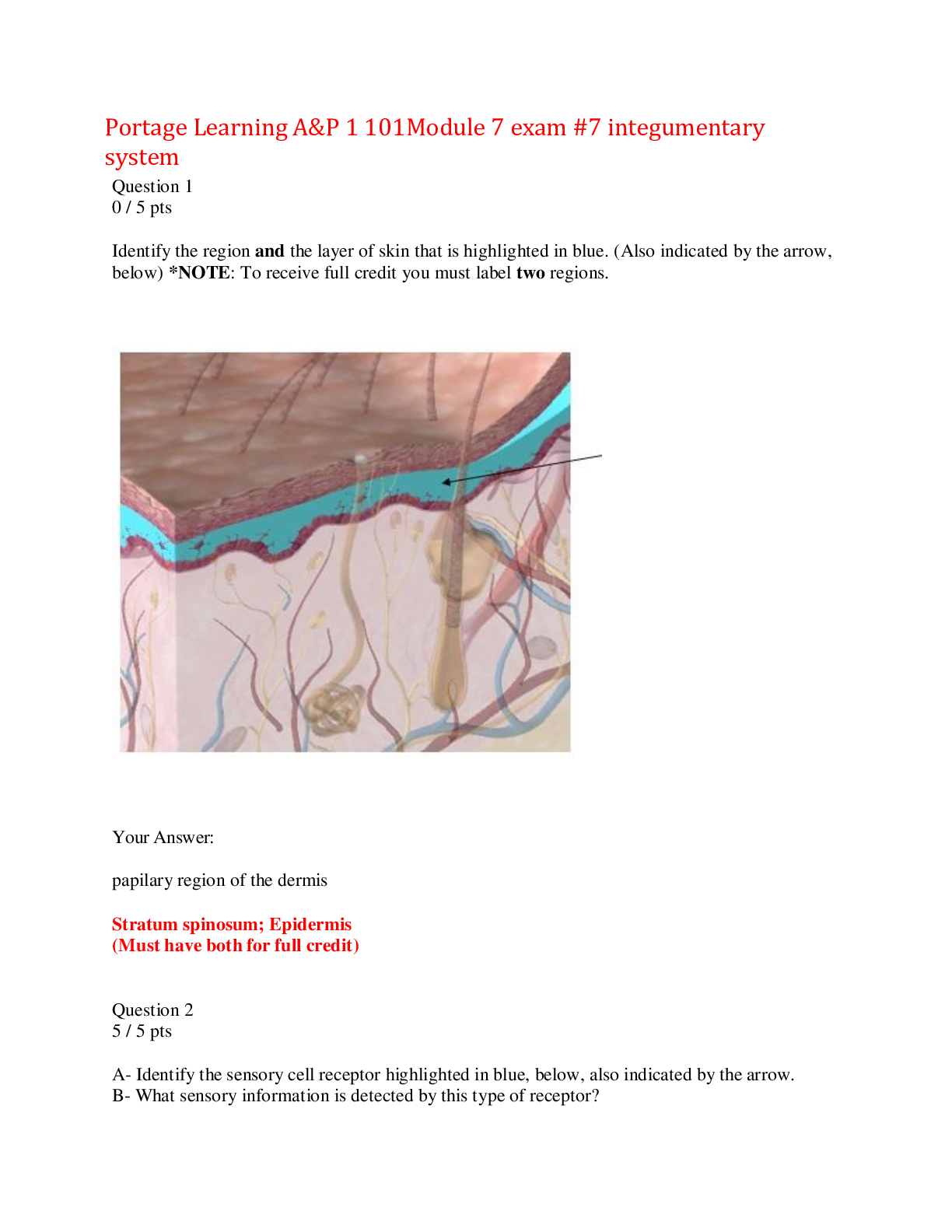
NURS 206 Mental Health 2 Questions and Answers,100%CORRECT
Document Content and Description Below
NURS 206 Mental Health 2 Questions and Answers Chapter 11: Anxiety, Anxiety Disorders, and Obsessive-Compulsive Disorders 1. A nurse wishes to teach alternative coping strategies to a patient expe... riencing severe anxiety. The nurse will first need to: a. Verify the patients learning style. b. Create outcomes and a teaching plan. c. Lower the patients current anxiety level. d. Assess how the patient uses defense mechanisms. ANS: C A patient experiencing severe anxiety has a significantly narrowed perceptual field and difficulty attending to events in the environment. A patient experiencing severe anxiety will not learn readily. Determining preferred modes of learning, devising outcomes, and constructing teaching plans are relevant to the task but are not the priority measure. The nurse has already assessed the patient’s anxiety level. Using defense mechanisms does not apply. 2. A patient approaches the nurse and impatiently blurts out, Youve got to help me! Something terrible is happening. My heart is pounding. The nurse responds, it’s almost time for visiting hours. Let’s get your hair combed. Which approach has the nurse used? a. Bringing up an irrelevant topic b. Responding to physical needs c. Addressing false cognitions d. Focusing ANS: A The patient is experiencing anxiety. The nurse has closed off patient-centered communication by changing the subject. The introduction of an irrelevant topic makes the nurse feel better. The nurse may be uncomfortable dealing with the patient’s severe anxiety. The nurse has not responded to the patients’ physical needs. There is no evidence of false cognition. Focusing is a therapeutic communication technique used to concentrate attention on a single issue. 3. A patient experiencing moderate anxiety says, I feel undone. An appropriate response for the nurse would be: a. Why do you suppose you are feeling anxious? b. What would you like me to do to help you? c. I’m not sure I understand. Give me an example. d. You must get your feelings under control before we can continue. ANS: C Increased anxiety results in scattered thoughts and an inability to articulate clearly. Clarification helps the patient identify his or her thoughts and feelings. Asking the patient why he or she feels anxious is nontherapeutic, and the patient will not likely have an answer. The patient may be unable to determine what he or she would like the nurse to do to help. Telling the patient to get his or her feelings under control is a directive the patient is probably unable to accomplish. 4. A patient with a high level of motor activity runs from chair to chair and cries, they’re coming! They’re coming! The patient does not follow instructions or respond to verbal interventions from staff. The initial nursing intervention of highest priority is to: a. provide for patient safety. b. increase environmental stimuli. c. respect the patients personal space. d. encourages the clarification of feelings. ANS: A Safety is of highest priority; the patient who is experiencing panic is at high risk for self- injury related to an increase in nongoal-directed motor activity, distorted perceptions, and disordered thoughts. The goal should be to decrease the environmental stimuli. Respecting the patient’s personal space is a lower priority than safety. The clarification of feelings cannot take place until the level of anxiety is lowered. 5. A patient with a high level of motor activity runs from chair to chair and cries, they’re coming! They’re coming! The patient is unable to follow instructions or respond to verbal interventions from staff. Which nursing diagnosis has the highest priority? a. Risk for injury b. Self-care deficit c. Disturbed energy field d. Disturbed thought processes ANS: A A patient who is experiencing panic-level anxiety is at high risk for injury, related to an increase in nongoal- directed motor activity, distorted perceptions, and disordered thoughts. Existing data do not support the nursing diagnoses of Self-care deficit or Disturbed energy field. This patient has disturbed thought processes, but the risk for injury has a higher priority. 6. A supervisor assigns a worker a new project. The worker initially agrees but feels resentful. The next day, when asked about the project, the worker says, I’ve been working on other things. When asked 4 hours later, the worker says, someone else was using the copier, so I couldn’t finish it. The workers behavior demonstrates: a. acting out. b. projection. c. suppression. d. passive aggression. ANS: D A passive-aggressive person deals with emotional conflict by indirectly expressing aggression toward others. Compliance on the surface masks covert resistance. Resistance is expressed through procrastination, inefficiency, and stubbornness in response to assigned tasks. Acting out refers to behavioral expression of conflict. Projection is a form of blaming. Suppression is the conscious denial of a disturbing situation or feeling. 7. A patient is undergoing diagnostic tests. The patient says nothing is wrong with me except a stubborn chest cold. The spouse reports that the patient smokes, coughs daily, has recently lost 15 pounds, and is easily fatigued. Which defense mechanism is the patient using? a. Displacement b. Regression c. Projection d. Denial ANS: D Denial is an unconscious blocking of threatening or painful information or feelings. Regression involves using behaviors appropriate at an earlier stage of psychosexual development. Displacement shifts feelings to a more neutral person or object. Projection attributes one’s own unacceptable thoughts or feelings to another. 8. A patient with a mass in the left upper lobe of the lung is scheduled for a biopsy. The patient has difficulty understanding the nurses’ comments and asks, what are they going to do? Assessment findings include a tremulous voice, respirations 28 breaths per minute, and pulse rate 110 beats per minute. What is the patient’s level of anxiety? a. Mild b. Moderate c. Severe d. Panic ANS: B Moderate anxiety causes the individual to grasp less information and reduces his or her problem-solving ability to a less-than-optimal level. Mild anxiety heightens attention and enhances problem-solving abilities. Severe anxiety causes great reduction in the perceptual field. Panic-level anxiety results in disorganized behavior. 9. A patient who is preparing for surgery has moderate anxiety and is unable to understand preoperative information. Which nursing intervention is appropriate? a. Reassure the patient that all nurses are skilled in providing postoperative care. b. Describe the procedure again in a calm manner, using simple language. c. Tell the patient that the staff is prepared to promote recovery. d. Encourage the patient to express feelings to his or her family. ANS: B Providing information in a calm, simple manner helps the patient grasp the important facts. Introducing extraneous topics as described in the incorrect options will further scatter the patient’s attention. 10. A nurse encourages an anxious patient to talk about feelings and concerns. What is the rationale for this intervention? a. Offering hope allays and defuses the patient’s anxiety. b. Concerns stated aloud become less overwhelming and help problem solving to begin. c. Anxiety is reduced by focusing on and validating what is occurring in the environment. d. Encouraging patients to explore alternatives increases the sense of control and lessens anxiety. ANS: B All principles listed are valid, but the only rationale directly related to the intervention of assisting the patient to talk about feelings and concerns is the one that states that concerns spoken aloud become less overwhelming and help problem solving to begin. 11. Which assessment question would be most appropriate for the nurse to ask a patient who has possible generalized anxiety disorder (GAD)? a. Have you been a victim of a crime or seen someone badly injured or killed? b. Do you feel especially uncomfortable in social situations involving people? c. Do you repeatedly do certain things over and over again? d. Do you find it difficult to control your worrying? ANS: D Patients with GAD frequently engage in excessive worrying. They are less likely to engage in ritualistic behavior, fear social situations, or have been involved in a highly traumatic event. 12. A patient in the emergency department has no physical injuries but exhibits disorganized behavior and incoherence after minor traffic accident. In which room should the nurse place the patient? a. Interview room furnished with a desk and two chairs b. Small, empty storage room with no windows or furniture c. Room with an examining table, instrument cabinets, desk, and chair d. Nurse’s office, furnished with chairs, files, magazines, and bookcases ANS: A Individuals who are experiencing severe to panic-level anxiety require a safe environment that is quiet, no stimulating, structured, and simple. A room with a desk and two chairs provides simplicity, few objects with which the patient could cause self-harm, and a small floor space around which the patient can move. A small, empty storage room without windows or furniture would be like a jail cell. The nurse’s office or a room with an examining table and instrument cabinets may be overstimulating and unsafe. 13. A person has minor physical injuries after an automobile accident. The person is unable to focus and says, I feel like something awful is going to happen. This person has nausea, dizziness, tachycardia, and hyperventilation. What is this person’s level of anxiety? a. Mild b. Moderate c. Severe d. Panic ANS: C The person whose anxiety is severe is unable to solve problems and may have a poor grasp of what is happening in the environment. Somatic symptoms such as those described are usually present. The individual with mild anxiety is only mildly uncomfortable and may even find his or her performance enhanced. The individual with moderate anxiety grasps less information about a situation and has some difficulty with problem solving. The individual in panic-level anxiety demonstrates significantly disturbed behavior and may lose touch with reality. 14. Two staff nurses applied for a charge nurse position. After the promotion was announced, the nurse who was not promoted said, the nurse manager had a headache the day I was interviewed. Which defense mechanism is evident? a. Introjection b. Conversion c. Projection d. Splitting ANS: C Projection is the hallmark of blaming, scapegoating, thinking prejudicially, and stigmatizing others. Conversion involves the unconscious transformation of anxiety into a physical symptom. Introjection involves intense, unconscious identification with another person. Splitting is the inability to integrate the positive and negative qualities of oneself or others into a cohesive image. 15. A patient tells a nurse, my new friend is the most perfect person one could imagine kind, considerate, and good looking. I can’t find a single flaw. This patient is demonstrating a. denial. b. projection. c. idealization. d. compensation. ANS: C Idealization is an unconscious process that occurs when an individual attributes exaggerated positive qualities to another. Denial is an unconscious process that calls for the nurse to ignore the existence of the situation. Projection operates unconsciously and results in blaming behavior. Compensation results in the nurse unconsciously attempting to make up for a perceived weakness by emphasizing a strong point. 16. A patient experiences an episode of severe anxiety. Of these medications in the patients’ medical record, which is most appropriate to administer as an as-needed (PRN) anxiolytic medication? a. buspirone (BuSpar) b. lorazepam (Ativan) c. amitriptyline (Elavil) d. desipramine (Norpramin) ANS: B Lorazepam is a benzodiazepine medication used to treat anxiety; it may be administered as needed. Buspirone is long acting and not useful as an as-needed drug. Amitriptyline and desipramine are tricyclic antidepressants and considered second- or third-line agents. 17. Two staff nurses applied for promotion to nurse manager. Initially, the nurse not promoted had feelings of loss but then became supportive of the new manager by helping make the transition smooth and encouraging others. Which term best describes the nurse’s response? a. Altruism b. Sublimation c. Suppression d. Passive aggression ANS: A Altruism is the mechanism by which an individual deals with emotional conflict by meeting the needs of others and vicariously receiving gratification from the responses of others. The nurse’s reaction is conscious, not unconscious. No evidence of aggression is exhibited, and no evidence of conscious denial of the situation exists. Passive aggression occurs when an individual deals with emotional conflict by indirectly and unassertively expressing aggression toward others. 18. A person who feels unattractive repeatedly says, Although I’m not beautiful, I am smart. This is an example of: a. repression. b. devaluation. c. identification. d. compensation. ANS: D Compensation is an unconscious process that allows an individual to make up for deficits in one area by excelling in another area to raise self-esteem. Repression unconsciously puts an idea, event, or feeling out of awareness. Identification is an unconscious mechanism calling for an imitation of the mannerisms or behaviors of another. Devaluation occurs when the individual attributes negative qualities to self or to others. 19. A person who is speaking about a contender for a significant others affection says in a gushy, syrupy voice, What a lovely person. That’s someone I simply adore. The individual is demonstrating: a. reaction formation. b. repression. c. projection. d. denial. ANS: A Reaction formation is an unconscious mechanism that keeps unacceptable feelings out of awareness by using the opposite behavior. Instead of expressing hatred for the other person, the individual gives praise. Denial operates unconsciously to allow an anxiety- producing idea, feeling, or situation to be ignored. Projection involves unconsciously disowning an unacceptable idea, feeling, or behavior by attributing it to another. Repression involves unconsciously placing an idea, feeling, or event out of awareness. 20. An individual experiences sexual dysfunction and blames it on a partner by calling the person unattractive and unromantic. Which defense mechanism is evident? a. Rationalization b. Compensation c. Introjection d. Regression ANS: A Rationalization involves unconsciously making excuses for one’s behavior, inadequacies, or feelings. Regression involves the unconscious use of a behavior from an earlier stage of emotional development. Compensation involves making up for deficits in one area by excelling in another area. Introjection is an unconscious, intense identification with another person. 21. A student says, before taking a test, I feel a heightened sense of awareness and restlessness. The nurse can correctly assess the students experience as: a. culturally influenced. b. displacement. c. trait anxiety. d. mild anxiety. ANS: D Mild anxiety is rarely obstructive to the task at hand. It may be helpful to the patient because it promotes study and increases awareness of the nuances of questions. The incorrect responses have different symptoms. 22. A student says, before taking a test, I feel a heightened sense of awareness and restlessness. The nursing intervention most suitable for assisting the student is to: a. explain that the symptoms are the result of mild anxiety and discuss the helpful aspects. b. advise the student to discuss this experience with a health care provider. c. encourage the student to begin antioxidant vitamin supplements. d. listen without comment. ANS: A Teaching about the symptoms of anxiety, their relation to precipitating stressors, and, in this case, the positive effects of anxiety serves to reassure the patient. Advising the patient to discuss the experience with a health care provider implies that the patient has a serious problem. Listening without comment will do no harm but deprives the patient of health teaching. Antioxidant vitamin supplements are not useful in this scenario. 23. If a cruel and abusive person rationalizes this behavior, which comment is most characteristic of this person? a. I don’t know why it happens. b. I have always had poor impulse control. c. That person should not have provoked me. d. Inside I am a coward who is afraid of being hurt. ANS: C Rationalization consists of justifying one’s unacceptable behavior by developing explanations that satisfy the teller and attempt to satisfy the listener. The abuser is suggesting that the abuse is not his or her fault; it would not have occurred except for the provocation by the other person. 24. A patient experiencing severe anxiety suddenly begins running and shouting, I’m going to explode! The nurse should: a. says, I’m not sure what you mean. Give me an example. b. chase after the patient and give instructions to stop running. c. capture the patient in a basket-hold to increase feelings of control. d. assemble several staff members and state, we will help you regain control. ANS: D The safety needs of the patient and other patients are a priority. The patient is less likely to cause self-harm or hurt others when several staff members take responsibility for providing limits. The explanation given to the patient should be simple and neutral. Simply being told that others can help provide the control that has been lost may be sufficient to help the patient regain control. Running after the patient will increase the patient’s anxiety. More than one staff member is needed to provide physical limits if they become necessary. Asking the patient to give an example is futile, a patient in panic processes information poorly. 25. A person who has been unable to leave home for more than a week because of severe anxiety says, I know it does not make sense, but I just can’t bring myself to leave my apartment alone. Which nursing intervention is appropriate? a. Teach the person to use positive self-talk. b. Assist the person to apply for disability benefits. c. Ask the person to explain why the fear is so disabling. d. Advise the person to accept the situation and use a companion. ANS: A This intervention, a form of cognitive restructuring, replaces negative thoughts such as I can’t leave my apartment with positive thoughts such as I can control my anxiety. This technique helps the patient gain mastery over the symptoms. The other options reinforce the sick role. 26. Which comment by a person experiencing severe anxiety indicates the possibility of obsessive- compulsive disorder? a. I check where my car keys are eight times. b. My legs often feel weak and spastic. c. I’m embarrassed to go out in public. d. I keep reliving the car accident. ANS: A Recurring doubt (obsessive thinking) and the need to check (compulsive behavior) suggest obsessive-compulsive disorder. The repetitive behavior is designed to decrease anxiety but fails and must be repeated. The statement, my legs feel weak most of the time, is more in keeping with a somatoform disorder. Being embarrassed to go out in public is associated with an avoidant personality disorder. Reliving a traumatic event is associated with post- traumatic stress disorder. 