*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > NUR-631-Final Exam-Study Guide- Grand Canyon University (All)
NUR-631-Final Exam-Study Guide- Grand Canyon University
Document Content and Description Below
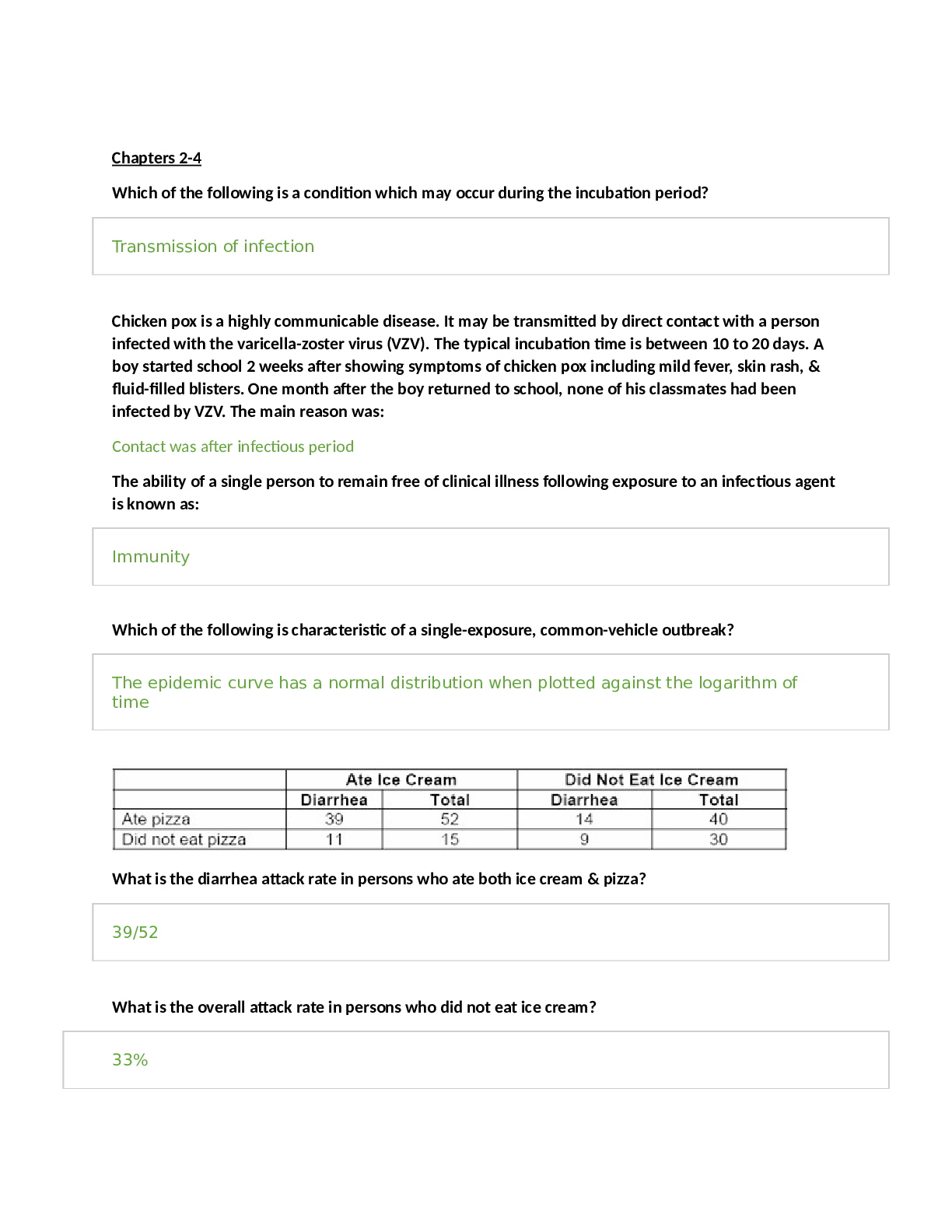
Final Exam – Study Guide Definitions/Descriptions Describe the type of lesions found in psoriasis & seborrheic and actinic keratosis. Elevated, firm, and rough lesion with flat top surface great... er than 1 cm in diameter Describe the skin lesions found in Varicella (chickenpox) and herpes zoster (shingles). Elevated circumscribed, superficial lesion filled with serous fluid, less than 1 cm in diameter Describe the pathogenetic mechanism of polycystic ovarian syndrome (POS). POS has at least two of the following conditions: oligo-ovulation or anovulation, elevated lev- els of androgens, or clinical signs of hyperandrogenism and polycystic ovaries. Of the options available, only this answer accurately defines the pathogenetic mechanisms of POS. Describe Hirschsprung’s disease. Congenital aganglionic megacolon. Mechanical obstruction caused by inadequate motility of part of the intestine, Accounts for ¼ of all cases of neonatal obstruction, Associated with Down’s syndrome, May be acute, life-threatening, or chronic. Absence of ganglion cells in 1 or more segments of the colon, Affects the distal portion ofStool accumulates the GI tract, Lack of enervation produces the functional defects that results in absence of peristalsis, Sphincter fails to relax, Results in obstruction due to failure of evacuation of stool, gas, & liquids, Enterocolitis occurs. Define marasmus and kwashiorkor. Marasmus – Severe wasting, < 70% or <3SD weight/height , No obvious pathology, Looks very skinny. Kwashiorkor- Severe malnutrition with the presence of edema, Multiple pathologies, Looks pudgy. Define deafferentation pain. Type of centrally generated neuropathic pain, injury to either the peripheral or central nervous system Describe myofascial pain syndrome. An acute or chronic painful condition of muscles and their related structures characterized by the presence of myofascial trigger points regional muscle pain syndrome of any soft tissue origin that is associated with muscle tenderness Describe Koplik spots. Describe neuropathic pain. Indicates pain that doesn’t not adhere to typical phases inherent in nociceptive pain on a deeper level. Describe rticarial as seen in an allergic reaction. The smooth, raised red lesions with central blanching that occur because of vasodilation of the capillaries during an allergic reaction What is a varicocele? Dilation of the vein that drains the testes, scrotum feels warm, left side of the scrotum; #1 cause of sterility today Describe the pathophysiology of cystic fibrosis. Alteration in function of CFTR channel. Respiratory tract Thick mucus impairs mucociliary function Recurrent pulmonary infections Acute bronchitis Pneumonia Chronic inflammatory state Airway restriction Fibrosis/Scarring Bronchiectasis Chronic bronchitis Cycle of progression – one thing leads to another Describe Raynaud’s disease. Vasospastics disorder of the large arteries and veins of the upper and lower extremities. attacks of vasospasm in the small arteries and arterioles of the fingers and, less commonly, of the toes characterize Raynaud phenomenon and Raynaud disease and is the only option that actually describe. What medical term is used to identify an inflammatory disorder of the skin that is often considered synonymous with dermatitis and characterized by pruritus with lesions that have an indistinct border? The most common inflammatory disorder of the skin is eczema, or dermatitis. Eczema and dermatitis are general terms that describe a particular type of inflammatory response in the skinÑthese terms can be used interchangeably. Pruritus, lesions with indistinct borders, and epidermal changes generally characterize diseases that are considered eczematous. Of the available options, only eczema is associated with these characteristics What is a painless diverticulum of the epididymis located between the head of the epididymis and the testis called? Spermatocele Describe intestinal malrotation. Intestinal malrotation is a condition that is congenital (present at birth) and results from a problem in the normal formation of the fetal intestines. There is a disruption in the usual