Pharmacology > EXAM > NR-293 Week 2 Quiz 1 (GRADED A) Question/Answers elaborations plus Rationales | 100% correct solutio (All)
NR-293 Week 2 Quiz 1 (GRADED A) Question/Answers elaborations plus Rationales | 100% correct solution
Document Content and Description Below
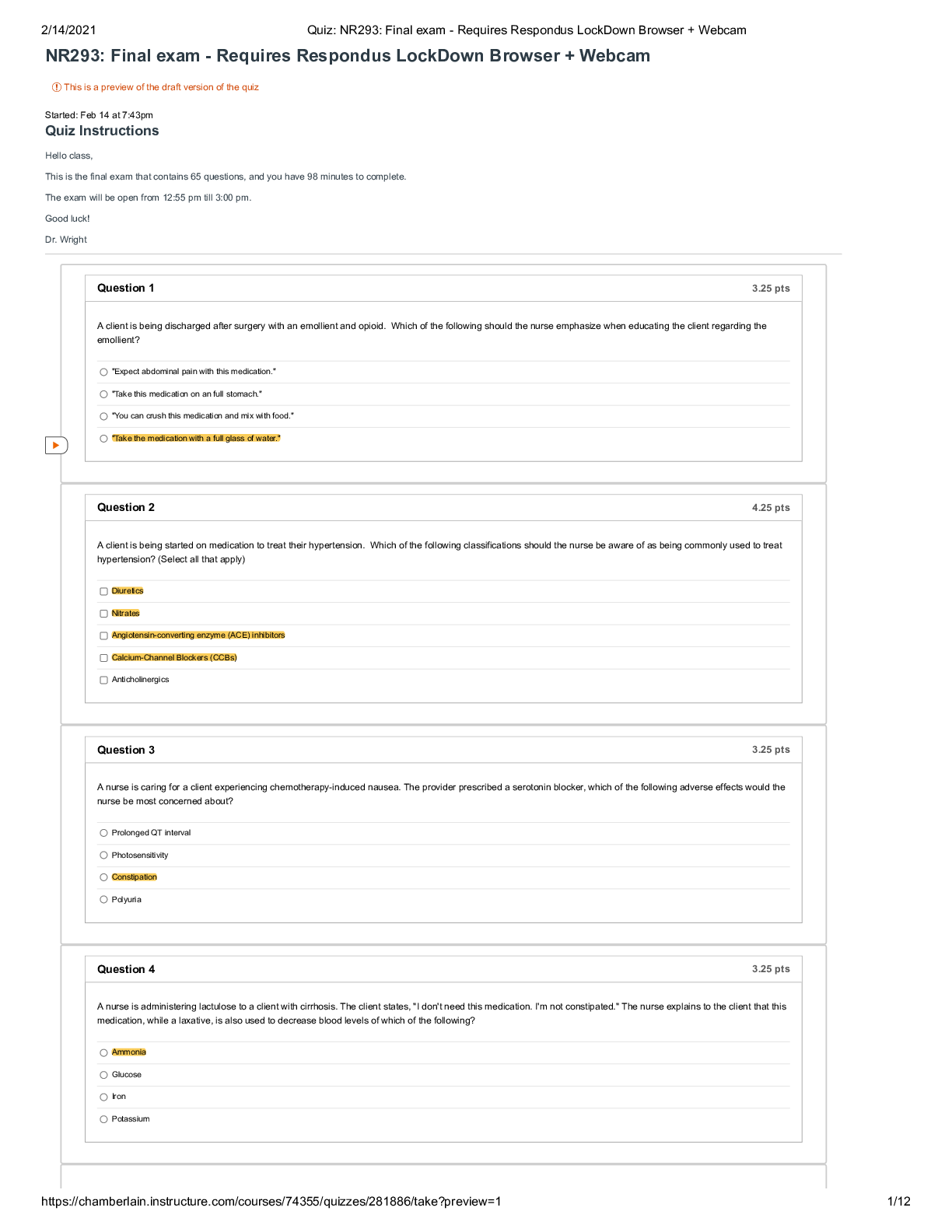
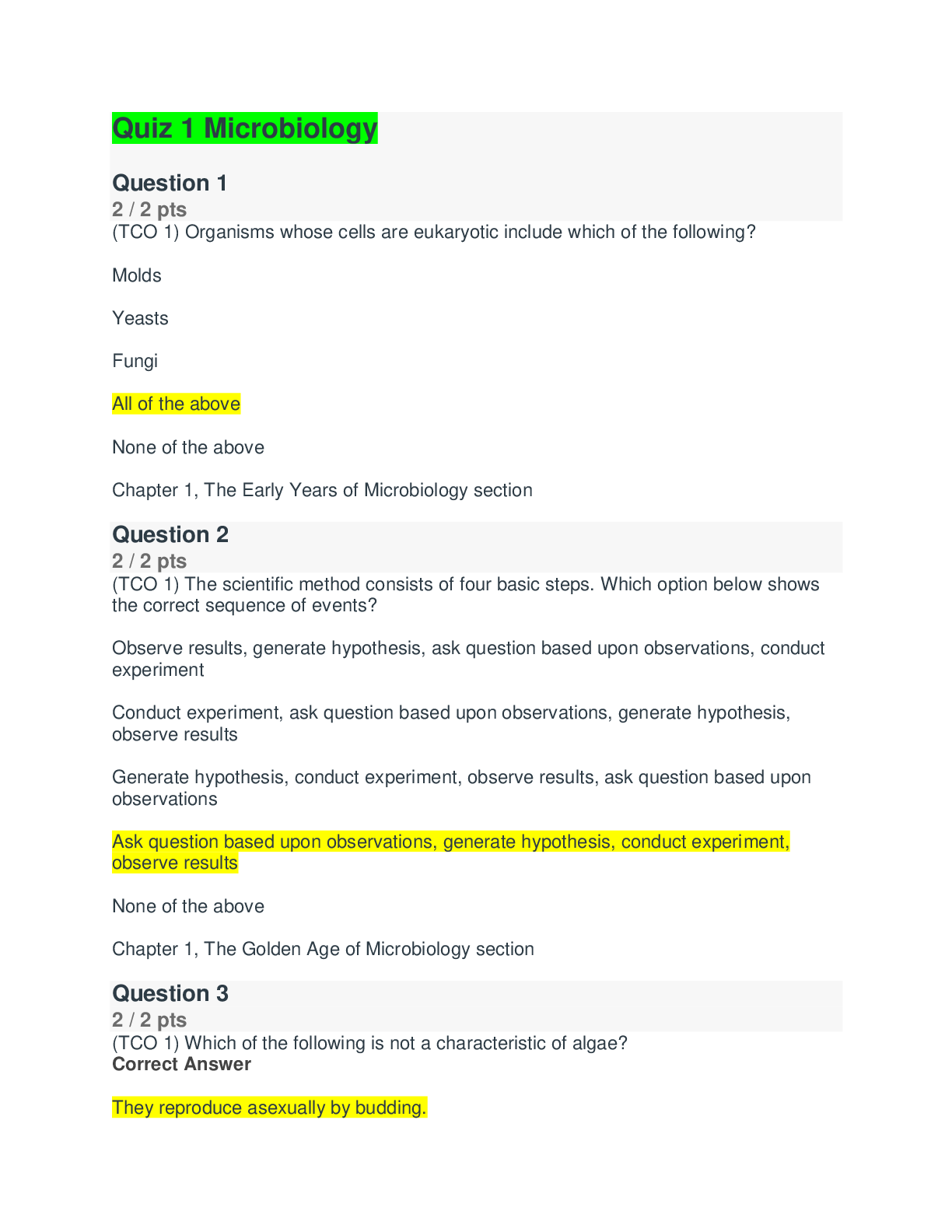
NR-293 Week 2 Quiz 1 – Question/Answers NR293 Pharmacology Pre-class Questions Week 1 Answer the following questions. Give rationales for each question asked and include the reference and page ... number where the answer was found. Rationales (include chapter and page no of where you found the answer.) should be TYPED. Upload test questions and rationales to the submission tab under the course shell. The assignment must be completed on the provided document. No other forms will be accepted. Questions will be graded for accuracy. Each question along with the rationale will be worth 0.5 points, for a total of 20 points possible. The assignment is due Sunday Jan 12, 2020 at 11:59 pm. No late submissions will be accepted. Late submissions will result in zero points for the assignment, no exceptions. 1. Which actions will the nurse document if an incorrect dosage of medication is administered to a patient? Select all that apply. a. The reason the mistake was made b. The route of the medication delivered c. That an incident report was completed d. The patient’s response to the medication e. The time, message, and response of the provider Rationale: The route of the medication should also be included to let others know all the information present regarding the medication for future dosages. The patient’s response is also a key factor when giving a wrong dosage. With a higher dosage, the patient can possibly have a reaction or an overdose if not given the correct dosage. The time, message, and response of the provider should also be documented to show that a provider was notified and to see the chain of communication and other further instructions. Chapter 1 page 65-68 2. Which statement reflects understanding of the nursing action to take when medication is refused? a. "Contact the family immediately." b. "Document the reason for refusal." c. "Force the patient to take the medication." d. "Return unwrapped medication to the container." Rationale: When a medication is refused by a patient, a nurse cannot force the patient to take the medication. The nurse must document the reason to let other medical personal know the reason for the refusal. Chapter 1 page 9 3. A prescription is written "Diltiazem 30 mg orally three times daily at 0700, 1300, and 1900." The nurse misreads the prescription and administers the drug at 1000. Which is the best nursing action before administration of the next dose? a. Consult the peer group. b. Calculate the next dose time. c. Calculate the dose accordingly. d. Consult the health care provider. Rationale: If a medication is administered at the wrong time, the first step is to notify the provider to provide any changes for future dosages. Chapter 1 page 7,8 4. The nurse reviews a chart and suspects a medication order is written incorrectly. Which is the nurse’s best action? a. Call the pharmacy. b. Administer the medication as written. c. Call the health care provider. d. Discuss the issue with the nurse manager. Rationale: When a medication order is written incorrectly, the nurse must