Mathematics > PROJECT FINAL > MATH 533 Week 6 Course Project Part B: Hypothesis Testing (GRADED A+) (All)
MATH 533 Week 6 Course Project Part B: Hypothesis Testing (GRADED A+)
Document Content and Description Below
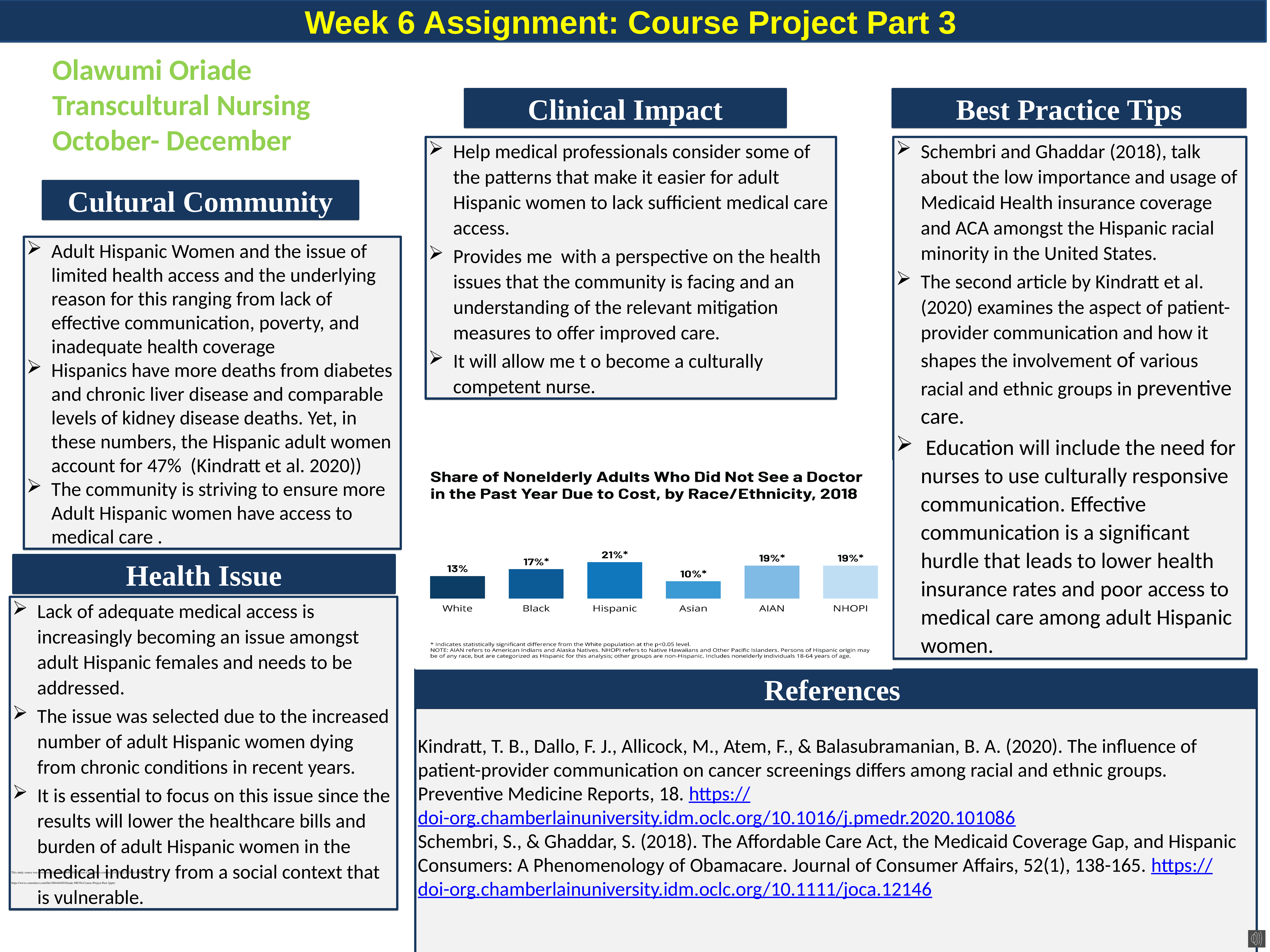
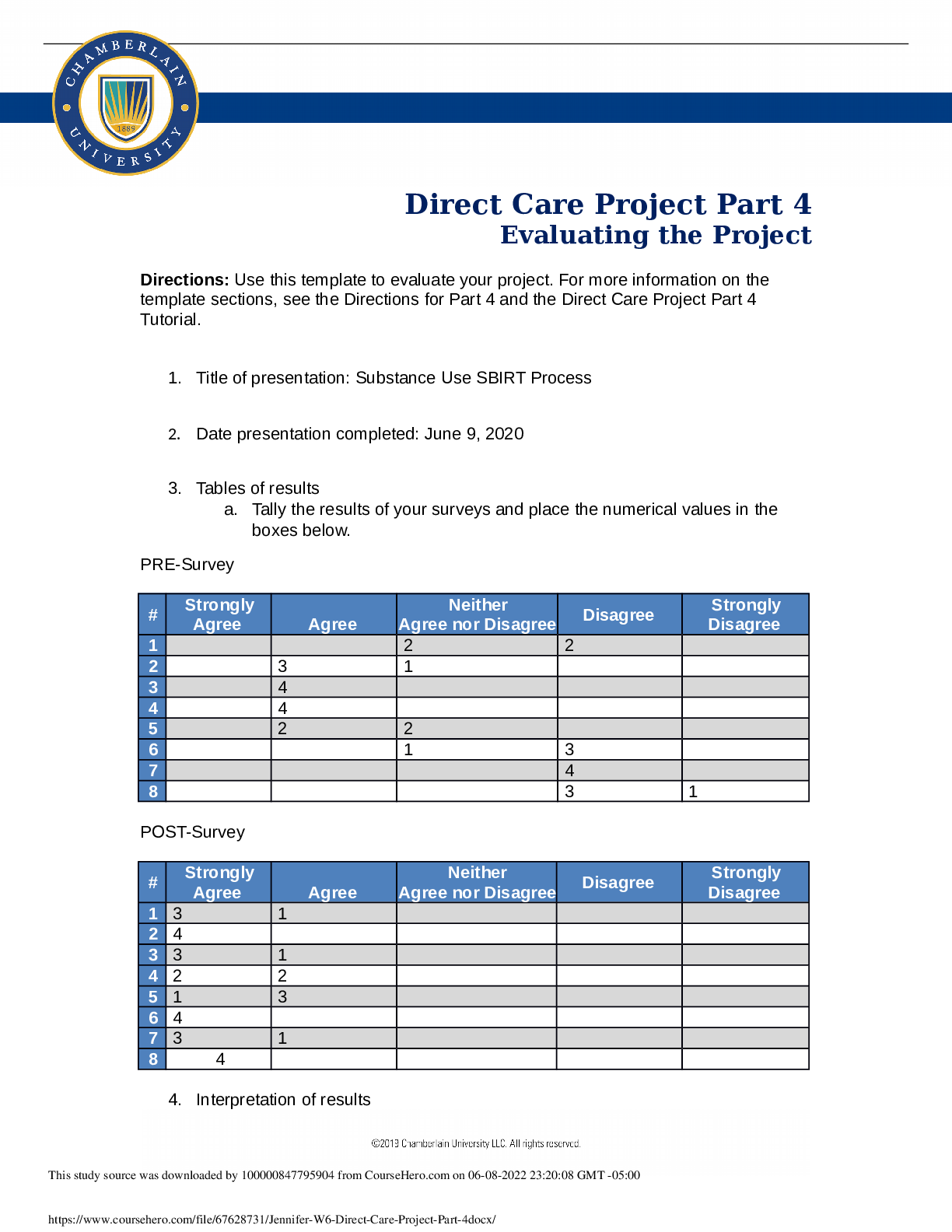
Math-533 Hypothesis Testing Keller Graduate School of Management A hypothesis testing involves the testing of the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis. When testing the hypoth... esis, either the null hypothesis or the alternative hypotheses is rejected. The Company can use hypothesis testing to examine if it should keep a current process, change a current process or start a new process. It can also examine different areas to see if an employee or manager’s ideas would prove more productive. The hypothesis testing can quickly be applied or tested saving the Company time and money. Requirement A: The Average Mean Sales per Week exceeds 41.5 per salesperson. Key Statistics were computed using Minitab Descriptive Statistics: Sales (Y) Variable SALES NUMBER 100 MEAN 42.55 SE MEAN 0.717 7.1708937 ST.DEVIATION VARIANCE 5 51.421717 2 MINIMUM 21 Q1 39 MEDIAN 43 Q3 47 MAXIMUM 67 RANGE 46 One-Sample Z: Sales (Y) The assumed standard deviation = 7.171 Variable N Mean St-Dev Sales (Y) 100 42.550 7.171 SE Mean 0.717 95% CI (41.145, 43.955) One-Sample Z: Sales (Y) Test of mu = 41.5 vs > 41.5 The assumed standard deviation = 7.171 Variable N Mean St-Dev SE Mean 95% Lower Bound Z P Sales (Y) 100 42.550 7.171 0.717 41.370 1.46 0.072 Step 1- Hypothesis Ho: μ = 41.5 Ha: μ> 41.5 Step 2-Level of Significance The a = 0.05 is given. Step 3- Identify the statistical test to use Use z-test because the Standard Deviation is known and the sample (n=100) is a large sample (n > 30). The test will let us decide, if we are going to accept or reject that sales will exceed 41.5 per salesperson per week. To test this, a single tail test will be conducted. Z score Test – Single Tail (Result According to Minitab) One-Sample Z = 1.464 and P = 0.072 Step- 4 Decision Rule The alternative hypothesis states that mean sales per week exceeds 41.5; this is a one tailed test to the right. The given a = .05 is to the right of Z = 1.645. Therefore, we reject the null hypothesis if the Z > 1.645. If the p value is less than the a = .05 then reject the null hypothesis. Step- 5 Decision Making The 100 salespersons average mean is 42.55. The computed Z score is = 1.464. The computed score is less than 1.645, we do not reject the null hypothesis. We can be 95% confident