*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > EMT 084 FINAL EXAM Study Guide – AAOS 13th Edition. Comprehensive Content For Quick Exam Preparati (All)
EMT 084 FINAL EXAM Study Guide – AAOS 13th Edition. Comprehensive Content For Quick Exam Preparation.
Document Content and Description Below
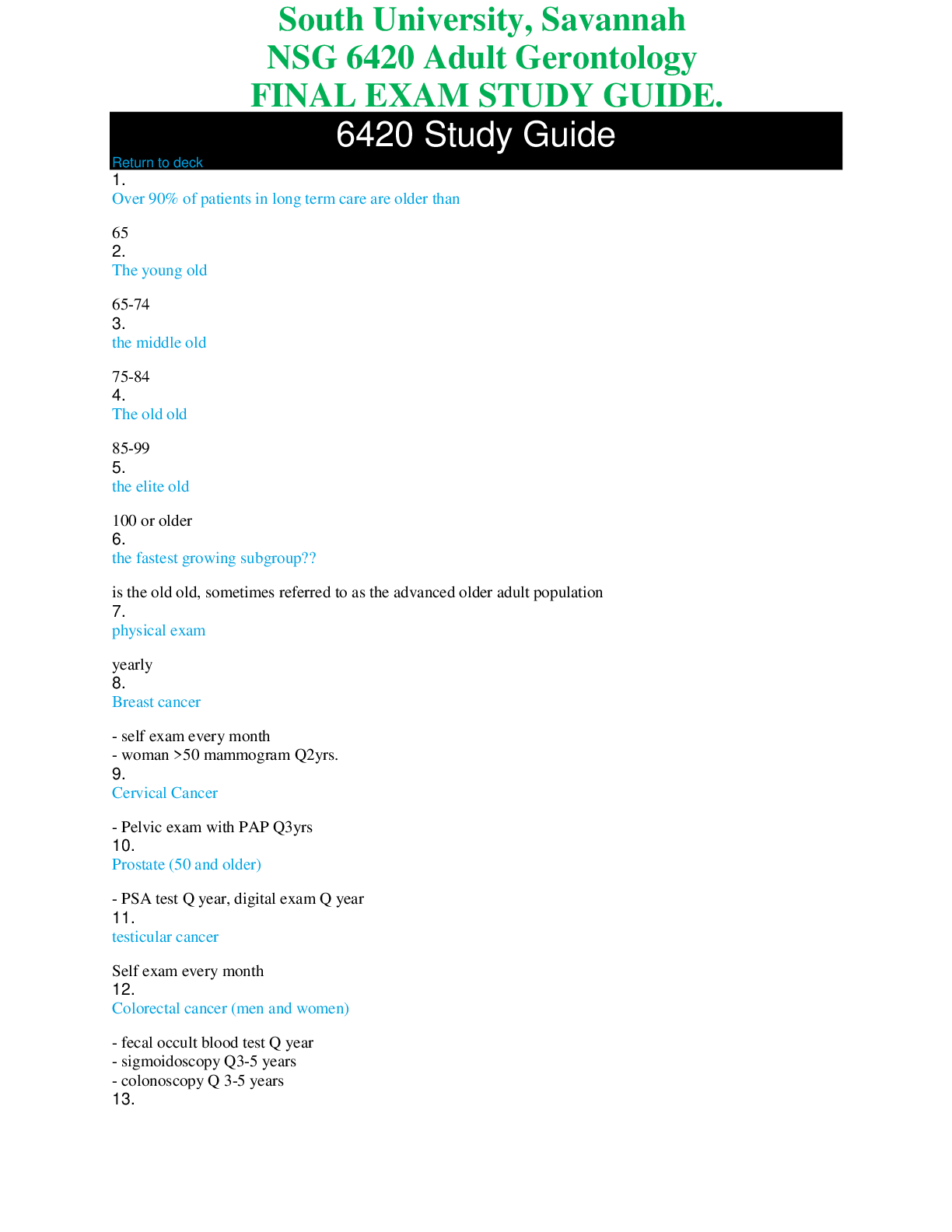
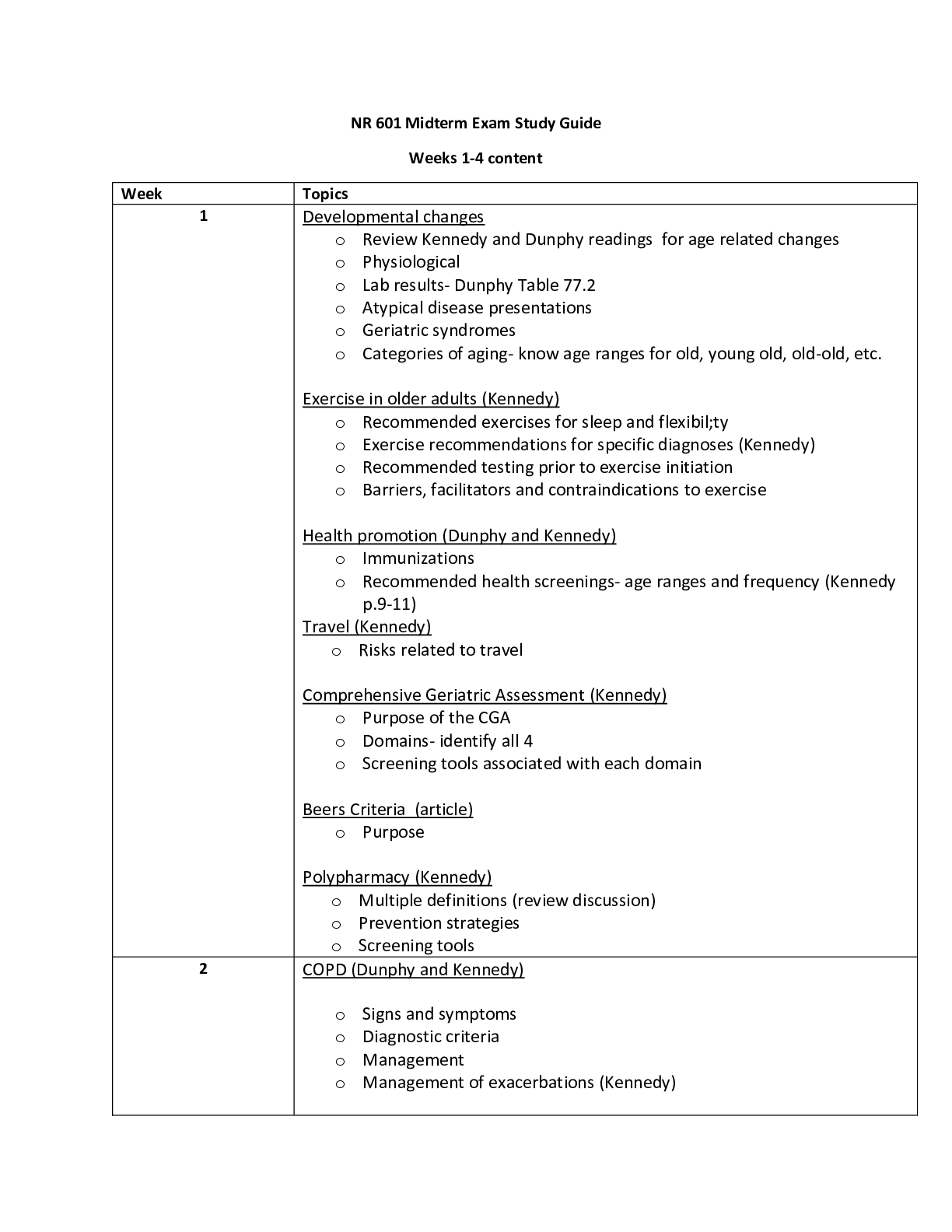
• Patients that are apneic and have weak pulses that are pulled from cold water with unknown submersion time should be provided rescue breathing, remove his wet clothing, immobilize his entire spi... ne, keep him warm, and transport carefully. Hypothermia is diagnosed when the core temp of the body –the temp of the heart, lungs, and vital organs-falls below 95*F (35*C) Never assume that a cold, pulseless PT is dead. PTs may survive severe hypothermia if proper emergency care is provided. It is critical that you perform an extended pulse check (up to a full minute). Asses at the carotid or femoral pulse. A PT in apparent cardiac arrest from hypothermia should not be considered dead until aggressive rewarming has been attempted, along with resuscitation. No one is dead unless they are warm and dead. • Patients that are hypotensive and have bilateral femur fracture; their legs should be bound together on the backboard, kept warm, and transported immediately. The most common life-threatening musculoskeletal injuries are multiple fractures, open fractures with arterial bleeding, pelvic fractures, bilateral femur fractures, and limb amputation. All PTs with a hip fracture (fractures of the proximal femur) may have a significant amount of blood loss. Therefore, you should treat with high-flow O2, monitor vital signs frequently, and be alert for S/S of shock. Following a fracture, the large muscles of the thigh spasm in an attempt to “splint” the unstable limb. The muscle spam often produces significant deformity of the limb, with severe angulation or external rotation at the fracture site. If the fracture is open (fragments of bone protruding through the skin) never attempt to push the bone back into the skin. After a femur fracture there is usually a significant amount of blood loss, thus it is not unusual for hypovolemic shock to develop. Handle these PTs with care because any extra movement or fracture manipulation may increase the amount of blood loss. If there are no distal pulses or PMSCs are off, apply gentle longitudinal