Business Analytics > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > MGT 6203 Homework 3- Questions & Answers | All Answers Correct (All)
MGT 6203 Homework 3- Questions & Answers | All Answers Correct
Document Content and Description Below
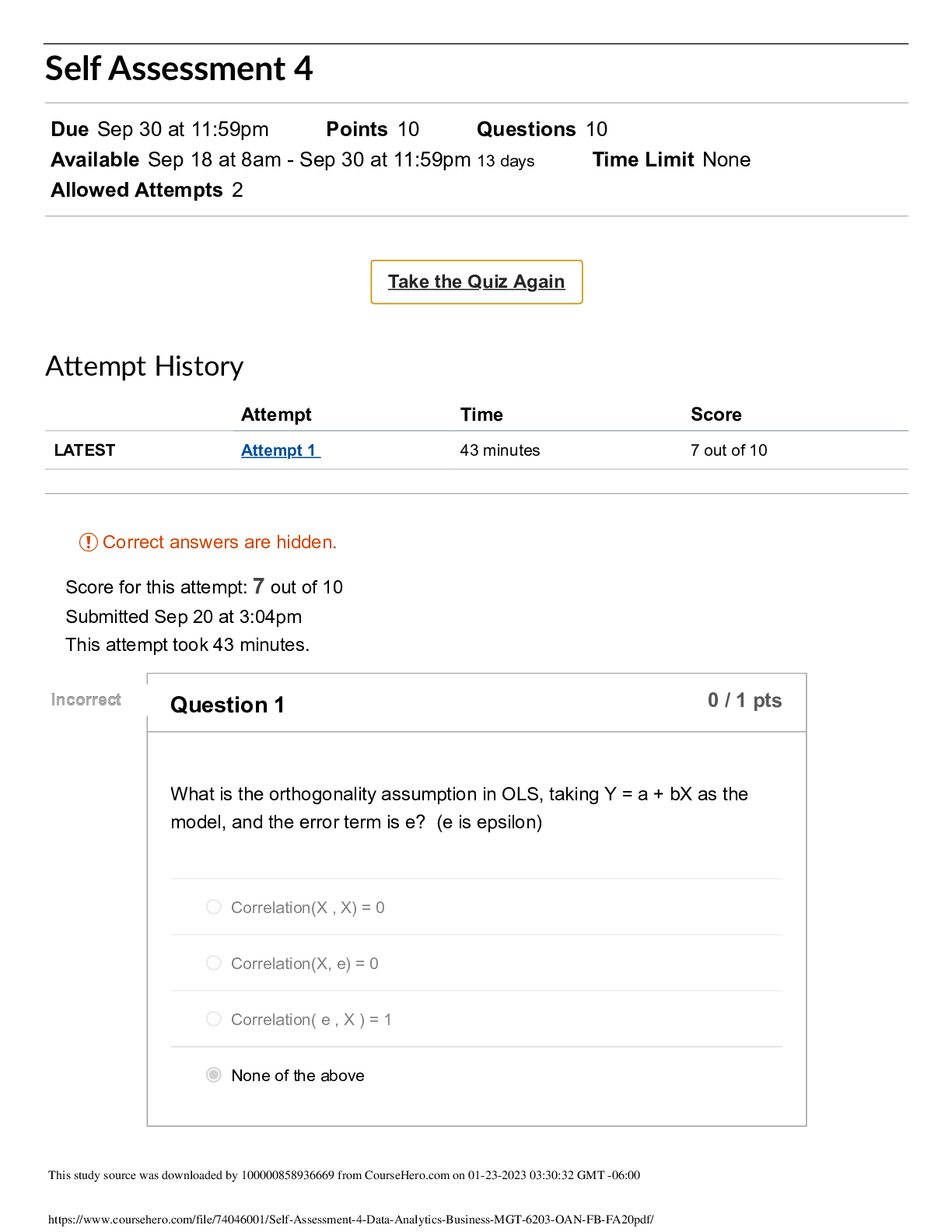
MGT – 6203: Homework 3 100 points: Part 1 (60 points Quiz) + Part 2 (40 points Peer-Corrected) Part 1 (all questions 5 points) Q.1 From 2012 to 2018, which pricing model (Performance, CPM, Hybrid... ) has brought in the most revenue? a. Performance pricing model b. CPM pricing model c. Hybrid pricing model d. All models have performed the same Explanation: Week 7, Video 3, Slide 13 Q.2 What does CPM stand for? a. Cost Per Million b. Cost Per Thousand c. Counts Per Hundred d. None of the Above Explanation: CPM = Cost Per Mille = Cost Per Thousand Q.3 Which of the following statements is correct with respect to Bounce Rate? A. Bounce Rate gives an indication of the proportion of visitors who did not interact with the website. B. Bounce Rate tells us how long, on average, visitors are staying on our website. C. Bounce Rate increases when someone loads a page and decreases after 30 minutes of inactivity. D. A high Bounce Rate generally indicates that the website entrance pages are very relevant to the website’s visitors. Answer: A Explanation: Statement A is correct. B) Average Session Duration defines how long, on average, visitors are staying on the website. C) A session starts right away when someone loads a page and ends after 30 minutes of inactivity. D) A high Bounce Rate generally indicates that the website entrance pages are not relevant to the website’s visitors. Q.4 A company is doing an ad campaign where the details of the ad are presented below. (Assume that a customer would purchase twice in his/her life-time upon watching the advertisement once) Metric Value Avg CPC (Cost per click) $1.05 Conversion Rate 7% Avg.Sale Value $80 Profit Margin 20% What is the break-even price of average CPC per customer over lifetime? A. $1.12 B. $2.24 C. $1.19 D. $2.48 Solution: 32*0.07 = 2.24 PPC Conversion cost = $1.05/0.07 = 15 Profit Margin per sale = $80*0.2 = 16 Profit Margin per customer over lifetime (excluding advertisement costs) = 32 Total profit per customer = 32 – 15 = 17 For break even the cost = 32*0.07 = 2.24 Q.5 The objective of Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO) is to: A. Increase number of website visitors B. Increase website sales C. Enhance engagement D. All the above Answer: D Explanation: From the slides, we learnt that Conversion rate optimization (CRO) is the systematic process of increasing the percentage