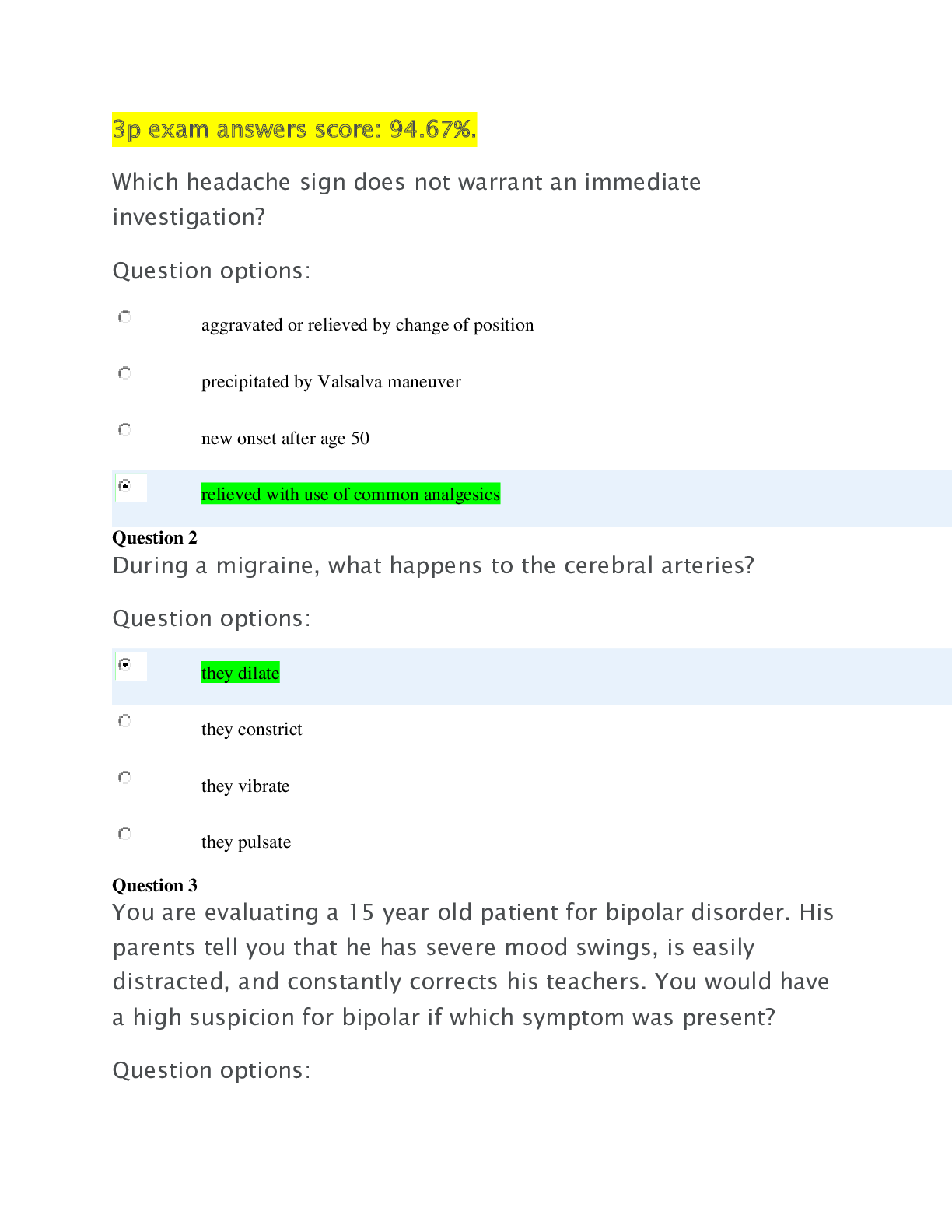
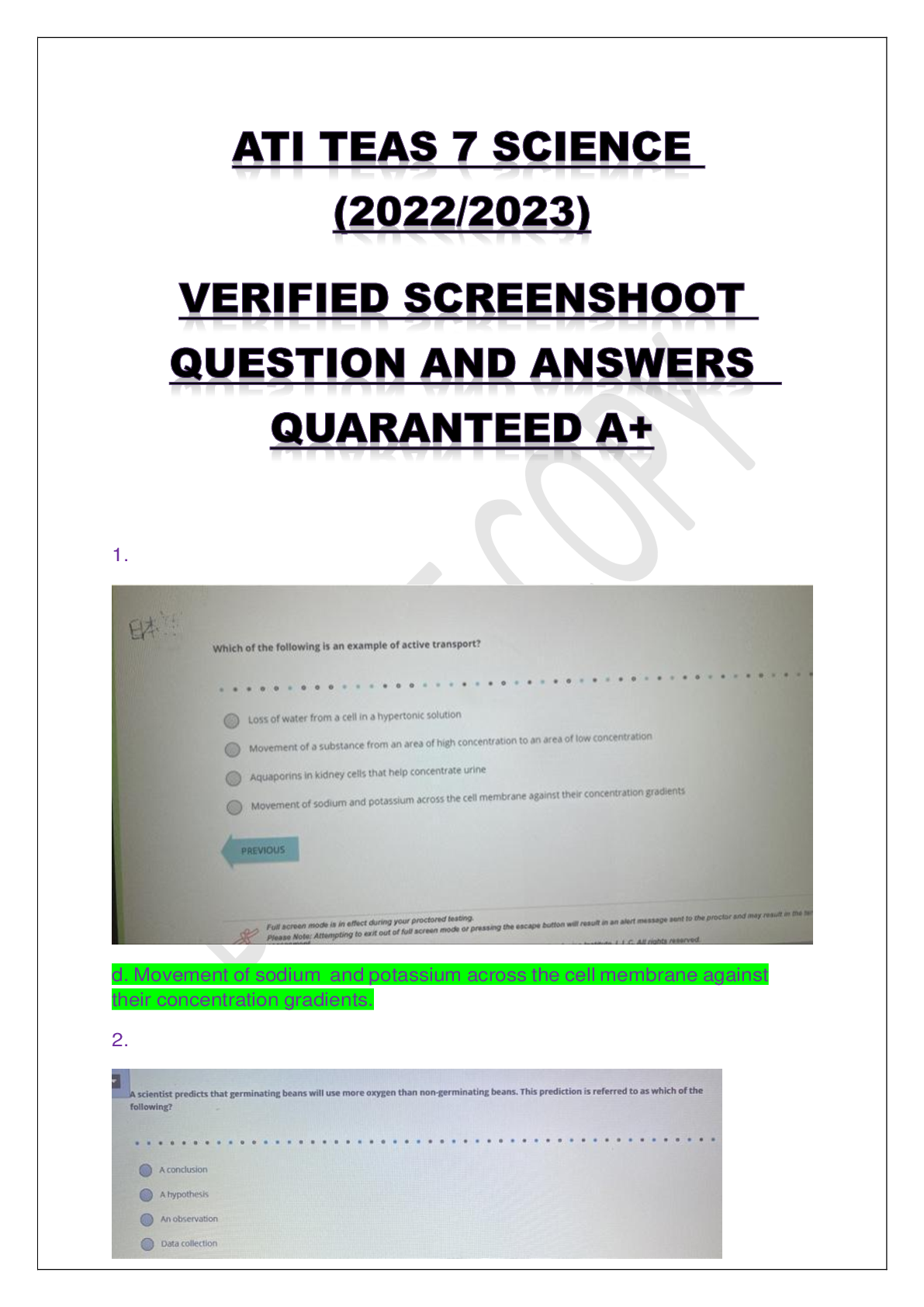
Pediatric ATI Exam Questions and Answers with Complete Solution
Document Content and Description Below
When does the posterior fontanel close? - ANSWER 6-8 weeks When does the anterior fontanel close? - ANSWER 12-18 months How many teeth should an infant have by age 1? - ANSWER 6-8 When is the... Moro reflex present? - ANSWER Birth-4 months When is the palmar grasp present? - ANSWER Birth -3 months When is the plantar grasp present? - ANSWER Birth-8 months When are the sucking and rooting reflexes present? - ANSWER Birth-4 months When is the startle reflex present? - ANSWER Birth-4 months When is the tonic neck reflex present? - ANSWER Birth-3-4 months When is the Babinski reflex present? - ANSWER Birth -1 year When is the stepping reflex present? - ANSWER Birth- 4 weeks 1 month - ANSWER Head lag, strong grasp reflex 2 months - ANSWER Lifts head off mattress when prone, holds hands in open position, grasp reflex fades 3 months - ANSWER Raises head and shoulders off mattress when prone, only slight head lag, no longer has a grasp reflex, keeps hands loosely open. 4 months - ANSWER Rolls from back to side, grasps objects with both hands 5 months - ANSWER Rolls from front to back, uses palmar grasp dominantly. 6 months - ANSWER Rolls from back to front, holds bottle 7 months - ANSWER Bears full weight on feet, sits, moves objects from hand to hand 8 months - ANSWER Sits unsupported, begins using pincer grasp. 9 months - ANSWER Pulls to a standing position, creeps on hands and knees instead of crawling, has a crude pincer grasp, dominant hand preference is evident 10 months - ANSWER Changes from a prone to a sitting position, grasps rattle by its handle. 11 months - ANSWER Cruises or walks while holding onto something, walks with one hand held, places objects into container, neat pincer grasp. 12 months - ANSWER Sits down from a standing position without assistance, tries to build a two-block tower without success, can turn pages in a book. 15 months - ANSWER Walks without help, creeps upstairs, uses a cup well, builds a tower of two blocks 18 months - ANSWER Runs clumsily, falls often, throws ball overhand, jumps in place with both feet, pulls and pushes toys, manages a spoon without rotation, turns pages in a book, builds tower of three or four blocks 2 years - ANSWER Walks up and down stairs by placing both feet on each step, builds a tower of six or seven blocks, turns pages of books one at a time 2.5 years - ANSWER Jumps access the floor and off a chair or step using both feet, stands on one foot momentarily, takes a few steps on tiptoe, draws circles, has good hand-finger coordination. 