traction to the deformed limb in line with the long axis of the limb. Gradually turn the leg from the deformed position to restore the limb’s overall alignment. Often this restores or improves circulation to the foot. If it does not, the PT may have sustained a serious vascular injury and may be in need of prompt medical attention. Afracture of the femoral shaft is best stabilized with a traction splint, such as a Sager splint. • Patients that are kicked or punched in the abdomen, have stable vital signs, and do not have any c-spine injuries should be transported in the position you find them (aka: position of comfort). / And keep them warm.. Pain in the abdomen can often be deceiving because it is often diffuse in nature and may be referred from the site of injury to another location in the body. In PTs with liver and spleen injuries, and bleeding into the peritoneal space, pain is referred to the shoulder. Bleeding from an injury to the spleen can result in referred pain to the tip of the left shoulder. when a PT reports pain that is tearing and describes it as going from the abdomen posteriorly, he or she is often describing symptoms of an abdominal aneurysm that is dissecting. pain that is following the angle from the lateral hip to the midline of the groin can be the result of damage to the kidneys or the ureters. Pain in the right lower quadrant can indicate an inflamed or ruptured appendix. A PT who sustained a blunt abdominal injury should be log rolled to a supine position unto a backboard. • Suction the oropharynx for 15 seconds maximum. Suction with the appropriate suction tip, suction while moving out of the mouth. • When one eye is injured, cover both eyes to minimize movement and damage to the injured eye. • Patients in anaphylactic shock should be administered a dose of epinephrine with an auto-injector, record the time of the injection, and transport immediately. Also note PTs condition before use of drug, including if possible VS, note why you used the drug, dose, route, and time used. Then note condition PT condition after use of drug, and vital sings after, and response to drug. • When a patient becomes unresponsive, pulseless, and apneic during transport, you should stop the ambulance, begin CPR, and attach the AED as soon as possible. • If a metal object such as a bicycle kickstand impales a patient, it would be best to unbolt the kickstand from the bike frame and stabilize it with bulky dressings.