of website visitors who take a desired action. Desired actions are different based on website goals. So above choices are general goals of all websites, and they are CRO goals. Q.6 A website that uses Google Analytics wants to know the percentage of visitors that do not interact with the website. Which metric should be used? A. Page per sessions B. Pageviews C. Users D. Bounce Rate Answer: D Explanation: The following is how every choice may be defined – A: Page Per Session-dividing the total number of pageviews by the total number of sessions. It is good indicator of overall user engagement. B: Pageviews -any view of a page that is being tracked by Google Analytics. C: Users -Total number of unique visitors to the website D: Bounce Rate -It is the number of single-page sessions (bounces) divided by the total number of sessions. It shows the proportion of visitors who did not interact with the website. Questions 7-8 can be answered using case study: Chase Q.7 In the Chase case, Chase segmented customers based on the types of rewards they preferred. Which segmentation strategy does Chase use? A. Behavioural method B. Demographic method C. Psychographic method Answer: A Explanation: The following line from the case study may be used to answer the above question– “Behavioral/attitudinal segmentation provided insight into how consumers used their cards andhow much they valued rewards and/or what types of rewards they preferred (cashback, miles, points) as well as their channel preferences.” Q.8 A complete economics of credit card transaction includes: A. Card Issuer; Merchant Acquirer; Merchant B. Card Issuer; Cardholder; Merchant Issuer; Merchant C. Card Issuer; Cardholder; Merchant; Merchant Acquirer; Credit Card Network D. Card Issuer; Cardholder; Merchant; Merchant Issuer; Credit Card Network Q9 The following questions are based on the Advertising dataset (Advertising_Updated.csv). The sales are in thousands of units, while the advertising budgets (TV, Radio, Newspaper) are in thousands of doll [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 15 pages
Instant download

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Also available in bundle (1)
MGT 6203 COMPLETE COURSE
MGT 6203 Homework 3- Questions & Answers | All Answers Correct Week 10 Self Assessment 6_ Data Analytics Business - MGT-6203-OAN MGT 6203 Homework 3- Questions & Answers | All Answers Correct...
By d.occ 2 years ago
$36
18
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Oct 21, 2021
Number of pages
15
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Oct 21, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
350





.png)

.png)