed for a patient diagnosed with a somatic symptom disorder? Antidepressant medications to treat underlying depression 100. A medical-surgical nurse works with a patient diagnosed with a somatic symptom disorder. Care planning is facilitated by understanding that the patient will probably: be resistant to accepting psychiatric help 101. A patient has blindness related to conversion (functional neurological) disorder but is unconcerned about this problem. Which understanding should guide the nurse's planning for this patient? The patient's anxiety is relieved through the physical symptom. 102. A patient has blindness related to conversion (functional neurological) disorder. To help the patient eat, the nurse should: expect the patient to feed self after explaining arrangement of the food on the tray 103. A patient with blindness related to conversion (functional neurological) disorder says, "All the doctors and nurses in the hospital stop by often to check on me. Too bad people outside the hospital don't find me as interesting." Which nursing diagnosis is most relevant? Chronic low self-esteem 104. To assist patients diagnosed with somatic symptom disorders, nursing interventions of high priority: shift focus from somatic symptoms to feelings 105. A patient with fears of serious heart disease was referred to the mental health center by a cardiologist. Extensive diagnostic evaluation showed no physical illness. The patient says, "My chest is tight, and my heart misses beats. I'm often absent from work. I don't go out much because I need to rest." Which health problem is most likely? Illness anxiety disorder (hypochondriasis) 106. A nurse assessing a patient diagnosed with a somatic symptom disorder is most likely to note that the patient: has altered comfort and activity needs 107. To plan effective care for patients diagnosed with somatic symptom disorders, the nurse should understand that patients have difficulty giving up the symptoms because the symptoms: provide relief from health anxiety 108. A patient with a somatic symptom disorder has the nursing diagnosis Interrupted family processes related to patient's disabling symptoms as evidenced by spouse and children assuming roles and tasks that previously belonged to patient. An appropriate outcome is that the patient will: demonstrate performance of former roles and tasks 109. Which comment by a patient who recently experienced a myocardial infarction indicates use of maladaptive, ineffective coping strategies? "My employer should have paid for a health club membership for me." 110. A nurse assesses a patient diagnosed with conversion (functional neurological) disorder. Which comment is most likely from this patient? "Since my father died, I've been short of breath and had sharp pains that go down my left arm, but I think it's just indigestion." 111. A patient who experienced a myocardial infarction was transferred from critical care to a step-down unit. The patient then used the call bell every 15 minutes for minor requests and complaints. Staff nurses reported feeling inadequate and unable to satisfy the patient's needs. When the nurse manager intervenes directly with this patient, which comment is most therapeutic? "I'm wondering if you are feeling anxious about your illness and being left alone." 112. A patient reports fears of having cervical cancer and says to the nurse, "I've had Pap smears by six different doctors. The results were normal, but I'm sure that's because of errors in the laboratory." Which disorder would the nurse suspect? Illness anxiety disorder (hypochondriasis) 113. A patient diagnosed with a somatic symptom disorder says, "My pain is from an undiagnosed injury. I can't take care of myself. I need pain medicine six or seven times a day. I feel like a baby because my family has to help me so much." It is important for the nurse to assess: secondary gains 114. What is an essential difference between somatic symptom disorders and factitious disorders? Factitious disorders are under voluntary control, whereas somatic symptom disorders involve expression of psychological stress through somatization. 115. A patient says, "I know I have a brain tumor despite the results of the MRI. The radiologist is wrong. People who have brain tumors vomit, and yesterday I vomited all day." Which response by the nurse fosters cognitive reframing? "Let's see if there are any other possible explanations for your vomiting." 116. Which treatment modality should a nurse recommend to help a patient diagnosed with a somatic symptom disorder to cope more effectively? Relaxation techniques 117. Which assessment question could a nurse ask to help identify secondary gains associated with a somatic symptom disorder? "What are you unable to do now but were previously able to do?" 118. A patient diagnosed with a somatic symptom disorder has been in treatment for 4 weeks. The patient says, "Although I'm still having pain, I notice it less and am able to perform more activities." The nurse should evaluate the treatment plan as: partially successful 119. A child has a history of multiple hospitalizations for recurrent systemic infections. The child is not improving in the hospital, despite aggressive treatment. Factitious disorder by proxy is suspected. Which nursing interventions are appropriate? Select all that apply. - Keep careful, detailed records of visitation and untoward events. - Encourage family members to visit in groups of two or three. - Interact with the patient frequently during visiting hours. 