• The palm of the patient's hand is equal to one percent of his or her total BSA 2//// for an infant, the head is equal to 18% and legs are 13.5%. for a small child the head is 12% and legs are 16.5%. Adult head is 9% and legs are 18%. Front and back are 18% arms are 9% and groin is 1% • Many patients with Down syndrome also have heart conditions. Is characterized by a genetic chromosomal defect resulting in mild to severe intellectual impairment. The normal human somatic cell contains 23 pairs of chromosomes. In most cases, Down syndrome, also known as trisomy 21, occurs when the two 21st chromosomes fail to separate, so that the ovurym or sperm contains 24 chromosomes. Also have thyroid problems; and hearing and vision problems. Increased risk for medical complications, including those that affect the cardiovascular, sensory, endocrine, musculoskeletal, dental, and gastrointestinal systems, as well as neurologic development. airway management is difficult because most have larger tongs, and small oral and nasal cavities. • The most likely cause of a depressed skull fracture of a patient who suffered a blast injury would be the stationary object they hit when thrown. Result from high-energy direct trauma to the head with a blunt object. The frontal and parietal bones of the skull are most susceptible to these types of fractures because the bones in these types of fractures because the bones in these areas are relatively thin. As a consequence, bony fragments may be driven into the brain, resulting in injury. The scalp may or may not be lacerated. PTs with depressed skull fractures often present with neurologic signs. Loss of consciousness. • Respiration is the process of gas exchange, whereas ventilation is the movement of air between the lungs and the environment. • Patients that are partially immune to a particular disease may develop illness from germs that lie dormant from the initial infection. Sepsis or secondary infection. • Two pieces of equipment to take with you, in addition to your red bag, should be an AED and portable suction unit. • Hyperglycemia can only be corrected in the hospital setting [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 25 pages
Instant download

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Nov 22, 2021
Number of pages
25
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Nov 22, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
108