3 years - ANSWER Rides tricycle, jumps off bottom step, stands on one foot for a few seconds 4 years - ANSWER Skips and hops on one foot, throws ball overhead, catches ball reliably 5 years - ANSWER Jumps rope, walks backward with heel to toe, throws a ball and catches ball with ease If the infant clenches their eyes closed when administering eye drops, where should you administer the drops? - ANSWER In the nasal corner because when he opens his eyes, the meds will enter the eye. When should lidocaine or prilocaine be applied before a puncture? - ANSWER 60 minutes before a superficial puncture or 2.5 hours prior to a deep puncture. Fentanyl - ANSWER used for children older than 12 for continuous pain control When does stranger anxiety usually occur in infants? - ANSWER 6-18 months Preschooler reaction to illness - ANSWER Might believe illness and hospitalization are a punishment. Knows what illness feels like, but limited ability to understand illness. Solitary play - ANSWER Child plays alone Parallel play - ANSWER Children playing independently but among other children. Characteristic of toddlers Associative play - ANSWER Children playing together without organization. Characteristic of preschoolers Manifestations of meningitis in newborns - ANSWER Poor muscle tone, weak cry, poor suck, refuses feeding, v/d, neck is supple without nuchal rigidity, bulging fontanels are a late sign Manifestations of meningitis in 3-month-2 years - ANSWER Seizures with high-pitches cry, fever/irritability, bulging fontanels, possible nuchal rigidity, poor feeding, vomiting Manifestations of meningitis in 2 year-adolescences - ANSWER Seizures, nuchal rigidity, positive Brudzinski’s sign, positive kerning's sign, fever and chills, headaches, vomiting, irritability, restlessness, drowsiness, delirium, stupor, coma, petechiae or purpuric-type rash, involvement of joints, chronic draining ear. Brudzinski's sign - ANSWER flexion of extremities occurring with deliberate flexion of child's neck. Kerning's sign - ANSWER Resistance to extension of the child's leg from a flexed position. What is the definitive diagnostic test for meningitis? - ANSWER Lumbar puncture Nursing actions for a lumbar puncture - ANSWER Topical anesthetic 45 min-1 hour before; side-lying position with head flexed and knees drawn up towards chest, apply pressure and elastic bandage to puncture site after needle is removed. What requires immediate medical attention with meningitis? - ANSWER Presence of purpuric-type rash or petechiae. Meningitis isolation precaution - ANSWER Droplet How long should client stay on isolation precaution with meningitis? - ANSWER 24 hour after first dose of antibiotics