steps that the intestines follow to arrive at the correct position within the abdomen. Malrotation causes the parts of the intestine to settle in the wrong part of the abdomen, which can cause them to become blocked or to twist. What is the medical term for a fungal infection of the nail plate? Onychomycosis is a fungal infection of the fingernails or toenails. The actual infection is of the bed of the nail and of the plate under the surface of the nail. Content Questions What type of necrosis is associated with wet gangrene? Wet gangrene develops only when neutrophils invade the site, causing liquefactive necrosis. After ovulation, the uterine endometrial cells divide under the influence of estrogen. This process is an example of hormonal . Hormonal hyperplasia chiefly occurs in estrogen-dependent organs, such as the uterus and breast. After ovulation, for example, estrogen stimulates the endometrium to grow and thicken for reception of the fertilized ovum. The other options do not accurately describe the process identified in the question Removal of part of the liver leads to the remaining liver cells undergoing compensatory . Compensatory hyperplasia is an adaptive mechanism that enables certain organs to regenerate. For example, the removal of part of the liver leads to hyperplasia of the remaining liver Cells (hepatocytes) to compensate for the loss. The other options do not accurately identify the compensatory process described in the question Why is insulin used to treat hyperkalemia? Insulin contributes to the regulation of plasma potassium levels by stimulating the Na+, potassium Dadenosine triphosphatase (K=Datpase) pump, thereby promoting the movement of potassium simultaneously into the liver and muscle cells with glucose transport after eating. What 3 substances influence the calcium and phosphate balance in the body? Three hormones regulate calcium and phosphate balance: parathyroid hormone (PTH), vitamin D, and calcitonin. Vasopressin, thyroid hormone, and vitamin A do not influence calcium and phosphate balance What is the risk for the recurrence of autosomal dominant diseases? The recurrence risk for autosomal dominant diseases is usually 50% What cancer does human herpes virus (HHV) 8 cause? HHV-8 infection causes Kaposi sarcoma The BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations increase the risk of which cancer in women? BRCA1 mutations increase the risk of ovarian cancer among women (20% to 50% lifetime risk), and BRCA2 mutations also confer an increased risk of ovarian cancer (10% to 20% life- time prevalence). BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations are not currently believed to be linked with risks of lung, uterine, or pancreatic cancers. How is chronic myelogenous leukemia diagnosed? Is based on the histopathologic findings in the peripheral blood and the Philadelphia chromosome in bone marrow cells How does obesity act as an important risk factor for type 2 diabetes mellitus? People with type 2 diabetes mellitus su²er from insulin resistance (i.e., their cells have di³culty using insulin). The other options are not associated with the e²ect of obesity regarding insulin production What does hypomethylation and the resulting effect on oncogenes result in? Tumor cells typically exhibit hypomethylation (decreased methylation), which can increase the activity of oncogenes. Hypomethylation increases as tumors progress from benign neo- plasms to malignancy. Only the correct option accurately describes hypomethylation and its resulting effects Which component of the plasma protein system tags pathogenic microorganisms for destruction by neutrophils and macrophages? C3b (a component of the complement cascade) adheres to the surface of a pathogenic microorganism and serves as an eFcient opsonin. Opsonins are molecules that tag microorganisms for destruction by cells of the in±ammatory system, primarily neutrophils and macrophages. The other options do not accurately identify a component capable of tagging pathogenic microorganisms. What causes meconium ileus? Meconium ileus is intestinal obstruction caused by meconium formed in utero that is abnor- mally sticky and adheres firmly to the mucosa of the small intestine, resisting passage beyond the terminal ileum. The cause is usually a lack of digestive enzymes during fetal life. Which cell is the body’s primary defense against