first verify the medication with the ordering physician to clarify and prescribe the correct medication. Chapter 1 page 5-8 5. The nurse is to administer a medication at 0730 that is prescribed three times a day. Which times are acceptable for administration of the drug? Select all that apply. a. 0600 e. 0900 Rationale: Medication should be given no more than half an hour before or after the designated time. Chapter 1 page 7 6. Which symptom is an example of an allergic reaction? a. Hives b. Dry eyes c. Constipation d. Frequent urination Rationale: Patients that have allergic reactions tend to have hives, wheezing, tachycardia, or hypotension. Chapter 36 page 562 7. The nurse administers a drug to a patient that has a half-life of 6 hours. If the dose of the drug is 200 mg/L, what would be the concentration of the drug after 12 hours? Record your answer using a whole number. mg/L 50 mg/L, the time it takes for the body to eliminate 50% of the drug 1 half-life (6 hours) is 100 mg/L 12 hours is 2 half-lives is 50 mg/L Chapter 2 page 25 8. A patient is given a drug that has a half-life of 8 hours. The peak level of this drug is 100 mg/L. What would be the concentration of the drug after two half-lives? Record your answer using a whole number. mg/L 25 mg/L, the time it takes for the body to eliminate 50% of the drug 1 half-life (8 hours) is 50 mg/L 16 hours is 2 half-lives is 25 mg/L Chapter 2 page 25 9. A swab of a wound infection is sent for culture and, pending culture results, the health care provider starts an intravenous antibiotic. Which type of therapy has been prescribed for this patient? a. Empiric b. Palliative c. Prophylactic d. Maintenance Rationale: Empiric therapy is caused by an apparent infection before specific culture information has been obtained. Chapter 38 page 586 10. Which type of therapy has been prescribed when a patient is prescribed an oral antidiabetic drug? a. Acute b. Palliative c. Maintenance d. Supplemental Rationale: Maintenance Therapy is to help maintain the patient in a stable state of a disease or a condition however this may not cure the disease. Chapter 2 page 27 11. Which action, when performed by the nurse, will increase the absorption of a medication administered intramuscularly? a. Massaging the site after injection b. Applying cold packs to the injection site c. Lowering the extremity below the level of the heart d. Administering the medication via the Z-track method Rationale: Massaging the site after performing an intramuscular injection helps increase the rate of the absorption because it helps move the solution through the muscle. Chapter 2 page 19 12. To achieve the most rapid onset of action, the health care provider would prescribe medication to be administered by which route? a. Intrathecally b. Intravenously c. Subcutaneously d. Intramuscularly Rationale: Intravenous is the most rapid onset of action because it goes directly into the blood stream to work as fast as possible. Chapter 2 page 19 13. Which category of drugs is contraindicated in pregnancy according to the five-category system that will be phased out? a. Category A b. Category C c. Category D d. Category X Rationale: Category X deals with fetal abnormalities have been reported and positive evidence of fetal risk in humans is available. Should not be taken by pregnant woman. Chapter 3 page 34 14. The nurse will administer medication to