Corticosteroids: dexamethasone - ANSWER Not indicated for viral meningitis. Assists in initial management of increased ICP, not effective for long-term. Reduces neurologic complications in children who have infections caused by Hib. Pain medications for meningitis - ANSWER Codeine and acetaminophen. Newborn complications of increased ICP - ANSWER Bulging or tense fontanels, increased head circumference, high-pitched cry, distended scalp veins, irritability, bradycardia, respiratory changes. Children complications of increased ICP - ANSWER Increased irritability, headache, nausea, vomiting, diplopia, seizures, bradycardia, respiratory changes. What organs does Reye syndrome primarily affect? - ANSWER Liver and brain (causes liver dysfunction and cerebral edema) Expected findings for Reye syndrome - ANSWER Lethargy, irritability, combativeness, confusion, delirium, profuse vomiting, seizures, decreased LOC Nursing care with reye's syndrome - ANSWER Avoid extreme flexion, extension, rotation, maintain head in a midline neutral position. HOB elevated 30 degrees. Monitor coagulation. Implement seizure precautions. Epilepsy - ANSWER Chronic, recurring, and diagnosed after two or more unprovoked seizures. Tonic phase of tonic clonic seizure findings - ANSWER 10-30 seconds. Eyes roll up, LOC, contractions of body, mouth shuts, piercing cry, increased salivation, flushing, BP and HR increase, loss of swallowing reflex, apnea. Clonic phase of tonic conic seizure findings - ANSWER 30-50 seconds. Violent jerking movements of the body, trunk and extremities experience rhythmic contraction and relaxation, foaming in mouth, incontinent of urine and feces, gradual slowing of movements. Postictal state of tonic clonic seizure findings - ANSWER 30 minutes. Remains semiconscious but arouses with difficulty, confused for several hours, impaired fine motor movements, lack of coordination, vomiting, headache, sleeps for several hours, sore muscles, no recollection of seizure. Absence seizure - ANSWER LOC lasting 5-10 seconds. Resembles daydreaming or inattentiveness. Lip smacking, twitching of eyelids or face, or slight hand movements. Little to no changes. Myoclonic seizure - ANSWER Variety of seizure episodes, might not lose consciousness. Atonic or akinetic seizure - ANSWER Onset between 2 and 5 years of age. Muscle tone is lost for a few seconds, then followed by a period of confusion. Loss of muscle tone frequently results in falling. West syndrome (infantile spasms) - ANSWER Rare disorder with a peak onset between 3 and 7 months. Twice as common in boys. Sudden, brief, symmetric muscle contractions, possible LOC, flushing, pallor, cyanosis. Aversive seizure - ANSWER Eyes and