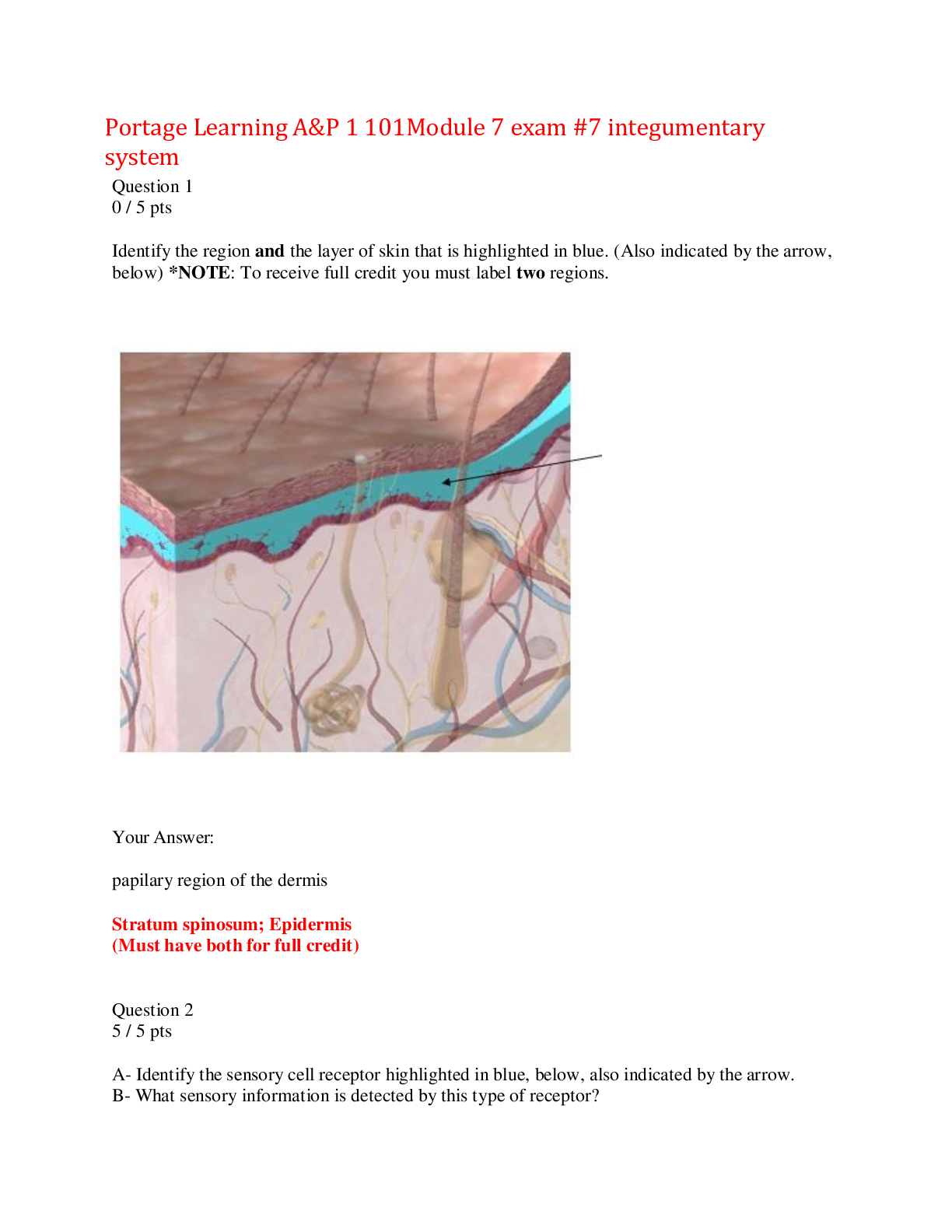
NURSING NCLEX Module 4 Exam Questions and Answers,100% CORRECT
Document Content and Description Below
NURSING NCLEX Module 4 Exam Questions and Answers Submission Details • Submission Date: 1/13/2017 • Submission Time: 9:48 PM • Points Awarded: 93 • Points Missed: 7 • Number of Attempt... s Allowed: 1 • Not Scored: 0 • Percentage: 93% 1. Questions 1. 1.ID: 9476884715 A schizophrenic client says, “I’m away for the day ... but don’t think we should play or do we have feet of clay?” Which alteration in the client’s speech does the nurse document? A. Neologism B. Word salad C. Clang association Correct D. Associative looseness Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 2. 2.ID: 9476884735 A client with schizophrenia and his parents are meeting with the nurse. One of the young man’s parents says to the nurse, “We were stunned when we learned that our son had schizophrenia. He was no different than from his older brother when they were growing up. Now he’s had another relapse, and we can’t understand why he stopped his medication.” Which response by the nurse is appropriate? A. Telling the parents, “Medication noncompliance is the most frequent reason that people with this diagnosis relapse.” B. Telling the parents, “Well, it’s his decision to take his medicine, but it’s yours to have him live with you if he stops the medication.” C. Asking the client, “How can we help you to take your medicine or to tell us when you’re having problems so that your medication can be adjusted?” Correct D. Saying to the parents, “Your concerns are appropriate, but I wonder whether your son was having trouble telling someone that he had concerns about his medication.” Rationale: The therapeutic response is the one in which the nurse models speaking directly to the client. This facilitates further assessment of the situation and helps elicit the causes of and motivations for the client’s behavior for both the nurse and the family. In the correct option, the nurse also seeks clarification of the degree of openness and mutuality felt by the client and his family toward each other. The nurse provides information to the family when stating that noncompliance is the most frequent reason for relapse in people with this diagnosis. However, the statement is nontherapeutic at this time because it does not facilitate the expression of feelings. The nurse uses a superego style of communication when stating, “Well, it’s his decision to take his medicine, but it’s yours to have him live with you if he stops the medication.” The content of this statement may be true, but it is nontherapeutic in that it carries a threatening message and may prevent the family from trusting the nurse. By stating, “Your concerns are appropriate, but I wonder whether your son was having trouble telling someone that he had concerns about his medication,” the nurse gives approval and prematurely analyzes the client’s motivation without sufficient assessment. TestTaking Strategy: Use your knowledge of therapeutic communication techniques and remember to focus on the client’s feelings. Also note that the correct option is the only option in which the nurse directly addresses the client. Review: therapeutic communication techniques . Reference: Stuart, G. (2009). Principles & practice of psychiatric nursing (9th ed., pp. 2731). St. Louis: Mosby. Varcarolis, E., & Halter, M. (2009). Essentials of psychiatric mental health nursing: A communication approach to evidencebased care (p. 297). St. Louis: Saunders. Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Psychosocial Integrity Integrated Process: Communication and Documentation Content Area: Mental Health Giddens Concepts: Adherence, Psychosis HESI Concepts: Behaviors—Adherence, Cognition—Psychosis Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 3. 3.ID: 9476898981 An acutely ill schizophrenic client says to the nurse, “He keeps saying that he likes you, and I keep telling him you’re married, but he won’t listen, and I think he’s going to get fresh with you.” Once the nurse has determined that the client is hallucinating, which response to the client would be most appropriate statement? A. “Try not to listen to the voices right now so that I can talk with you.” Correct B. “I think that you can help him stop his behavior if you concentrate.” C. “Tell him I said to mind his p’s and q’s or I’ll call the police on him.” D. “I think that you’re trying to share your own feelings toward me, but you’re shy.” Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 4. 4.ID: 9476882056 A client says to the nurse, “It’s over for me — the whole thing is over.” Which response by the nurse would be therapeutic? A. “What do you mean, ‘The whole thing is over’?” B. “Over? Well, that sounds pretty drastic to me. Let’s discuss this in the strictest confidence.” C. “Can you tell me more about why it’s over for you? I’ll keep your thoughts strictly confidential.” D. “Let’s talk more about your feeling that the whole thing is over for you. This is important, and I may need to share your feelings with other staff members.” Correct Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 5. 5.ID: 9476895020 The nurse performing a lethality assessment asks the client whether he is thinking of suicide. Which statement by the client would be of most concern to the nurse? A. “No, I wasn’t, but I am now, thanks to you.” Correct B. “I hadn’t thought of that, but I can see that you are.” C. “Of course not, but there are days when I think that I should be.” D. “What is suicide going to do for me except get me excommunicated from the church?” Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 6. 6.ID: 9476886322 A client who has expressed suicidal ideation in the past says to the nurse, while shuffling several documents in an effort to organize them, “Well, I’m feeling so much better now since I got organized. My lawyer wrote my will and durable power of attorney.” Which response by the nurse is most appropriate? A. “Good grief! You don’t look organized to me.” B. “Okay, what are you up to today? Your behavior is not appropriate.” C. “You talk about getting organized. Are you thinking of killing yourself?” Correct D. “If you keep behaving like this, you know that I’ll have to tell the health care provider, and we’ll have to seclude you.” Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 7. 7.ID: 9476896317 An adolescent client says, “I’m just a burden to my folks. They wish I’d never been born. My dad told me he had to marry Mom because she got pregnant.” Which response by the nurse would be therapeutic? A. “You’re feeling that your folks didn’t want you, but they chose to marry and have you.” Correct B. “You feel that you were a burden and not wanted? Let’s talk with your parents to see whether you’re right.” C. “Let’s speak with your parents about what you’ve just told me. Let’s ask whether you were truly unwanted.” D. “Sounds like your father was very inappropriate, but I’m certain that he didn’t mean that you were a burden to him.” Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 8. 