120. Which presentations suggest the possibility of a factitious disorder, self- directed type? Select all that apply. - History of multiple hospitalizations without findings of physical illness - History of multiple medical procedures or exploratory surgeries 121. A patient diagnosed with a somatic symptom disorder says, "Why has God chosen me to be sick all the time and unable to provide for my family? The burden on my family is worse than the pain I bear." Which nursing diagnoses apply to this patient? Select all that apply. - Spiritual distress - Ineffective role performance 122. A nurse assesses a patient suspected of having somatic symptom disorder. Which assessment findings regarding this patient support the suspected diagnosis? Select all that apply. - Female - Reports frequent syncope - Reports insomnia often results from back pain 123. A nurse's neighbor says, "I saw a news story about a man without any known illness who died suddenly after his ex-wife committed suicide. Was that a coincidence, or can emotional shock be fatal?" The nurse should respond by noting that some serious medical conditions may be complicated by emotional stress, including: (select all that apply) -cancer -hypertension -immune disorders -cardiovascular disease 124. Over the past year, a woman has cooked gourmet meals for her family but eats only tiny servings. This person wears layered loose clothing. Her current weight is 95 pounds, a loss of 35 pounds. Which medical diagnosis is most likely? Anorexia nervosa Overly controlled eating behaviors, extreme weight loss, preoccupation with food, and wearing several layers of loose clothing to appear larger are part of the clinical picture of an individual with anorexia nervosa. 125. Which anorexia nervosa symptom is physical in nature? - Dry, yellow skin Dry yellow skin is a physical symptom of anorexia. This is due to the release of carotenes as fat stores are burned for energy. 126. A nurse sitting with a client diagnosed with anorexia nervosa notices that the client has eaten 80% of lunch. The client asks the nurse "What do you like better, hamburgers or spaghetti?" Which is the best response by the nurse? Let's focus on your continued improvement. You ate 80% of your lunch It is important to offer support and positive reinforcement for improvements in eating behaviors. Because clients diagnosed with anorexia nervosa are obsessed with food, discussion of food can provide unintended positive reinforcement for negative behaviors. 127. Which outcome indicates that the client's problem of impaired body image has improved? The client has acknowledged that perception of being fat is incorrect When clients can acknowledge that their perception of being fat is incorrect, they perceive a body image that is realistic and not distorted. This is evidence that the client's impaired body image has improved. 128. A client on an inpatient unit has been diagnosed with bulimia nervosa. The client states' "I'm going to the bathroom and will be back in a few minutes." Which nursing response is most appropriate? I will accompany you to the bathroom Any client suspected of self-induced vomiting should be accompanied to the bathroom for the nurse to be able to deter this behavior. 129. A client with a long history of bulimia nervosa is seen in the emergency department. The client is seeing things that others do not, is restless, and has dry mucous membranes. Which is most likely the cause of this client's symptoms? Vomiting, which may lead to dehydration and electrolyte imbalance Purging behaviors, such as vomiting, may lead to dehydration and electrolyte imbalance. Hallucinations and restlessness are signs of electrolyte imbalance. Dry mucous membranes indicated dehydration. 130. A client diagnosed with an eating disorder has a nursing diagnosis of low self-esteem. Which nursing intervention would address this client's problem? Offer independent decision-making opportunities Offering independent decision-making opportunities promotes feelings of control. Making decisions and dealing with the consequences of these decisions should increase independence and improve the client's self-esteem. 131. A 5-year-old child was diagnosed with encopresis. Which assessment finding would the nurse expect associated with this diagnosis? The child: has accidents of defecation at kindergarten three times a week Encopresis refers to unsuccessful bowel control. Bowel control is expected by age 5, so frequent involuntary defecation is associated with this diagnosis. 