head turn away from the side of focus, with or without LOC. Most common. Rolandic seizure - ANSWER Tonic-clonic movements involving the face, salivation, arrested sleep, and most common during sleep Complex sensory aura - ANSWER strange feeling in the stomach that rises to the throat, auditory or visual hallucinations, feelings of fear, distorted sense of time and self. Can indicate the origin of the seizure in the brain. Client education for an electroencephalogram (EEG) - ANSWER Abstain from caffeine, wash hair, take deep breaths, will not be painful, may be allowed to sleep during, but might be asked to withhold sleep prior to. Status epilepticus - ANSWER Prolonges seizure activity that lasts longer than 30 minutes or continuous seizure activity in which client does not enter a poetical phase. Normal levels of ICP - ANSWER 1-10mmHg Myopia - ANSWER Sees close objects clearly, but not objects in the distance. Signs of myopia - ANSWER Headaches and vertigo, eye rubbing, difficulty reading, clumsiness, poor school performance Hyperopia - ANSWER Farsightedness. Astigmatism - ANSWER Uneven vision in which only parts of letters on a page can be seen. Headache and vertigo. Anisometropia - ANSWER Different refractive strength in each eye. Amblyopia - ANSWER Lazy eye. Reduced visual acuity in one eye. Strabismus: Esotropia - ANSWER Inward deviation of eye. Strabismus: Exotropia - ANSWER Outward deviation of eye. Cataracts - ANSWER Decreased ability to see clearly Glaucoma - ANSWER Loss of peripheral vision Legal blindness - ANSWER 20/200 or worse Metered Dose Inhaler education - ANSWER Shake inhaler 5-6 times, attach spacer, take deep breath then exhale, tilt head back slightly, breath for 3-5 seconds and hold breath for 5-10 seconds. Wait 1 minute between puffs. Dry Powder Inhaler education - ANSWER Do not shake, exhale completely, hold breath 5-10 seconds. Rinse inhaler, spacer, and cap once per day with warm running water. How long should you suction infants? - ANSWER Less than 5 seconds How long should you suction children? - ANSWER Less than 10 seconds. Accidental decantation in the first 72 hours after surgery - ANSWER An emergency! Early indication of hypoxemia in and infant - ANSWER Cyanosis How long does nebulized aerosol therapy take? - ANSWER 10-15 minutes Hydrocodone - ANSWER Indicated for child having difficulty drinking fluids How long is the recovery period after a tonsillectomy? - ANSWER 14 days [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 8 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jun 28, 2022
Number of pages
8
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jun 28, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
83