that the average sales per week will fall within the 95% Confidence Interval (CI) of (41.145, 43.955). The Company can expect a salesperson to achieve sales an average of 42.55 sales a week. Requirement B: Testing to see if a proportion of salespeople that received online training is less than 55%. Descriptive Statistics: Sales (Y) Variable SALES NUMBER 100 MEAN 42.55 SE MEAN 0.717 7.1708937 ST.DEVIATION VARIANCE 5 51.421717 2 MINIMUM 21 Q1 39 MEDIAN 43 Q3 47 MAXIMUM 67 RANGE 46 Descriptive Statistics: Sales (Y) Variable N N* Mean SE Mean StDev Minimum Q1 Median Q3 Sales (Y) 50 0 43.840 0.949 6.708 29.000 40.000 44.000 48.000 Variable Sales (Y) Maximum 67.000 Uh[] Test and CI for One Proportion: Test of p = 0.55 vs p not = 0.55 Exact Sample X N Sample p 95% CI P-Value 1 50 100 0.500000 (0.398321, 0.601679) 0.366 Test and CI for One Proportion: Test of p = 0.55 vs p < 0.55 Sample X N Sample p 95% Upper Bound Exact P-Value 1 50 100 0.500000 0.586378 0.183 Step 1- Hypotheses Ho: μ = 55% Ha: μ < 55% Step 2- Level of Significance The a = 0.05 is given. Step 3- Identify the statistical test to use Use 1 Proportion because Standard Deviation is known and the sample (n=50) is a large sample (n > 30). 1Proportion score Test – Single Tail One Proportion- Z = -1.01 and a P-Value of 0.157. Step 4- Decision Rule The alternative hypothesis states that the true population proportion of salespeople that received online training is less than 55%. This will be a one tailed test to the left. The given a = . 05 is to the left of Z = -1.645. Therefore, we reject the null hypothesis if Z> -1.645. Step 5-Decision Making The online trained salesperson mean is 43.84. The computed, using Minitab, Z score -1.01 and P value of 0.157. The computed Z score is greater than -1.645, do not reject the null hypothesis. We can be 95% confident that the true population mean that received online training will not fall within the Confidence Interval (CI) of (0.3983, 0.6017). The Company can expect that 43.84% of salespersons will have received online training. Requirement C: The mean number of calls made per week by salespeople that had no training is less than 145. Descriptive Statistics: Calls (X1) CALLS NUMBE R 20 MEAN 140.3 SE MEAN 2.44 ST. DEVIATION 10.8923 118.642 VARIANCE 1 MINIMUN 120 Q1 131.75 MEDIAN 141 Q3 145 MAXIMUM 160 RANGE 40 One-Sample T: Calls (X1) Test of μ = 145 vs ≠ 145 N Mean St-Dev SE Mean 95% CI T P 20 140.30 10.89 2.44 (135.20, 145.40) -1.93 0.069 One-Sample Z: Calls (X1) Test of μ = 145 vs < 145 The assumed standard deviation = 10.89 N Mean SE