parasitic invasion? Eosinophils serve as the bodyOs primary defense against parasites. T lymphocytes and B lymphocytes are involved in acquired immunity. Neutrophils are the predominant phagocytes in the early inflammatory site. What type of immunity is produced when an immunoglobulin crosses the placenta? An individual produces active-acquired immunity (active immunity) after natural exposure to an antigen or after immunization, whereas passive-acquired immunity (passive immunity) does not involve the host’s immune response at all. The innate immune system, also known as nonspecific immune system and the first line of defense, is composed of the cells and mechanisms that defend the host from infection by other organisms in a nonspecific manner, which means that the cells of the innate system recognize and respond to pathogens in a generic way Which antibody initially indicates a typical primary immune response? Typically, IgM is produced frst (primary immune response), Followed by IgG against the same antigen. The other options are not involved During an IgE-mediated hypersensitivity reaction, which leukocyte is activated? Only eosinophils are activated during IgE- mediated hypersensitivity reactions. Tissue damage caused by the deposition of circulating immune complexes containing an antibody against the host DNA is the cause of which disease? Only the deposition of circulating immune complexes containing an antibody against the host DNA produce tissue damage in individuals with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). List 4 disorders which are considered autoimmune. Rheumatoid arthritis, Systemic lupus erythematosus (lupus), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), Multiple sclerosis (MS). Which organism is a common sexually transmitted bacterial infection? Treponema pallidum (spirochete, syphilis) is a sexually transmitted disease. Staphylococcus aureus is commonly ingested, causing food poisoning; Clostridium perfringens (gas gangrene) is a skin or wound infection; and Helicobacter pylori (gastritis, peptic ulcers) is found in the gastrointestinal tract What does stress-induced sympathetic stimulation of the adrenal medulla cause secretion of? The sympathetic nervous system is aroused during the stress response and causes the medulla of the adrenal gland to release catecholamines (80% epinephrine and 20% norepinephrine) into the bloodstream. The stress-induced efforts on the adrenal medulla do not include any of the other options What is the effect of increased secretions of epinephrine, glucagon, and growth hormone? Cortisol enhances the elevation of blood glucose promoted by other hormones, such as epi- nephrine, glucagon, and growth hormone. This effect is not true of the other options. What disorder results from collection of fluid in the tunica vaginalis? hydrocele What is the most commonly reported symptom of cancer treatment? Fatigue is the most frequently reported symptom of cancer and cancer treatment. Although patients report the other options, they are not as frequently experienced as fatigue Research has shown a link between cancer and which sexually transmitted disease? Human papillomavirus (HPV) is the most common sexually transmitted virus in the United States. High-risk, or oncogenic, HPVs can cause cancer. A persistence of infection with high- risk HPV is a prerequisite for the development of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) le- sions and invasive cervical cancers. No research supports such a link between the remaining options and cancer. What is the function of arachnoid villi? CSF is reabsorbed by means of a pressure gradient between the arachnoid villi and the cere- bral venous sinuses. The remaining options do not accurately describe the function of arach- noid villi. What provides the collateral blood flow to the brain? The arterial circle (circle of Willis) (see Figure 15-20) is a structure credited with the ability to compensate for reduced blood flow from any one of the major contributors (collateral blood flow). The remaining options are not considered sources of collateral blood flow Dilation of the ipsilateral pupil, following herniation, is the result of pressure on which cranial nerve (CN)? The oculomotor CN (III) is involved in this manifestation of pupil dilation. None of the other options would result in pupil dilation when subjected