a child with an ordered dose of 2 mg/kg of body weight. The child weighs 10 pounds. What is the appropriate dose for this child? Record your answer using a whole number. mg. 9 mg 2mg x 1kg x 10 lbs 1kg x 2.2 lbs Chapter 1 page 7- right dose 15. Which actions will the nurse perform to ensure that the medication dose for a pediatric patient is correct? Select all that apply. a. Determine the safe range. b. Use the patient’s weight in pounds. c. Determine the usual dosage per 24 hours. d. Determine the amount of drug to administer per dose and per day. e. Compare the drug dosage prescribed with the calculated safe range. f. If the drug dosage prescribed varies from the recommended reference range, notify the provider. Rationale: When verifying the medication dosage for a pediatric patient, the nurse must make sure that the medication dosage is in the safe range at the current time and during 24 hours per day. The nurse must also compare the prescribed dosage to the prescribed and safe dosage however, if the dosage is not in the recommended reference range, the nurse must notify the provider to see if there should be changes in the medication or medication dosage. Chapter 1 Page 5- 9, nine rights 16. What category of drugs in the five-category system is reported to have fetal risks but can be used in a pregnant woman if the potential benefit outweighs the risk? a. Category B b. Category C c. Category D d. Category X Rationale: Category D drugs do cause possible fetal risks in humans however in certain cases the medication in necessary and the potential benefit override the negatives. Chapter 3 page 34 17. What will a nurse need to know about differences in drug distribution in neonates compared with drug distribution in adults? Select all that apply. a. Neonates have increased body fat. b. Neonates have reduced protein synthesis. c. Neonates have an immature blood–brain barrier. d. Neonates have total body water of 85% if full term. e. Neonates have total body water of 70% if premature. Rationale: Protein binding decreases because the liver is not mature yet. The neonate’s blood brain barrier is not fully developed yet which lets more drugs pass through. Chapter 3 page 39 18. The primary health care provider has ordered acetaminophen for a child who has fever at a dose of 10 mg/kg body weight every 6 hours. What is the total dose that may be administered over 24 hours if the child weighs 15 kg? Record your answer using a whole number. mg 600 mg 10mg x 15kg x 1 x 24hrs = 600 mg 1kg x 1 x 6hrs x 1 19. After finishing a stressful day at work the nurse logs on to a social media website and discusses the day, including the patients at the clinic. Which legal or ethical principle does this violate? a. Veracity b. Autonomy c. Confidentiality d. Nonmaleficence Rationale: Breaking confidentiality is when the nurse does not respect the patient’s privacy and discusses the patient’s personal information in public. Chapter 4 page 56 20. The nurse is responsible for dispensing medications and notes that diazepam is a C-IV drug. Which information can the nurse interpret from this? Select all that apply. a. The drug container must have a warning label. b. The prescription can be refilled for only a year. c. The drug is dispensed via an approved protocol. Rationale: Category 4 drugs must be written or oral prescription that expires in 6 months. There can also be no more