27. Alprazolam (Xanax) is prescribed for a patient experiencing acute anxiety. Health teaching should include instructions to: a. report drowsiness. b. eats a tyramine-free diet. c. avoids alcoholic beverages. d. adjusts dose and frequency based on anxiety level. ANS: C Drinking alcohol or taking other anxiolytic medications along with the prescribed benzodiazepine should be avoided because depressant effects of both drugs will be potentiated. Tyramine-free diets are necessary only with monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs). Drowsiness is an expected effect and needs to be reported only if it is excessive. Patients should be taught not to deviate from the prescribed dose and schedule for administration. 28. Which statement is mostly likely to be made by a patient diagnosed with agoraphobia? a. Being afraid to go out seems ridiculous, but I can’t go out the door. b. I’m sure I’ll get over not wanting to leave home soon. It takes time. c. When I have a good incentive to go out, I can do it. d. My family says they like it now that I stay home. ANS: A Individuals who are agoraphobic generally acknowledge that the behavior is not constructive and that they do not really like it. Patients state they are unable to change the behavior. Patients with agoraphobia are not optimistic about change. Most families are dissatisfied when family members refuse to leave the house. 29. A patient has the nursing diagnosis Anxiety, related to , as evidenced by an inability to control compulsive cleaning. Which phrase correctly completes the etiologic portion of the diagnosis? a. ensuring the health of household members b. attempting to avoid interactions with others c. having persistent thoughts about bacteria, germs, and dirt d. needing approval for cleanliness from friends and family ANS: C Many compulsive rituals accompany obsessive thoughts. The patient uses these rituals to relief anxiety. Unfortunately, the anxiety relief is short lived, and the patient must frequently repeat the ritual. The other options are unrelated to the dynamics of compulsive behavior. 30. A patient performs ritualistic hand washing. What should the nurse do to help the patient develop more effective coping strategies? a. Allow the patient to set a hand-washing schedule. b. Encourage the patient to participate in social activities. c. Encourage the patient to discuss hand-washing routines. d. Focus on the patients’ symptoms rather than on the patient. ANS: B Because patients diagnosed with obsessive-compulsive disorder become overly involved in rituals, promoting involvement with other people and activities is necessary to improve the patients coping strategies. Daily activities prevent the constant focus on anxiety and its symptoms. The other interventions focus on the compulsive symptom. 31. For a patient experiencing panic, which nursing intervention should be implemented first? a. Teach relaxation techniques. b. Administer an anxiolytic medication. c. Provide calm, brief, directive communication. d. Gather a show of force in preparation for gaining physical control. ANS: C Calm, brief, directive verbal interaction can help the patient gain control of the overwhelming feelings and impulses related to anxiety. Patients experiencing panic-level anxiety are unable to focus on reality; thus, learning relaxation techniques is virtually impossible. Administering an anxiolytic medication should be considered if providing calm, brief, directive communication is ineffective. Although the patient is disorganized, violence may not be imminent, ruling out the intervention of preparing for physical control until other, less-restrictive measures are proven ineffective. 32. Which finding indicates that a patient with moderate-to-severe anxiety has successfully lowered the anxiety level to mild? The patient: a. asks, What’s the matter with me? b. stays in a room alone and paces rapidly. c. can concentrate on what the nurse is saying. d. states, I dent want anything to eat. My stomach is upset. ANS: C The ability to concentrate and attend to reality is increased slightly in mild anxiety and decreased in moderate-, severe-, and panic-level anxiety. Patients with high levels of anxiety often ask, What’s the matter with me? Staying in a room alone and pacing suggest moderate anxiety. Expressing a lack of hunger is not necessarily a criterion for evaluating anxiety. 33. A patient tells the nurse, I don’t go to restaurants because people might laugh at the way I eat, or I could spill food and be laughed at. The nurse assesses this behavior as consistent with: a. acrophobia. b. agoraphobia. c. social anxiety disorder (social phobia). d. post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). ANS: C The fear of a potentially embarrassing situation represents social anxiety disorder (social phobia). Acrophobia is the fear of heights. Agoraphobia is the fear of a place in the environment. Post-traumatic stress disorder is associated with a major traumatic event. 34. A patient checks and rechecks electrical cords related to an obsessive thought that the house may burn down. The nurse and patient explore the likelihood of an actual fire. The patient states that a house fire is not likely. This counseling demonstrates the principles of a. flooding. b. desensitization. c. relaxation technique. d. cognitive restructuring. ANS: D Cognitive restructuring involves the patient in testing automatic thoughts and drawing new conclusions. Desensitization involves a graduated exposure to a feared object. Relaxation training teaches the patient to produce the opposite of the stress response. Flooding exposes the patient to a large amount of undesirable stimuli in an effort to extinguish the anxiety response. 35. A patient has a fear of public speaking. The nurse should be aware that social anxiety disorders (social phobias) are often treated with which type of medication? a. Beta-blockers b. Antipsychotic medications c. Tricyclic antidepressant agents d. Monoamine oxidase inhibitors ANS: A Beta-blockers, such as propranolol, are often effective in preventing symptoms of anxiety associated with social phobias. Neuroleptic medications are major tranquilizers and not useful in treating social phobias. Tricyclic antidepressants are rarely used because of their side effect profile. MAOIs are administered for depression and only by individuals who can observe the special diet required. 36. A patient tells the nurse, I wanted my health care provider to prescribe diazepam (Valium) for my anxiety disorder, but buspirone (BuSpar) was prescribed instead. Why? The nurses reply should be based on the knowledge that buspirone: a. does not produce blood dyscrasias. b. does not cause dependence. c. can be administered as needed. d. is faster acting than diazepam. ANS: B Buspirone is considered effective in the long-term management of anxiety because it is not habituating. Because it is long acting, buspirone is not valuable as an as-needed or as a fast-acting medication. The fact that buspirone does not produce blood dyscrasias is less relevant in the decision to prescribe buspirone. SELECT ALL THAT APPLY 1. A child is placed in a foster home after being removed from parental contact because of abuse. The child is apprehensive and overreacts to environmental stimuli. The foster parents ask the nurse how to help the child. What should the nurse recommend? Select all that apply. a. Use a calm manner and low voice. b. Maintain simplicity in the environment. c. Avoid repetition in what is said to the child. d. Minimize opportunities for exercise and play. e. Explain and reinforce reality to avoid distortions. ANS:A,B,E The child can be hypothesized to have moderate-to-severe anxiety. A calm manner calms the child. A simple, structured, predictable environment is less anxiety provoking and reduces overreaction to stimuli. Calm, simple explanations that reinforce reality validate the environment. Repetition is often needed when the child is unable to concentrate because of elevated levels of anxiety. Opportunities for play and exercise should be provided as avenues to reduce anxiety. Physical movement helps channel and lower anxiety. Play also helps by allowing the child to act out concerns. 2. A nurse plans health teaching for a patient diagnosed with generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) who takes lorazepam (Ativan). What information should be included? Select all that apply. a. Use caution when operating machinery. b. Allow only tyramine-free foods in diet. c. Restrict intake of caffeine. d. Avoid using alcohol and other sedatives. e. Take the medication on an empty stomach. ANS:A,C,D Caffeine is a central nervous system stimulant that acts as an antagonist to the benzodiazepine lorazepam. Daily caffeine intake should be reduced to the amount contained in one cup of coffee. Benzodiazepines are sedatives, thus the importance of exercising caution when driving or using machinery and the importance of not using other central nervous system depressants such as alcohol or sedatives to avoid potentiation. Benzodiazepines do not require a special diet. Food will reduce gastric irritation from the medication. 3. Which assessment questions are most appropriate to ask a patient with possible obsessive-compulsive disorder? Select all that apply. a. Have you been a victim of a crime or seen someone badly injured or killed? b. Are there certain social situations that cause you to feel especially uncomfortable? c. Do you have to do things in a certain way to feel comfortable? d. Is it difficult to keep certain thoughts out of awareness? e. Do you do certain things over and over again? ANS:C,D,E The correct questions refer to obsessive thinking and compulsive behaviors. The incorrect responses are more pertinent to a patient with suspected post-traumatic stress disorder or with suspected social anxiety disorder (social phobia). Chapter 13: Personality Disorders 1. A therapist recently convicted of multiple counts of Medicare fraud says, Sure I overbilled. Why not? Everyone takes advantage of the government, so I did too. These statements show: a. shame. b. suspiciousness. c. superficial remorse. d. lack of guilt feelings. ANS: D Rationalization is being used to explain behavior and deny wrongdoing. The individual who does not believe he or she has done anything wrong will not exhibit anxiety, remorse, or guilt about the act. The patients remarks cannot be assessed as shameful. Lack of trust or concern that other are determined to cause harm is not evident. 2. Which intervention is appropriate for a patient diagnosed with an antisocial personality disorder who frequently manipulates others? a. Refer the patients requests and questions to the case manager. b. Explore the patients’ feelings of fear and inferiority. c. Provide negative reinforcement for acting-out behavior. d. Ignore, rather than confront, inappropriate behavior. ANS: A Manipulative patients frequently make requests of many different staff members, hoping someone will give in. Having only one decision-maker provides consistency and avoids the potential for playing one staff member against another. Positive reinforcement of appropriate behaviors is more effective than negative reinforcement. The behavior should not be ignored; judicious use of confrontation is necessary. Patients with antisocial personality disorders rarely have feelings of fear and inferiority. 3. As a nurse prepares to administer a medication to a patient diagnosed with a borderline personality disorder, the patient says, just leave it on the table. I’ll take it when I finish combing my hair. What is the nurses best response? a. Reinforce this assertive action by the patient. Leave the medication on the table as requested. b. Respond to the patient, I’m worried that you might not take it. I will come back later. c. Say to the patient, I must watch you take the medication. Please take it now. d. Ask the patient, why don’t you want to take your medication now? ANS: C The individual with a borderline personality disorder characteristically demonstrates manipulative, splitting, and self-destructive behaviors. Consistent limit setting is vital for the patient’s safety, as well as to prevent splitting other staff members. Why questions are not therapeutic. 4. What is an appropriate initial outcome for a patient diagnosed with a personality disorder who frequently manipulates others? The patient will: a. identifies when feeling angry. b. use manipulation only to get legitimate needs met. c. acknowledges manipulative behavior when it is called to his or her attention. d. accept fulfillment of his or her requests within an hour rather than immediately. ANS: C Acknowledging manipulative behavior is an early outcome that paves the way for taking greater responsibility for controlling manipulative behavior at a later time. Identifying anger relates to anger and aggression control. Using manipulation to get legitimate needs is an inappropriate outcome. Ideally, the patient will use assertive behavior to promote the fulfillment of legitimate needs. Accepting fulfillment of requests within an hour rather than immediately relates to impulsivity and immediacy control. 5. Consider these comments made to three different nurses by a patient diagnosed with an antisocial personality disorder: You’re a better nurse than the day shift nurse said you were Another nurse said you don’t do your job right; You think you’re perfect, but I’ve seen you make three mistakes. Collectively, these interactions can be assessed as: a. seductive. b. detached. c. manipulative. d. guilt producing. ANS: C Patients manipulate and control staff members in various ways. By keeping staff members off balance or fighting among themselves, the person with an antisocial personality disorder is left to operate as he or she pleases. Seductive behavior has sexual connotations. The patient is displaying the opposite of detached behavior. Guilt is not evidenced in the comments. 6. A nurse reports to the interdisciplinary team that a patient diagnosed with an antisocial personality disorder lies to other patients, verbally abuses a patient diagnosed with dementia, and flatters the primary nurse. This patient is detached and superficial during counseling sessions. Which behavior most clearly warrants limit setting? a. Flattering the nurse b. Lying to other patients c. Verbal abuse of another patient d. Detached superficiality during counseling ANS: C Limits must be set in areas in which the patients behavior affects the rights of others. Limiting verbal abuse of another patient is a priority intervention. The other concerns should be addressed during therapeutic encounters. 7. A patient diagnosed with borderline personality disorder has a history of self-mutilation and suicide attempts. The patient reveals feelings of depression and anger with life. The psychiatrist suggests the use of a medication. Which type of medication should the nurse expect? a. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) b. Monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) c. Benzodiazepine d. Antipsychotic ANS: A SSRIs are used to treat depression. Many patients with borderline personality disorder are fearful of taking something over which they have little control. Because SSRIs have a good side effect profile, the patient is more likely to comply with the medication. Low-dose antipsychotic or anxiolytic medications are not Test Bank: Essentials of Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing (3rd Edition by Varcarolis) 96 supported by the data given in this scenario. MAOIs require great diligence in adherence to a restricted diet and are rarely used for patients who are impulsive. 8. A persons spouse filed charges of battery. The person has a long history of acting-out behaviors and several arrests. Which statement by the person suggests an antisocial personality disorder? a. I have a quick temper, but I can usually keep it under control. b. I’ve done some stupid things in my life, but I’ve learned a lesson. c. I’m feeling terrible about the way my behavior has hurt my family. d. I hit because I’m tired of being nagged. My spouse deserved the beating. ANS: D The patient with an antisocial personality disorder often impulsively acts out feelings of anger and feels no guilt or remorse. Patients with antisocial personality disorders rarely seem to learn from experience or feel true remorse. Problems with anger management and impulse control are common. 9. What is the priority nursing diagnosis for a patient diagnosed with antisocial personality disorder who has made threats against staff, ripped art off the walls, and thrown objects? a. Disturbed sensory perception auditory b. Risk for other-directed violence c. Ineffective denial d. Ineffective coping ANS: B Violence against property, along with threats to harm staff, makes this diagnosis the priority. Patients with antisocial personality disorders rarely have psychotic symptoms. When patients with antisocial personality disorders use denial, they use it effectively. Although ineffective coping applies, the risk for violence is a higher priority. 10. A patient diagnosed with a personality disorder has used manipulation to get his or her needs met. The staff decides to apply limit-setting interventions. What is the correct rationale for this action? a. It provides an outlet for feelings of anger and frustration. b. It respects the patient’s wishes so assertiveness will develop. c. External controls are necessary while internal controls are developed. d. Anxiety is reduced when staff members assume responsibility for the patient’s behavior. ANS: C A lack of internal controls leads to manipulative behaviors such as lying, cheating, conning, and flattering. To protect the rights of others, external controls must be consistently maintained until the patient is able to behave appropriately. 