Mean 95% Upper Bound Z P 20 140.30 2.44 144.31 -1.93 0.027 Step 1- Hypotheses Ho: μ = 145 Ha:μ < 145 Step 2- Level of Significance The a = 0.05 is given. Step 3- Identify the statistical test to use Use On-Sample T-test because Standard Deviation is known and the sample (n=20) is a small sample (n < 30).This will be a one tailed test to the left.T score Test – Single Tail test to the leftOne-Sample Z= -1.93and P = 0.027 Step 4- Decision Rule The alternative hypothesis states Less than 145 calls, on average, are made by salespeople that have had no training. The given a = .05 is to the right of Z = -1.645. Therefore, we reject the null hypothesis if Z > -1.645. If the P value is more than the given a of .05 then rejecting the null hypothesis is supported by the evidence. Step 5- Decision Making The average number of calls made by salespeople that received no training is 140.30. The computed Z score is -1.93 and the P value is 0.027, which is less than the given a of .05. The null hypothesis is not accurate when stated that the mean number of calls made per week is equal to 145, therefore, we should rely on the alternative hypothesis data that mean number of calls made per week by salespeople that have not received training is less than 145. The computed Minitab result for the mean is 140.30. This is within the computed 95% Confidence Interval of (135.20, 145.40). Requirement D: To test the mean time per call to see if it is greater than 15 minutes Descriptive Statistics: Time (X2) Variable NUMBER TIME 100 MEAN 15.3 SE MEAN 0.23 ST.DEVIATION 2.299880541 VARIANCE 5.289450505 MINIMUM 10.0 Q1 13.6 MEDIAN 15.1 Q3 17.075 MAXIMUM 20.0 RANGE 10.0 One-Sample Z: Time (X2) Test of μ = 15 vs > 15 The assumed standard deviation = 2.3 N Mean SE Mean 95% Lower Bound Z P 100 15.338 0.230 14.960 1.47 0.071 One-Sample Z: Time (X2) Test of μ = 15 vs ≠ 15 The assumed standard deviation = 2.3 N Mean SE Mean 95% CI Z P 100 15.338 0.230 (14.887, 15.789) 1.47 0.142 In this scenario, the Z score with single tail test will be used due the same reason as mentioned in first scenario. Step 1- Hypotheses Ho: μ = 15minutes Ha:μ > 15 minutes Step 2- Level of Significance The a = 0.05 is given. Step 3- Identify the statistical test to use Use z-test because Standard Deviation is known and the sample (n=100) is a large sample (n > 30). This test will be a single tailed test to the right. The computed Z Score Test – Single Tail, to the right, One-Sample Z = 1.47 and P = 0.071 Step 4- Rejection Region The alternative hypothesis states the average time per call is