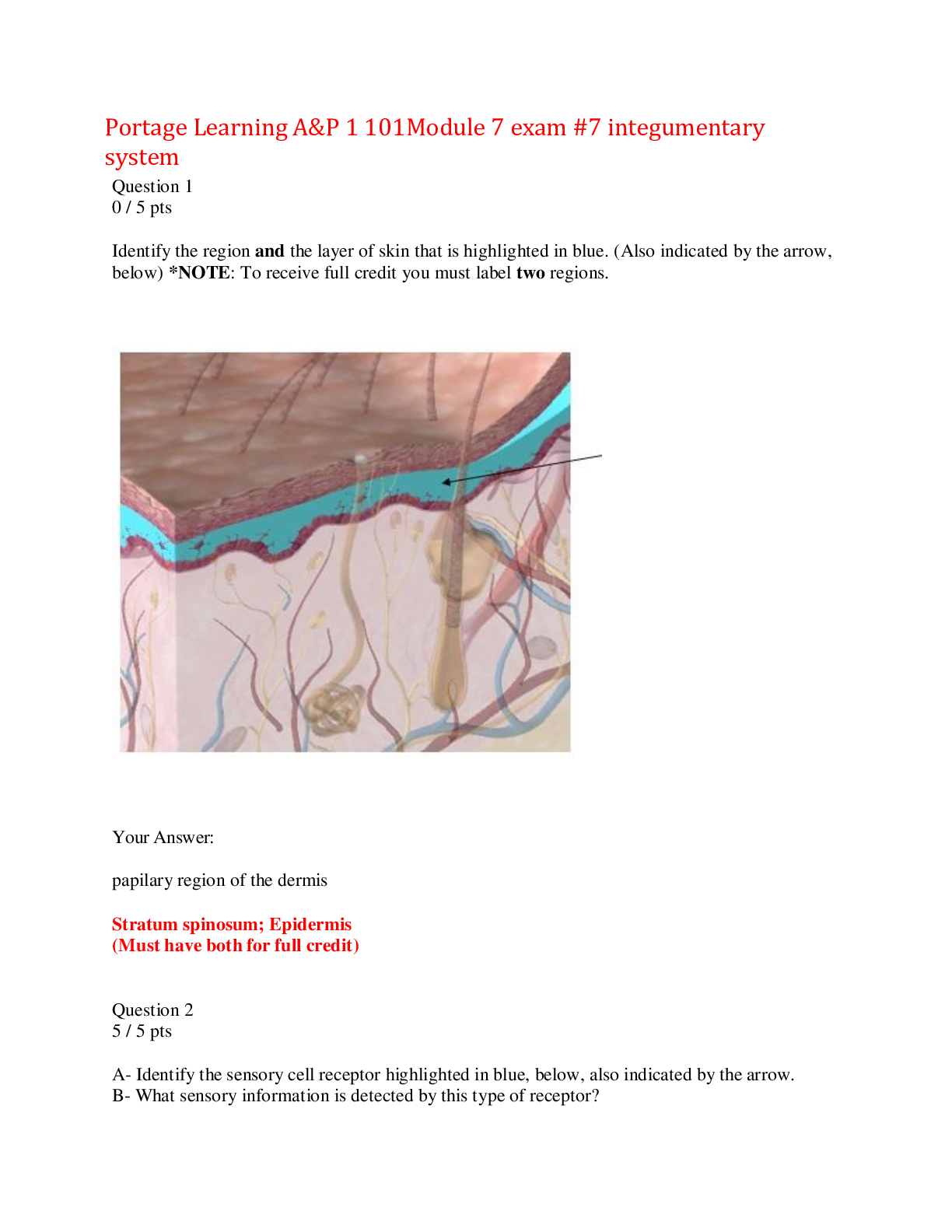
*NURSING > EXAM > Rasmussen College :NUR MISCMDC4 exam 1 review 1_LATEST 2021/2022,100% CORRECT (All)
Rasmussen College :NUR MISCMDC4 exam 1 review 1_LATEST 2021/2022,100% CORRECT
Document Content and Description Below
Rasmussen College :NUR MISCMDC4 exam 1 review 1_LATEST 2021/2022 • What is the most common type of dementia? - Alzheimer's disease • Is Alzheimer's reversible? - No • What is the etiology ... of Alzheimer's? - Unknown • Alzheimer's is the result of? - changes in personality, memory, and/or judgement • What are risk factors for Alzheimer's? - 65+ years * female * head injury * APOE gene • what is the patho of Alzheimer's - plaques, tangles, degeneration of neurons • How is Alzheimer's diagnosed? - biopsy at autopsy is the only definitive way but dementia can be ruled out with CT, labs, UA, and MRI • Early s/s of Alzheimer's Disease - decreased short term memory - decreased sense of smell - misplaced items • Middle s/s of Alzheimer's Disease - wander - agitated - incontinent - money issues • late s/s of Alzheimer's disease - bed ridden - agnosia (inability to recognize objects, people, or sounds) • Medications used for Alzheimer's - Cholinesterase inhibitors - slow breakdown of Ach - Donepezil and Rivastigimine - NMDA receptor antagonists - block excess amounts of glutamate - Memantine • Nursing care for Alzheimer's - safe environment (#1) good lighting, no clutter - stick with a routine - offer walks, exercise - reduce distractions - avoid use of restraints • What is Parkinson's Disease - Movement disorder caused by the death of cells that generate dopamine in the basal ganglia and substantial nigra. Low levels of dopamine and high levels of Ach • How does Parkinson's progress? - slowly, but will eventually lead to disability • How is parkinson's diagnosed - history and s/s • s/s of parkinsons - tremors - muscle rigidity - mak like facial expression - bradykinesia - shuffling gait - cogwheel rigidity in limbs - propulsive gait (head and neck forward, back is slouched) • nursing care for parkinson's - safe environment - sit up when eating, thick liquids - encourage ROM and exercise • Medication for Parkinson's - Sinemet - Levodopa (increases dopamine levels in CNS) and Carbidopa (prevents levodpa breakdown) - take at same time every day - know that increased protein can alter effectiveness - Benztropine - decreases Ach levels • What are headaches? - vasodilation of blood vessels in the brain • What causes headaches - genetics, stress, hormones • What can trigger a headache? - coffee, yogurt, alcohol, MSG, marinated foods • s/s of headache - head pain for 4-72 hours, N/V, unilateral pain, may come with aura • what are cluster headaches? - happen at night, stuffy nose • treatment of headache - Prophylactic = propranolol ▪ Mild = NSAID ▪ Severe = sumatriptan - ergotamine tartrate - 6 tabs in 1 day - take as soon as pain starts - MOA = constricts cerebral blood vessels • What is increased ICP made of? - CSF, blood, brain • what causes increased ICP - infection, trauma, increased CSF, hemorrhage, tumors • s/s of increased ICP - MIND CRUSH M: mental status change (early sign) = decreased LOC, irritable, confusion I: irregular breathing (late sighn) = Cheyene Stokes N: nerve damage to eye = pupil changes D: decerebrate (limbs out) and decorticate (limbs to core) posturing C: cushing's triad (late) = HTN + brady + wide pule pressure R: reflux - N/V U: unconscious S: seizures H: headaches • Nursing care for Increased ICP - PRESS P: position HOB @ 30 degrees and make sure body's midline (no flexion of neck or hips) R: respiratory we want to prevent hypercapnia by hyperventilating (limit suctioning) E: elevated temp - prevent it! S: system checks = neuro checks S: straining things - avoid it (no lifting, blowing nose, cough/sneeze) • Additional Nursing care measures for ICP - turn down the lights - no TV or noise - put sign on door telling visitors to see nurse first • What do you NOT do when someone has increased ICP? - Lumbar Puncture • What is the Glasgow Coma Scale? - A brain injury severity scale that assesses depth and duration of impaired consciousness and coma. • what 3 areas make up the Glasgow coma scale? - eyes score 1-4 - verbal score 1-5 - motor score 1-6 Total score 3-15 **lower the score = more severe injury/status • Eyes for Glasgow Coma Scale - ESPN E - eyes open spontaneously (4) S - sound (3) P - pain (2) N - not open (1) • Verbal for Glasgow coma scale - Our Country WIN O: oriented (5) C: confusion (4) W: words are inappropriate (3) I: incomprehensible sounds (2) N: nothing (1) • Motor for Glasgow coma scale - Can't Live Without FANs C: commands followed (6) L: localize to pain (5) W: withdrawal from pain (4) F: flexion - decorticate posturing (3) A: abnormal extension-decerebrate (2) N: nothing (1) • what are seizure - abnormal and increase in firing of neurons • what is epilepsy - chronic seizures • what triggers seizures - stress, fatigue, coffee • what are risk factors for seizures - infection, trauma, fever, withdrawal, imbalances • How do you diagnose siezures - EEG (wash hair prior) • Seizure Precautions - padded bed rails - O2 and suction at bedside - IV access - lowest bed setting • Types of siezures - absence, atonic, tonic clonic, status epilepticus • Absence Seizures - day dreaming - LOC for a few seconds - s/s = pick at clothes, lip smack, blank stare • Atonic Seizures - loss of muscle tone - fall • Tonic Clonic seizure - tonic = stiffening - clonic = rhythmic jerking - postictal phase = coming back to - confused/sleepy • Status Epilepticus - medical emergency! - 1 seizure that lasts > 5 mins - repeat of seizure w/in 30 min • nursing care during siezure - turn patient on left side (#1) - loosen restrictive clothing - note onset and duration - do NOT insert anything by mouth • Nursing care after seizure - take vitals - perform neuro checks - determine what trigger was - maintain left lying position • Treatment of seizures - Phenytoin - narrow range (10-20), s/s= gingival hyperplasia Valproic acid - s/s = hepatotoxic Carbamazepine - can cause a rash (Steven Johnson syndrome) • Education for Seizures and Seizure treatment - medication compliance (abrupt withdrawal = rebound seizures) - do not drive - wear medical alert bracelet • surgical treatment of seizure - vagal nerve stimulator - craniotomy • What is encephalitis? - infection & inflammation of the brain tissue ***life threatening • How is encephalitis diagnosed? - CSF analysis or EEG • What are the s/s of encephalitis? - stiff neck, n/v, fever • What can encephalitis increase risk of? - increased ICP • Nursing care for encephalitis - turn down lights and noise - keep midline and HOB @ 30 degrees - avoid straining activities • What is meningitis - inflammation of meninges (around brain and spinal cord) • what are the two main types of meningitis - viral - more common - bacterial - cause is step • Prevention of meningitis - vaccination - Hib for baby - MCV4 for teens • Diagnosis of meningitis - CSF analysis • What does CSF analysis look like for viral meningitis? - clear, increased wbc and protein • what does CSF analysis look like for bacterial meningitis - cloudy, decreased glucose, increased wbc, and protein • s/s of meningitis - nuchal rigidity, n/v, photophobia, Brudzinski's sign, Kernig's sign • What is Brudzinski's sign? - After forced flexion of the neck there is a reflex flexion of the hip and knee and abduction of the leg. • What is Kernig's sign? - After flexing the hip and knee at 90 degree angles, pain and resistance are noted. • Nursing care for Meningitis - bacterial = antibiotics - viral = acyclovir - steroids (decrease inflammation, increased infection) - prophylaxis treatment for anyone in contact/exposed - implement droplet precautions for first 24 hours of treatment - Decrease ICP risk by elevating HOB, keep body midline, avoid straining activities, turn everything down • What is MS? - Autoimmune disease with chronic inflammation and no cure; just periods of relapse and remition • what is patho of MS - body attacking its own myelin sheath • what causes MS - genetic, autoimmune, infection • what are risk factors of MS - female, white, 20-50 y/o • diagnosis of MS - no 100% way - MRI - CSF analysis (increased WBC, proteins, IgG) • S/S of MS - muscle weakness - intention tremors - tinnitus - vision (diplopia, nystagmus) • Nursing care for MS - protect from injury - allow for periods of rest - help manage stress b/c this can lead to relapse/remit • Meds for MS Immunomodulators, immunosuppressants (decreased inflammation, increase infection) - muscle relaxant = baclofen • what is Autonomic dysreflexia - Firing of SNS with no PNS response • what injury causes autonomic dysreflexia? - injury above T6 • what causes autonomic dysreflexia? - bowel, bladder, breakdown of skin • s/s of autonomic dysreflexia - severe htn - bradycardia - headache - diaphoresis - blurry vision - facial flush above injury - pale below injury • nursing care for autonomic dysreflexia - Prevent: - bladder distention (empy it, check tubing for kinks, use bladder scanner) - bowel - check for impactation - skin breakdown - remove tight clothing Detect: at risk above T6 injury, report of headache, check BP Action: elevate HOB, Remove restrictive clothing, schedule bowel and bladder maintenance • What is true for spinal cord injury - the higher the injury, the more system affected and shorter the lifespan • diagnosis of spinal cord injury - X-ray, CT scan, MRI • prevention of spinal cord injury - stop drugs and alcohol • causes of spinal cord injury - traumatic: falls, MVA, violence Non-traumatic: tumors, RA Direct: fracture, hyperflexion (diving), hyperextension, penetration (GSW), axial load • types of spinal cord injuries - Complete: complete severed spinal cord, complete loss of function below injury Incomplete: spinal cord is partially severed, partial loss of function Quadriplegia - at C6 - Unable to move all 4 extremeties - MVA, fall Paraplegia - below T1, paralysis of lower extremities, can be result of GSW • what is the main cause of death for people with spinal cord injuries - sepsis, pneumonia, PE • Acute management of spinal cord