to pressure What is the central component of the pathogenic model of multiple sclerosis? Demyelination of nerve fibers in the CNS What hematologic disorder is diagnosed by the Philadelphia chromosome? Chronic myelogenous leukemia Where is antidiuretic hormone (ADH) synthesized, and where does it act? Once synthesized in the hypothalamus, ADH acts on the vasopressin 2 (V2) receptors of the renal duct cells to increase their permeability. This information helps eliminate the other op- tions. What is diabetes insipidus the result of? Diabetes insipidus results from an imbalance of the hormone antidiuretic hormone (ADH) or its receptor and creates polyuria or frequent urination. Renal failure is the most common cause of which type of hyperparathyroidism? Chronic renal failure is the most common cause of secondary hyperparathyroidism because of the resulting hyperphosphatemia that stimulates parathyroid hormone secretion. Although the other options may occur, they are not the most common types of the disorder. What directly causes ovulation during the menstrual cycle? Menstrual cyclicity and regular ovulation are dependent on (1) the activity of the gonadostat (GnRH pulse generator); (2) the pituitary secretion of gonadotropins; and (3) estrogen (estra- diol)Ðpositive feedback for the preovulatory LH and FSH surges, oocyte maturation, and cor- pus luteum formation What condition results from the rotation of a testis, which twists blood vessels of the spermatic cord? Testicular torsion Identify the functions of the following cranial nerves. • Trigeminal nerve- The sensory function of the trigeminal nerve is to provide tactile, proprioceptive, and nociceptive afference to the face and mouth. Its motor function activates the muscles of mastication, the tensor tympani, tensor veli palatini, mylohyoid and the anterior belly of the digastric • Hypoglossal nerve- is primarily responsible for the movement of the tongue. It's a mixed nerve, meaning it has both a sensory (going to the brain) and motor (going to the tongue) pathway. Its function, however, is mostly motor in controlling the muscle that makes up the tongue. • Abducens nerve- It controls the eye's lateral rectus muscle, which moves the eye sideways, away from the nose. • Olfactory nerve- It relays sensory data to the brain, and it is responsible for the sense of smell. Which virus is a precursor for developing cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) and cervical cancer? Infection with high-risk (oncogenic) types of HPV (predominantly 16 and 18) is a necessary precursor to the development of precancerous dysplasia of the cervix that leads to invasive cancer. The other options are not precursors to CIN and cervical cancer The risk of which cancer is greater if the man has a history of cryptorchidism? The risk of testicular cancer is 35 to 50 times greater in men with cryptorchidism or in those with a history of cryptorchidism than it is for the general male population. This is not true of the other options Which age group should be targeted for testicular cancer education and screening? Overall, testicular cancers are rare, yet they are the most common form of cancer in young men between the ages of 15 and 35 years Which organism is responsible for the development of syphilis? T. pallidum is the only cause of syphilis Which is a characteristic lesion of secondary syphilis? The only secondary syphilis lesion is the condylomata lata Which skin disorder results in an elevated, firm circumscribed area less than 1 cm in diameter? Papule What does celiac sprue cause? Celiac Sprue, also known as celiac disease, is a condition in the small intestine caused by an immunological reaction to gluten (proteins found in wheat) which in turn, causes destruction in the inner lining of the small intestine. What causes condylomata acuminata or genital warts? Genital warts, or condylomata acuminata, are caused by various strains of papillomavirus. Male patients may have warts anywhere on the external genitalia, but commonly on the penile shaft or glans. Warts may also be found in the urethra, as well as around or within the anus. Patients with genital herpes have type 2 virus, that result in vesicles grouped together on an erythematous base. Nongonococcal urethritis has several specific causes. Which substance is used to correct the chronic anemia associated with chronic renal