Biology > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Chapter 04—CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION. Quiz and Answers (All)
Chapter 04—CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION. Quiz and Answers
Document Content and Description Below
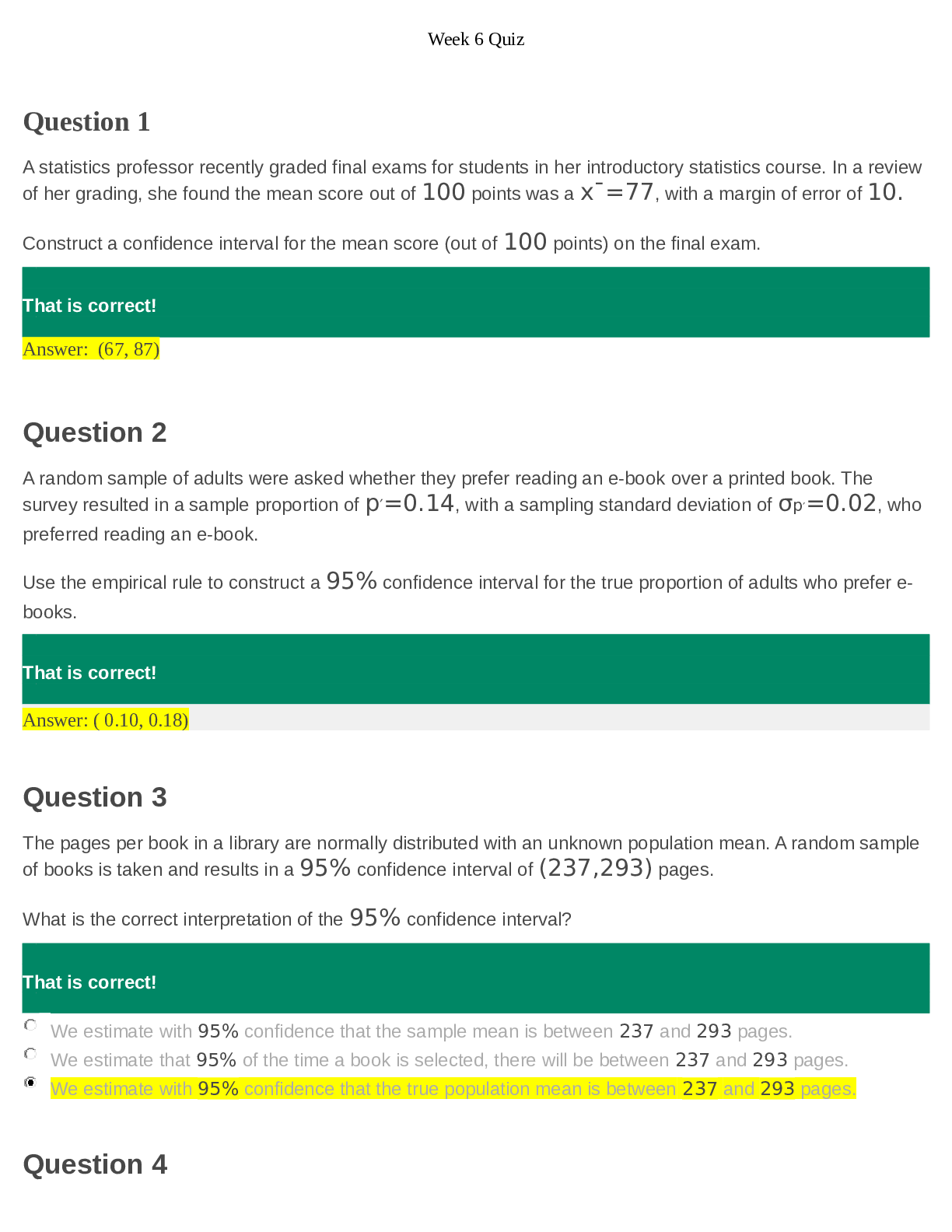
Multiple Choice 1. What happens when a round cell expands in diameter? a. Its surface area and diameter increase with the cube of its diameter. b. Its surface area and diameter increase wit... h the square of its diameter. c. Its volume increases faster than its surface area does. d. Its surface area increases faster than its volume does. e. Its volume and surface area expand by the same proportion. : c POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.1 What is a cell? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.1.3 - Define surface-to-volume ratio and describe how it limits cell size. KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Understand NOTES: New 2. One portion of the cell theory states that ____. a. all cells have a nucleus b. all cells divide by meiosis c. all living organisms are made up of one or more cells d. cells arise through spontaneous generation e. growth is solely the result of cell division : c POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.1 What is a cell? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.1.1 - List some postulates of the cell theory. KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Understand Selecting the Exception 3. Four of the five s listed below are generalizations of the cell theory. Select the exception. a. Cells are the structural and functional components of living things. b. Cells arise from preexisting cells. c. All organisms are composed of cells. d. Cells are the basic living unit or organization of living things. e. All cells have a nucleus. : e POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.1 What is a cell? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.1.1 - List some postulates of the cell theory. KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Understand OTHER: Selecting the Exception 4. Four of the five s listed below are characteristics of a plasma membrane. Select the exception. a. phospholipid b. fluid mosaic c. lipid bilayer d. hydrophilic tails e. membrane proteins : d POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.3 What is a membrane? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.3.2 - Why is a eukaryotic or bacterial cell membrane described as a fluid mosaic? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember OTHER: Selecting the Exception 5. Four of the five s listed below are organelles in the cytoplasm. Select the exception. a. nucleolus b. mitochondrion c. ribosome d. Golgi apparatus e. chloroplast : a POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.5 What do eukaryotic cells have in common? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.5.1 - What is the significance of membranes in organelles? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember OTHER: Selecting the Exception 6. Four of the five organelles listed below are part of the endomembrane system. Select the exception. a. smooth ER b. peroxisomes c. Golgi bodies d. vesicles e. mitochondria : e POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.6 What is the endomembrane system? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.6.1 - List the main functions of the endomembrane system. KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember OTHER: Selecting the Exception NOTES: Modified 7. Four of the five animals listed below can harbor E. coli 0157:H7 without becoming ill. Select the exception. a. goats b. cattle c. deer d. sheep e. humans : e POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.12 Application: Food for thought LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.12 - Describe the causes and consequences of Escherichia coli poisoning. KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember OTHER: Selecting the Exception 8. All cells have: a. a nucleus, but not necessarily DNA b. a plasma membrane, but not necessarily DNA c. cytoplasm, but not necessarily a plasma membrane d. cytoplasm and a plasma membrane, but not necessarily DNA e. cytoplasm, a plasma membrane, and DNA : e POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.1 What is a cell? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.1.2 - Describe the three components that are common to all cells. KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember NOTES: New 9. To see objects smaller than those that can be resolved by a light microscope, we usually use microscopes that employ a beam of: a. electrons b. photons c. protons d. neutrons e. X-rays : a POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.2 How do we see cells? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.2.2 - Describe some techniques used to observe finer cellular details. KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Understand 10. Which structure is large enough to be seen under a light microscope? a. small molecule b. protein c. virus d. chloroplast e. complex carbohydrate : d POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.2 How do we see cells? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.2.1 - Explain the working of a light microscope. KEYWORDS: Bloom's: application 11. The most detailed image of the surface of a cell would be found on a ____. a. light micrograph from a phase contrast microscope b. transmission electron micrograph c. scanning electron micrograph d. light micrograph from a light microscope e. transmission electron micrograph : c POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.2 How do we see cells? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.2.3 - Differentiate between a scanning electron microscope and a transmission electron microscope. KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Understand NOTES: Modified 12. The phospholipid molecules of most membranes have a ____. a. hydrophobic head and a hydrophilic tail b. hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail c. hydrophobic head and two hydrophobic tails d. hydrophilic head and two hydrophobic tails e. hydrophilic head and tail : d POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.3 What is a membrane? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.3.1 - Describe the structure of a lipid bilayer. KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember NOTES: Modified 13. If free phospholipids were swirled into water, they would ____. a. form pairs b. form spheres with the phosphate-containing heads at the centre c. dissolve d. form a lipid bilayer sheet, with the hydrophobic tails in the centre e. form a lipid bilayer sheet, with the phosphate-containing heads in the centre : d POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.3 What is a membrane? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.3.2 - Why is a eukaryotic or bacterial cell membrane described as a fluid mosaic? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Understand NOTES: New 14. Archaea use molecules with reactive side chains in their plasma membrane, so the tails of archaeal phospholipids form covalent bonds with one another. As a result, the plasma membrane is ____. a. more fluid b. less rigid c. less fluid d. able to contain more membrane proteins e. easily disturbed : c POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.3 What is a membrane? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.3.3 - How are the membranes of archaea different from those of eukaryotes? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Understand NOTES: New 15. Different cell membranes can have different functions depending on which ____ are associated with them. a. cholesterol molecules b. fatty acid lengths c. fatty acid saturations d. proteins e. phospholipid heads : d POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.3 What is a membrane? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.3.4 - Explain the functions of different types of proteins in the plasma membrane. KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Understand NOTES: New 16. Which membrane proteins move specific substances across a membrane, typically by forming a channel? a. transport b. receptor c. recognition d. adhesion e. enzymes : a POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.3 What is a membrane? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.3.4 - Explain the functions of different types of proteins in the plasma membrane. KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember NOTES: New 17. Hydrophobic reactions of phospholipids may produce clusters of their fatty acid tails, which form a. a lipid bilayer. b. hydrolysis of the fatty acids. c. a protein membrane. d. a cytoskeleton. e. a nonpolar membrane. : a POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.3 What is a membrane? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.3.1 - Describe the structure of a lipid bilayer. KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember 18. Which membrane protein is responsible for binding hormones that can trigger changes in the cell’s activity? a. recognition proteins b. receptor proteins c. transport proteins d. adhesion proteins e. channel proteins : b POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.3 What is a membrane? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.3.4 - Explain the functions of different types of proteins in the plasma membrane. KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Understand NOTES: Modified Figure 4.8 Generalized body plan of a prokaryote. 19. Which letter identifies this cell’s nucleus? a. A b. B c. C d. D e. There is no nucleus. : e POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.4 How are bacteria and archaea alike? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.4.2 - Describe the cellular structure of bacteria and archaea. KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Apply NOTES: Modified 20. Which letter identifies this cell’s flagellum? a. A b. B c. C d. D e. E : a POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.4 How are bacteria and archaea alike? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.4.2 - Describe the cellular structure of bacteria and archaea. KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember NOTES: Modified 21. Which structure helps these cells move across or cling to surfaces? a. A b. B c. C d. D e. E : b POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.4 How are bacteria and archaea alike? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.4.2 - Describe the cellular structure of bacteria and archaea. KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Understand NOTES: New 22. Which structure do prokaryotic cells lack? a. nucleoid regions b. membrane-bound nuclei c. cytoplasm d. a plasma membrane e. DNA : b POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.4 How are bacteria and archaea alike? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.4.1 - Why is the term “prokaryotes” insufficient for describing archaea and bacteria? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember NOTES: Modified 23. Most archaeal cell walls consist of ____; most bacterial cell walls consist of a polymer of peptides and polysaccharides. a. lipids b. proteins c. phospholipids d. glycoproteins e. glycolipids : b POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.4 How are bacteria and archaea alike? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.4.2 - Describe the cellular structure of bacteria and archaea. KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember NOTES: New 24. Many species of bacteria live bound together by a gluelike substance that, among other things, makes up the plaque on human teeth. This is an example of a ____. a. pilus b. mass c. vesicle d. colony e. biofilm : e POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.4 How are bacteria and archaea alike? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.4.4 - What is a biofilm and why is it useful for bacteria? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Understand NOTES: New 25. What are organized clusters of membrane proteins that selectively allow substances to cross into and out of the nucleus? a. nuclear pore b. passive transport protein c. receptor d. nuclear envelope e. ribosome : a POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.5 What do eukaryotic cells have in common? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.5.1 - What is the significance of membranes in organelles? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Understand NOTES: New 26. Which structure consists of two lipid bilayers folded together as a single membrane? a. cell wall b. cell membrane c. nuclear envelope d. ribsome e. Golgi body : c POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.5 What do eukaryotic cells have in common? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.5.1 - What is the significance of membranes in organelles? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember NOTES: New 27. A dense, irregularly shaped region within the nucleus in which subunits of ribosomes are synthesized is called the: a. plastid b. vacuole c. microvillus d. nucleolus e. basal body : d POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.5 What do eukaryotic cells have in common? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.5.2 - What are the functions of the cell nucleus in eukaryotes? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember 28. Which structures are the primary cellular sites for the production of polypeptide chains? a. Golgi bodies b. ribosomes c. mitochondria d. lysosomes e. smooth endoplasmic reticula : b POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.6 What is the endomembrane system? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.6.1 - List the main functions of the endomembrane system. KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember NOTES: Modified 29. Where are lipids that are destined for cell membranes synthesized? a. Golgi bodies b. ribosomes c. mitochondria d. lysosomes e. smooth endoplasmic reticula : e POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.6 What is the endomembrane system? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.6.4 - What is the function of the endoplasmic reticulum? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember 30. What are the primary structures for modifying and packaging of cellular secretions for export from the cell? a. Golgi bodies b. ribosomes c. mitochondria d. lysosomes e. chloroplasts : a POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.6 What is the endomembrane system? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.6.6 - What is the function of a Golgi body? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember NOTES: Modified 31. Fluid-filled sacs that may store amino acids, sugars, toxins, and ions in plant cells are called ____. a. plastids b. central vacuoles c. peroxisomes d. vesicles e. Golgi bodies : b POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.6 What is the endomembrane system? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.6.3 - What are vacuoles? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember NOTES: Modified 32. Polypeptide chains take on their tertiary structure and assemble with other polypeptide chains in which organelle? a. ribosomes b. rough endoplasmic reticulum c. smooth endoplasmic reticulum d. Golgi body e. vesicles : b POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.6 What is the endomembrane system? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.6.5 - Describe how smooth ER differs from rough ER KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember NOTES: New 33. Which organelles are sometimes referred to as rough or smooth, depending on their appearance in electron micrographs? a. Golgi bodies b. ribosomes c. mitochondria d. lysosomes e. endoplasmic reticulum : e POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.6 What is the endomembrane system? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.6.5 - Describe how smooth ER differs from rough ER KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember 34. Which cellular component’s main function is to make lipids, enzymes, and proteins for secretion to the external environment? a. nucleus b. mitochondria c. endomembrane system d. cytoskeleton e. cell membrane : c POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.6 What is the endomembrane system? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.6.1 - List the main functions of the endomembrane system. KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember NOTES: New 35. Characteristics of mitochondria include that they ____. a. have two membranes, with the outer membrane being highly folded b. are least abundant in metabolically active cells c. does not require oxygen for its functioning d. function in photosynthesis e. have their own DNA and ribosomes and divide independently of the cell : e POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.7 What do mitochondria do? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.7.1 - Why are mitochondria important for cells? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Understand NOTES: New 36. Which organelles produce ATP by aerobic respiration? a. Golgi bodies b. ribosomes c. mitochondria d. lysosomes e. endoplasmic reticula : c POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.7 What do mitochondria do? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.7.1 - Why are mitochondria important for cells? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember NOTES: Modified 37. Mitochondria convert the energy stored in _____ to usable energy for the cell. a. water b. organic compounds c. NAD d. ATP e. carbon dioxide : b POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.7 What do mitochondria do? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.7.1 - Why are mitochondria important for cells? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember 38. Nearly all eukaryotic cells have mitochondria, but the number varies by the type of cell and by the organism. In general, cells that have the highest demand for energy tend to have: a. the least mitochondria b. the most mitochondria c. slow dividing mitochondria d. larger mitochondria in lower numbers e. no mitochondria : b POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.7 What do mitochondria do? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.7.2 - Describe the structure of mitochondria. KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Understand NOTES: New 39. What are the primary cellular sites for the production of ATP? a. endoplasmic reticulum b. ribosomes c. mitochondria d. chloroplasts and mitochondria e. ribosomes and Golgi bodies : d POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.7 What do mitochondria do? Section 4.8 What are plastids? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.7 - Describe the structure and function of mitochondria. BCA.SES.4.8 - Explain the function of various types of plastids. KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember NOTES: Modified 40. What is the general term for double-membrane organelles that function in photosynthesis, storage, or pigmentation in plant and algal cells? a. chloroplasts b. chromoplasts c. amyloplasts d. plastids e. chlorophylls : d POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.8 What are plastids? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.8.1 - What are plastids? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember NOTES: New 41. Which organelles make and store pigments other than chlorophylls? a. plastids b. chloroplasts c. chromoplasts d. central vacuoles e. vesicles : c POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.8 What are plastids? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.8.4 - What are chromoplasts? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember NOTES: New 42. Short hairlike structures on the cell surface that stir fluid around stationary cells are called: a. cilia b. flagella c. intermediate filaments d. microfilaments e. pili : a POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.9 What is a cytoskeleton? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.9.5 - Describe the arrangement of microtubules in eukaryotic cilia and flagella. KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember 43. Structural features that contain the protein actin and help to strengthen and change the shapes of eukaryotic cells are known as ____. a. plastids b. vacuoles c. microvilli d. nucleoli e. microfilaments : e POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.9 What is a cytoskeleton? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.9.2 - Explain the structure and function of microfilaments. KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember 44. Before a eukaryotic cell divides, ____ assemble, separate the cell’s duplicated DNA molecules, and then disassemble. a. cilia b. flagella c. microtubules d. microfilaments e. intermediate filaments : c POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.9 What is a cytoskeleton? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.9.2 - Explain the structure and function of microfilaments. KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember NOTES: New 45. Microtubules grow from a barrel-shaped organelle called the ____, which remains below the finished array as a ____. a. cilium; motor protein b. cell cortex; centriole c. microfilament; basal body d. centriole; intermediate filament e. centriole; basal body : e POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.9 What is a cytoskeleton? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.9.5 - Describe the arrangement of microtubules in eukaryotic cilia and flagella. KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember NOTES: New 46. Plasmodesmata are ____. a. used in energy transformations within the cell b. typical of animal cells more than plant cells c. arrays of adhesion proteins that join epithelial cells and collectively prevent fluids from leaking between them d. open channels that extend across plant cell walls to connect the cytoplasm of adjacent cells e. complex mixture of extracellular cell secretions : d POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.10 What structures form on the outside of eukaryotic cells? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.10.2 - Describe the structure and composition of a plant cell wall. KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember NOTES: Modified 47. Which type of junctions prevent fluid leakage between cells? a. gap junctions b. plasmodesmata c. tight junctions d. adhering junctions e. blocking proteins : c POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.10 What structures form on the outside of eukaryotic cells? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.10.4 - What are cell junctions? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember NOTES: Modified 48. Which type of junctions involves closable channels that connect the cytoplasm of adjoining animal cells? a. gap junctions b. plasmodesmata c. tight junctions d. adhering junctions e. blocking proteins : a POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 4.10 What structures form on the outside of eukaryotic cells? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.10.5 - Describe the function of the three types of cell junctions. KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember Matching Match each membrane protein with the best description. a. recognition protein b. active transport protein c. receptor d. adhesion proteins e. enzyme REFERENCES: Section 4.3 What is a membrane? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.3 - Describe the structure and function of membranes. KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember NOTES: New 49. Initiates change in a cell activity by responding to an outside signal : c POINTS: 1 50. Identifies a cell as belonging to self : a POINTS: 1 51. Helps cells stick to one another : d POINTS: 1 52. Speeds up a specific reaction : e POINTS: 1 53. Pumps ions or molecules through membranes : b POINTS: 1 The following items are organelles found in animal cells. the question(s) with reference to these organelles. a. ribosomes b. mitochondria c. lysosomes d. Golgi bodies e. endoplasmic reticulum REFERENCES: Section 4.6 What is the endomembrane system? Section 4.7 What do mitochondria do? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.4.6 - Describe the components of the endomembrane system. BCA.SES.4.7 - Describe the structure and function of mitochondria. KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember OTHER: Classification Questions 54. The packaging of secretory proteins usually occurs in association with this structure. : d POINTS: 1 55. This organelle is involved in lipid production and protein transport. : e POINTS: 1 56. DNA synthesis occurs in the nucleus. Its breakdown can occur in this organelle. : c POINTS: 1 57. These are the structures upon which proteins are assembled. : a POINTS: 1 58. The cellular digestion and disposal of biological molecules occurs inside this organelle. : c POINTS: 1 59. Ribosomes are often found on the surface of this organelle. 60. Aerobic respiration occurs in this organelle. 61. Sugar metabolism occurs in association with this organelle. Match the endomembrane system components with the best description. a. vesicles b. lysosomes c. peroxisomes d. vacuoles 62. Take part in intracellular digestion : b POINTS: 1 63. Break down fatty acids, amino acids, and poisons such as alcohol : c POINTS: 1 64. Any small, membrane enclosed sac : a POINTS: 1 65. Forms by the fusion of multiple vesicles : d POINTS: 1 Subjective Short 66. What term describes the characteristic of a plasma membrane that allows only certain materials to cross? 67. Explain how the term “fluid mosaic” describes the plasma membrane. 68. Nuclear pores function as gateways for molecules to enter and exit a nucleus. Protein synthesis offers an example of why this movement is important. Explain. 69. Why is the nuclear envelope important? 70. What is the difference between a primary and secondary cell wall in plants? 71. What measures can the average citizen take to reduce the likelihood of infection with E. coli or other foodborne organisms? Figure 4.8 Generalized body plan of a prokaryote. 72. What are the three cell coverings present in this generalized body plan of a prokaryote? Provide a brief description of each. 73. Figure 4.24 Typical plant cell components. 1. ____ the cell wall. 2. ____ a major storage organelle of the cell. 3. ____ the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). 4. ____ the organelle that converts light energy to ATP energy. 5. ____ the mitochondrion. 74. Figure 4.24 Typical animal cell components. 1. ____ organelle that converts food energy to ATP energy 2. ____ organelle on which the ribosomes serve as sites for protein (polypeptide) assembly 3. ____ organelle where proteins and lipids are modified and packaged for export 4. ____ area where RNA is synthesized 5. ____ selectively controls the entry and exit of materials from the cell Essay 75. What limits cell size? 76. How do plants form primary cell walls? 77. How do biologists define “life”? [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 22 pages
Instant download

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Nov 08, 2019
Number of pages
22
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Nov 08, 2019
Downloads
0
Views
78














 answers.png)


.png)