*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > NUR6550 Final Exam Study Test Questions (All)
NUR6550 Final Exam Study Test Questions
Document Content and Description Below
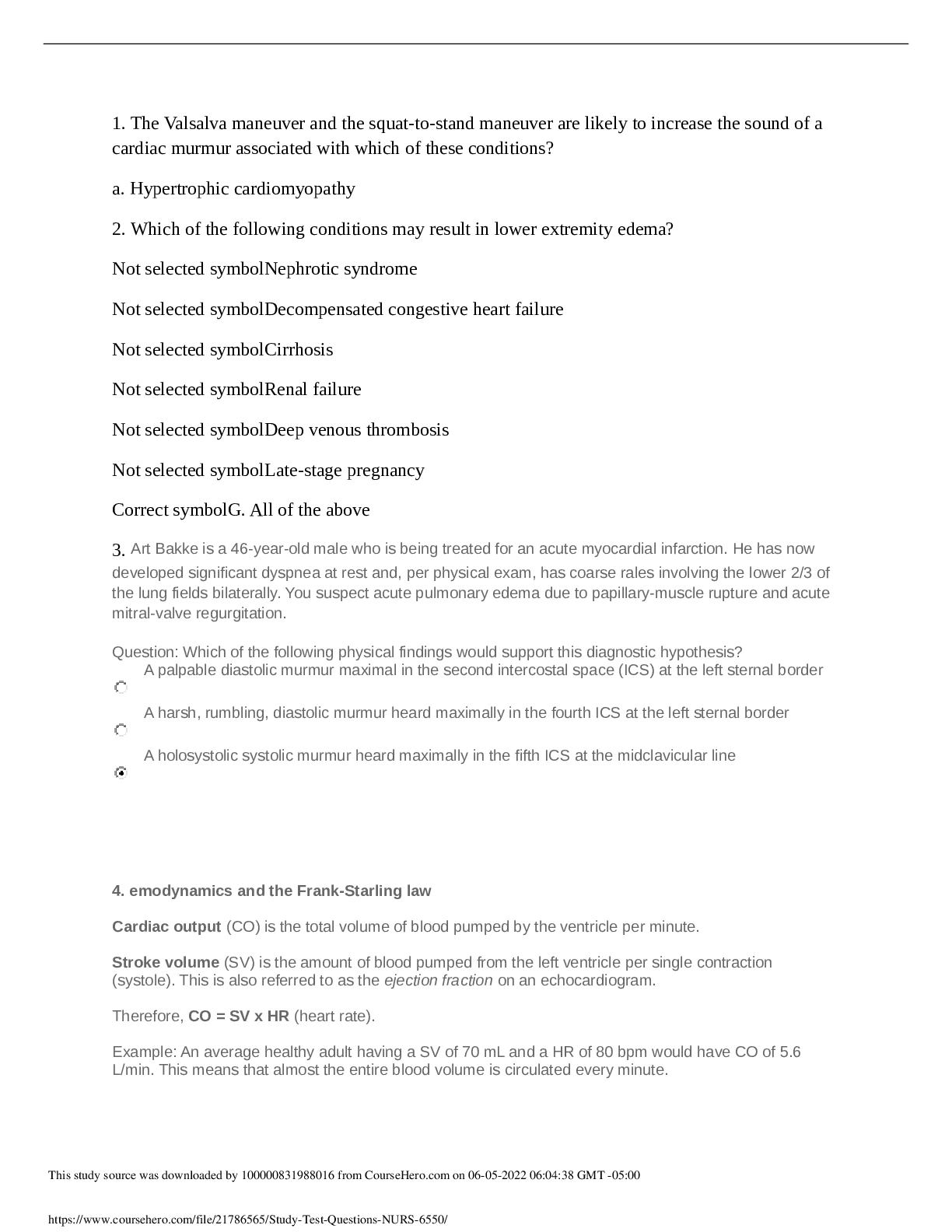
1. The Valsalva maneuver and the squat-to-stand maneuver are likely to increase the sound of a cardiac murmur associated with which of these conditions? a. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy 2. Which of t... he following conditions may result in lower extremity edema? Not selected symbolNephrotic syndrome Not selected symbolDecompensated congestive heart failure Not selected symbolCirrhosis Not selected symbolRenal failure Not selected symbolDeep venous thrombosis Not selected symbolLate-stage pregnancy Correct symbolG. All of the above 3. Art Bakke is a 46-year-old male who is being treated for an acute myocardial infarction. He has now developed significant dyspnea at rest and, per physical exam, has coarse rales involving the lower 2/3 of the lung fields bilaterally. You suspect acute pulmonary edema due to papillary-muscle rupture and acute mitral-valve regurgitation. Question: Which of the following physical findings would support this diagnostic hypothesis? A palpable diastolic murmur maximal in the second intercostal space (ICS) at the left sternal border A harsh, rumbling, diastolic murmur heard maximally in the fourth ICS at the left sternal border A holosystolic systolic murmur heard maximally in the fifth ICS at the midclavicular line 4. emodynamics and the Frank-Starling law Cardiac output (CO) is the total volume of blood pumped by the ventricle per minute. Stroke volume (SV) is the amount of blood pumped from the left ventricle per single contraction (systole). This is also referred to as the ejection fraction on an echocardiogram. Therefore, CO = SV x HR (heart rate). Example: An average healthy adult having a SV of 70 mL and a HR of 80 bpm would have CO of 5.6 L/min. This means that almost the entire blood volume is circulated every minute. This study source was downloaded by 100000831988016 from CourseHero.com on 06-05-2022 06:04:38 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/21786565/Study-Test-Questions-NURS-6550/ Although in general an increase of heart rate increases cardiac output, when the heart rate increases significantly (>160 bpm), there is less time for the ventricles to fill with blood (decreased diastolic filling time). This results in