*NURSING > NCLEX-PN > PSYCHIATRIC HESI prep - HESI Study guide completed Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing (University of (All)
PSYCHIATRIC HESI prep - HESI Study guide completed Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing (University of Rhode Island). The Last minute study Materials in 32 pages of information with HESI Hints you MUST know to pass your exam. Below is the content in brief.
Document Content and Description Below
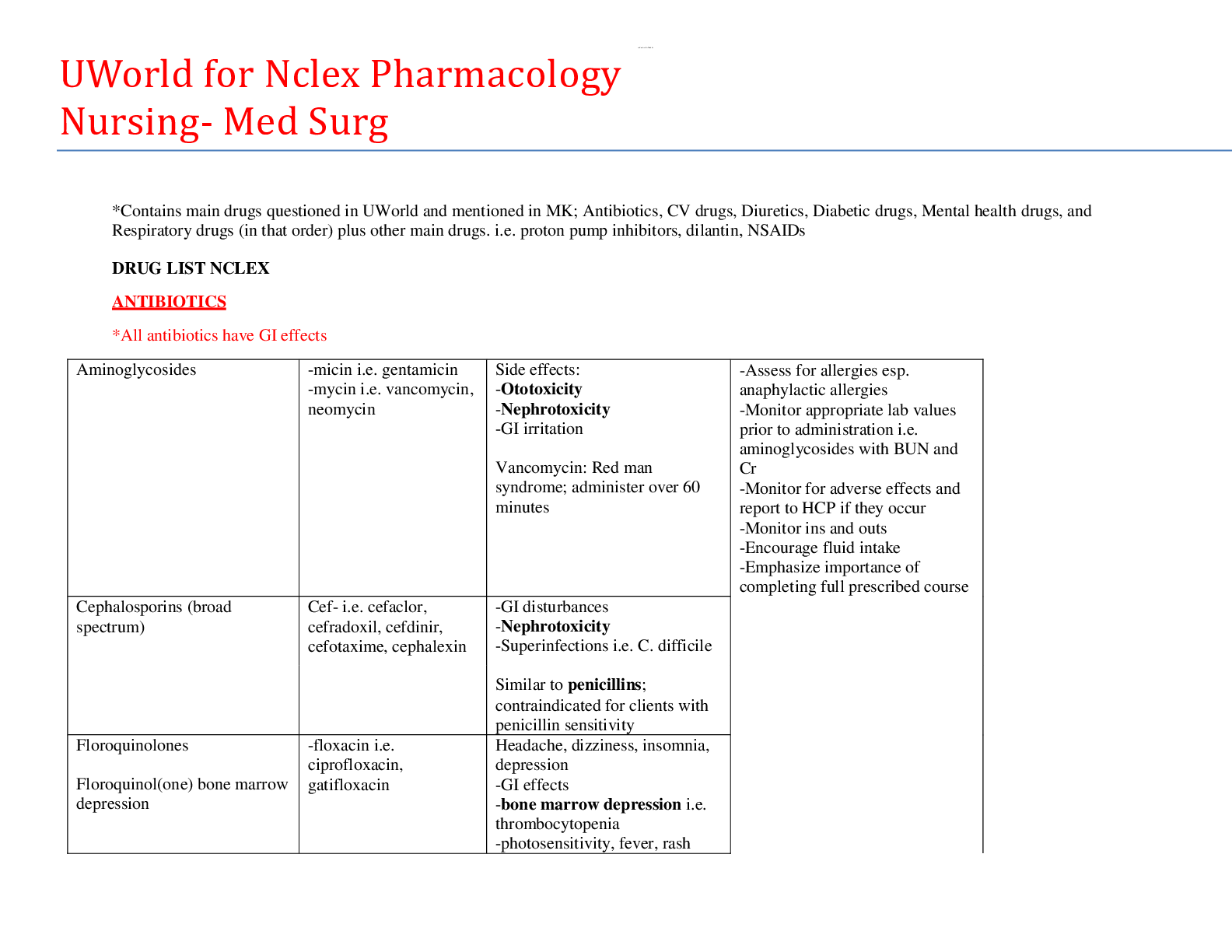
Therapeutic Communication A. Purpose of therapeutic interaction w/ pts a. Allow them autonomy to make choices when appropriate B. Keep statements value-free, advice-free, and re-assurance-free C. ... JUST THE FACTS! NO opinions D. What to do when there’s a psych situation and the pt describes a physical problem a. ASSESS!!!! b. Need to attend to physiologic needs E. Forbidden phrases a. “You should…” F. Basic communications applied to all pts a. Establish trust b. Demonstrate non-judgmental attitude c. Offer self; be empathetic, not sympathetic Types of Treatment Modalities A. Milieu therapy a. Planned use of people, resources, and activities in the environment to assist in improving interpersonal skills, social functioning, and performing ADLs, as well as safety and protection for all pts b. Inpt. And outpt settings c. Provide pt’s an opportunity to gain insight into their behavior via staff limit setting and pt responses to maladaptive social responses Levels of Anxiety A. Mild Anxiety a. Associated w/ daily life b. Produces inc. levels of sensory awareness and alertness c. Allows for thoughts that are logical d. Pt is able to concentrate and problem-solve F. EASILY contagious—can be transferred from ptnurse or nursept a. Nurse must 1st assess own level of anxiety & remain calm b. Calm nurse helps pt gain control, dec. anxiety, & inc. feelings of security Generalized Anxiety Disorders Panic Disorders & Phobias A. Discrete periods of intense fear/discomfort that are unexpected and may be incapacitating B. Characterized by: irrational fear of an external object, activity, situation, and feelings of impending doom Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) A. Anxiety associated w/ repetitive thoughts (obsession) or irresistible impulses (compulsion) to perform an action Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) A. Pts who have experienced or witnessed a highly traumatic event (war, earthquake, watching someone die in a bad accident) or repeatedly exposed to stories of traumatic events E. For pts w/ PTSD, the nurse should a. Actively listen to pt’s stories of experiences surrounding the traumatic event b. Assess suicide risk c. Assist pt to dev’p objectivity about event + problem solve