11. A patient diagnosed with borderline personality disorder and a history of self-mutilation has now begun dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) on an outpatient basis. Counseling focuses on self-harm behavior management. Today the patient telephones to say, I’m feeling empty and want to cut myself. The nurse should: a. arranges for emergency inpatient hospitalization. b. sends the patient to the crisis intervention unit for 8 to 12 hours. c. assists the patient to identify the trigger situation and choose a coping strategy. d. advises the patient to take an antianxiety medication to decrease the anxiety level. ANS: C The patient has responded appropriately to the urge for self-harm by calling a helping individual. A component of dialectical behavior therapy is telephone access to the therapist for coaching during crises. The nurse can assist the patient to choose an alternative to self- mutilation. The need for a protective environment may not be necessary if the patient is able to use cognitive strategies to determine a coping strategy that reduces the urge to mutilate. Taking a sedative and going to sleep should not be the first-line intervention; sedation may reduce the patient’s ability to weigh alternatives to mutilating behavior. 12. The most challenging nursing intervention for patients diagnosed with personality disorders who use manipulation to get their needs met is: a. supporting behavioral change. b. monitoring suicide attempts. c. maintaining consistent limits. d. using aversive therapy. ANS: C Maintaining consistent limits is by far the most difficult intervention because of the patients’ superior skills at manipulation. Supporting behavioral change and monitoring patient safety are less difficult tasks. Aversive therapy would probably not be part of the care plan; positive reinforcement strategies for acceptable behavior are more effective than aversive techniques. 13. The history shows that a newly admitted patient has impulsivity. The nurse would expect behavior characterized by: a. adherence to a strict moral code. b. manipulative, controlling strategies. c. postponing gratification to an appropriate time. d. little time elapsed between thought and action. ANS: D The impulsive individual acts in haste without taking time to consider the consequences of the action. None of the other options describes impulsivity. 14. A patient tells a nurse; I sometimes get into trouble because I make quick decisions and act on them. A therapeutic response would be: a. Let’s consider the advantages of being able to stop and think before acting. b. It sounds as though you’ve developed some insight into your situation. c. I’ll bet you have some interesting stories to share about overreacting. d. It’s good that you’re showing readiness for behavioral change. ANS: A the patient is showing openness to learning techniques for impulse control. One technique is to teach the patient to stop and think before acting impulsively. The patient can then be taught to evaluate the outcomes of possible actions and choose an effective action. The incorrect responses shift the encounter to a social level or are judgmental. 15. A patient diagnosed with borderline personality disorder is hospitalized several times after self-inflicted lacerations. The patient remains impulsive. Dialectical behavior therapy starts on an outpatient basis. Which nursing diagnosis is the focus of this therapy? a. Risk for self-mutilation b. Impaired skin integrity c. Risk for injury d. Powerlessness ANS: A Risk for self-mutilation is a nursing diagnosis relating to patient safety needs and is therefore a high priority. Impaired skin integrity and powerlessness may be appropriate foci for care but are not the priority or related to this therapy. Risk for injury implies accidental injury, which is not the case for the patient diagnosed with borderline personality disorder. 16. Which statement made by a patient diagnosed with borderline personality disorder indicates the treatment plan is effective? a. I think you are the best nurse on the unit. b. I’m never going to get high on drugs again. c. I hate my doctor for not giving me what I ask for. d. I felt empty and wanted to cut myself, so I called you. ANS: D Seeking a staff member instead of impulsively self-mutilating shows an adaptive coping strategy. The incorrect responses demonstrate idealization, devaluation, and wishful thinking. 17. When preparing to interview a patient diagnosed with narcissistic personality disorder, a nurse can anticipate the assessment findings will include: a. preoccupation with minute details; perfectionism. b. charm, drama, seductiveness; seeking admiration. c. difficulty being alone; indecisiveness, submissiveness. d. grandiosity, attention seeking, and arrogance. ANS: D According to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), the characteristics of grandiosity, attention seeking, and arrogance are consistent with narcissistic personality disorder. Charm, drama, seductiveness, and admiration seeking are observed in patients diagnosed with histrionic personality disorder. Preoccupation with minute details and perfectionism are observed in individuals diagnosed with obsessive- compulsive personality disorder. Patients diagnosed with dependent personality disorder often express difficulty being alone and are indecisive and submissive. 18. For which behavior would limit setting be most essential? The patient: a. clings to the nurse and asks for advice about inconsequential matters. b. is flirtatious and provocative with staff members of the opposite sex. c. is hypervigilant and refuses to attend unit activities. d. urges a suspicious patient to hit anyone who stares. ANS: D The correct option is an example of a manipulative behavior. Because manipulation violates the rights of others, limit setting is absolutely necessary. Furthermore, limit setting is necessary in this case because the safety of patients is at risk. Limit setting may be occasionally used with dependent behavior (clinging to the nurse) and histrionic behavior (flirting with staff members), but other therapeutic techniques are also useful. Limit setting is not needed for a patient who is hypervigilant and refuses to attend unit activities; rather, the need to develop trust is central to patient compliance. 19. A nurse in the emergency department tells an adult, your mother had a severe stroke. The adult tearfully says, who will take care of me now? My mother always told me what to do, what to wear, and what to eat. I need someone to reassure me when I get anxious. Which term best describes this behavior? a. Histrionic b. Dependent c. Narcissistic d. Borderline ANS: B The main characteristic of the dependent personality is a pervasive need to be taken care of that leads to submissive behaviors and a fear of separation. Histrionic behavior is characterized by flamboyance, attention seeking, and seductiveness. Narcissistic behavior is characterized by grandiosity and exploitive behavior. Patients with borderline personality disorder demonstrate separation anxiety, impulsivity, and splitting. 20. Others describe a worker as very shy and lacking in self-confidence. This worker stays in an office cubicle all day and never comes out for breaks or lunch. Which term best describes this behavior? a. Avoidant b. Dependent c. Histrionic d. Paranoid ANS: A Patients with avoidant personality disorder are timid, socially uncomfortable, and withdrawn and avoid situations in which they might fail. They believe themselves to be inferior and unappealing. Individuals with dependent personality disorder are clinging, needy, and submissive. Individuals with histrionic personality disorder are seductive, flamboyant, shallow, and attention seeking. Individuals with paranoid personality disorder are suspicious and hostile and project blame. 21. What is the priority intervention for a nurse beginning a therapeutic relationship with a patient diagnosed with a schizotypal personality disorder? a. Respect the patients need for periods of social isolation. b. Prevent the patient from violating the nurses’ rights. c. Engage the patient in many community activities. d. Teach the patient how to match clothing. ANS: A Patients diagnosed with schizotypal personality disorder are eccentric and often display perceptual and cognitive distortions. They are suspicious of others and have considerable difficulty trusting. They become highly anxious and frightened in social situations, thus the need to respect their desire for social isolation. Teaching the patient to match clothing is not the priority intervention. Patients diagnosed with schizotypal personality disorder rarely engage in behaviors that violate the nurses’ rights or exploit the nurse. 22. A patient diagnosed with borderline personality disorder self-inflicted wrist lacerations after gaining new privileges on the unit. The cause of the self-mutilation is probably related to: a. inherited disorder that manifests itself as an incapacity to tolerate stress. b. use of projective identification and splitting to bring anxiety to manageable levels. c. constitutional inability to regulate affect, predisposing to psychic disorganization. d. fear of abandonment associated with progress toward autonomy and independence. ANS: D Fear of abandonment is a central theme for most patients diagnosed with borderline personality disorder. This fear is often exacerbated when patients diagnosed with borderline personality disorder experience success or growth. The incorrect options are not associated with self-mutilation. 23. A patient diagnosed with borderline personality disorder has self-inflicted wrist lacerations. The health care provider prescribes daily dressing changes. The nurse performing this care should: a. encourages the patient to express anger. b. provide care in a matter-of-fact manner. c. be very kind, sympathetic, and concerned. d. offer to listen to the patients’ feelings about cutting. ANS: B A matter-of-fact approach does not provide the patient with positive reinforcement for self- mutilation. The goal of providing emotional consistency is supported by this approach. The incorrect options provide positive reinforcement of the behavior. 24. A nurse set limits for a patient diagnosed with a borderline personality disorder. The patient tells the nurse, you used to care about me. I thought you were wonderful. Now I can see I was mistaken. You’re terrible. This outburst can be assessed as: a. denial. b. splitting. c. reaction formation. d. separation-individuation strategies. ANS: B Splitting involves loving a person and then hating the person; the patient is unable to recognize that an individual can have both positive and negative qualities. Denial is an unconscious motivated refusal to believe something. Reaction formation involves unconsciously doing the opposite of a forbidden impulse. Separation-individuation strategies refer to childhood behaviors related to developing independence from the caregiver. 25. Which characteristic of individuals diagnosed with personality disorders makes it most necessary for staff to schedule frequent meetings? a. Ability to achieve true intimacy b. Flexibility and adaptability to stress c. Ability to evoke interpersonal conflict d. Inability to develop trusting relationships ANS: C Frequent team meetings are held to counteract the effects of the patients attempts to split staff and set them against one another, causing interpersonal conflict. Patients with personality disorders are inflexible and demonstrate maladaptive responses to stress. They are usually unable to develop true intimacy with others and are unable to develop trusting relationships. Although problems with trust may exist, it is not the characteristic that requires frequent staff meetings. 26. Which common assessment finding would be most applicable to a patient diagnosed with any personality disorder? The patient: a. demonstrates behaviors that cause distress to self rather than to others. b. has self-esteem issues, despite his or her outward presentation. c. usually becomes psychotic when exposed to stress. d. does not experience real distress from symptoms. ANS: B Self-esteem issues are present, despite patterns of withdrawal, grandiosity, suspiciousness, or unconcern. They seem to relate to early life experiences and are reinforced through unsuccessful experiences in loving and working. Personality disorders involve lifelong, inflexible, dysfunctional, and deviant patterns of behavior that cause distress to others and, in some cases, to self. Patients with personality disorders may experience very real anxiety and distress when stress levels rise. Some individuals with personality disorders, but not all, may decompensate and show psychotic behaviors under stress. SELECT ALL THAT APPLY 1. A nurse plans the care for an individual diagnosed with antisocial personality disorder. Which characteristic behaviors will the nurse expect? Select all that apply. a. Reclusive behavior b. Callous attitude c. Perfectionism d. Aggression e. Clinginess f. Anxiety ANS: B, D Individuals diagnosed with antisocial personality disorders characteristically demonstrate manipulative, exploitative, aggressive, callous, and guilt-instilling behaviors. Individuals diagnosed with antisocial personality disorders are more extroverted than reclusive, rarely show anxiety, and rarely demonstrate clinging or dependent behaviors. Individuals diagnosed with antisocial personality disorders are more likely to be impulsive than to be perfectionists. 2. For which patients diagnosed with personality disorders would a family history of similar problems be most likely? Select all that apply. a. Obsessive-compulsive b. Antisocial c. Dependent d. Schizotypal e. Narcissistic ANS:A,B,D Some personality disorders have evidence of genetic links; therefore the family history would show other family members with similar traits. Heredity plays a role in schizotypal and antisocial problems, as well as obsessive- compulsive personality disorder. Chapter 14: Eating Disorders 1. Over the past year, a woman has cooked gourmet meals for her family but eats only tiny servings. She wears layered, loose clothing and now has amenorrhea. Her current weight is 95 pounds, a loss of 35 pounds. Which medical diagnosis is most likely? a. Binge eating disorder b. Anorexia nervosa c. Bulimia nervosa d. Pica ANS: B Overly controlled eating behaviors, extreme weight loss, amenorrhea, preoccupation with food, and wearing several layers of loose clothing to appear larger are part of the clinical picture of an individual with anorexia nervosa. The individual with bulimia usually is near normal weight. The binge eater is often overweight. Pica refers to eating nonfood items. 2. Disturbed body image is the nursing diagnosis for a patient diagnosed with an eating disorder. Which outcome indicator is most appropriate to monitor? a. Weight, muscle, and fat are congruent with height, frame, age, and sex. b. Calorie intake is within the required parameters of the treatment plan. c. Weight reaches the established normal range for the patient. d. Patient expresses satisfaction with body appearance. ANS: D Body image disturbances are considered improved or resolved when the patient is consistently satisfied with his or her own appearance and body function. This consideration is subjective. The other indicators are more objective but less related to the nursing diagnosis. 3. A patient who is referred to the eating disorders clinic has lost 35 pounds in the past 3 months. To assess the patient’s oral intake, the nurse should ask: a. Do you often feel fat? b. Who plans the family meals? c. What do you eat in a typical day? d. What do you think about your present weight? ANS: C Although all the questions might be appropriate to ask, only What do you eat in a typical day? focuses on the eating patterns. Asking if the patient often feels fat focuses on distortions in body image. Questions about family meal planning are unrelated to eating patterns. Asking for the patients’ thoughts on present weight explores the patients’ feelings about weight. 4. A patient diagnosed with anorexia nervosa virtually stopped eating 5 months ago and has lost 25% of body weight. A nurse asks, describe what you think about your present weight and how you look. Which response by the patient is most consistent with the diagnosis? a. I am fat and ugly. b. What I think about myself is my business. c. I am grossly underweight, but that’s what I want. d. I am a few pounds overweight, but I can live with it. ANS: A Patients diagnosed with anorexia nervosa do not recognize their thinness. They perceive themselves to be overweight and unattractive. The patient with anorexia will usually disclose perceptions about self to others. The patient with anorexia will persist in trying to lose more weight. 5. A patient was diagnosed with anorexia nervosa. The history shows the patient virtually stopped eating 5 months ago and has lost 25% of body weight. The patient’s current serum potassium is 2.7 mg/dl. Which nursing diagnosis applies? a. Adult failure to thrive, related to abuse of laxatives as evidenced by electrolyte imbalances and weight loss b. Disturbed energy field, related to physical exertion in excess of energy produced through caloric intake as evidenced by weight loss and hyperkalemia c. Ineffective health maintenance, related to self-induced vomiting as evidenced by swollen parotid glands and hyperkalemia d. Imbalanced nutrition: less than body requirements, related to malnutrition as evidenced by loss of 25% of body weight and hypokalemia ANS: D The patient’s history and laboratory results support the correct nursing diagnosis. Available data do not confirm that the patient uses laxatives, induces vomiting, or exercises excessively. The patient has hypokalemia rather than hyperkalemia. 6. Outpatient treatment is planned for a patient diagnosed with anorexia nervosa. Select the most important outcome related to the nursing diagnosis: Imbalanced nutrition: less than body requirements. Within 1 week, the patient will: a. weigh self accurately using balanced scales. b. limit exercise to less than 2 hours daily. c. select clothing that fits properly. d. gain 1 to 2 pounds. ANS: D Only the outcome of a gain of 1 to 2 pounds can be accomplished within 1 week when the patient is an outpatient. The focus of an outcome is not on the patient weighing self. Limiting exercise and selecting proper clothing are important, but weight gain takes priority. 7. Which nursing intervention has priority as a patient diagnosed with anorexia nervosa begins to gain weight? a. Assess for depression and anxiety. b. Observe for adverse effects of re-feeding. c. Communicate empathy for the patients’ feelings. d. Help the patient balance energy expenditure and caloric intake. ANS: B The nursing intervention of observing for adverse effects of re-feeding most directly relates to weight gain and is a priority. Assessing for depression and anxiety and communicating empathy relate to coping. Helping the patient balance energy expenditure and caloric intake is an inappropriate intervention. 