8.ID: 9476897762 A client says to the nurse, “I’ve ruined my life. I left college with only a few credits to go. I keep telling myself that I’m going to make it as a writer, but I’ll be a loser and a nothing for the rest of my life.” Which response by the nurse is therapeutic? A. “What are you saying? Sounds like you need to pull yourself together and go back to school.” B. “Having faith in yourself is one thing, but looking at your alternatives realistically is another.” C. “You seem to be saying that your choices are final and that you’ve lost any other opportunities.” Correct D. “Sounds like you feel that things should come easy for you, unlike the rest of us, who work for what we get.” Rationale: The client in this question is engaging in catastrophizing rather than reframing and viewing other alternatives. The task for the nurse is to assess the lethality of the client’s situation and to help the client feel empowered to take another course of action and find the perseverance and confidence to do so. The therapeutic response here is the one that is nonjudgmental. In responding, “What are you saying? Sounds like you need to pull yourself together and go back to school,” or “Sounds like you feel that things should come easy for you, unlike the rest of us, who work for what we get,” the nurse communicates with the client as a parent, using a judging style. In stating, “Having faith in yourself is one thing, but looking at your options realistically is another,” the nurse communicates prematurely and gives advice. TestTaking Strategy: Use your knowledge of therapeutic communication techniques. Eliminate the options that are comparable or alike in that the nurse uses a judging style to deal with the client. To select from the remaining options, eliminate the option that is nontherapeutic in that the nurse gives advice. Review: therapeutic communication techniques . Reference: Stuart, G. (2009). Principles & practice of psychiatric nursing (9th ed., pp. 2731, 94). St. Louis: Mosby. Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Psychosocial Integrity Integrated Process: Communication and Documentation Content Area: Mental Health Giddens Concepts: Communication, Mood and Affect HESI Concepts: Communication, Mood and Affect Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 9. 9.ID: 9476898996 A client who has twice attempted suicide says, “If people would just leave me alone and let me do what I want with my life, I could get on with what I want to do.” Which response should the nurse give to the client? A. “Of course you can’t be left alone to get on with what you want to do.” B. “Okay, go ahead and do whatever you want to do. Human beings have free will.” C. “You’ve tried to end your life twice, yet you feel that everyone should let you do what you want to do?” Correct D. “Sounds like you’re angry with people for caring enough about you to try to keep you from hurting yourself.” Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 10. 10.ID: 9476887480 A homeless client with an antisocial disorder is brought to the emergency department by the police after disturbing customers in a department store. The client says to the nurse, “I need to be hospitalized. It’s getting cold out, and I need a warm bed. If you don’t get me into a hospital, I’ll jump off a bridge.” Which nursing intervention would be therapeutic? A. Sending the client to the psychiatric hospital intake center immediately for evaluation B. Asking the police to pick the client up and arrest him for vagrancy, as they should have done immediately C. Discharging the client with a followup appointment for the next day and guaranteeing him a hospital bed if he shows up D. Sending the client to a shelter that will provide temporary housing if he signs a contract agreeing not to attempt suicide Correct Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 11. 11.ID: 9476891424 A client is admitted to the medicalsurgical unit of a hospital, and suicide precautions are taken until the client can be admitted to the psychiatric unit. Which nursing intervention should the nurse implement? A. Placing the client in a private room and locking the client’s closets and bathroom B. Placing the client in a private room and removing all knives and glass from the client’s meal tray C. Allowing the client to go out on pass as long as the client is accompanied by a responsible adult D. Placing the client in a semiprivate room, providing plastic utensils for eating, and keeping an arm’s distance from the client at all times Correct Rationale: When a client is suicidal, someone must be at arm’s length at all times, observing the client, and the client must be in view at all times, even while toileting and showering. Plastic utensils are used for eating. A semiprivate room is better than isolation in a private room. Searching the client and the client’s room for harmful objects is done openly and randomly. Glass mirrors are removed and the bathroom is harmproofed by replacing the metal shower curtain rod with a plastic rod that falls when 50 pounds of pressure is placed on it. Offunit passes are not issued when a client is suicidal. TestTaking Strategy: Focus on the subject, suicide precautions. Eliminate the options that are comparable or alike and involve the provision of a private room, because this environment further isolates the client. Next recall that a suicidal client would not be allowed off the nursing unit. Review: suicide precautions . References: Stuart, G. (2009). Principles & practice of psychiatric nursing (9th ed., p. 327). St. Louis: Mosby. Varcarolis, E., & Halter, M. (2009). Essentials of psychiatric mental health nursing: A communication approach to evidencebased care (p. 417). St. Louis: Saunders. Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Safe and Effective Care Environment Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Implementation Content Area: Mental Health Giddens Concepts: Care Coordination, Safety HESI Concepts: Collaboration/Managing Care—Care Coordination, Safety Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 12. 12.ID: 9476896394 A client is admitted to the psychiatric inpatient unit and suicide precautions are instituted. Which intervention should the nurse implement? A. Restricting visitors B. Placing the client in a private room and locking the bathroom door C. Removing perfume, shampoo, and other toiletries from the client’s room Correct D. Placing flowers brought to the client in a small glass vase and putting them in the client’s room Rationale: When suicide precautions are instituted, all of the client’s belongings that are potentially harmful are removed and placed in a locked area from which the nursing staff can retrieve them as Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 13. 13.ID: 9476898961 A client who is undergoing psychiatric counseling calls a nurse on a hotline, crying, and states, “My priest assaulted me when I was an altar boy, and my dad just found out. He’s got a gun, and he’s driving over to the church rectory. I don’t know what to do.” Which response by the nurse is most appropriate initially? A. “How did your dad learn of your abuse by clergy?” B. “Call the police immediately and then call the priest to warn him that your dad has a gun.” C. “Call the priest immediately and tell him to lock the doors until the police arrive. I’ll call the police.” Correct D. “You will want to come in to see our psychiatrist with your father, but, for now, call the police and tell them what happened.” Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 14. 14.ID: 9476897703 The nurse determines that a client whose son died in a car accident is at risk for selfharm. Which intervention is most appropriate initially? A. Making a “no suicide” contract with the client Correct B. Telling the client that anger should be suppressed C. Providing a peaceful place for the client to meditate D. Helping the client control expression of his feelings Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 15. 15.ID: 9476891476 A client says to the nurse, “I’m worried about my husband. He’s talking about ending it all since his law practice dropped off and his son by his late first wife died of a drug overdose — but he’s too intelligent to hurt himself, isn’t he?” Which response by the nurse is appropriate? A. “Yes, he’s too intelligent to end it all.” B. “I’m not sure. I don’t know him that well.” C. “Most people who talk about ending it all are just looking for attention.” D. “Your husband is displaying behaviors that indicate a risk for self harm.” Correct Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 16. 16.ID: 9476895046 A client says to the nurse, “I came in to see you because I’ve been off my medication for 4 years but I feel as though I may be getting depressed again. I’ve been despondent again and thinking I should have ended it. That’s why I’m here to get help.” Which response by the nurse would be therapeutic? A. “Well, you really have had a good long drugfree time, but it sounds as if the health care provider needs to reorder your medication at once.” B. “If you’ve been able to be drug free all this time, you probably don’t need to restart the medicine. You probably just need some therapy to help you manage stress.” C. “Well, it’s been more than 4 years, so you’ve done really well. Sounds like you’re right about getting depressed again, though. Can you tell me what’s been happening with you lately?” Correct D. “Well, it’s similar to when a client is battered — things have to boil over before the police can act — so you need to be suicidal to get admitted to a hospital or hurt yourself before the health care provider can restart the medication.” Rationale: The therapeutic response is the one in which the nurse validates the client’s drugfree time. In addition, in the correct option the nurse validates the client’s selfassessment and supports and offers positive reinforcement. Finally the nurse begins to assess the client completely and attempts to identify precipitants. By stating, “Well, you really have had a good long drugfree time, but it sounds as if the health care provider needs to reorder your medication at once,” the nurse is premature in determining that the medication needs to be restarted; a thorough assessment must be performed first. In stating, “If you’ve been able to be drug free all this time, you probably don’t need to restart the medicine. You probably just need some therapy to help you manage stress,” the nurse jumps to giving advice and offering suggestions without performing a complete assessment. In stating, “Well, it’s similar to when a client gets battered — things have to boil over before the police can act — so you need to be suicidal to get admitted to a hospital or hurt yourself before the health care provider can restart the medication,” the nurse provides an incorrect statement and sarcastic information. TestTaking Strategy: Use your knowledge of therapeutic communication techniques and the steps of the nursing process, remembering that assessment is the first step. The only option that involves the process of assessment is the correct option. Review: therapeutic communication techniques . References: Stuart, G. (2009). Principles & practice of psychiatric nursing (9th ed., pp. 2731, 286 287). St. Louis: Mosby. Varcarolis, E., & Halter, M. (2009). Essentials of psychiatric mental health nursing: A communication approach to evidencebased care (p. 221). St. Louis: Saunders. Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Psychosocial Integrity Integrated Process: Communication and Documentation Content Area: Mental Health Giddens Concepts: Mood and Affect, Safety HESI Concepts: Mood and Affect, Safety Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 17. 17.ID: 9476888992 A client who delivered a baby 4 months ago says, “I keep thinking that this boy is some sort of demon. All he does is cry. It’s as if I can’t feed him enough or satisfy him in any way. My daughter never gave me this kind of trouble. I really can’t stand it.” Which statement by the nurse is most important? A. “Have you been having any thoughts of hurting your baby?” Correct B. “Do you think that something physically wrong is causing your baby to cry?” C. “Do you think that your baby cries so frequently because he’s not getting enough nourishment from breastfeeding?” D. “You say that he doesn’t seem to be satisfied. Do you feel that this is significantly different from when your daughter was a baby?” Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 18. 18.ID: 9476887499 An alcoholic client who has been admitted to the mental health unit states to the nurse, “The judge made me come in here. My blood alcohol level was only 0.20% when the cop pulled me over in my car.” Which statement by the nurse is most appropriate? A. “Did you ask the judge to clarify his decision to make you come here?” B. “This limit means that you had consumed enough alcohol to put you close to the legal intoxication level. You were lucky because you just missed that level.” C. “Well, the legal limit is much less than that, so you avoided a drunken driving charge by coming here. Seems to me that the judge treated you pretty leniently by allowing you to take refuge here. Don’t you agree?” D. “This level means that you consumed several drinks of alcohol and would be experiencing depressed motor function of the brain. You would have been staggering and clumsy and your judgment would have been impaired, but you seem to feel that the judge was unreasonable for sending you here.” Correct Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 19. 19.ID: 9476896365 An adolescent client has graduated high school and is preparing to leave home to attend college. The adolescent is distressed about this life change. The nurse plans to implement crisis interventions, knowing that this situation is characteristic of which type of crisis? A. A situational crisis B. An individual crisis C. A maturational crisis Correct D. An adventitious crisis Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 20. 20.ID: 9476892711 A heroin addict who overdoses on the drug is brought into the emergency department. The client is having seizures, and the nurse notes that his pupils are dilated. Which intervention does the nurse anticipate that the emergency department health care provider will prescribe? A. Gastric lavage B. Intravenous fluid C. Naloxone (Narcan) Correct D. Ammonium chloride Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 21. 