132. Three months ago a patient diagnosed with binge eating disorder weighed 198 pounds. Lorcaserin (Belviq) was prescribed. Which current assessment finding indicates the need for reevaluation of this treatment approach? The patient: now weighs 196 pounds Lorcaserin is designed to make people feel full after eating smaller meals by activating a serotonin 2c receptor in the brain and blocking appetite signals. According to the FDA, this drug should be stopped if a patient does not have 5% weight loss after 12 weeks of use. If the patient now weighs 196 pounds, the medication has not been effective. 133. Disturbed body image is a nursing diagnosis established for a patient diagnosed with an eating disorder. Which outcome indicator is most appropriate to monitor? Patient expresses satisfaction with body appearance Body image disturbances are considered improved or resolved when the patient is consistently satisfied with his or her own appearance and body function. This is a subjective consideration. 134. A patient referred to the eating disorders clinic has lost 35 pounds during the past 3 months. To assess eating patterns, the nurse should ask the patient: "What do you eat in a typical day?" Although all the questions might be appropriate to ask, only "What do you eat in a typical day?" focuses on the eating patterns. 135. A patient diagnosed with anorexia nervosa virtually stopped eating 5 months ago and lost 25% of body weight. A nurse asks, "Describe what you think about your present weight and how you look." Which response by the patient is most consistent with the diagnosis? "I am fat and ugly." Untreated patients with anorexia nervosa do not recognize their thinness. They perceive themselves to be overweight and unattractive. The patient with anorexia will usually tell people perceptions of self. The patient with anorexia does not recognize his or her thinness and will persist in trying to lose more weight. 136. A patient was diagnosed with anorexia nervosa. The history shows the patient virtually stopped eating 5 months ago and lost 25% of body weight. The serum potassium is currently 2.7 mg/dL. Which nursing diagnosis applies? Imbalanced nutrition: less than body requirements related to reduced oral intake as evidenced by loss of 25% of body weight and hypokalemia The patient's history and lab result support the nursing diagnosis Imbalanced nutrition: less than body requirements. 137. Outpatient treatment is planned for a patient diagnosed with anorexia nervosa. Select the most important desired outcome related to the nursing diagnosis Imbalanced nutrition: less than body requirements. Within 1 week, the patient will gain 1 to 2 pounds Only the outcome of a gain of 1 to 2 pounds can be accomplished within 1 week when the patient is an outpatient. 138. Which nursing intervention has the highest priority as a patient diagnosed with anorexia nervosa begins to gain weight? Observe for adverse effects of refeeding The nursing intervention of observing for adverse effects of refeeding most directly relates to weight gain and is a priority. 139. A patient diagnosed with anorexia nervosa is resistant to weight gain. What is the rationale for establishing a contract with the patient to participate in measures designed to produce a specified weekly weight gain? Patient involvement in decision making increases sense of control and promotes adherence to the plan of care. A sense of control for the patient is vital to the success of therapy. A diet that controls weight gain can allay patient fears of too-rapid weight gain. 140. The nursing care plan for a patient diagnosed with anorexia nervosa includes the intervention "monitor for complications of refeeding." Which system should a nurse closely monitor for dysfunction? Cardiovascular Refeeding resulting in too-rapid weight gain can overwhelm the heart, resulting in cardiovascular collapse. Focused assessment is a necessity to ensure the patient's physiological integrity. 141. A psychiatric clinical nurse specialist uses cognitive-behavioral therapy for a patient diagnosed with anorexia nervosa. Which statement by the staff nurse supports this type of therapy? "Being thin doesn't seem to solve your problems. You are thin now but still unhappy." The correct response is the only strategy that questions the patient's distorted thinking. 142. An appropriate intervention for a patient diagnosed with bulimia nervosa who binges and purges is to teach the patient not to skip meals or restrict food One goal of health teaching is normalization of eating habits. Food restriction and skipping meals lead to rebound bingeing. 143. A nurse provides care for an adolescent patient diagnosed with an eating disorder. Which behavior by this nurse indicates that additional clinical supervision is needed? The nurse interacts with the patient in a protective fashion In the effort to motivate the patient and take advantage of the decision to seek help and be healthier, the nurse must take care not to cross the line toward authoritarianism and assumption of a parental role. 144. A nursing diagnosis for a patient diagnosed with bulimia nervosa is Ineffective coping related to feelings of loneliness as evidenced by overeating to comfort self, followed by self-induced vomiting. The best outcome related to this diagnosis is that within 2 weeks the patient will identify two alternative methods of coping with loneliness The outcome of identifying alternative coping strategies is most directly related to the diagnosis of Ineffective coping. 