failure? One of the most significant advances in the study of hematopoietic growth factors has been the development of erythropoietin for individuals with chronic renal failure. The other options are not associated with the treatment of chronic anemia After a person has a subtotal gastrectomy for chronic gastritis, which type of anemia will result? From the options available, only pernicious anemia is caused by vitamin B 12 deficiency, which is often associated with the end-stage type A chronic atrophic gastritis When considering hemolytic anemia, why does jaundice occur? Jaundice (icterus) is present when heme destruction exceeds the liverÕs ability to conjugate and excrete bilirubin. This selection is the only option that accurately describes the process that affects the occurrence of hemolytic anemiaÐrelated jaundice What type of cancer could HPV cause? Cervical Cancer Hemophilia A is considered to be what type of inherited disorder? Hemophilia A (classic hemophilia) is inherited as an X-linked recessive disorder. This selection is the only option that correctly identifies how this disorder is inherited Which type of cancer could Helicobacter pylori cause? Stomach cancer In which type of pleural effusion does the fluid become watery and diffuse out of the capillaries as a result of increased blood pressure or decreased capillary oncotic pressure? In transudative pleural effusion, the fluid, or transudate, is watery and diffuses out of the cap- illaries as a result of disorders that increase intravascular hydrostatic pressure or decrease cap- illary oncotic pressure. The described mechanism is not associated with the other forms of pleural effusion Which hormone is required for water to be reabsorbed in the distal tubule and collecting duct? Antidiuretic hormone is required for water to be reabsorbed in the distal tubule and collecting duct. The later, straight segment of the distal tubule and the collecting duct are permeable to water as controlled by antidiuretic hormone. The other options are not involved in this process With which medical diagnosis is meconium ileus often associated? The detection of albumin in meconium has been used as a screening test for cystic fibrosis. This condition is not associated with any of the other options What type of fracture occurs at a site of a preexisting bone abnormality is a result of a force that would not normally cause a fracture? Only a pathologic fracture is a break at the site of a preexisting abnormality, usually by force that would not fracture a normal bone Considering the pathophysiologic process of osteoporosis, which hormone exerts antiapoptotic effects on osteoblasts but proapoptotic effects on osteoclasts? Postmenopausal osteoporosis occurs in middle-aged and older women. It can occur because of estrogen deficiency, as well as estrogen-independent, age-related mechanisms (e.g., sec- ondary causes such as hyperparathyroidism and decreased mechanical stimulation). Recent studies indicate that increased oxidative stress (OS) and increased intracellular reactive oxy- gen species (ROS) play significant roles in the development of age-related bone loss, as well as other age- related changes in the body. Hormonal deficiency also can increase with stress, excessive exercise, and low body weight. Increased formation and longevity of osteoclasts re- sults in increased bone resorption and is associated with a cascade of proinflammatory cy- tokines Which disorder is characterized by the formation of abnormal new bone at an accelerated rate beginning with excessive resorption of spongy bone? Of the available options, only Paget disease (osteitis deformans) is a state of increased meta- bolic activity in bone characterized by abnormal and excessive bone remodeling, both resorp- tion and formation. Chronic accelerated remodeling eventually enlarges and softens the af- fected bones Which medical diagnosis is described as a chronic inflammatory joint disease characterized by stiffening and fusion of the spine and sacroiliac joints? Of the options available, only ankylosing spondylitis (spondyloarthritis) is described as a chronic, inflammatory joint disease characterized by stiffening and fusion (ankylosis) of the spine and sacroiliac joints People with gout are at high risk for which co-morbid condition? Renal stones are 1000 times more prevalent in individuals with primary gout