greater than 15 minutes. The given probability of .05 is to the right of Z. Thus, we reject the null hypothesis if Z > 1.645. We accept the alternative hypothesis that the average call time is greater than 15 minutes. Step 5- Decision Making The sample of 100 calls yielded an average time of calls made of 15.338 minutes. The computed Z score is 1.47 and the P value is 0.071, which is greater than the given a of .05. The null hypothesis is rejected and the average time of calls is greater than 15 minutes. The P value is greater than the a, which gives further evidence to reject the null hypothesis. Management can expect that the average time spent on a call is greater than 15 minutes. The computed mean time is 15.338. This time falls within the 95 % confidence interval of (14.887, 15.789). We can be 95 % certain that the average time of a call will be between 14.887, 15.789minutes long. Appendix- I Descriptive Statistics: Sales (Y), Calls (X1), Time (X2), Years (X3) Variable N N* Mean SE Mean StDev Minimum Q1 Median Q3 Sales (Y) 100 0 42.550 0.717 7.171 21.000 39.000 43.000 47.000 Calls (X1) 100 0 161.88 1.84 18.43 120.00 149.00 160.50 176.75 Time (X2) 100 0 15.338 0.230 2.300 10.000 13.600 15.050 17.075 Years (X3) 100 0 2.300 0.142 1.418 0.000 1.000 2.000 3.000 Variable Maximum Sales (Y) 67.000 Calls (X1) 201.00 Time (X2) 20.000 Years (X3) 5.000 One-Sample Z: Sales (Y) The assumed standard deviation = 7.171 Variable N Mean StDev Sales (Y) 100 42.550 7.171 SE Mean 0.717 95% CI (41.145, 43.955) One-Sample Z: Sales (Y) Test of mu = 41.5 vs > 41.5 The assumed standard deviation = 7.171 Variable N Mean StDev SE Mean 95% Lower Bound Z P Sales (Y) 100 42.550 7.171 0.717 41.370 1.46 0.072 Appendix- II Descriptive Statistics: Sales (Y), Calls (X1), Time (X2), Years (X3) Variable Type N Mean SE Mean StDev Minimum Q1 Median Sales (Y) GROUP 30 42.77 1.31 7.16 31.00 38.75 43.00 NONE 20 39.30 1.89 8.44 29.00 35.25 37.00 ONLINE 50 43.720 0.896 6.338 21.000 41.000 44.000 Calls (X1) GROUP 30 156.57 2.51 13.74 131.00 149.75 154.50 NONE 20 140.30 2.44 10.89 120.00 131.25 141.00 ONLINE 50 173.70 1.89 13.38 149.00 162.50 174.00 Time (X2) GROUP 30 15.853 0.369 2.021 12.400 14.450 15.300 NONE 20 16.290 0.552 2.469 10.000 14.850 16.450 ONLINE 50 14.648 0.313 2.211 10.900 13.000 14.250 Years (X3) GROUP 30 2.467 0.238 1.306 1.000 1.000 2.000 NONE 20 2.050 0.285 1.276 0.000 1.000 2.000 ONLINE 50 2.300 0.218 1.542 0.000 1.000 2.000 Variable Sales (Y) Type GROUP N 30 Q3 47.00 Maximum 67.00 NONE 20 39.75 67.00 ONLINE 50 48.000 56.000 Calls (X1) GROUP 30 166.50 