21.ID: 9476897793 A client in a retirement center rings the night alarm and says to the nurse, “Look at this old man! He keeps breaking into my apartment! You’ve got to get him to stay out of here so I can sleep.” Which statement by the nurse would be most therapeutic? A. “Why not just throw him out yourself and lock up once and for all?” B. “Now, you know that you’re always seeing things and people at night who aren’t there.” C. “This must be very troubling to you, but I can’t see the old man. Perhaps I could stay with you for an hour or so while you try to rest.” Correct D. “I’m sure you’re very frightened right now. Do you recall my telling you that this is called sundowner syndrome? Go to sleep and he’ll leave your apartment.” Rationale: The most therapeutic nursing response is the one that expresses empathy and helps orient the client to reality. It also offers self, builds trust, and provides support for the client’s distress. In asking, “Why not just throw him out yourself and lock up once and for all?” the nurse reinforces the hallucination and delusional thinking by responding as if the old man is really there. In stating, “Now, you know that you’re always seeing things and people at night who aren’t there,” the nurse is patronizing and belittling in responding to the client’s concerns, a nontherapeutic communication. In responding, “I’m sure that you’re very frightened right now. Do you recall my telling you that this is called sundowner syndrome? Go to sleep and he’ll leave your apartment,” the nurse is lecturing the client and giving advice, which is not therapeutic. TestTaking Strategy: Note the strategic word “most.” Use your knowledge of therapeutic communication techniques. The only option that addresses the client’s fears and feelings is the correct option. Review: therapeutic communication techniques . References: Stuart, G. (2009). Principles & practice of psychiatric nursing (9th ed., pp. 2731). St. Louis: Mosby. Varcarolis, E., & Halter, M. (2009). Essentials of psychiatric mental health nursing: A communication approach to evidencebased care (p. 480). St. Louis: Saunders. Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Psychosocial Integrity Integrated Process: Communication and Documentation Content Area: Mental Health Giddens Concepts: Cognition, Clinical Judgment HESI Concepts: Clinical DecisionMaking/Clinical Judgment, Cognition Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 22. 22.ID: 9476891495 A schizophrenic client is seen seemingly talking to someone who isn’t there. Which nursing statement would be most therapeutic initially? A. “Today is my birthday. Would you like to go on an outing with my family?” B. “You need to wash up and get ready to go to supper in the cafeteria with the other clients now.” C. “I’ve noticed your eyes darting back and forth, and I wondered whether you might be hearing voices.” Correct D. “You were telling me yesterday that your mother died last June of cancer. Can you tell me more about that?” Rationale: The most therapeutic nursing statement is the one in which the nurse addresses the client’s behavior and asks whether the client is hearing voices. With this statement, the nurse also assesses the client’s behavior. If the client is hearing voices, the nurse prevents reinforcement of the hallucinatory thinking by telling the client that he or she does not hear them. In asking, “Today is my birthday. Would you like to go on an outing with my family?” the nurse nontherapeutically changes the focus from the client. In stating, “You need to wash up and get ready to go to supper in the cafeteria with the other clients now,” the nurse ignores the client’s obvious psychotic behavior and directs the client to socialize with others. Such an intervention is not usually positive, because it floods the client with stimuli that may contribute to an escalation of psychotic behavior. In asking, “You were telling me yesterday that your mother died last June of cancer. Can you tell me more about that?” the nurse uses distraction, summarization, and refocusing. TestTaking Strategy: Note the strategic words “most” and “initially” and eliminate the options that are unrelated to the client’s behavior. Also, focus on the data in the question. The correct option is the only one that addresses the client’s behavior. Review: care of the client who is hallucinating . Reference: Varcarolis, E., & Halter, M. (2009). Essentials of psychiatric mental health nursing: A communication approach to evidencebased care (pp. 287, 288). St. Louis: Saunders. Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Psychosocial Integrity Integrated Process: Communication and Documentation Content Area: Mental Health Giddens Concepts: Communication, Psychosis HESI Concepts: Cognition—Psychosis, Communication Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 23. 23.ID: 9476884705 The nurse brings a meal tray to a psychotic client in his hospital room. The client refuses the meal and says, “I’m not eating any more poisoned food while I’m vacationing here. I’m starting on a fast to stay healthy and alive.” Which nursing intervention would be most appropriate initially? A. Taking the tray away and canceling all meals until further notice B. Having the client eat with other clients in the community dining room Correct C. Eating some of the food from the client’s tray to prove that it isn’t poisoned D. Telling the client that the psychiatrist will be called for a prescription for a tube feeding Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 24. 24.ID: 9476897755 The nurse caring for a schizophrenic client is assessing the client’s ability to control distorted thought processes. Which finding indicates a positive outcome? A. The client is able to identify when hallucinations or delusions are real. B. The client can describe in detail the frequency and context of the hallucinatory and delusional behavior. C. The client can describe the hallucinations and delusions in detail and is able to interact with others and share in their delusional systems. D. The client can identify the recurrence of hallucinations, can refrain from responding to them, and reports a significant decrease in the incidence of hallucinations. Correct Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 25. 25.ID: 9476898969 A schizophrenic client says, “I feel like I’m rotting away inside and all of my organs are rusting.” Which type of delusion does the nurse identify in the client’s statement? A. Somatic Correct B. Jealousy C. Persecution D. Idea of reference Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 26. 