8. A patient diagnosed with anorexia nervosa is resistant to weight gain. What is the rationale for establishing a contract with the patient to participate in measures designed to produce a specified weekly weight gain? a. Because severe anxiety concerning eating is expected, objective and subjective data must be routinely collected. b. Patient involvement in decision-making increases a sense of control and promotes compliance with the treatment. c. A team approach to planning the diet ensures that physical and emotional needs of the patient are met. d. Because of increased risk for physical problems with re-feeding, obtaining patient permission is required. ANS: B A sense of control for the patient is vital to the success of therapy. A diet that controls weight gain can allay patient fears of a too-rapid weight gain. Data collection is not the reason for contracting. A team approach is wise but is not a guarantee that the patients’ needs will be met. Permission for treatment is a separate issue. The contract for weight gain is an additional aspect of treatment. 9. The nursing care plan for a patient diagnosed with anorexia nervosa includes the intervention Monitor for complications of re-feeding. Which body system should a nurse closely monitor for dysfunction? a. Renal b. Endocrine c. Central nervous d. Cardiovascular ANS: D Re-feeding resulting in a too-rapid weight gain can overwhelm the heart, resulting in cardiovascular collapse. focused assessment becomes a necessity to ensure patient physiologic integrity. The other body systems are not initially involved in the re-feeding syndrome. 10. A psychiatric clinical nurse specialist uses cognitive therapy techniques with a patient diagnosed with anorexia nervosa. Which statement by the staff nurse supports this type of therapy? a. What are your feelings about not eating the food that you prepare? b. You seem to feel much better about yourself when you eat something. c. It must be difficult to talk about private matters to someone you just met. d. Being thin does not seem to solve your problems. You are thin now but still unhappy. ANS: D The correct response is the only strategy that attempts to question the patients distorted thinking. 11. An appropriate intervention for a patient diagnosed with bulimia nervosa who binges, and purges is to teach the patient to: a. eats a small meal after purging. b. avoids skipping meals or restricting food. c. concentrates oral intake after 4 PM daily. d. understands the value of reading journal entries aloud to others. ANS: B One goal of health teaching is the normalization of eating habits. Food restriction and skipping meals lead to rebound bingeing. Teaching the patient to eat a small meal after purging will probably perpetuate the need to induce vomiting. Teaching the patient to concentrate intake after 4 PM will lead to late-day bingeing. Journal entries are private. 12. What behavior by a nurse caring for a patient diagnosed with an eating disorder indicates the nurse needs supervision? a. The nurses’ comments are nonjudgmental. b. The nurse uses an authoritarian manner when interacting with the patient. c. The nurse teaches the patient to recognize signs of increasing anxiety and ways to intervene. d. The nurse refers the patient to a self-help group for individuals with eating disorders. ANS: B In the effort to motivate the patient and take advantage of the decision to seek help and be healthier, the nurse must take care not to cross the line toward authoritarianism and assume the role of a parent. The helpful nurse uses a problem-solving approach and focuses on the patients’ feelings of shame and low self-esteem. Referral to a self-help group is an appropriate intervention. 13. A nursing diagnosis for a patient diagnosed with bulimia nervosa is: Ineffective coping, related to feelings of loneliness as evidenced by overeating to comfort self, followed by self-induced vomiting. The best outcome related to this diagnosis is, Within 2 weeks the patient will: a. appropriately express angry feelings. b. verbalizes two positive things about self. c. verbalizes the importance of eating a balanced diet. d. identifies two alternative methods of coping with loneliness. ANS: D The outcome of identifying alternative coping strategies is most directly related to the diagnosis of Ineffective coping. Verbalizing positive characteristics of self and verbalizing the importance of eating a balanced diet are outcomes that might be used for other nursing diagnoses. Appropriately expressing angry feelings is not measurable. 14. Which nursing intervention has the highest priority for a patient diagnosed with bulimia nervosa? a. Assist the patient to identify triggers to binge eating. b. Provide corrective consequences for weight loss. c. Explore patient needs for health teaching. d. Assess for signs of impulsive eating. ANS: A For most patients with bulimia nervosa, certain situations trigger the urge to binge; purging then follows. The triggers are often anxiety-producing situations. Identifying these triggers makes it possible to break the binge-purge cycle. Because binge eating and purging directly affect physical status, the need to promote physical safety assumes the highest priority. The question calls for an intervention rather than an assessment. 15. One bed is available on the inpatient eating disorders unit. Which patient should be admitted? The patient whose weight dropped from: a. 150 to 100 pounds over a 4-month period. Vital signs: temperature, 35.9 C; pulse, 38 beats/min; blood pressure, 60/40 mm Hg b. 120 to 90 pounds over a 3-month period. Vital signs: temperature, 36 C; pulse, 50 beats/min; blood pressure, 70/50 mm Hg c. 110 to 70 pounds over a 4-month period. Vital signs: temperature, 36.5 C; pulse, 60 beats/min; blood pressure, 80/66 mm Hg d. 90 to 78 pounds over a 5-month period. Vital signs: temperature, 36.7 C; pulse, 62 beats/min; blood pressure, 74/48 mm Hg ANS: A Physical criterion for hospitalization include weight loss of more than 30% of body weight within 6 months, temperature below 36 C (hypothermia), heart rate less than 40 beats/min, and systolic blood pressure less than 70 mm Hg. 16. While providing health teaching for a patient diagnosed with bulimia nervosa, a nurse should emphasize information about: a. self-monitoring of daily food and fluid intake. b. establishing the desired daily weight gain. c. recognizing symptoms of hypokalemia. d. self-esteem maintenance. ANS: C Hypokalemia results from potassium loss associated with vomiting. Physiologic integrity can be maintained if the patient can self-diagnose potassium deficiency and adjust the diet or seek medical assistance. Self-monitoring of daily food and fluid intake is not useful if the patient purges. Daily weight gain may not be desirable for a patient with bulimia nervosa. Self-esteem is an identifiable problem but is of lesser priority than the risk for hypokalemia. 17. As a patient admitted to the eating disorders unit undresses, a nurse observes that the patient’s body is covered by fine, downy hair. The patient weighs 70 pounds and is 5 feet, 4 inches tall. Which condition should be documented? a. Amenorrhea b. Alopecia c. Lanugo d. Stupor ANS: C The fine, downy hair noted by the nurse is called lanugo. It is frequently seen in patients with anorexia nervosa. None of the other conditions can be supported by the data the nurse has gathered. 18. A patient being admitted to the eating disorders unit has a yellow cast to the skin and fine, downy hair covering the body. The patient weighs 70 pounds; height is 5 feet, 4 inches. The patient is quiet and says only, I won’t eat until I look thin. What is the priority initial nursing diagnosis? a. Anxiety, related to fear of weight gain b. Disturbed body image, related to weight loss c. Ineffective coping, related to lack of conflict resolution skills d. Imbalanced nutrition: less than body requirements, related to self-starvation ANS: D The physical assessment shows cachexia, which indicates imbalanced nutrition. Addressing the patient’s self- starvation is the priority above the incorrect responses. 19. A nurse conducting group therapy on the eating disorders unit schedules the sessions immediately after meals for the primary purpose of: a. maintaining patient’s concentration and attention. b. shifting the patients focus from food to psychotherapy. c. focusing on weight control mechanisms and food preparation. d. processing the heightened anxiety associated with eating. ANS: D Eating produces high anxiety for patients with eating disorders. Anxiety levels must be lowered if the patient is to be successful in attaining therapeutic goals. Shifting the patients focus from food to psychotherapy and focusing on weight control mechanisms and food preparation are not desirable. Maintaining patient’s concentration and attention is important, but not the primary purpose of the schedule. 20. Physical assessment of a patient diagnosed with bulimia nervosa often reveals: a. prominent parotid glands. b. peripheral edema. c. thin, brittle hair. d. amenorrhea. ANS: A Prominent parotid glands are associated with repeated vomiting. The other options are signs of anorexia nervosa and are not usually observed in bulimia. 21. Which personality characteristic is a nurse most likely to assess in a patient diagnosed with anorexia nervosa? a. carefree flexibility b. Rigidity, perfectionism c. Open displays of emotion d. High spirits and optimism ANS: B Rigid thinking, inability to demonstrate flexibility, and difficulty changing cognitions are characteristic of patients diagnosed with eating disorders. The incorrect options are rare in a patient with anorexia nervosa. Inflexibility, controlled emotions, and pessimism are more the norm. 22. Which assessment finding for a patient diagnosed with an eating disorder meets a criterion for hospitalization? a. Urine output: 40 ml/hr b. Pulse rate: 58 beats/min c. Serum potassium: 3.4 mEq/L d. Systolic blood pressure: 62 mm Hg ANS: D Systolic blood pressure less than 70 mm Hg is an indicator for inpatient care. Many people without eating disorders have bradycardia (pulse less than 60 beats/min). Urine output should be more than 30 ml/hr. A potassium level of 3.4 mEq/L is within the normal range. 23. Which statement is a nurse most likely to hear from a patient diagnosed with anorexia nervosa? a. I would be happy if I could lose 20 more pounds. b. My parents don’t pay much attention to me. c. I’m thin for my height. d. I have nice eyes. ANS: A Patients with eating disorders have distorted body images and cognitive distortions. They see themselves as overweight even when their weight is subnormal. I’m thin for my height is therefore unlikely to be heard from a patient with anorexia nervosa. Poor self-image precludes making positive statements about self, such as I have nice eyes. Many patients with eating disorders see supportive others as intrusive and out of tune with their needs. 24. Which nursing diagnosis is more applicable for a patient diagnosed with anorexia nervosa who restricts intake and is 20% below normal weight than for a 130-pound patient diagnosed with bulimia nervosa who purges? a. Powerlessness b. Ineffective coping c. Disturbed body image d. Imbalanced nutrition: less than body requirements ANS: D The patient with bulimia nervosa usually maintains a close to normal weight, whereas the patient with anorexia nervosa may approach starvation. The incorrect options may be appropriate for patients with either anorexia nervosa or bulimia nervosa. 25. An outpatient diagnosed with anorexia nervosa has begun re-feeding. Between the first and second appointments, the patient gained 8 pounds. The nurse should: a. assess lung sounds and extremities. b. suggests the use of an aerobic exercise program. c. positively reinforce the patient for the weight gain. d. establish a higher goal for weight gain the next week. ANS: A Weight gain of more than 2 to 5 pounds weekly may overwhelm the hearts capacity to pump, leading to cardiac failure. The nurse must assess for signs of pulmonary edema and congestive heart failure. The incorrect options are undesirable because they increase the risk for cardiac complications. 26. When a nurse finds a patient diagnosed with anorexia nervosa vigorously exercising before gaining the agreed-upon weekly weight, the nurse should state: a. You and I will have to sit down and discuss this problem. b. It bothers me to see you exercising. You’ll lose more weight. c. Let’s discuss the relationship between exercise and weight loss and how that affects your body. d. According to our agreement, no exercising is permitted until you have gained a specific amount of weight. ANS: D A matter-of-fact statement that the nurses’ perceptions are different helps avoid a power struggle. Treatment plans have specific goals for weight restoration. Exercise is limited to promote weight gain. Patients must be held accountable for required behaviors. 27. A patient diagnosed with anorexia nervosa has a body mass index (BMI) of 14.8 kg/m2. Which assessment finding is most likely to accompany this value? a. Cachexia b. Leukocytosis c. Hyperthermia d. Hypertension ANS: A The BMI value indicates extreme malnutrition. Cachexia is a hallmark of this problem. The patient would be expected to have leukopenia rather than leukocytosis. Hypothermia and hypotension are likely assessment findings. SELECT ALL THAT APPLY 1. A patient referred to the eating disorders clinic has lost 35 pounds in 3 months and has developed amenorrhea. For which physical manifestations of anorexia nervosa should a nurse assess? Select all that apply. a. Peripheral edema b. Parotid swelling c. Constipation d. Hypotension e. Dental caries f. Lanugo ANS:A,C,D,F Peripheral edema is often present because of hypoalbuminemia. Constipation related to starvation is often present. Hypotension is often present because of dehydration. Lanugo is often present and is related to starvation. Parotid swelling is associated with bulimia. Dental caries are associated with bulimia. 2. A patient diagnosed with anorexia nervosa is hospitalized for treatment. What features should the milieu provide? Select all that apply. a. Flexible mealtimes b. Unscheduled weight checks c. Adherence to a selected menu d. Observation during and after meals e. Monitoring during bathroom trips f. Privileges correlated with emotional expression ANS:C,D,E Priority milieu interventions support the restoration of weight and a normalization of eating patterns. These goals require close supervision of the patients eating habits and the prevention of exercise, purging, and other activities. Menus are strictly adhered to. Patients are observed during and after meals to prevent them from throwing away food or purging. All trips to the bathroom are monitored. Mealtimes are structured, not flexible. Weighing is performed on a regular schedule. Privileges are correlated with weight gain and treatment plan compliance. Chapter 15: Mood Disorders: Depression 1. A patient became severely depressed when the last of six children moved out of the home 4 months ago. The patient repeatedly says, No one cares about me. I’m not worth anything. Which response by the nurse would be the most helpful? a. Things will look brighter soon. Everyone feels down once in a while. b. The staff here cares about you and wants to try to help you get better. c. It is difficult for others to care about you when you repeatedly say negative things about yourself. d. I’ll sit with you for 10 minutes now and return for 10 minutes at lunchtime and again at 2:30 this afternoon. ANS: D Spending time with the patient at intervals throughout the day shows acceptance by the nurse and helps the patient establish a relationship with the nurse. The therapeutic technique is called offering self. Setting definite times for the therapeutic contacts and keeping the appointments show predictability on the part of the nurse, an element that fosters the building of trust. The incorrect responses would be difficult for a person with profound depression to believe, provide trite reassurance, and are counterproductive. The patient is unable to say positive things at this point. 2. A patient became depressed after the last of six children moved out of the home 4 months ago. The patient has been self-neglectful, slept poorly, lost weight, and repeatedly says, No one cares about me anymore. I’m not worth anything. Select an appropriate initial outcome for the nursing diagnosis: Situational low self-esteem, related to feelings of abandonment. The patient will: a. verbalizes realistic positive characteristics about self by (date) . b. consent to take antidepressant medication regularly by (date) . c. initiate social interaction with another person daily by (date) . d. identifies two personal behaviors that alienate others by (date) . ANS: A Low self-esteem is reflected by making consistently negative statements about self and self- worth. Replacing negative cognitions with more realistic appraisals of self is an appropriate intermediate outcome. The incorrect options are not as clearly related to the nursing diagnosis. Outcomes are best when framed positively; identifying two personal behaviors that might alienate others is a negative concept. 3. A nurse wants to reinforce positive self-esteem for a patient diagnosed with major depressive disorder. Today, the patient is wearing a new shirt and has neat, clean hair. Which remark is most appropriate? a. You look nice this morning. b. You are wearing a new shirt. c. I like the shirt you’re wearing. d. You must be feeling better today. ANS: B Patients with depression usually see the negative side of things. The meaning of compliments may be altered to I didn’t look nice yesterday or They didn’t like my other shirt. Neutral comments such as an observation avoid negative interpretations. Saying You look nice, or I like your shirt gives approval (nontherapeutic techniques). Saying You must be feeling better today is an assumption, which is nontherapeutic. 4. An adult diagnosed with major depressive disorder was treated with medication and cognitive behavioral therapy. The patient now recognizes how passivity contributed to the depression. Which intervention should the nurse suggest? a. social skills training b. Relaxation training classes c. Use of complementary therapy d. Learning desensitization techniques ANS: A Social skills training is helpful in treating and preventing the recurrence of depression. Training focuses on assertiveness and coping skills that lead to positive reinforcement from others and the development of a patients support system. The use of complementary therapy refers to adjunctive therapies such as herbals. Assertiveness would be of greater value than relaxation training because passivity is a concern. Desensitization is used in the treatment of phobias. 