145. Which nursing intervention has the highest priority for a patient diagnosed with bulimia nervosa? Assist the patient to identify triggers to binge eating For most patients with bulimia nervosa, certain situations trigger the urge to binge; purging then follows. Often the triggers are anxiety-producing situations. Identification of triggers makes it possible to break the binge-purge cycle. Because binge eating and purging directly affect physical status, the need to promote physical safety assumes highest priority. 146. One bed is available on the inpatient eating-disorder unit. Which patient should be admitted to this bed? The patient whose weight decreased from 150 to 100 pounds over a 4-month period. Vital signs are temperature, 35.9 C; pulse, 38 beats/min; blood pressure 60/40 mm Hg Physical criteria for hospitalization include weight loss of more than 30% of body weight within 6 months, temperature below 36 C (hypothermia), heart rate less than 40 beats/min, and systolic blood pressure less than 70 mm Hg. 147. A nurse provides health teaching for a patient diagnosed with bulimia nervosa. Priority information the nurse should provide relates to how to recognize hypokalemia Hypokalemia results from potassium loss associated with vomiting. Physiological integrity can be maintained if the patient can self-diagnose potassium deficiency and adjust the diet or seek medical assistance. 148. As a patient admitted to the eating-disorder unit undresses, a nurse observes that the patient's body is covered by fine, downy hair. The patient weighs 70 pounds and is 5'4" tall. Which term should be documented? Lanugo The fine, downy hair noted by the nurse is called lanugo. It is frequently seen in patients with anorexia nervosa. 149. A patient being admitted to the eating-disorder unit has a yellow cast to the skin and fine, downy hair over the trunk. The patient weighs 70 pounds; height is 5'4". The patient says, "I won't eat until I look thin." Select the priority initial nursing diagnosis. Imbalanced nutrition: less than body requirements related to self- starvation The physical assessment shows cachexia, which indicates imbalanced nutrition. Addressing the patient's self-starvation is the priority. 150. A nurse conducting group therapy on the eating-disorder unit schedules the sessions immediately after meals for the primary purpose of promoting processing of anxiety associated with eating Eating produces high anxiety for patients with eating disorders. Anxiety levels must be lowered if the patient is to be successful in attaining therapeutic goals. 151. Physical assessment of a patient diagnosed with bulimia often reveals prominent parotid glands Prominent parotid glands are associated with repeated vomiting. 152. Which personality characteristic is a nurse most likely to assess in a patient diagnosed with anorexia nervosa? Rigidity, perfectionism Rigid thinking, inability to demonstrate flexibility, and difficulty changing cognitions are characteristic of patients with eating disorders. 153. Which assessment finding for a patient diagnosed with an eating disorder meets criteria for hospitalization? Systolic blood pressure 62 mm Hg Systolic blood pressure less than 70 mm Hg is an indicator for inpatient care. Many people without eating disorders have bradycardia (pulse less than 60 beats/min). 154. A nurse finds a patient diagnosed with anorexia nervosa vigorously exercising before gaining the agreed-upon weekly weight. Which response by the nurse is appropriate? "According to our agreement, no exercising is permitted until you have gained a specific amount of weight." A matter-of-fact statement that the nurse's perceptions are different will help to avoid a power struggle. Treatment plans have specific goals for weight restoration. 155. Which nursing diagnosis is more appropriate for a patient diagnosed with anorexia nervosa who restricts intake and is 20% below normal weight than for a 130-pound patient diagnosed with bulimia nervosa who purges? Imbalanced nutrition: less than body requirements The patient with bulimia nervosa usually maintains a close to normal weight, whereas the patient with anorexia nervosa may approach starvation. 156. An outpatient diagnosed with anorexia nervosa has begun refeeding. Between the first and second appointments, the patient gained 8 pounds. The nurse should assess lung sounds and extremities Weight gain of more than 2 to 5 pounds weekly may overwhelm the heart's capacity to pump, leading to cardiac failure. The nurse must assess for signs of pulmonary edema and congestive heart failure. 