26.ID: 9476897731 A schizophrenic client attending a support group held by a clinic nurse says to the nurse and the group, “I’ve been laid off from my job at the factory, and so have 300 other people, so I’ll have to get a new job. For now, there’s unemployment.” Which statement by the nurse would be most therapeutic at this time? A. “It seems that the stock market is responsible for mass unemployment in our factorybased city.” B. “I’m sorry to hear that you’ve lost your job. Why not make an appointment to come in and talk with me this week?” C. “How do people feel about this loss of employment? Does anyone in the group who experienced this have any advice?” Incorrect D. “Have other people in the group been feeling the job crunch this week? When changes like this occur, it’s best to increase the number of your appointments with me for a short time.” Correct Rationale: The nurse is leading a support group for schizophrenic clients, so it is important to address every group member when possible and not single out one member for special attention. The correct option is openended, encourages group sharing of experiences and support, and teaches the members about the need to increase visits whenever schedules change abruptly and create stressful situations. In stating, “It seems that the stock market is responsible for mass unemployment in our factorybased city,” the nurse changes the focus from feelings and experiences to intellectualize, a nontherapeutic intervention. In responding, “I’m sorry to hear that you’ve lost your job. Why not make an appointment to come in and talk with me this week?” the nurse expresses sympathy rather than empathy and personalizes the invitation for an appointment that may cause jealousy among the other clients in the group. In asking, “How do people feel about this loss of employment? Does anyone in the group who experienced this have any advice?” the nurse asks a question of the group that is off focus. TestTaking Strategy: Focus on the environment of the question, a support group. The only option that addresses all members of the group is the correct option. It is also the umbrella option. Review: the functions of support groups . Reference: Varcarolis, E., & Halter, M. (2009). Essentials of psychiatric mental health nursing: A communication approach to evidencebased care (pp. 39, 40). St. Louis: Saunders. Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Psychosocial Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Implementation Content Area: Mental Health Giddens Concepts: Anxiety, Psychosis HESI Concepts: Cognition—Psychosis, Mood and Affect—Anxiety Awarded 0.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 27. 27.ID: 9476888918 A schizophrenic client arrives for a scheduled appointment with the mental health nurse. The nurse notes that the client’s hygiene is poor and that the client is having difficulty concentrating on what the nurse is saying and responding appropriately. Which nursing intervention would be most appropriate? A. Saying nothing and contacting the psychiatrist to sign a commitment order B. Saying, “I notice that you don’t seem to be caring for yourself. Are you taking your medication?” Correct C. Giving the client his antipsychotic medication and asking him to return in the morning for a followup visit D. Asking, “Will you voluntarily admit yourself for a couple of days so that you can straighten out your medicine and thinking?” Rationale: When the nurse’s observations indicate that the client is noncompliant with his medicine, the most appropriate intervention is the one in which the nurse makes observations and assesses noncompliance. Saying nothing and contacting the psychiatrist to sign a commitment order is inappropriate. Commitment proceedings may be necessary if the client is a danger to self or others. Giving the client his antipsychotic medication and asking him to return in the morning for a followup visit is inappropriate because the client needs assessment and intervention immediately. Waiting until the next morning does not meet the client’s immediate needs. In asking, “Will you voluntarily admit yourself for a couple of days so that you can straighten out your medicine and thinking?” the nurse asks the client to enter the hospital voluntarily. This intervention is premature, because further assessment of the client is needed. TestTaking Strategy: Eliminate the options that are comparable or alike and involve a delay in addressing the client’s needs. To select from the remaining options, focus on the data in the question and choose the one that addresses observations made by the nurse. Review: care of the schizophrenic client and observations that indicate medication noncompliance . Reference: Stuart, G. (2009). Principles & practice of psychiatric nursing (9th ed., pp. 2731). St. Louis: Mosby. Varcarolis, E., & Halter, M. (2009). Essentials of psychiatric mental health nursing: A communication approach to evidencebased care (p. 279). St. Louis: Saunders. Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Psychosocial Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Implementation Content Area: Mental Health Giddens Concepts: Adherence, Psychosis HESI Concepts: Behaviors—Adherence, Cognition—Psychosis Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 28. 28.ID: 9476882048 A postpartum client says to the nurse, “Sometimes I hear voices telling me to kill my baby to save her all the heartache I’ve been through.” Which statement by the nurse would be most therapeutic? A. “The voices will disappear in a few weeks as your hormones stabilize.” B. “This must be very distressing to you. Can you tell me more about the voices?” Incorrect C. “It is so good that you shared your feelings and thoughts with me. I’m going to help you get immediate attention for your voices.” Correct D. “You will want to tell the health care provider about them when you visit him next week. He is very interested in these voices and will want to help you with them.” Awarded 0.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 29. 29.ID: 9476886376 A schizophrenic client exhibits confused and unintelligible speech. Which nursing statement would be most therapeutic? A. “Got it. The ‘blinks’ are ‘taking over’ the ‘bumpers.’” B. “I can’t understand what you’re saying. You have to talk more clearly!” C. “This morning you are participating in the treedecorating ceremony for the unit.” Correct D. “I can’t understand you. Are you asking me to stay with you while you eat supper?” Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 30. 30.ID: 9476897747 A schizophrenic client says to the nurse, “I keep getting these thoughts and hearing voices. They worry and consume me so that I can’t always stop myself like my health care provider told me to.” Which intervention would the nurse suggest as a distraction technique? A. “Pretend that you’re on the phone and talk to the voices.” B. “Have you tried to count back from 100 or listen to music?” Correct C. “The next time this happens, try telling the voices to go away.” D. “Tell the voices that you will only listen to them just before you watch television at 8:30 in the evening.” Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 31. 31.ID: 9476892771 The nurse plans outcomes for a client who is being treated for psychosis. Which step would be included during the stable or discharge phase of treatment? A. Evaluation of neurological status B. Use of directive communications with the client C. Administration of acute psychotropic medications D. Keeping the client active with hobbies, exercise, and work Correct Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 32. 32.ID: 9476898928 A schizophrenic client is admitted to the inpatient psychiatric unit. The client is exhibiting clang associations, word salad, and loose associations. Which problem does the nurse recognize that the client is experiencing? A. Defensive coping B. Inability to cope effectively C. Sensory perception alterations D. Inability to communicate effectively Correct Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 33. 