5. A priority nursing intervention for a patient diagnosed with major depressive disorder is: a. distracting the patient from self-absorption. b. carefully and inconspicuously observing the patient around the clock. c. allowing the patient to spend long periods alone in self-reflection. d. offering opportunities for the patient to assume a leadership role in the therapeutic milieu. ANS: B Approximately two thirds of people with depression contemplate suicide. Patients with depression who exhibit feelings of worthlessness are at higher risk. Regularly planned observations of the patient with depression may prevent a suicide attempt on the unit. 6. When counseling patients diagnosed with major depressive disorder, an advanced practice nurse will address the negative thought patterns by using: a. psychoanalytic therapy. b. desensitization therapy. c. cognitive behavioral therapy. d. alternative and complementary therapies. ANS: C Cognitive behavioral therapy attempts to alter the patients’ dysfunctional beliefs by focusing on positive outcomes rather than negative attributions. The patient is also taught the connection between thoughts and resultant feelings. Research shows that cognitive behavioral therapy involves the formation of new connections among nerve cells in the brain and that it is at least as effective as medication. Evidence does not support superior outcomes for the other psychotherapeutic modalities mentioned. 7. A patient says to the nurse, my life does not have any happiness in it anymore. I once enjoyed holidays, but now they’re just another day. How would the nurse document the complaint? a. Vegetative symptom b. Anhedonia c. Euphoria d. Anergia ANS: B Anhedonia is a common finding in many types of depression and refers to feelings of a loss of pleasure in formerly pleasurable activities. Vegetative symptoms refer to somatic changes associated with depression. Euphoria refers to an elated mood. Anergia means without energy. 8. A patient diagnosed with major depressive disorder is taking a tricyclic antidepressant. The patient says, I don’t think I can keep taking these pills. They make me so dizzy, especially when I stand up. The nurse should: a. explain how to manage postural hypotension, and educate the patient that side effects go away after several weeks. b. tell the patient that the side effects are a minor inconvenience compared with the feelings of depression. c. withhold the drug, force oral fluids, and notify the health care provider to examine the patient. d. teach the patient how to use pursed-lip breathing. ANS: A Drowsiness, dizziness, and postural hypotension usually subside after the first few weeks of therapy with tricyclic antidepressants. Postural hypotension can be managed by teaching the patient to stay well hydrated and rise slowly. Knowing these facts may be enough to convince the patient to remain medication compliant. The minor inconvenience of side effects as compared with feelings of depression is a convincing reason to remain on the medication. Withholding the drug, forcing oral fluids, and having the health care provider examine the patient are unnecessary steps. Independent nursing action is appropriate. Pursed-lip breathing is irrelevant. 9. A patient diagnosed with major depressive disorder is receiving imipramine (Tofranil) 200 mg every night at bedtime. Which assessment finding would prompt the nurse to collaborate with the health care provider regarding potentially hazardous side effects of this drug? a. Dry mouth b. Blurred vision c. Nasal congestion d. Urinary retention ANS: D All the side effects mentioned are the result of the anticholinergic effects of the drug. Only urinary retention and severe constipation warrant immediate medical attention. Dry mouth, blurred vision, and nasal congestion may be less troublesome as therapy continues. 10. A patient diagnosed with major depressive disorder tells the nurse, Bad things that happen are always my fault. To assist the patient in reframing this overgeneralization, the nurse should respond: a. I really doubt that one person can be blamed for all the bad things that happen. b. Let’s look at one bad thing that happened to see if another explanation exists. c. You are being exceptionally hard on yourself when you say those things. d. How does your belief in fate relate to your cultural heritage? ANS: B By questioning a faulty assumption, the nurse can help the patient look at the premise more objectively and reframe it as a more accurate representation of fact. The incorrect responses are judgmental, irrelevant to an overgeneralization, and cast doubt without requiring the patient to evaluate the statement. 11. A nurse worked with a patient diagnosed with major depressive disorder who was severely withdrawn and dependent on others. After 3 weeks, the patient did not improve. The nurse is at risk for feelings of: a. overinvolvement. b. guilt and despair. c. interest and pleasure. d. ineffectiveness and frustration. ANS: D Nurses may have expectations for self and patients that are not wholly realistic, especially regarding the patients progress toward health. Unmet expectations result in feelings of ineffectiveness, anger, or frustration. Guilt and despair might be observed when the nurse experiences feelings about patients because of sympathy. Interest is possible but not the most likely result. The correct response is more global than overinvolvement. 12. A patient diagnosed with major depressive disorder begins selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressant therapy. Priority information given to the patient and family should include a directive to: a. avoid exposure to bright sunlight. b. report increased suicidal thoughts. c. restricts sodium intake to 1 g daily. d. maintains a tyramine-free diet. ANS: B Some evidence indicates that suicidal ideation may worsen at the beginning of antidepressant therapy; thus, close monitoring is necessary. Avoiding exposure to bright sunlight and restricting sodium intake are unnecessary. Tyramine restriction is associated with monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) therapy. 13. A nurse teaching a patient about a tyramine-restricted diet would approve which meal? a. Mashed potatoes, ground beef patty, corn, green beans, apple pie b. Avocado salad, ham, creamed potatoes, asparagus, chocolate cake c. Macaroni and cheese, hot dogs, banana bread, caffeinated coffee d. Noodles with cheddar cheese sauce, smoked sausage, lettuce salad, yeast rolls ANS: A The correct answer describes a meal that contains little tyramine. Vegetables and fruits contain little or no tyramine, and fresh ground beef and apple pie should be safe. The other meals contain various amounts of tyramine-rich foods or foods that contain vasopressors: avocados, ripe bananas (banana bread), sausages and hot dogs, smoked meat (ham), cheddar cheese, yeast, caffeine drinks, and chocolate. 14. What is the focus of priority nursing interventions for the period immediately after electroconvulsive therapy treatment? a. Supporting physiologic stability b. Reducing disorientation and confusion c. Monitoring pupillary responses d. Assisting the patient to identify and test negative thoughts ANS: A During the immediate post-treatment period, the patient is recovering from general anesthesia, hence the need to establish and support physiologic stability. Monitoring pupillary responses is not a priority. Reducing disorientation and confusion is an acceptable intervention but not the priority. Assisting the patient in identifying and testing negative thoughts is inappropriate in the immediate post-treatment period because the patient may be confused. 15. A nurse provided medication education for a patient who takes phenelzine (Nardil) for depression. Which behavior indicates effective learning? The patient: a. monitors sodium intake and weight daily. b. wears support stockings and elevates the legs when sitting. c. consults the pharmacist when selecting over-the-counter medications. d. can identify foods with high selenium content, which should be avoided. ANS: C Over-the-counter medicines may contain vasopressor agents or tyramine, a substance that must be avoided when the patient takes MAOI antidepressants. Medications for colds, allergies, or congestion or any preparation that contains ephedrine or phenylpropanolamine may precipitate a hypertensive crisis. MAOI antidepressant therapy is unrelated to the need for sodium limitation, support stockings, or leg elevation. MAOIs interact with tyramine-containing foods, not selenium, to produce dangerously high blood pressure. 16. A patient’s employment is terminated and major depressive disorder results. The patient says to the nurse, I’m not worth the time you spend with me. I’m the most useless person in the world. Which nursing diagnosis applies? a. Powerlessness b. Defensive coping c. Situational low self-esteem d. Disturbed personal identity ANS: C The patients statement express feelings of worthlessness and most clearly relate to the nursing diagnosis of Situational low self-esteem. Insufficient information exists to justify the other diagnoses. 17. A patient diagnosed with major depressive disorder does not interact with others except when addressed and then only in monosyllables. The nurse wants to show nonjudgmental acceptance and support for the patient. Select the nurses most effective approach to communication. a. Make observations. b. Ask the patient direct questions. c. Phrase questions to require yes or no answers. d. Frequently reassure the patient to reduce guilt feelings. ANS: A Making observations about neutral topics such as the environment draws the patient into the reality around him or her but places no burdensome expectations on the patient for answers. Acceptance and support are shown by the nurse’s presence. Direct questions may make the patient feel that the encounter is an interrogation. Open-ended questions are preferable if the patient is able to participate in dialog. Platitudes are never acceptable; they minimize patient feelings and can increase feelings of worthlessness. 18. A patient being treated for major depressive disorder has taken 300 mg amitriptyline (Elavil) daily for a year. The patient calls the case manager at the clinic and says, I stopped taking my antidepressant 2 days ago. Now I am having cold sweats, nausea, a rapid heartbeat, and nightmares. The nurse should advise the patient: a. Go to the nearest emergency department immediately. b. Do not to be alarmed. Take two aspirin and drink plenty of fluids. c. Take one dose of the antidepressant. Come to the clinic to see the health care provider. d. Resume taking the antidepressant for 2 more weeks, and then discontinue it again. ANS: C The patient has symptoms associated with abrupt withdrawal of the tricyclic antidepressant. Taking a dose of the drug will ameliorate the symptoms. Seeing the health care provider will allow the patient to discuss the advisability of going off the medication and to be given a gradual withdrawal schedule if discontinuation is the decision. This situation is not a medical emergency, although it calls for medical advice. Resuming taking the antidepressant for 2 more weeks and then discontinuing again would produce the same symptoms the patient is experiencing. 19. Which documentation indicates the treatment plan of a patient diagnosed with major depressive disorder was effective? a. Slept 6 hours uninterrupted. Sang with activity group. Anticipates seeing grandchild. b. Slept 10 hours uninterrupted. Attended craft group; stated project was a failure, just like me. c. Slept 5 hours with brief interruptions. Personal hygiene adequate with assistance. Weight loss of 1 pound. d. Slept 7 hours uninterrupted. Preoccupied with perceived inadequacies. States, I feel tired all the time. ANS: A Sleeping 6 hours, participating in a group activity, and anticipating an event are all positive happenings. All the other options show at least one negative finding. 20. A woman gave birth to a healthy newborn 1 month ago. The patient now reports she cannot cope and is unable to sleep or eat. She says, I feel like a failure. This baby is the root of my problems. The priority nursing diagnosis is: a. Insomnia b. Ineffective coping c. Situational low self-esteem d. Risk for other-directed violence ANS: D When a new mother develops depression with a postpartum onset, ruminations or delusional thoughts about the infant often occur. The risk for harming the infant is increased; thus, it becomes the priority diagnosis. The other diagnoses are relevant but are of lower priority. 21. A patient diagnosed with major depressive disorder repeatedly tells staff members, I have cancer. It’s my punishment for being a bad person. Diagnostic tests reveal no cancer. Select the priority nursing diagnosis. a. Powerlessness b. Risk for suicide c. Stress overload d. Spiritual distress ANS: B A patient with depression who feels so worthless as to believe cancer is deserved is at risk for suicide. Safety concerns take priority over the other diagnoses listed. 22. Which beverage should the nurse offer to a patient diagnosed with major depressive disorder who refuses solid food? a. Tomato juice b. Orange juice c. Hot tea d. Milk ANS: D Milk is the only beverage listed that provides protein, fat, and carbohydrates. In addition, milk is fortified with vitamins. 23. During a psychiatric assessment, the nurse observes a patient’s facial expressions that are without emotion. The patient says, Life feels so hopeless to me. I’ve been feeling sad for several months. How should the nurse document the patients affect and mood? a. Affect depressed; mood flat b. Affect flat; mood depressed c. Affect labile; mood euphoric d. Affect and mood are incongruent ANS: B Mood is a person’s self-reported emotional feeling state. Affect is the emotional feeling state that is outwardly observable by others. 24. A disheveled patient with severe depression and psychomotor retardation has not bathed for several days. The nurse should: a. avoid forcing the issue. b. bring up the issue at the community meeting. c. calmly tell the patient, You must bathe daily. d. firmly and neutrally assist the patient with showering. ANS: D When patients are unable to perform self-care activities, staff members must assist them rather than ignore the issue. Better grooming increases self-esteem. Calmly telling the patient to bathe daily and bringing up the issue at a community meeting are punitive. 25. A patient was started on escitalopram (Lexapro) 5 days ago and now says, this medicine isn’t working. The nurse’s best intervention would be to: a. discuss with the health care provider the need to change medications. b. reassure the patient that the medication will be effective soon. c. explain the time lag before antidepressants relieve symptoms. d. critically assess the patient for symptom relief. ANS: C Escitalopram is an SSRI antidepressant. Between 1 and 3 weeks of treatment are usually necessary before a relief of symptoms occurs. This information is important to share with patients. 26. A nurse is caring for a patient with low self-esteem. Which nonverbal communication should the nurse anticipate? a. Arms crossed b. Staring at the nurse c. Smiling inappropriately d. Eyes pointed downward ANS: D Nonverbal communication is usually considered more powerful than verbal communication. Downward-casted eyes suggest feelings of worthlessness or hopelessness. 27. A patient diagnosed with major depressive disorder was hospitalized for 8 days. Treatment included six electroconvulsive therapy sessions and aggressive dose adjustments of antidepressant medications. The patient owns a small business and was counseled not to make major decisions for a month. Select the correct rationale for this counseling. a. Temporary memory impairments and confusion can be associated with electroconvulsive therapy. b. Antidepressant medications alter catecholamine levels, which impair decision-making abilities. c. Antidepressant medications may cause confusion related to a limitation of tyramine in the diet. d. The patient needs time to reorient himself or herself to a pressured work schedule. ANS: A Recent memory impairment or confusion or both are often present during and for a short time after electroconvulsive therapy. An inappropriate business decision might be made because of forgotten and important details. The incorrect responses contain rationales that are untrue. The patient needing time to reorient himself or herself to a pressured work schedule is less relevant than the correct rationale. 28. A nurse instructs a patient taking a drug that inhibits the action of monoamine oxidase (MAO) to avoid certain foods and drugs because of the risk of: a. hypotensive shock. b. hypertensive crisis. c. cardiac dysrhythmia. d. cardiogenic shock. ANS: B Patients taking MAOIs must be on a tyramine-free diet to prevent hypertensive crisis. In the presence of MAOIs, tyramine is not destroyed by the liver and, in high levels, produces intense vasoconstriction, resulting in elevated blood pressure. SELECT ALL THAT APPLY 1. The admission note indicates a patient diagnosed with major depressive disorder has anergia and anhedonia. For which measures should the nurse plan? Select all that apply. a. Channeling excessive energy b. Reducing guilty ruminations c. Instilling a sense of hopefulness d. Assisting with self-care activities e. Accommodating psychomotor retardation ANS:C,D,E Anhedonia refers to the inability to find pleasure or meaning in life; thus planning should include measures to accommodate psychomotor retardation, assist with activities of daily living, and instill hopefulness. Anergia is the lack of energy, not excessive energy. Anhedonia does not necessarily imply the presence of guilty ruminations. 2. A student nurse caring for a patient diagnosed with major depressive disorder reads in the patients’ medical record, this patient shows vegetative signs of depression. Which nursing diagnoses most clearly relate to the vegetative signs? Select all that apply. a. Imbalanced nutrition: less than body requirements b. Chronic low self-esteem c. Sexual dysfunction d. Self-care deficit e. Powerlessness f. Insomnia ANS:A,C,D,F Vegetative signs of depression are alterations in the body processes necessary to support life and growth, such as eating, sleeping, elimination, and sexual activity. These diagnoses are more closely related to vegetative signs than to diagnoses associated with feelings about self. 3. A patient diagnosed with major depressive disorder will begin electroconvulsive therapy tomorrow. Which interventions are routinely implemented before the treatment? Select all that apply. a. Administer pretreatment medication 30 to 45 minutes before treatment. b. Withhold food and fluids for a minimum of 6 hours before treatment. c. Remove dentures, glasses, contact lenses, and hearing aids. d. Restrain the patient in bed with padded limb restraints. e. Assist the patient to prepare an advance directive. ANS:A,B,C The correct interventions reflect routine electroconvulsive therapy preparation, which is similar to preoperative preparation: sedation and anticholinergic medication before anesthesia, maintaining nothing-by-mouth status to prevent aspiration during and after treatment, airway maintenance, and general safety by removing prosthetic devices. Restraint is not part of the pretreatment protocol. An advance directive is prepared independent of this treatment. 