than they are in the general population. This statement is not true of any of the other options An insufficient dietary intake of which vitamin can lead to rickets in children? Rickets results from either insufficient vitamin D, insensitivity to vitamin D, wasting of vita- min D by the kidney, or inability to absorb vitamin D and calcium in the gut. Vitamin D is the only vitamin associated with rickets Which virus is associated with infectious mononucleosis? Epstein-Barr virus, and patients often exhibit a fever, sore throat, swollen glands, and fatigue for several weeks. In some patients, the virus can reactivate later and cause physical symptoms once again. the virus was latent in these patients, and then switched to the active form and began making new virus particles Which protein, absent in muscle cells of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, mediates the anchoring of skeletal muscle fibers to the basement membrane? Dystrophin What is the most common malignant bone tumor diagnosed during childhood? Of the options available, osteosarcoma is the most common bone tumor that occurs during childhood; it originates from bone-producing mesenchymal cells Chickenpox (varicella) may be followed years later by which disorder? The same herpesvirusÑ varicella zoster virus (VZV)Ñcauses both herpes zoster (shingles) and varicella (chickenpox). Varicella is the primary infection, followed years later by herpes zoster, particularly among those who are immunosuppressed. These statements are not true of any of the other options. The staff member of a crowded day care center is a source for which bacterial infection? Impetigo is a common bacterial skin infection in infants and children and is particularly infec- tious among people living in crowded conditions with poor sanitary facilities or in settings such as day care facilities. The other options are not as infectious as impetigo Which of the following disorders has a mode of inheritance similar to hemophilia A? Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) Which organism could cause stomach cancer? Helicobacter pylori List 3 types/conditions of arteritis. Osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Psoriatic Arthritis List 3 conditions jaundice could be attributed to. Acute inflammation of the liver, Hemolytic anemia, Cholestasis What is the primary cause of respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) of the newborn? RDS is primarily caused by surfactant deficiency and secondarily by a deficiency in alveolar surface area for gas exchange. None of the other options are related to the cause of RDS What is the most common cause of uncomplicated urinary tract infections? The most common infecting microorganisms are uropathic strains of E. coli (80% to 85%) List 4 conditions that prerenal injury from poor perfusion can result from. Poor perfusion can result from renal artery thrombosis, hypotension related to hypovolemia (dehydration, diarrhea, fluid shifts) or hemorrhage, renal vasoconstriction and alterations in renal regional blood flow, microthrombi, or kidney edema that restricts arterial blood flow. Bi- lateral ureteral obstruction is not associated with prerenal injuries. In immunoglobulin G (IgG) nephropathies such as glomerulonephritis, IgG is deposited in which location? Glomerulonephritis develops with the deposition of antigen-antibody complexes (IgG, im- munoglobulin A [IgA], and C3 complement) in the glomerulus, or the antigen may be trapped within the glomerulus and immune complexes formed in situ. Immunofluorescence mi- croscopy shows lumpy deposits of IgG and C3 complement on the glomerular basement mem- brane (see Figure 39-5). When considering IgG nephropathies, the only location of the IgG immunoglobulins is the correct option By what mechanism does intussusception cause an intestinal obstruction? Intussusception is the telescoping of part of the intestine into another section of intestine, usu- ally causing strangulation of the blood supply. This selection is the only option that accurately describes how intussusception causes an intestinal obstruction. Clinical Scenarios 1. A patient presents with vomiting a coffee-ground looking substance; fatigue, postural hypotension; new onset systolic murmur; and cool, pale peripheries. 