33.ID: 9476897775 A 24yearold schizophrenic client says, “I was in college and suddenly I was hearing voices telling me I was no good and that I should jump off the bridge by our college. My parents came and got me when I called them. We thought that I had inadvertently taken drugs at a party or something. My psychiatrist says that if I can improve, I can return to college next semester.” Which guideline does the nurse plan to incorporate into teaching of the client and family about selfcare on the client’s return to college? A. Compliance with the treatment regimen, immediate reporting of any relapse signs, avoidance of alcohol and drugs, and living a balanced lifestyle Correct B. Telling all friends about the illness so that they support the client’s avoidance of alcohol and drugs and help the client maintain a balanced lifestyle C. Limiting college attendance to commuter status to maintain a supportive family group and avoiding drugs, alcohol, and the strain of socialization D. Compliance with treatment, immediate reporting of any relapse signs, avoidance of alcohol and drugs, and socialization with one supportive friend Rationale: Selfcare guidelines for the client include compliance with the treatment regimen, immediate reporting of any relapse signs, avoidance of alcohol and drugs, and living a balanced lifestyle. Telling all friends about the illness so that they can support the client’s avoidance of alcohol and drugs and help the client maintain a balanced lifestyle is incorrect. Although the closest supportive friends need to know and understand the illness, not everybody does. Limiting college attendance to commuter status to maintain a supportive family group and avoiding drugs, alcohol, and the strain of socialization is incorrect. Not allowing the client to be independent and follow a normal growth and development pattern would retard the client’s growth. Socializing with one supportive friend is incorrect because it is best to bring as many supportive persons to the client as possible. TestTaking Strategy: Focus on the data in the question and the subject, selfcare. Eliminate the options that contain the words “one,” “all,” and “limiting". Also note that the correct option is the umbrella option. Review: care of the client with schizophrenia . Reference: Varcarolis, E., & Halter, M. (2009). Essentials of psychiatric mental health nursing: A communication approach to evidencebased care (p. 293). St. Louis: Saunders. Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Psychosocial Integrity Integrated Process: Teaching and Learning Content Area: Mental Health Giddens Concepts: Adherence, Psychosis HESI Concepts: Behaviors—Adherence, Cognition—Psychosis Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 34. 34.ID: 9476888910 A schizophrenic client in the psychiatric inpatient unit is yelling, “The CIA is trying to kill me. I know they’re plotting to kill me so they can overthrow the government.” Based on the client’s statement, which clinical manifestation should the nurse document in the client record? A. Demonstrates paranoia B. Exhibits ideas of reference C. Evidence of persecutory delusions Correct D. Evidence of ideas of somatic delusions Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 35. 35.ID: 9476887453 A manic client who tends to be manipulative says angrily, “You had better let me out of here, or I’m going to call my lawyer. My boss has good friends with the owners of this tinpot place you call a ‘mind holism respite.’” Which statement by the nurse would be most therapeutic? A. “When you can speak to me without yelling and being aggressive, I’ll be happy to speak with you.” B. “Just get your anger out with me, because we’re not going to allow you be discharged until you calm down.” C. “Do threats and namecalling usually work for you? Do people tend to listen to you and do as you order them to?” D. “I know that you feel that you’re doing your very best right now, but you are yelling. Take some time out and some deep breaths, and I’ll speak to you in half an hour.” Correct Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 36. 36.ID: 9476888999 A client in a mental health unit gets into a fight with another client over the use of the public telephone on the unit. The client is accused of making two telephone calls and staying on the telephone for 1 hour. Which intervention by the nurse would be most therapeutic? A. Taking telephone privileges away from both clients for the day and giving them timeouts in their rooms B. Saying to the clients, “Okay, this is the last straw. Neither of you may use the telephone until tomorrow, and then only with a nurse timing you.” C. Saying to the clients, “Go to your rooms, both of you. I don’t want to hear anything more about the telephone on this unit for at least 2 hours.” D. Saying to the clients, “You may each use the phone for 10 minutes. I will time the calls for both of you. Do you both agree to abide by my decision?” Correct Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 37. 37.ID: 9476884721 The nursing instructor enters a classroom to begin class and finds two students yelling and physically assaulting each other. Which intervention by the instructor would be most appropriate? A. Walking out of the classroom and asking the secretary to call security, then telling all of the students to leave and go to the nursing laboratory B. Getting the class to leave with her and sending everyone to the nursing laboratory, then calling security to the classroom and reentering to observe what is happening with the two students. C. Telling the class, “Take a break. I’ll come and get you to restart class as soon as I can,” then closing the classroom door, refusing to let anyone else in, and asking a passing instructor to get security Incorrect D. Telling the class to go to the nursing laboratory at once, then asking a student to tell the nursing secretary to have security come to the classroom, and asking the students who are fighting to stop fighting and take their seats Correct Awarded 0.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 38. 