regarding possible means of controlling anxiety r/t event d. Encourage group therapy w/ other pts who have experienced the same or related traumatic events Dissociative Disorders A. Alt. in function or consciousness, personality, memory, or identity B. May be sudden and temporary or gradual and chronic C. Persons afflicted handle stressful situations by “splitting” from situation and going into fantasy state D. d/o are unconscious defense mechanism that protects pt against overwhelming anxiety Personality Disorders Cluster A A. Characteristics a. Suspicious b. Strange behavior—odd or eccentric c. May be precipitated by stressful event d. May manifest as hypochondriasis HESI Hints • Long-standing behavioral traits that are maladaptive responses to anxiety • Cause difficulty in relating to & working w/ others • Pts w/ personality d/o’s are usually comfortable w/ their d/o and believe they’re right and the world is wrong • Usually have little motivation to change Eating Disorders Anorexia Nervosa A. Distorted body image & fear of becoming obeseexcessive dieting and exercise B. Females > males C. Possible causes a. Dysfunctional family system Bulimia Nervosa A. Characterized by: eating excessive amounts of food self induced purging by vomiting, misuse of laxatives, diuretics, or other meds, fasting and/or excessive exercise Bipolar Disorder, or Manic-Depressive Illness A. Affective d/o B. Manifested by mood swings involving: euphoria, grandiosity, and inflated sense of self-worth C. DSM 5—must have 1+ episode of major depression D. Pt may cycle from elevation to depression w/ periods of normal activity in b/w E. Characteristics of Varying Degrees of Mania Schizophrenia Spectrum & Other Psychotic Disorders Schizophrenia A. Characterized by a. Thought disturbance b. Altered affect c. Withdrawal from reality Substance Abuse • Regular use of substances that affect the CNS behavioral changes • Chemicals involved produce physiologic and psychological dependence HESI Hints: Neurocognitive Disorder • Basic difference b/w delirium & dementia o Delirium- acute & reversible o Dementia- gradual & permanent • Confabulation is NOT lying, it’s used by pt to dec. anxiety & to protect the ego • Nursing interventions for confused OA: o Maintain pt’s health & safety o Encourage self-care o Reinforce reality orientation (“today’s Monday”, call pt by name) o Engage pt in simple tasks & activities to build self-esteem • Change inc. anxiety & confusion [Show More]
Last updated: 11 months ago
Preview 1 out of 32 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 01, 2020
Number of pages
32
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 01, 2020
Downloads
1
Views
229








 Practice Test (Total Questions 725).png)


.png)