192.00 NONE 20 145.00 160.00 ONLINE 50 184.25 201.00 Time (X2) GROUP 30 17.825 19.400 NONE 20 18.075 19.900 ONLINE 50 16.400 20.000 Years (X3) GROUP 30 3.000 5.000 NONE 20 3.000 4.000 ONLINE 50 3.000 5.000 Descriptive Statistics: Sales (Y) Variable N N* Mean SE Mean StDev Minimum Q1 Median Q3 Sales (Y) 50 0 43.840 0.949 6.708 29.000 40.000 44.000 48.000 Variable Sales (Y) Maximum 67.000 Test and CI for One Proportion Test of p = 0.55 vs p not = 0.55 Exact Sample X N Sample p 95% CI P-Value 1 50 100 0.500000 (0.398321, 0.601679) 0.366 Test and CI for One Proportion Test of p = 0.55 vs p < 0.55 Sample X N Sample p 95% Upper Bound Exact P-Value 1 50 100 0.500000 0.586378 0.183 Appendix- III Descriptive Statistics: Calls (X1) Variable Type N Mean SE Mean StDev Minimum Q1 Median Calls (X1) GROUP 30 156.57 2.51 13.74 131.00 149.75 154.50 NONE 20 140.30 2.44 10.89 120.00 131.25 141.00 ONLINE 50 173.70 1.89 13.38 149.00 162.50 174.00 Variable Type N Q3 Maximum Calls (X1) GROUP 30 166.50 192.00 NONE 20 145.00 160.00 ONLINE 50 184.25 201.00 Descriptive Statistics: Calls (X1) Variable Type N N* Mean SE Mean StDev Minimum Q1 Median Q3 Calls (X1) NONE 20 0 140.30 2.44 10.89 120.00 131.25 141.00 145.00 Variable Type Maximum Calls (X1) NONE 160.00 One-Sample T: Calls (X1) Test of μ = 145 vs ≠ 145 N Mean StDev SE Mean 95% CI T P 20 140.30 10.89 2.44 (135.20, 145.40) -1.93 0.069 One-Sample Z: Calls (X1) Test of μ = 145 vs < 145 The assumed standard deviation = 10.89 N Mean SE Mean 95% Upper Bound Z P 20 140.30 2.44 144.31 -1.93 0.027 Appendix IV Descriptive Statistics: Time (X2) Variable N N* Mean SE Mean StDev Minimum Q1 Median Q3 Time (X2) 100 0 15.338 0.230 2.300 10.000 13.600 15.050 17.225 Variable Maximum Time (X2) 20.000 Descriptive Statistics: Time (X2) Variable N N* Mean SE Mean StDev Minimum Q1 Median Q3 Time (X2) 50 0 17.206 0.204 1.444 15.100 15.800 17.150 18.500 Variable Maximum Time (X2) 20.000 One-Sample Z: Time (X2) Test of mu = 15 vs > 15 The assumed standard deviation = 1.444 95% Lower Variable N Mean StDev SE Mean Bound Z P Time (X2) 50 17.206 1.444 0.204 One-Sample Z: Time (X2) 16.870 10.80 0.000 Test of mu = 15 vs not = 15 The assumed standard deviation = 1.444 Variable N Mean StDev SE Mean 95% CI Z P Time (X2) 50 17.206 1.444 0.204 (16.806, 17.606) 10.80 0.000 [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 16 pages
.png)
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jan 19, 2022
Number of pages
16
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jan 19, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
69