38.ID: 9476891444 A student calls the campus crisis hotline and tells the nurse, “I went out to a sorority party last week and drank too much. Someone raped me, but when I told my folks about it, they acted like it was my fault. I feel so dirty and used.” Which statement by the nurse would be most therapeutic? A. “Would you come in to talk with me in the strictest confidence?” B. “I believe that you can feel a lot better about yourself. Won’t you come in to see me tomorrow?” C. “Parents always feel that their daughters could never be raped. I could talk to them for you, if you’ll let me.” D. “You’ve had an awful experience, but it’s not your fault that it happened. Can you come in and talk to me about it in more detail?” Correct Rationale: Rape is vaginal or anal penetration against the victim’s will and consent. The student is in crisis and needs counseling. Her call seems to be the result of her being unable to turn to her parents as she might have been able to in the past. The nurse needs to let the student know that the rape was not her fault. Many students overdrink but are not raped just because they were inebriated. By asking, “Would you come in to talk with me in the strictest confidence?” the nurse assures confidentiality, but this option is nontherapeutic because a bridge of trust has not yet been established with the client. In responding, “I believe that you can feel a lot better about yourself. Won’t you come in to see me tomorrow?” the nurse offers opinions on outcomes and delays treatment, which is nontherapeutic. In responding, “Parents always feel that their daughter could never be raped. I could talk to them for you, if you'll let me,” the nurse lectures the student on why her parents are not supportive without ever having met them. This answer is nontherapeutic and insensitive. TestTaking Strategy: and your knowledge of therapeutic communication techniques. The correct option, the umbrella option, acknowledges the client’s experience, informs the client that the rape was not her fault, expresses support, and provides immediate treatment. Review: interventions for the client who is a victim of abuse . Reference: Varcarolis, E., & Halter, M. (2009). Essentials of psychiatric mental health nursing: A communication approach to evidencebased care (p. 408). St. Louis: Saunders. Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Psychosocial Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Implementation Content Area: Mental Health Giddens Concepts: Coping, Sexuality HESI Concepts: Sexuality/Reproduction, Stress and Coping Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 39. 39.ID: 9476887491 A psychiatric nurse is playing a card game with a client in the day room. The client states to the nurse, "The voice in my head is telling me that you're cheating." Which response by the nurse is therapeutic? A. "Is the voice telling you to do anything?" Incorrect B. "I don't believe that you are hearing voices." C. "It isn't possible for people to hear voices in their head." D. "I do not hear any voices. Has the voice said anything else?" Correct Awarded 0.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 40. 40.ID: 9476884783 A client says to the nurse, “I’m really phobic about flying, so my husband and I always drove or took the train everywhere. Now he’s been offered a big job in Europe, and if I don’t get over this and fly with him, he says we’re done. I’ll be left to bring up our three children by myself.” Which statement by the nurse would be therapeutic? A. “No problem. You can be hypnotized to sleep through your trip.” B. “I’m interested that it took his threat of leaving you to motivate you to seek help.” C. “You seem more anxious and afraid of raising three children alone than of flying.” D. “I can teach you strategies to help master your panic. An antianxiety medicine would also help you.” Correct Rationale: A phobia is a persistent, irrational fear of a specific object, activity, or situation that leads to a desire for avoidance or actual avoidance of the object, activity, or situation. The nurse can teach strategies, such as relaxation training and thoughtstopping, to help the client master her anxiety. There are also medications that the psychiatrist can prescribe to help ease the client’s phobia. In stating, “No problem. You can be hypnotized to sleep through your trip,” the nurse provides false reassurance and belittles the client’s worries and fears. In responding, “I’m interested that it took his threat of leaving you to motivate you to seek help,” the nurse uses a nontherapeutic change of subject that can only increase the client’s anxiety and fear. This response also lowers the client’s trust in her relationship with the nurse. In stating, “You seem more anxious and afraid of raising three children alone than of flying,” the nurse changes the subject. TestTaking Strategy: and therapeutic communication techniques. Eliminate the options that do not focus on the client’s concern or provide false reassurance. The correct option is focused on the client’s concern and provides a reasonable solution. Review: therapeutic communication techniques . References: Stuart, G. (2009). Principles & practice of psychiatric nursing (9th ed., pp. 2731). St. Louis: Mosby. Varcarolis, E., & Halter, M. (2009). Essentials of psychiatric mental health nursing: A communication approach to evidencebased care (p. 141). St. Louis: Saunders. Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Psychosocial Integrity Integrated Process: Communication and Documentation Content Area: Mental Health Giddens Concepts: Anxiety, Client Education HESI Concepts: Mood and Affect—Anxiety, Teaching and Learning/Client Education Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 41. 41.ID: 9476892760 The nurse is trying to deescalate aggressive behavior exhibited by a client with schizophrenia. Which nursing action would be contraindicated in this situation? A. Being assertive with the client B. Negotiating options with the client C. Maintaining a nonaggressive posture D. Standing close to the client and telling the client that the behavior is unacceptable Correct Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 42. 42.ID: 9476895003 A client is scheduled to undergo electroconvulsive therapy (ECT). Which client concern is of the highest priority? A. Fear B. Anxiety C. Distorted body image D. Risk for impaired breathing Correct Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 43. 43.ID: 9476888955 The mother of a child who is taking methylphenidate hydrochloride (Ritalin) tells the school nurse that she is administering an overthecounter (OTC) cough syrup to her son. Which response by the nurse would be appropriate? A. “His cough could be a side effect of the Ritalin.” B. “Your son should never take any medicine, even if it’s OTC.” C. “You may administer a small amount of OTC cough syrup without a problem, but not for more than 3 days.” D. “I think that you should stop giving this medicine to your son until I can check its content with the pharmacy.” Correct Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 44. 44.ID: 9476897798 A nurse notices a paranoid stare during a conversation with a client. The client then begins to fidget and gets up to pace around the room. Which action by the nurse would be beneficial? A. Allowing the client to pace B. Escorting the client to a quiet room C. Changing the conversation to a less threatening subject D. Sharing the observation with the client and helping the client recognize and acknowledge his or her feelings Correct Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 45. 45.ID: 9476897709 The nurse working in a mental health unit reads a client’s medical record and notes documentation that the client has been experiencing flashbacks. The nurse interprets this as a classic sign of which disorder? A. Depression B. Schizophrenia C. Post–traumatic stress disorder Correct D. Obsessivecompulsive disorder Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 46. 