1. BP 86/42, P 124, R 28 and labored, T 97.5 2. Na 130, Cl 87, K 4.3, Glucose 58, Bun 46, Creat 3.6, Hgb 6.2 3. UA ketone positive 4. pH 7.10, PCO2 20, HCO3 14 Using the information above, evaluate the lab findings (indicate low, normal, or high). Na – low, CL – low, K – normal, Glucose – low, Bun – normal, Crea – high, Hgb – low. UA – Abnormal. PH – low, PCO2 – low, HCO3 - low 2. A person diagnosed with type 1 diabetes experiences hunger, lightheadedness, tachycardia, pallor, headache, and confusion. What is the most probable cause of these symptoms? Hypoglycemia caused by increased exercise. The most likely cause of these symptoms is hypoglycemia, which is often caused by a lack of systemic glucose resulting from muscular activity 3. After a partial gastrectomy or pyloroplasty, clinical manifestations that include increased pulse, hypotension, weakness, pallor, sweating, and dizziness are the results of which mechanism? Dumping syndrome occurs with varying severity in 5% to 10% of individuals who have un- dergone partial gastrectomy or pyloroplasty. Rapid gastric emptying and the creation of a high osmotic gradient in the small intestine cause a sudden shift of fluid from the vascular compart- ment to the intestinal lumen. Plasma volume decreases, causing vasomotor responses, such as increased pulse rate, hypotension, weakness, pallor, sweating, and dizziness. Rapid distention of the intestine produces a feeling of epigastric fullness, cramping, nausea, vomiting, and diar- rhea. This selection is the only option that accurately identifies the mechanism responsible for the described situation. 4. Klinefelter’s syndrome is a chromosomal abnormality with an XXY outcome. What does that mean for the patient? small testes, other abnormalities. Patient B’s karyotype was noted as 47 XXY, meaning that this patient has 47 chromosomes, is a male, and has an extra sex chromosome. The diagnosis would be Klinefelter’s syndrome because he presents with one or more sex chromosomes. 5. On review of a patient’s X-ray, you discover punched out lesions. What disease is responsible? Multiple Myeloma 6. Provide two examples of nutrition related anemia. Provide the correct medical terminology (size and shape). Include how you would evaluate a CBC for the findings of this type of anemia. 1. Pernicious Anemia- Macrocytic-normochromic anemia: large, abnormally shaped erythrocytes but normal hemoglobin concentration. CBC- Hgb, Hema, Reticulocyte and Serum b12 (low). Mean corpus, Plasma Iron and ferritin (high). Billirubin and Transferrin (slightly high). Folate, Total Iron Binding and Free erythrocytes (normal). 2. Iron deficiency anemia- Microcytic-hypochromic anemia: small, abnormally shaped erythrocytes and reduced hemoglobin concentration. CBC- Hgb, Hema, Mean corpu, Plasma Iron, Ferritin and Transferrin (low). Total Iron and Free Erythrocyte (high). Serum b12, folate and bilirubin (normal). Reticulocyte count (Could be normal or slightly high or low). 7. A patient is diagnosed with pulmonary disease and elevated pulmonary vascular resistance. Which form of heart failure may result from pulmonary disease and elevated pulmonary vascular resistance? Right side hearth failure is defined as the inability of the right ventricle to provide adequate blood flow into the pulmonary circulation at a normal central venous pressure. This condition is often a result of pulmonary disease and the resulting elevated pulmonary vascular resistance. 8. Which compensatory mechanism is spontaneously used by children diagnosed with Tetralogy of Fallot to relieve hypoxic spells? Squatting is a spontaneous compensatory mechanism used by older children to alleviate hy- poxic spells. Squatting and its variants increase systemic resistance while decreasing venous return to the heart from the inferior vena cava. The other options would not result in these changes. 9. What are the TLC, FEV1, and V/Q for silicosis (increased, decreased, normal). TLC decreased, FEV1 Decreased, V/Q decreased 10. A patient presents with right ventricular hypertrophy seen as a right axis deviation on the EKG and a loud systolic murmur heard at the left sternal border. What valve is the cause? Mitral Stenosis [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 14 pages
Instant download

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 11, 2021
Number of pages
14
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 11, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
33