157. The treatment team discusses adding a new prescription for lisdexamfetamine dimesylate to the plan of care for a patient diagnosed with binge eating disorder. Which finding from the nursing assessment is most important for the nurse to share with the team? The patient's history of poly-substance abuse Lisdexamfetamine dimesylate is designed to suppress the appetite and presents a risk for abuse. The patient with a history of substance abuse is at risk to abuse this medication as well. 158. A 7-year-old child was diagnosed with pica. Which assessment finding would the nurse expect associated with this diagnosis? The child frequently eats newspapers and magazines Pica refers to eating nonfood items after maturing past toddlerhood. 159. A patient referred to the eating disorders clinic has lost 35 pounds in 3 months. For which physical manifestations of anorexia nervosa should a nurse assess? (Select all that apply.) - Peripheral edema - Constipation - Hypotension - Lanugo Peripheral edema is often present because of hypoalbuminemia. Constipation related to starvation is often present. Hypotension is often present because of dehydration. Lanugo is often present and is related to starvation. 160. A patient diagnosed with anorexia nervosa is hospitalized for treatment. What features should the milieu provide? (Select all that apply.) - Adherence to a selected menu - Observation during and after meals - Monitoring during bathroom trips Priority milieu interventions support restoration of weight and normalization of eating patterns. This requires close supervision of the patient's eating and prevention of exercise, purging, and other activities. There is strict adherence to menus. Observe patients during and after meals to prevent throwing away food or purging. Monitor all trips to the bathroom. 161. A health care provider recently convicted of Medicare fraud says to a nurse, Sure I overbilled. Everyone takes advantage of the government. There are too many rules to follow and I should get the money. These statements show: lack of guilt feelings 162. Which intervention is appropriate for an individual diagnosed with an antisocial personality disorder who frequently manipulates others? Refer requests and questions related to care to the case manager 162. As a nurse prepares to administer medication to a patient diagnosed with a borderline personality disorder, the patient says, just leave it on the table. I’ll take it when I finish combing my hair. What is the nurses best response? Say to the patient, I must watch you take the medication. Please take it now. 163. What is an appropriate initial outcome for a patient diagnosed with a personality disorder who frequently manipulates others? The patient will: acknowledge manipulative behavior when it is called to his or her attention 164. Consider this comment to three different nurses by a patient diagnosed with an antisocial personality disorder, Another nurse said you dont do your job right. Collectively, these interactions can be assessed as: Manipulative 165. A nurse reports to the treatment team that a patient diagnosed with an antisocial personality disorder has displayed the behaviors below. This patient is detached and superficial during counseling sessions. Which behavior by the patient most clearly warrants limit setting? Verbal abuse of another patient 166. A patient diagnosed with borderline personality disorder has a history of self-mutilation and suicide attempts. The patient reveals feelings of depression and anger with life. Which type of medication would the nurse expect to be prescribed? Mood stabilizing medication 167. A patient’s spouse filed charges after repeatedly being battered. The patient sarcastically says, Im sorry for what I did. I need psychiatric help. Which statement by the patient supports an antisocial personality disorder? I hit because I am tired of being nagged. My spouse deserves the beating. 168. What is the priority nursing diagnosis for a patient diagnosed with antisocial personality disorder who has made threats against staff, ripped art off the walls, and thrown objects? Risk for other-directed violence 169. When a patient diagnosed with a personality disorder uses manipulation to get needs met, the staff applies limit-setting interventions. What is the correct rationale for this action? External controls are necessary due to failure of internal control 170. One month ago, a patient diagnosed with borderline personality disorder and a history of self-mutilation began dialectical behavior therapy. Today the patient phones to say, I feel empty and want to hurt myself. The nurse should: assist the patient to choose coping strategies for triggering situations 171. What is the most challenging nursing intervention with patients diagnosed with personality disorders who use manipulation? Maintaining consistent limits 172. The history shows that a newly admitted patient is impulsive. The nurse would expect behavior characterized by: acting without thought on urges or desires 173. A patient says, I get in trouble sometimes because I make quick decisions and act on them. Select the nurses most therapeutic response. Let’s consider the advantages of being able to stop and think before acting. 