4. A patient diagnosed with major depressive disorder shows vegetative signs of depression. Which nursing actions should be implemented? Select all that apply. a. Offer laxatives, if needed. b. Monitor food and fluid intake. c. Provide a quiet sleep environment. d. Eliminate all daily caffeine intake. e. Restrict the intake of processed foods. ANS:A,B,C The correct options promote a normal elimination pattern. Although excessive intake of stimulants such as caffeine may make the patient feel jittery and anxious, small amounts may provide useful stimulation. No indication exists that processed foods should be restricted. 5. A patient being treated with paroxetine (Paxil) 50 mg/day orally for major depressive disorder reports to the clinic nurse, I took a few extra tablets earlier in the day and now I feel bad. Which aspects of the nursing assessment are most critical? Select all that apply. a. Vital signs b. Urinary frequency c. Increased suicidal ideation d. Presence of abdominal pain and diarrhea e. Hyperactivity or feelings of restlessness ANS:A,D,E The patient is taking the maximum dose of this SSRI and has ingested an additional unknown amount of the drug. Central serotonin syndrome must be considered. Symptoms include abdominal pain, diarrhea, tachycardia, elevated blood pressure, hyperpyrexia, increased motor activity, and muscle spasms. Central serotonin syndrome may progress to a full medical emergency if not treated early. Although assessing for suicidal ideation is never inappropriate, in this situation physiologic symptoms should be the initial focus. The patient may have urinary retention, but frequency would not be expected. Chapter 16: Bipolar Spectrum Disorders 1. A person is directing traffic on a busy street while shouting and making obscene gestures at passing cars. The person has not slept or eaten for 3 days. What features of mania are evident? a. Increased muscle tension and anxiety b. Vegetative signs and poor grooming c. Poor judgment and hyperactivity d. Cognitive deficit and sad mood ANS: C Hyperactivity (directing traffic) and poor judgment (putting self in a dangerous position) are characteristic of manic episodes. The distractors do not specifically apply to mania. 2. A patient diagnosed with bipolar disorder is dressed in a red leotard and brightly colored scarves. The patient says, Ill punch you, munch you, crunch you, while twirling and shadowboxing. Then the patient says gaily, do you like my scarves? Here they are my gift to you. How should the nurse document the patient’s mood? a. Labile and euphoric b. Irritable and belligerent c. Highly suspicious and arrogant d. Excessively happy and confident ANS: A The patient has demonstrated angry behavior and pleasant, happy behavior within seconds of each other. Excessive happiness indicates euphoria. Mood swings are often rapid and seemingly without understandable reason in patients who are manic. These swings are documented as labile. Irritability, belligerence, excessive happiness, and confidence are not entirely correct terms for the patient’s mood. A high level of suspicion is not evident. 3. A patient experiencing mania has not eaten or slept for 3 days. Which nursing diagnosis has priority? a. Risk for injury b. Ineffective coping c. Impaired social interaction d. Ineffective therapeutic regimen management ANS: A Although each of the nursing diagnoses listed is appropriate for a patient having a manic episode, the priority lies with the patient’s physiologic safety. Hyperactivity and poor judgment place the patient at risk for injury. 4. A patient diagnosed with bipolar disorder is hyperactive and manic after discontinuing lithium. The patient threatens to hit another patient. Which comment by the nurse is appropriate? a. Stop that! No one did anything to provoke an attack by you. b. If you do that one more time, you will be secluded immediately. c. Do not hit anyone. If you are unable to control yourself, we will help you. d. You know we will not let you hit anyone. Why do you continue this behavior? ANS: C When the patient is unable to control his or her behavior and violates or threatens to violate the rights of others, limits must be set in an effort to de-escalate the situation. Limits should be set in simple, concrete terms. The incorrect responses do not offer appropriate assistance to the patient and threaten the patient with seclusion as punishment. Asking why does not provide for environmental safety. 5. This nursing diagnosis applies to a patient experiencing mania: Imbalanced nutrition: less than body requirements, related to insufficient caloric intake and hyperactivity as evidenced by 5-pound weight loss in 4 days. Select the most appropriate outcome. The patient will: a. ask staff for assistance with feeding within 4 days. b. drink six servings of a high-calorie, high-protein drink each day. c. consistently sit with others for at least 30 minutes at mealtime within 1 week. d. consistently wears appropriate attire for age and sex within 1 week while in the psychiatric unit. ANS: B High-calorie, high-protein food supplements will provide the additional calories needed to offset the patient’s extreme hyperactivity. Sitting with others or asking for assistance does not mean the patient will eat or drink. Appropriate attire is unrelated to the nursing diagnosis. 6. A patient develops mania after discontinuing lithium. New prescriptions are written to resume lithium twice daily and begin olanzapine (Zyprexa). The addition of olanzapine to the medication regimen will: a. minimize the side effects of lithium. b. bring hyperactivity under rapid control. c. enhance the antimanic actions of lithium. d. provide long-term control of hyperactivity. ANS: B Manic symptoms are controlled by lithium only after a therapeutic serum level is attained. Because this takes several days to accomplish, a drug with rapid onset is necessary to reduce the hyperactivity initially. Antipsychotic drugs neither enhance lithium’s antimanic activity nor minimize the side effects. Lithium is used for long- term control. 7. A patient diagnosed with bipolar disorder has rapid cycles. The health care provider prescribes an anticonvulsant medication. To prepare teaching materials, which drug should the nurse anticipate will be prescribed? a. phenytoin (Dilantin) b. clonidine (Catapres) c. carbamazepine (Tegretol) d. chlorpromazine (Thorazine) ANS: C Some patients with bipolar disorder, especially those who have only short periods between episodes, have a favorable response to the anticonvulsants carbamazepine and valproate. Phenytoin is also an anticonvulsant but is not used for mood stabilization. Carbamazepine seems to work better in patients with rapid cycling and in severely paranoid, angry patients with manic episodes. 8. The cause of bipolar disorder has not been determined, but: a. several factors, including genetics, are implicated. b. brain structures were altered by stresses early in life. c. excess norepinephrine is probably a major factor. d. excess sensitivity in dopamine receptors may exist. ANS: A At this time, the interplay of complex independent variables is most likely the best explanation of the cause for bipolar disorder. Various theories implicate genetics, endocrine imbalance, early stress, and neurotransmitter imbalances. 9. The spouse of a patient diagnosed with bipolar disorder asks what evidence supports the possibility of genetic transmission of bipolar disorders. Select the nurse’s best response. a. A high proportion of patients diagnosed with bipolar disorders are found among creative writers. b. A higher rate of relatives diagnosed with bipolar disorder is found among patients with bipolar disorder. c. Patients diagnosed with bipolar disorder have higher rates of relatives who respond in an exaggerated way to daily stresses. d. More individuals diagnosed with bipolar disorder come from high socioeconomic and educational backgrounds. ANS: B Evidence of genetic transmission is supported when twins or relatives of patients with a particular disorder also show an incidence of the disorder that is higher than the incidence in the general public. The incorrect options do not support the theory of genetic transmission of bipolar disorder. 10. A patient diagnosed with bipolar disorder commands other patients, Get me a book. Take this stuff out of here, and other similar demands. The nurse wants to interrupt this behavior without entering into a power struggle. Select the best initial approach by the nurse. a. Distraction: Lets go to the dining room for a snack. b. Humor: How much are you paying servants these days? c. Limit setting: You must stop ordering other patients around. d. Honest feedback: Your controlling behavior is annoying others. ANS: A The distractibility characteristic of manic episodes can assist the nurse to direct the patient toward more appropriate, constructive activities without entering into a power struggle. Humor usually backfires by either encouraging the patient or inciting anger. Limit setting and honest feedback may seem heavy-handed to a labile patient and may incite anger. 11. A nurse receives this laboratory result for a patient diagnosed with bipolar disorder: lithium level 1 mEq/L. This result is: a. within therapeutic limits b. below therapeutic limits c. above therapeutic limits d. incorrect because of inaccurate testing ANS: A The normal range for a blood sample taken 8 to 12 hours after the last dose of lithium is 0.4 to 1 mEq/L. 12. Consider these three drugs: divalproex (Depakote), carbamazepine (Tegretol), and gabapentin (Neurontin). Which drug also belongs to this group? a. clonazepam (Klonopin) b. risperidone (Risperdal) c. lamotrigine (Lamictal) d. aripiprazole (Abilify) ANS: C The three drugs in the stem of this question are all anticonvulsants. Lamotrigine is also an anticonvulsant. Clonazepam is an anxiolytic; aripiprazole and risperidone are antipsychotic drugs. 13. When a hyperactive patient experiencing acute mania is hospitalized, what initial nursing intervention is a priority? a. Allow the patient to act out his or her feelings. b. Set limits on the patient’s behavior as necessary. c. Provide verbal instructions to the patient to remain calm. d. Restrain the patient to reduce hyperactivity and aggression. ANS: B This intervention provides support through the nurse’s presence and provides structure as necessary while the patients control is tenuous. Acting out may lead to the loss of behavioral control. The patient will probably be unable to focus on instructions and comply. Restraint is used only after other interventions have proved ineffective. 14. At a unit meeting, staff members discuss the decor for a special room for patients experiencing mania. Select the best option. a. Extra-large window with a view of the street b. Neutral walls with pale, simple accessories c. Brightly colored walls and print drapes d. Deep colors for walls and upholstery ANS: B The environment for a patient experiencing mania should be as simple and as non-stimulating as possible. Patients experiencing mania are highly sensitive to environmental distractions and stimulation. Draperies present a risk for injury. 15. A patient experiencing acute mania has exhausted the staff members by noon. The patient has joked, manipulated, insulted, and fought all morning. Staff members are feeling defensive and fatigued. Which is the best action? a. Confer with the health care provider regarding use of seclusion for this patient. b. Hold a staff meeting to discuss consistency and limit-setting approaches. c. Conduct a meeting with all patients to discuss the behavior. d. Explain to the patient that the behavior is unacceptable. ANS: B When staff members are overwhelmed, the patient has succeeded in keeping the environment unsettled and avoided outside controls on behavior. Staff meetings can help minimize staff splitting and feelings of anger, helplessness, confusion, and frustration. Criteria for seclusion have not been met. 16. A patient experiencing acute mania undresses in the group room and dances. The nurses first intervention would be to: a. quietly ask the patient, Why don’t you put on your clothes? b. firmly tell the patient, Stop dancing, and put on your clothing. c. put a blanket around the patient, and walk with the patient to a quiet room. d. allow the patient stay in the group room. Move the other patients to a different area. ANS: C Patients must be protected from the embarrassing consequences of their poor judgment whenever possible. Protecting the patient from public exposure by matter-of-factly covering the patient and removing him or her from the area with a sufficient number of staff members to avoid argument and provide control is an effective approach. 17. A patient experiencing acute mania waves a newspaper and says, I must have my credit card and use the computer right now. A store is having a big sale and I need to order 10 dresses and four pairs of shoes. Select the nurses most appropriate intervention. a. Suggest to the patient to ask a friend do the shopping and bring purchases to the unit. b. Invite the patient to sit with the nurse and look at new fashion magazines. c. Tell the patient that computer use is not allowed until self-control improves. d. Ask whether the patient has enough money to pay for the purchases. ANS: B Situations such as this offer an opportunity to use the patient’s distractibility to the staff’s advantage. Patients become frustrated when staff members deny requests that the patient sees as entirely reasonable. Distracting the patient can avoid power struggles. Suggesting that a friend do the shopping would not satisfy the patients need for immediacy and would ultimately result in the extravagant expenditure. Asking whether the patient has enough money would likely precipitate an angry response. 18. A patient diagnosed with bipolar disorder is being treated on an outpatient basis with lithium carbonate 300 mg three times daily. The patient complains of nausea. To reduce the nausea, the nurse can suggest that the lithium be taken with: a. meals. b. an antacid. c. a large glass of juice. d. an antiemetic medication. ANS: A Some patients find that taking lithium with meals diminishes nausea. The incorrect options are less helpful. 19. A health teaching plan for a patient taking lithium should include instructions to: a. maintain normal salt and fluids in the diet. b. drink twice the usual daily amount of fluids. c. double the lithium dose if diarrhea or vomiting occurs. d. avoid eating aged cheese, processed meats, and red wine. ANS: A Sodium depletion and dehydration increase the chance for developing lithium toxicity. The incorrect options offer inappropriate information. 20. Which nursing diagnosis would most likely apply to both a patient diagnosed with major depressive disorder (MDD) as well as one experiencing acute mania? a. Deficient diversional activity b. Disturbed sleep pattern c. Fluid volume excess d. Defensive coping ANS: B Patients diagnosed with mood disorders, both depression and mania, experience sleep pattern disturbances. Assessment data should be routinely gathered about this possible problem. Deficient diversional activity is more relevant for patients diagnosed with MDD. Defensive coping is more relevant for patients experiencing mania. Fluid volume excess is less relevant for patients diagnosed with mood disorders than is deficient fluid volume. 21. Which dinner menu is best suited for the patient diagnosed with bipolar disorder experiencing acute mania? a. Spaghetti and meatballs, salad, a banana b. Beef and vegetable stew, a roll, chocolate pudding c. Broiled chicken breast on a roll, an ear of corn, apple d. Chicken casserole, green beans, flavored gelatin with whipped cream ANS: C The correct foods provide adequate nutrition but, more importantly, are finger foods that the hyperactive patient could eat on the run. The foods in the incorrect options cannot be eaten without utensils. 22. Outcome identification for the treatment plan of a patient with grandiose thinking associated with acute mania focuses on: a. maintaining an interest in the environment. b. developing an optimistic outlook. c. self-control of distorted thinking. d. stabilizing the sleep pattern. ANS: C The desired outcome is that the patient will be able to control the grandiose thinking associated with acute mania as evidenced by making realistic comments about self, abilities, and plans. Patients with acute mania are already unduly optimistic as a result of their use of denial, and they are overly interested in their environment. Sleep stability is a desired outcome but is not related to distorted thought processes. 23. Which documentation indicates that the treatment plan for a patient experiencing acute mania has been effective? a. Converses without interrupting; clothing matches; participates in activities. b. Irritable, suggestible, distractible; napped for 10 minutes in afternoon. c. Attention span short; writing copious notes; intrudes in conversations. d. Heavy makeup; seductive toward staff; pressured speech. ANS: A The descriptors given indicate the patient is functioning at an optimal level, using appropriate behavior, and thinking without becoming overstimulated by unit activities. The incorrect options reflect manic behavior. 24. A patient experiencing mania dances around the unit, seldom sits, monopolizes conversations, interrupts, and intrudes. Which nursing intervention will best assist the patient with energy conservation? a. Monitor physiologic functioning b. Provide a subdued environment c. Supervise personal hygiene d. Observe for mood changes ANS: B All the options are reasonable interventions with a patient with acute mania, but providing a subdued environment directly relates to the outcome of energy conservation by decreasing stimulation and helping balance activity and rest. 25. A patient diagnosed with bipolar disorder has been hospitalized for 7 days and has taken lithium 600 mg three times daily. Staff members observe increased agitation, pressured speech, poor personal hygiene, hyperactivity, and bizarre clothing. What is the nurses best intervention? a. Educate the patient about the proper ways to perform personal hygiene and coordinate clothing. b. Continue to monitor and document the patient’s speech patterns and motor activity. c. Ask the health care provider to prescribe an increased dose and frequency of lithium. d. Consider the need to check the lithium level. The patient may not be swallowing medications. ANS: D The patient is continuing to exhibit manic symptoms. The lithium level may be low as a result of checking the medication. The prescribed dose is high, so one would not expect a need for the dose to be increased. 