injury - airway and breathing - immobilize head and neck (c-collar) - determine LOC by using GCS • Medications for spinal cord injuries - corticosteroid = methylprednisolone - first given as IV bolus - then IV continuous drip for 24 hours - needs to be given w/in 8 hrs of injury -s/s hyperglycemia, poor wound healing, infection - education: increae Ca intake, ROM, deep breathing • what is the number 1 thing to keep in mind with a spinal cord injury? - AIRWAY and BREATHING • Complications of Spinal cord injury - autonomic dysreflexia - neurogenic shock (hypo, bready, edema, temp) • what is a stroke? - alteration in blood flow to the brain • TIA - transient ischemic attack = mini stroke, warning sign • diagnosis of stroke - CT without contrast • Etiology of stroke - nonmodifiable = age, sex, history - modifiable = HTN, BC user, high cholesterol, smoker • s/s of stroke - FAST facial droop, arm drift, speech is slurred, time how much as passed • General Left vs Right side stroke - Left = language Right = impulse & judgement • Left-sided stroke s/s - receptive aphasia (unable to verbally communicate back) - right sided hemiparesis (weakness) - agraphia (unable to right) - Aware of their deficits - anxiety and depression • Right-sided stroke s/s - poor impulse control and judgement - 1 sided neglect syndrome (unaware of deficits on left side of body, big safety concern) - short attention span - proprioception (depth) issues • Broca's area - expressive aphasia: unable to communicate/express back in speech • Wernikies aphasia - receptive aphasia: unable to receive/understand what is being said • nursing care for both broca's and wernikies - be patient - use short phrases - use gestures/point - limit distractions around • Treatment of stroke - General - anticoagulants, stool softeners, benzo's Ischemic stroke aka clot - tPa = thrombolytics (must be w/in 3 hours, BP needs to be in range, neuro checks every 15 mins. NOT for bleeding, htn, >3hrs Hemorrhagic stroke - only treatment is surgery (BP must be in range, NOT for someone on blood thinners (coumadin), if blood is too thin, admin fresh plasma or Vit K) • Nursing care for stroke - safe environment (teach patient to scan before ambulating) - lots of eating concerns: - sit up - tuck chin - thick liquids - use dentures - no straws - take small bites - use mechanical soft diet Complications of stroke: increased ICP, seizures, HTN, headach • Who is at risk for TBI - infants, teens, older adults • how does TBI occur - falls, mva, gsw, sports • levels of tbi - mild - concussion moderate - decreased loc severe - prolonged LOC • types of TBI - subdural hematoma - bleeding below dura and above arachnoid - primary: open (directly to brain) closed (fracture) - secondary - result of primary • Nursing care for TBI - #1 determine what caused injury - monitor LOC by GCS - watch for CSF - clear drainage, shows halo with test - wiping = ok - blowing/inserting = NO - prevent increased ICP • Complications of ICP - hydrocephalus, infection, stroke, increased ICP • meds for icp - antiseizure, mannitol, corticosteroids [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 15 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$14.00
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Feb 16, 2022
Number of pages
15
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Feb 16, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
29