175. A patient diagnosed with borderline personality disorder was hospitalized several times after self-mutilating episodes. The patient remains impulsive. Which nursing diagnosis is the initial focus of this therapy? Risk for self-directed violence 176. Which statement made by a patient diagnosed with borderline personality disorder indicates the treatment plan is effective? I felt empty and wanted to hurt myself, so I called you 177. When preparing to interview a patient diagnosed with narcissistic personality disorder, a nurse can anticipate the assessment findings will include: grandiosity, self-importance, and a sense of entitlement 178. For which behavior would limit setting be most essential? The patient who: urges a suspicious patient to hit anyone who stares 179. The nurse caring for an individual demonstrating symptoms of schizotypal personality disorder would expect assessment findings to include: socially anxious, rambling stories, peculiar ideas 180. Others describe a worker as very shy and lacking in self-confidence. This worker stays in an office cubicle all day, never coming out for breaks or lunch. Which term best describes this behavior? Avoidant 181. What is the priority intervention for a nurse beginning to work with a patient diagnosed with a schizotypal personality disorder? Respect the patients need for periods of social isolation 182. A patient diagnosed with borderline personality disorder self-inflicted wrist lacerations after gaining new privileges on the unit. In this case, the self-mutilation may have been due to: fear of abandonment associated with progress toward autonomy and independence 183. A patient diagnosed with borderline personality disorder has self-inflicted wrist lacerations. The health care provider prescribes daily dressing changes. The nurse performing this care should: provide care in a matter-of-fact manner 184. A nurse set limits while interacting with a patient demonstrating behaviors associated with borderline personality disorder. The patient tells the nurse, You used to care about me. I thought you were wonderful. Now I can see I was wrong. Youre evil. This outburst can be assessed as: splitting 185. Which characteristic of personality disorders makes it most necessary for staff to schedule frequent team meetings in order to address the patients needs and maintain a therapeutic milieu? Ability to provoke interpersonal conflict 186. A nursing diagnosis appropriate to consider for a patient diagnosed with any of the personality disorders is: impaired social interaction 187. A new psychiatric technician says, Schizophreniaschizotypal! Whats the difference? The nurses response should include which information? With schizotypal personality disorder, the person can be made aware of misinterpretations of reality. 188. Personality traits most likely to be documented regarding a patient demonstrating characteristics of an obsessive-compulsive personality disorder are: perfectionist, inflexible 189. A nurse determines desired outcomes for a patient diagnosed with schizotypal personality disorder. Select the best outcome. The patient will: demonstrate ability to introduce self to a stranger in a social situation 190. A patient says, The other nurses wont give me my medication early, but you know what its like to be in pain and dont let your patients suffer. Could you get me my pill now? I wont tell anyone. Which response by the nurse would be most therapeutic? I understand that you have pain, but giving medicine too soon would not be safe 191. A nurse plans care for an individual diagnosed with antisocial personality disorder. Which characteristic behaviors will the nurse expect? Select all that apply. - Callous attitude - Aggression 192. For which patients diagnosed with personality disorders would a family history of similar problems be most likely? Select all that apply. - Obsessive-compulsive - Antisocial - Borderline - Schizotypal 193. A woman is 5'7", 160 lbs, and wears a size 8 shoe. She says, "My feet are huge. I've asked three orthopedists to surgically reduce my feet." This person tries to buy shoes to make her feet look smaller and, in social settings, conceals both feet under a table or chair. Which health problem is likely? Body dysmorphic disorder Body dysmorphic disorder refers to a preoccupation with an imagined defect in appearance in a normal-appearing person. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 38 pages
Instant download

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Also available in bundle (1)

Nursing 1950 Mental Health Module BUNDLE Exams 1-6 with Questions and Answers- SRTC
Nursing 1950 Mental Health Module BUNDLE Exams 1-6 with Questions and Answers- SRTC
By A+ Solutions 3 years ago
$14.5
6
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jun 24, 2021
Number of pages
38
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jun 24, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
68






.png)













 (1).png)