26. A patient experiencing acute mania has disrobed in the hall three times in 2 hours. The nurse should: a. direct the patient to wear clothes at all times. b. ask if the patient finds clothes bothersome. c. tell the patient that others feel embarrassed. d. arrange for one-on-one supervision. ANS: D A patient who repeatedly disrobes, despite verbal limit setting, needs more structure. One- on-one supervision may provide the necessary structure. Directing the patient to wear clothes at all times has not proved successful, considering the behavior has continued. Asking whether the patient is bothered by clothing serves no purpose. Telling the patient that others are embarrassed will not make a difference to the patient whose grasp of social behaviors is impaired by the illness. 27. A patient experiencing acute mania is dancing atop the pool table in the recreation room. The patient waves a cue in one hand and says, I’ll throw the pool balls if anyone comes near me. The nurses first intervention is to: a. tell the patient, You need to be secluded. b. help the patient down from the table. c. clear the room of all other patients. d. assemble a show of force. ANS: C Safety is of primary importance. Once other patients are out of the room, a plan for managing this patient can be implemented. A show of force is likely to frighten the patient and increase this risk for violence. 28. After hospital discharge, what is the priority intervention for a patient diagnosed with bipolar disorder who is taking antimanic medication, as well as for the patient’s family? a. Decreasing physical activity b. Increasing food and fluids c. Meeting self-care needs d. Psychoeducation ANS: D During the continuation phase of treatment for bipolar disorder, the physical needs of the patient are not as important an issue as they were during the acute episode. After hospital discharge, the treatment focuses on maintaining medication compliance and preventing a relapse, both of which are fostered by ongoing psychoeducation. 29. A patient receiving lithium should be assessed for which evidence of complications? a. Pharyngitis, mydriasis, and dystonia b. Alopecia, purpura, and drowsiness c. Diaphoresis, weakness, and nausea d. Ascites, dyspnea, and edema ANS: C Diaphoresis, weakness, and nausea are early signs of lithium toxicity. Problems mentioned in the incorrect options are unrelated to lithium therapy. 30. A patient diagnosed with bipolar disorder is in the maintenance phase of treatment. The patient asks, Do I have to keep taking this lithium even though my mood is stable now? Select the nurses most appropriate response. a. You will be able to stop the medication in approximately 1 month. b. Taking the medication every day helps prevent relapses and recurrences. c. Usually patients take this medication for approximately 6 months after discharge. d. Its unusual that the health care provider has not already stopped your medication. ANS: B Patients diagnosed with bipolar disorder may be indefinitely maintained on lithium to prevent recurrences. Helping the patient understand this need promotes medication compliance. The incorrect options offer incorrect or misleading information. 31. A patient diagnosed with bipolar disorder and who takes lithium telephones the nurse at the clinic to say, I’ve had severe diarrhea 4 days. I feel very weak and unsteady when I walk. My usual hand tremor has gotten worse. What should I do? The nurse should advise the patient: a. Restrict oral fluids for 24 hours and stay in bed. b. Have someone bring you to the clinic immediately. c. Drink a large glass of water with 1 teaspoon of salt added. d. Take an over-the-counter antidiarrheal medication hourly until the diarrhea subsides. ANS: B The symptoms described suggest lithium toxicity. The patient should have a lithium level drawn and may require further treatment. Because neurologic symptoms are present, the patient should not drive and should be accompanied by another person. The incorrect options will not address the patients’ symptoms. Restricting oral fluids will make the situation worse. 32. Lithium is prescribed for a new patient. Which information from the patient’s history indicates that monitoring serum concentrations of the drug will be especially challenging and critical? a. Arthritis b. Epilepsy c. Psoriasis d. Congestive heart failure ANS: D The patient with congestive heart failure will likely need diuretic drugs, which will complicate the maintenance of the fluid balance necessary to avoid lithium toxicity. Arthritis, epilepsy, and psoriasis do not directly involve fluid balance and kidney function. SELECT ALL THAT APPLY 1. A patient diagnosed with bipolar disorder is being treated as an outpatient during a hypomanic episode. Which suggestions should the nurse provide to the family? Select all that apply. a. Provide structure b. Limit credit card access c. Encourage group social interaction d. Limit work to half days e. Monitor the patients sleep patterns ANS:A,B,E A patient with hypomania is expansive, grandiose, and labile; uses poor judgment; spends inappropriately; and is overstimulated by a busy environment. Providing structure helps the patient maintain appropriate behavior. Financial irresponsibility may be avoided by limiting access to cash and credit cards. Continued decline in sleep patterns may indicate the condition has evolved to full mania. Group socialization should be kept to a minimum to reduce stimulation. A full leave of absence from work is necessary to limit stimuli and to prevent problems associated with poor judgment and the inappropriate decision making that accompany hypomania. 2. A nurse prepares the plan of care for a patient having a manic episode. Which nursing diagnoses are most likely? Select all that apply. a. Imbalanced nutrition: more than body requirements b. Disturbed thought processes c. Sleep deprivation d. Chronic confusion e. Social isolation ANS: B, C People with mania are hyperactive and often do not take the time to eat and drink properly. Their high levels of activity consume calories; therefore, deficits in nutrition may occur. Sleep is reduced. Their socialization is impaired but not isolated. Confusion may be acute but not chronic. 3. A patient tells the nurse; I am so ashamed of being bipolar. When I’m manic, my behavior embarrasses my family. Even if I take my medication, there’s no guarantee I won’t have a relapse. I am such a burden to my family. These statements support which nursing diagnoses? Select all that apply. a. Powerlessness b. Defensive coping c. Chronic low self-esteem d. Impaired social interaction e. Risk-prone health behavior ANS: A, C Chronic low self-esteem and powerlessness are interwoven in the patients’ statements. No data support the other diagnoses. Chapter 17: Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorders and Other Psychotic Disorders 1. A person diagnosed with schizophrenia has had difficulty keeping a job because of arguing with co-workers and accusing them of conspiracy. Today the person shouts, they’re all plotting to destroy me. Select the nurses most therapeutic response. a. Everyone here is trying to help you. No one wants to harm you. b. Feeling that people want to destroy you must be very frightening. c. That is not true. People here are trying to help if you will let them. d. Staff members are health care professionals who are qualified to help you. ANS: B Resist focusing on content; instead, focus on the feelings the patient is expressing. This strategy prevents arguing about the reality of delusional beliefs. Such arguments increase patient anxiety and the tenacity with which the patient holds to the delusion. The other options focus on content and provide opportunity for argument. 2. A newly admitted patient diagnosed with schizophrenia is hypervigilant and constantly scans the environment. The patient states, I saw two doctors talking in the hall. They were plotting to kill me. The nurse may correctly assess this behavior as: a. echolalia. b. an idea of reference. c. a delusion of infidelity. d. an auditory hallucination. ANS: B Ideas of reference are misinterpretations of the verbalizations or actions of others that give special personal meanings to these behaviors; for example, when seeing two people talking, the individual assumes they are talking about him or her. The other terms do not correspond with the scenario. 3. A patient diagnosed with schizophrenia says, my co-workers are out to get me. I also saw two doctors plotting to overdose me. How does this patient perceive the environment? a. Disorganized b. Unpredictable c. Dangerous d. Bizarre ANS: C The patient sees the world as hostile and dangerous. This assessment is important because the nurse can be more effective by using empathy to respond to the patient. Data are not present to support any of the other options. 4. When a patient diagnosed with schizophrenia was discharged 6 months ago, haloperidol (Haldol) was prescribed. The patient now says, I stopped taking those pills. They made me feel like a robot. What common side effects should the nurse validate with the patient? a. Sedation and muscle stiffness b. Sweating, nausea, and diarrhea c. Mild fever, sore throat, and skin rash d. Headache, watery eyes, and runny nose ANS: A Typical antipsychotic drugs often produce sedation and extrapyramidal side effects such as stiffness and gait disturbance, effects the patient might describe as making him or her feel like a robot. The side effects mentioned in the other options are usually not associated with typical antipsychotic therapy or would not have the effect described by the patient. 5. A nurse works with a patient diagnosed with schizophrenia regarding the importance of medication management. The patient repeatedly says, I don’t like taking pills. Which treatment strategy should the nurse discuss with the health care provider? a. Use of a long-acting antipsychotic injections b. Addition of a benzodiazepine, such as lorazepam (Ativan) c. Adjunctive use of an antidepressant, such as amitriptyline (Elavil) d. Inpatient hospitalization because of the high risk for exacerbation of symptoms ANS: A Medications such as fluphenazine decanoate and haloperidol decanoate are long-acting forms of antipsychotic medications. They are administered by depot injection every 2 to 4 weeks, thus reducing daily opportunities for nonadherence. The incorrect options do not address the patients dislike of taking pills. 6. A patients care plan includes monitoring for auditory hallucinations. Which assessment findings suggest the patient may be hallucinating? a. Aloofness, haughtiness, suspicion b. Darting eyes, tilted head, mumbling to self c. Elevated mood, hyperactivity, distractibility d. Performing rituals, avoiding open places ANS: B Clues to hallucinations include looking around the room as though to find the speaker; tilting the head to one side as though intently listening; and grimacing, mumbling, or talking aloud as though responding conversationally to someone. 7. A health care provider considers which antipsychotic medication to prescribe for a patient diagnosed with schizophrenia who has auditory hallucinations and poor social functioning. The patient is also overweight and has hypertension. Which drug should the nurse advocate? a. clozapine (Clozaril) b. ziprasidone (Geodon) c. olanzapine (Zyprexa) d. aripiprazole (Abilify) ANS: D Aripiprazole is an atypical antipsychotic medication that is effective against both positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia. It causes little or no weight gain and no increase in glucose, high- or low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels, or triglycerides, making it a reasonable choice for a patient with obesity or heart disease. Clozapine may produce agranulocytosis, making it a poor choice as a first-line agent. Ziprasidone may prolong the QT interval, making it a poor choice for a patient with cardiac disease. Olanzapine fosters weight gain. 8. A patient diagnosed with schizophrenia tells the nurse, I eat skiller. Tend to end. Easter. It blows away. Get it? Select the nurse’s best response. a. Nothing you are saying is clear. b. Your thoughts are very disconnected. c. Try to organize your thoughts, and then tell me again. d. I am having difficulty understanding what you are saying. ANS: D When a patient’s speech is loosely associated, confused, and disorganized, pretending to understand is useless. The nurse should tell the patient that he or she is having difficulty understanding what the patient is saying. If a theme is discernible, ask the patient to talk about the theme. The incorrect options tend to place blame for the poor communication with the patient. The correct response places the difficulty with the nurse rather than being accusatory. 9. A patient diagnosed with schizophrenia has catatonia. The patient has little spontaneous movement and waxy flexibility. Which patient needs are of priority importance? a. Psychosocial b. Physiologic c. Self-actualization d. Safety and security ANS: B Physiologic needs must be met to preserve life. A patient who is catatonic may need to be fed by hand or tube, toileted, and given range-of-motion exercises to preserve physiologic integrity. The assessment findings do not suggest safety concerns. Higher level needs (psychosocial and self-actualization) are of lesser concern. 10. A patient diagnosed with schizophrenia has catatonia. The patient is stuporous, demonstrates little spontaneous movement and has waxy flexibility. The patients’ activities of daily living are severely compromised. An appropriate outcome is that the patient will: a. demonstrate increased interest in the environment by the end of week 1. b. performs self-care activities with coaching by the end of day 3. c. gradually take the initiative for self-care by the end of week 2. d. voluntarily accept tube feeding by day 2. ANS: B Outcomes related to self-care deficit nursing diagnoses should deal with increasing the patient’s ability to perform self-care tasks independently, such as feeding, bathing, dressing, and toileting. Performing the tasks with coaching by the nursing staff denotes improvement over the complete inability to perform the tasks. The incorrect options are not directly related to self-care activities; they are difficult to measure and are unrelated to maintaining nutrition. 11. A nurse observes a patient who is diagnosed with schizophrenia. The patient is standing immobile, facing the wall with one arm extended in a salute. The patient remains immobile in this position for 15 minutes, moving only when the nurse gently lowers the arm. What is the name of this phenomenon? a. Echolalia b. Waxy flexibility c. Depersonalization d. Thought withdrawal ANS: B Waxy flexibility is the ability to hold distorted postures for extended periods, as though the patient were molded in wax. Echolalia is a speech pattern. Depersonalization refers to a feeling state. Thought withdrawal refers to an alteration in thinking. 12. Which patient diagnosed with schizophrenia would be expected to have the lowest level of overall functioning? a. 39 years old; paranoid ideation since age 35 years b. 32 years old; isolated episodes of catatonia since age 24 years; stable for 3 years c. 19 years old; diagnosed with schizophreniform disorder 6 months ago d. 40 years old; frequent relapses since age 18; often does not take medication as prescribed ANS: D The 40-year-old patient who has been diagnosed with schizophrenia since 18 years of age could logically be expected to have the lowest overall level of functioning secondary to deterioration associated with frequent relapses. The 39-year-old patient who has had paranoid ideation since 35 years of age could be expected to have a higher level because schizophrenia of short duration may be less impairing than other types. The patient who has had episodes of catatonia since the age of 24 years has been stable for more than 3 years, suggesting a higher functional ability. The 19-year-old patient diagnosed with schizophreniform disorder has been ill for only 6 months, and disability is likely to be minimal. 13. A patient with delusions of persecution about being poisoned has refused all hospital meals for 3 days. Which intervention is most likely to be acceptable to the patient? a. Allow the patient to have supervised access to food vending machines b. Allow the patient to telephone a local restaurant to deliver meals c. Offer to taste each portion on the tray for the patient d. Begin tube feedings or total parenteral nutrition ANS: A The patient who is delusional about food being poisoned is likely to believe restaurant food might still be poisoned and to say that the staff member tasting the food has taken an antidote to the poison before tasting. Attempts to tube feed or give nutrition intravenously are considered aggressive and usually promote violence. Patients often perceive foods in sealed containers, packages, or natural shells as being safe. 14. A community mental health nurse wants to establish a relationship with a very withdrawn patient diagnosed with schizophrenia. The patient lives at home with a supportive family. Select the nurse’s best plan. a. Visit daily for 4 days, then visit every other day for 1 week; stay with the patient for 20 minutes; accept silence; state when the nurse will return. b. Arrange to spend 1 hour each day with the patient; focus on asking questions about what the patient is thinking or experiencing; avoid silences. c. Visit twice daily; sit beside the patient with a hand on the patient’s arm; leave if the patient does not respond within 10 minutes. d. Visit every other day; remind the patient of the nurse’s identity; encourage the patient to talk while the nurse works on reports. ANS: A Severe constraint on the community mental health nurses time will probably not allow more time than what is mentioned in the correct option, yet important principles can be used. A severely withdrawn patient should be met at the patient’s own level, with silence accepted. Short periods of contact are helpful to minimize both the patients and the nurse’s anxiety. Predictability in returning as stated will help build trust. An hour may be too long to sustain a home visit with a withdrawn patient, especially if the nurse persists in leveling a barrage of questions at the patient. Twice-daily visits are probably not possible and leaving after 10 minutes would be premature. Touch may be threatening. Working on reports suggests the nurse is not interested in the patient. 