decreased stroke volume and, therefore, decreased cardiac output. Stroke volume is affected by preload and afterload. Preload is the amount of blood in the ventricles just prior to ventricular contraction (i.e., end-diastolic volume) and correlates with the degree to which the cardiac muscle (i.e., the sarcomere, the contractile unit of the myocardium) is stretched. Increasing preload increases stroke volume in a healthy heart, but only up to a maximum stretch. Afterload is the net of the hemodynamic forces that prevent blood from being ejected during ventricular contraction (systole); i.e., afterload is the amount of peripheral resistance. An increase in peripheral vascular resistance (e.g., uncontrolled hypertension) would increase afterload and thereby decrease stroke volume, unless the heart rate increases. The Frank-Starling law states that stroke volume increases in response to an increase in preload (but only up to a point, as will be discussed). That is, increased preload results in increased stretch of the sarcomere which triggers a more forceful contraction. In heart failure, the hemodynamic properties of the Frank-Starling curve are exceeded and increased preload now results in decreased cardiac output. If stroke volume cannot be increased, heart rate must increase in order to maintain an appropriate cardiac output to perfuse the body. 4. The most common ECG finding in a patient with a cardiomyopathy is an ST-elevation MI. -false 5. Nina Martinez is a 70-year-old female who experienced an episode of acute pulmonary edema following an endovascular aneurysm repair. She was discharged on furosemide 60 mg daily and instructed to follow up with cardiology. She is now seen in the office at 2 weeks post discharge. Her metabolic panel includes the following lab values: Na 126 mEq/L K 4.0 mEq/L Cl 93 mEq/L CO2 28 mEq/L BUN 40 mg/dL Cr 1.3 mg/dL This study source was downloaded by 100000831988016 from CourseHero.com on 06-05-2022 06:04:38 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/21786565/Study-Test-Questions-NURS-6550/ Question: This patient has which [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 8 pages
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$10.00
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jun 05, 2022
Number of pages
8
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jun 05, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
67

.png)


.png)




.png)

.png)
.png)