46.ID: 9476896356 A client arrives in the emergency department in a crisis state. The client demonstrates signs of profound anxiety and is unable to focus on anything but the object of the crisis and the impact on herself. The nurse plans to focus the initial assessment on which client factor? A. Sources of support B. The object of the crisis C. The client’s coping mechanisms D. The physical condition of the client Correct Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 47. 47.ID: 9476884748 The nurse has been closely observing a client who has been displaying aggressive behaviors and notes that the client’s aggressiveness is escalating. Which nursing intervention would be least helpful to this client at this time? A. Initiating confinement measures Correct B. Acknowledging the client’s behavior C. Assisting the client to an area that is quiet D. Maintaining a safe distance with the client Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 48. 48.ID: 9476896383 The nurse is assigned to care for a client experiencing a crisis. What is the appropriate initial nursing intervention for this client? A. Providing authority and action Correct B. Displaying an attitude of detachment and efficiency C. Providing hope and reassurance that the crisis is temporary Incorrect D. Demonstrating confidence in the client’s ability to deal with the crisis Awarded 0.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 49. 49.ID: 9476892786 The home care nurse makes a visit to a client with a diagnosis of depression. The nurse finds the client unconscious on the floor, with an empty bottle of a prescribed tricyclic antidepressant lying near the client. What action must the nurse take immediately? A. Inducing vomiting B. Calling an ambulance Correct C. Administering syrup of ipecac D. Counting the pills remaining in the bottle Rationale: An overdose of a tricyclic antidepressant can be fatal, regardless of the amount ingested. Serious lifethreatening symptoms may develop after an overdose. Immediate emergency medical attention and cardiac monitoring are needed in the event of an overdose of a tricyclic antidepressant. The nurse would not induce vomiting or administer anything by way of the oral route if the client is unconscious. Counting the remaining pills provides no useful information and delays necessary and immediate intervention. Additionally, the question notes that the bottle of pills is empty. TestTaking Strategy: Note the strategic word “immediately.” Eliminate the option that delays measures to provide immediate treatment and provides no useful information (i.e., counting the pills remaining in the bottle). Induction of vomiting or administration of an oral substance would not be performed in a client who is unconscious, so eliminate these options as well. Review: immediate measures required for an overdose of a tricyclic antidepressant . References: Stuart, G. (2009). Principles & practice of psychiatric nursing (9th ed., p. 519). St. Louis: Mosby. Varcarolis, E., & Halter, M. (2009). Essentials of psychiatric mental health nursing: A communication approach to evidencebased care (pp. 232, 234). St. Louis: Saunders. Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Psychosocial Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Implementation Content Area: Mental Health Giddens Concepts: Clinical Judgment, Interpersonal Violence HESI Concepts: Behaviors—Interpersonal Violence, Clinical DecisionMaking/Clinical Judgment Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 50. 50.ID: 9476891412 Which client is at the highest risk for suicide? A. A 24yearold man who is angry with his family B. A 71yearold man with mild depression and social withdrawal C. A 75yearold woman with severe depression and crippling arthritis Correct D. A 30yearold newly divorced woman who has custody of her children Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 51. 51.ID: 9476896348 A client brought to the emergency department by the police after being mugged is extremely agitated, trembling and hyperventilating. What is the appropriate initial nursing action? A. Staying with the client Correct B. Teaching the client how to relax C. Asking the client questions about the mugging D. Allowing the client to be alone in a room at the end of the emergency department corridor, where it is quiet Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 52. 52.ID: 9476892725 A woman is brought to the emergency department after an assault. She presents with complaints of dizziness, dyspnea, visual disturbance, and motor tension with hyperactivity. Which level of anxiety does the nurse recognize in the client’s presentation? A. Mild B. Panic C. Severe Correct D. Moderate Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 53. 53.ID: 9476886310 The nurse is monitoring a client who is in seclusion. The nurse determines that it is safe for the client to come out of seclusion when the client makes which statement? A. “I need to go to the bathroom.” B. “I’m no longer a threat to myself or others.” Correct C. “I want to be alone for a while in my own room.” D. “I can’t breathe in here. The walls are closing in on me.” Rationale: The client in seclusion must be assessed at regular intervals (usually every 15 to 30 minutes) for fulfillment of physical needs, safety, and comfort and should be released from seclusion as soon as possible, provided that safety has been ensured. The statement “I'm no longer a threat to myself or others” indicates that it may be safe to remove the client from seclusion. The statement “I need to go to the bathroom” indicates a physical need that could be met with a urinal or bedpan, if necessary. It does not indicate that the client has calmed down enough to leave the seclusion room. The statement “I want to be alone for a while in my own room” could be an attempt to manipulate the nurse. It gives no indication that the client will control him or herself when alone in his or her room. The statement “I can’t breathe in here. The walls are closing in on me” indicates the need for supportive communication or possibly a prescribed medication. It does not necessitate the discontinuation of seclusion. TestTaking Strategy: The subject of the question specifically relates to safety. to answer the question. Thinking about the purpose of seclusion will assist in directing you to the correct option. Review: seclusion procedures . Reference: Stuart, G. (2009). Principles & practice of psychiatric nursing (9th ed., pp. 587, 588). St. Louis: Mosby. Cognitive Ability: Evaluating Client Needs: Psychosocial Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Evaluation Content Area: Mental Health Giddens Concepts: Clinical Judgment, Safety HESI Concepts: Clinical DecisionMaking/Clinical Judgment, Safety Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 54. 54.ID: 9476882084 The nurse is preparing a discharge plan for a client who has attempted suicide. The nurse understands that the plan of care should have which focus? A. Followup appointments B. Providing the hospital phone number C. Contracts and immediate available crisis resources Correct D. Encouraging the family to always be with the client [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 44 pages
Instant download
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Oct 23, 2021
Number of pages
44
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Oct 23, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
98