15. Patients diagnosed with schizophrenia who are suspicious and withdrawn: a. universally fears sexual involvement with therapists. b. are socially disabled by the positive symptoms of schizophrenia. c. exhibit a high degree of hostility as evidenced by rejecting behavior. d. avoid relationships because they become anxious with emotional closeness. ANS: D When an individual is suspicious and distrustful and perceives the world and the people in it as potentially dangerous, withdrawal into an inner world can be a defense against uncomfortable levels of anxiety. When someone attempts to establish a relationship with such a patient, the patients anxiety rises until trust is established. No evidence suggests that withdrawn patients with schizophrenia universally fear sexual involvement with therapists. In most cases, it is not considered true that withdrawn patients with schizophrenia are socially disabled by the positive symptoms of schizophrenia or exhibit a high degree of hostility by demonstrating rejecting behavior. 16. A newly admitted patient diagnosed with schizophrenia says, the voices are bothering me. They yell and tell me I’m bad. I have got to get away from them. Select the nurse’s most helpful reply. a. Do you hear the voices often? b. Do you have a plan for getting away from the voices? c. I will stay with you. Focus on what we are talking about, not the voices. d. Forget the voices. Ask some other patients to sit and talk with you. ANS: C Staying with a distraught patient who is hearing voices serves several purposes: ongoing observation, the opportunity to provide reality orientation, a means of helping dismiss the voices, the opportunity of forestalling an action that would result in self-injury, and general support to reduce anxiety. Asking if the patient hears voices is not particularly relevant at this point. Asking if the patient plans to get away from the voices is relevant for assessment purposes but is less helpful than offering to stay with the patient while encouraging a focus on their discussion. Asking other patients to talk incorrectly shifts responsibility for intervention from the nurse to other patients. 17. A patient diagnosed with schizophrenia has taken fluphenazine (Prolixin) 5 mg orally twice daily for 3 weeks. The nurse now assesses a shuffling, propulsive gait; a masklike face; and drooling. Which term applies to these symptoms? a. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome b. Hepatocellular effects c. Pseudo parkinsonism d. Akathisia ANS: C Pseudo parkinsonism induced by antipsychotic medication mimics the symptoms of Parkinson disease. It frequently appears within the first month of treatment. Hepatocellular effects would produce abnormal liver Test Bank: Essentials of Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing (3rd Edition by Varcarolis) 136 test results. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome is characterized by autonomic instability. Akathisia produces motor restlessness. 18. A patient diagnosed with schizophrenia is acutely disturbed and violent. After several doses of haloperidol (Haldol), the patient is calm. Two hours later the nurse sees the patients head rotated to one side in a stiff position; the lower jaw is thrust forward, and the patient is drooling. Which problem is most likely? a. Acute dystonic reaction b. Tardive dyskinesia c. Waxy flexibility d. Akathisia ANS: A Acute dystonic reactions involve painful contractions of the tongue, face, neck, and back; opisthotonos and oculogyric crisis may be observed. Dystonic reactions are considered emergencies that require immediate intervention. Tardive dyskinesia involves involuntary spasmodic muscular contractions that involve the tongue, fingers, toes, neck, trunk, or pelvis; it appears after prolonged treatment. Waxy flexibility is a symptom observed in catatonic schizophrenia. Akathisia is evidenced by internal and external restlessness, pacing, and fidgeting. 19. An acutely violent patient diagnosed with schizophrenia receives several doses of haloperidol (Haldol). Two hours later the nurse notices the patients head rotated to one side in a stiffly fixed position; the lower jaw is thrust forward, and the patient is drooling. Which intervention by the nurse is indicated? a. Administer diphenhydramine (Benadryl) 50 mg IM from the PRN medication administration record. b. Reassure the patient that the symptoms will subside. Practice relaxation exercises with the patient. c. Give trihexyphenidyl (Artane) 5 mg orally at the next regularly scheduled medication administration time. d. Administer atropine sulfate 2 mg subcutaneously from the PRN medication administration record. ANS: A Diphenhydramine, trihexyphenidyl, benztropine, and other anticholinergic medications may be used to treat dystonias. Swallowing will be difficult or impossible; therefore, oral medication is not an option. Medication should be administered immediately; therefore, the intramuscular route is best. In this case, the best option given is diphenhydramine. 20. A patient has taken trifluoperazine (Stelazine) 30 mg/day orally for 3 years. The clinic nurse notes that the patient grimaces and constantly smacks both lips. The patients neck and shoulders twist in a slow, snakelike motion. Which problem would the nurse suspect? a. Agranulocytosis b. Tardive dyskinesia c. Tourette syndrome d. Anticholinergic effects ANS: B Tardive dyskinesia is a neuroleptic-induced condition involving the face, trunk, and limbs. Involuntary movements such as tongue thrusting; licking; blowing; irregular movements of the arms, neck, and shoulders; rocking; hip jerks; and pelvic thrusts are observed. These symptoms are frequently not reversible, even when the drug is discontinued. The scenario does not present evidence consistent with the other disorders mentioned. Agranulocytosis is a blood disorder. Tourette syndrome is a condition in which tics are present. Anticholinergic effects include dry mouth, blurred vision, flushing, constipation, and dry eyes. 21. A nurse sits with a patient diagnosed with schizophrenia. The patient starts to laugh uncontrollably, although the nurse has not said anything funny. Select the nurse’s best response. a. Why are you laughing? b. Please share the joke with me. c. I don’t think I said anything funny. d. You are laughing. Tell me what’s happening. ANS: D The patient is likely laughing in response to inner stimuli such as hallucinations or fantasy. Focusing on the hallucinatory clue (i.e., the patient’s laughter) and then eliciting the patient’s observation is best. The incorrect options are less useful in eliciting a response; no joke may be involved, why questions are difficult to answer, and the patient is probably not focusing on what the nurse has said in the first place. 22. Which symptoms are expected for a patient diagnosed with schizophrenia who has disorganization? a. Extremes of motor activity, from excitement to stupor b. Social withdrawal and ineffective communication c. Severe anxiety with ritualistic behavior d. Highly suspicious, delusional behavior ANS: B Patients with disorganization demonstrate the most regressed and socially impaired behaviors. Communication is often incoherent, with silly giggling and loose associations predominating. Highly suspicious, delusional behavior relates more to paranoia. Extremes of motor activity, from excitement to stupor, relate to catatonia. Severe anxiety and ritualistic behaviors relate to obsessive-compulsive disorder. 23. What assessment findings mark the prodromal stage of schizophrenia? a. Withdrawal, misinterpreting, poor concentration, and preoccupation with religion b. Auditory hallucinations, ideas of reference, thought insertion, and broadcasting c. Stereotyped behavior, echopraxia, echolalia, and waxy flexibility d. Loose associations, concrete thinking, and echolalia neologisms ANS: A Withdrawal, misinterpreting, poor concentration, and preoccupation with religion are prodromal symptoms, which are the symptoms present before the development of florid symptoms. The incorrect options each list the positive symptoms of schizophrenia that are more likely to be apparent during the acute stage of the illness. 24. A patient diagnosed with schizophrenia says, everyone has skin lice that jump on you and contaminate your blood. Which problem is evident? a. Poverty of content b. Concrete thinking c. Neologisms d. Paranoia ANS: D The patients unrealistic fear of contamination indicates paranoia. Neologisms are invented words. Concrete thinking involves literal interpretation. Poverty of content refers to an inadequate fund of information. 25. A patient diagnosed with schizophrenia has paranoid thinking. The patient angrily tells a nurse, You are mean and nasty. No one trusts you or wants to be around you. Select the most likely analysis. The patient: a. is trying to manipulate the nurse by using negative comments. b. is likely to experience disorganization and catatonia in the near future. c. is jealous of the nurse’s position of power in the relationship. d. may be identifying another person’s shortcomings in order to preserve his or her own self-esteem. ANS: D Patients with paranoid ideation often use disparaging comments to preserve one’s own self- esteem. There is no evidence the patient is trying to manipulate the nurse or is jealous. This behavior is not predictive of catatonia or disorganization. 26. A patient diagnosed with schizophrenia says, High heat. Last time here. Did you get a coat? What type of verbalization is evident? a. Neologism b. Idea of reference c. Thought broadcasting d. Associative looseness ANS: D Looseness of association refers to jumbled thoughts incoherently expressed to the listener. Neologisms are newly coined words. Ideas of reference are a type of delusion. Thought broadcasting is the belief that others can hear one’s thoughts. 27. A patient diagnosed with schizophrenia has taken a conventional antipsychotic medication for a year. Hallucinations are less intrusive, but the patient continues to have apathy, poverty of thought, and social isolation. The nurse expects a change to which medication? a. haloperidol (Haldol) b. olanzapine (Zyprexa) c. chlorpromazine (Thorazine) d. diphenhydramine (Benadryl) ANS: B Olanzapine is an atypical antipsychotic medication that targets both positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia. Haloperidol and chlorpromazine are conventional antipsychotic agents that target only positive symptoms. Diphenhydramine is an antihistamine. 28. The family of a patient diagnosed with schizophrenia is unfamiliar with the illness and the family’s role in recovery. Which type of therapy should the nurse recommend? a. Psychoeducational b. Psychoanalytic c. Transactional d. Family ANS: A A psychoeducational group explores the causes of schizophrenia, the role of medications, the significance of medication compliance, and the importance of support for the ill member of the family, and also provides recommendations for living with a person with schizophrenia. Such a group can be of practical assistance to the family members. The other types of therapy do not focus on psychoeducation. 29. A patient diagnosed with schizophrenia has been stable for a year; however, the family now reports the patient is tense, sleeps 3 to 4 hours per night, and has difficulty concentrating. The patient says, Demons are in the basement, and they can come through the floor. The nurse can correctly assess this information as an indication of: a. need for psychoeducation b. medication noncompliance c. chronic deterioration d. relapse ANS: D Signs of potential relapse include feeling tense, difficulty concentrating, trouble sleeping, increased withdrawal, and increased bizarre or magical thinking. Medication noncompliance may not be implicated. Relapse can occur even when the patient is regularly taking his or her medication. Psychoeducation is more effective when the patients’ symptoms are stable. Chronic deterioration is not the best explanation. 30. A patient diagnosed with schizophrenia begins to talk about cracklomers in the local shopping mall. The term cracklomers should be documented as: a. neologism. b. concrete thinking. c. thought insertion. d. an idea of reference. ANS: A A neologism is a newly coined word having special meaning to the patient. Cracklomers is not a known word. Concrete thinking refers to the inability to think abstractly. Thought insertion refers to thoughts of others that are implanted in one’s mind. An idea of reference is a type of delusion in which trivial events are given personal significance. 31. A patient diagnosed with schizophrenia anxiously says, I can see the left side of my body merging with the wall, then my face appears and disappears in the mirror. While listening, the nurse should: a. sits close to the patient. b. place an arm protectively around the patients’ shoulders. c. place a hand on the patients arms and exert light pressure. d. maintains a normal social interaction distance from the patient. ANS: D The patient is describing phenomena that indicate personal boundary difficulties. The nurse should maintain an appropriate social distance and not touch the patient, because the patient is anxious about the inability to maintain ego boundaries and merging with or being swallowed by the environment. Physical closeness or touch could precipitate panic. 32. A patient diagnosed with schizophrenia has auditory hallucinations. The patient anxiously tells the nurse, The voice is telling me to do things. Select the nurse’s priority assessment question. a. How long has the voice been directing your behavior? b. Do the messages from the voice frighten you? c. Do you recognize the voice speaking to you? d. What is the voice telling you to do? ANS: D Learning what a command hallucination is telling the patient to do is important; the command often places the patient or others at risk for harm. Command hallucinations can be terrifying and may pose a psychiatric emergency. The incorrect questions are of lesser importance than identifying the command. 33. A patient receiving risperidone (Risperdal) reports severe muscle stiffness at 10:30 AM. By noon, the patient is diaphoretic, drooling, and has difficulty swallowing. By 4:00 PM, vital signs are body temperature, 102.8 F; pulse, 110 beats per minute; respirations, 26 breaths per minute; and blood pressure, 150/90 mm Hg. Select the nurse’s best analysis and action. a. Agranulocytosis. Institute reverse isolation. b. Tardive dyskinesia. Withhold the next dose of medication. c. Cholestatic jaundice. Begin a high-protein, low fat diet. d. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome. Immediately notify the health care provider. ANS: D Taking an antipsychotic medication coupled with the presence of extrapyramidal symptoms, such as severe muscle stiffness and difficulty swallowing, hyperpyrexia, and autonomic symptoms (pulse elevation), suggest neuroleptic malignant syndrome, a medical emergency. The symptoms given in this scenario are not consistent with the medical problems listed in the incorrect options. 34. A patient diagnosed with schizophrenia begins a new prescription for lurasidone HCl (Latuda). The patient is 5?26?3? tall and currently weighs 204 pounds. Which topic is most important for the nurse to include in the teaching plan related to this medication? a. How to recognize tardive dyskinesia b. Weight management strategies c. Ways to manage constipation d. Sleep hygiene measures ANS: B Lurasidone HCl (Latuda) is an atypical antipsychotic medication. The incidence of weight gain, diabetes, and high cholesterol is high with this medication. The patient is overweight now, so weight management is especially important. The incidence of tardive dyskinesia is low with atypical antipsychotic medications. Constipation may occur, but it is less important than weight management. This drug usually produces drowsiness. 35. A patient diagnosed with schizophrenia has auditory hallucinations, delusions of grandeur, poor personal hygiene, and motor agitation. Which assessment finding would the nurse regard as a negative symptom of schizophrenia? a. Auditory hallucinations b. Delusions of grandeur c. Poor personal hygiene d. Motor agitation ANS: C Negative symptoms include apathy, anhedonia, poor social functioning, and poverty of thought. Poor personal hygiene is an example of poor social functioning. The distractors are positive symptoms of schizophrenia. SELECT ALL THAT APPLY 1. The family members of a patient newly diagnosed with schizophrenia state that they do not understand what has caused the illness. The nurse’s response should be based on which models? Select all that apply. a. Neurobiological b. Environmental c. Family theory d. Genetic e. Stress ANS: A, D Compelling evidence exists that schizophrenia is a neurologic disorder probably related to neurochemical abnormalities, neuroanatomical disruption of brain circuits, and genetic vulnerability. Stress and family disruption may contribute but are not considered etiologic factors. Environmental factors are not recognized as causative variables in schizophrenia. 2. A nurse at the mental health clinic plans a series of psychoeducational groups for persons diagnosed with schizophrenia. Which two topics would take priority? a. How to complete an application for employment b. The importance of correctly taking your medication c. How to dress when attending community events d. How to give and receive compliments e. Ways to quit smoking ANS: B, E Stabilization is maximized by the adherence to the antipsychotic medication regimen. Because so many patients with schizophrenia smoke cigarettes, this topic relates directly to the patient’s physiologic well-being. The other topics are also important but are not priority topics. 3. A patient diagnosed with schizophrenia is hospitalized after arguing with co-workers and threatening to harm them. The patient is aloof and suspicious and says, two staff members I saw talking were plotting to assault me. Based on data gathered at this point, which nursing diagnoses relate? Select all that apply. a. Risk for other-directed violence b. Disturbed thought processes c. Risk for loneliness d. Spiritual distress e. social isolation ANS: A, B Delusions of persecution and ideas of reference support the nursing diagnosis of Disturbed thought processes. Risk for other-directed violence is substantiated by the patients paranoia and feeling endangered by persecutors. Fearful individuals may strike out at perceived persecutors or attempt self-harm to get away from persecutors. Data are not present to support the other diagnoses. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 87 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$19.00
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Oct 23, 2021
Number of pages
87
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Oct 23, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
67