than 5 refills in a 6-month period and the medication container must have a warning label. The drugs are also considered controlled substances because they are regulated by the government and laws. Chapter 4 page 54 21. Which finding is correct for a drug classified as C-II? a. The drug is unacceptable for medical use. b. The drug may have moderate potential for abuse. c. The drug may cause limited physical dependency. d. The drug may cause severe psychological dependency. Rationale: Category 2 drugs may cause a severe physical and psychological dependency. Chapter 4 page 54 22. Which statement best reflects the nurse’s understanding of cultural influences on drug therapy and other health practices? a. Dietary habits and practices can be of little value to the care of an ill adult. b. Most cultures are fairly standard in reference to the use of medications during illness. c. Administration of some drugs may elicit varied responses in specific racial- ethnic groups. d. Regardless of one’s cultural background, it is important to always adhere to recommended medical practices. Rationale: Understanding a patient’s culture is very important when providing drug therapy because the patient can have certain reactions and responses depending on the culture. Chapter 4 page 48 23. A nurse is documenting the history of a patient and the patient states that she does not take any medications, but the nurse notes a bottle of capsules in the patient’s purse. Which information will the nurse collect next? a. Vital signs b. Insurance information c. Primary care provider name d. Use of herbs or over-the-counter medications Rationale: Some patient’s believe that if a doctor does not prescribe a medication then they are not taking any regardless if they are purchasing over the counter medications. Even medications that the patient can get freely, can influence how the patient is feeling or can cause a reaction with other possible medications prescribed. Chapter 7 page 85 24. Which information would the nurse document when completing an incident report for a medication error? Select all that apply. a. Any follow-up actions b. Dose of the medication given c. Patient response to the medication error d. The suspected reason the error occurred e. The time the health care provider was notified Rationale: When completing an incident, the medical personal should only include factual information about the error and the corrective actions taken. Factual information includes dosage of the medication given, and the patient’s response to the medication error. Follow up actions and including the time the health care provider was notified are part of the corrective actions taken. Chapter 5 page 67 25. When preparing to administer scheduled 0900 medications, a patient states, "I already took my blood pressure medicine this morning." Which is the priority action by the nurse? a. Do not administer the medication. b. Assess the patient’s blood pressure. c. Inform the patient that the blood pressure medication is only given at 0900. d. Contact the night shift nurse to determine if the medication was previously given. Rationale: Before the medication can be administered the nurse must verify the information that the patient is saying. Priority action is to contact the previous night nurse and determine if the medication was given at the earlier time. Chapter 1 page 7 26. Which action would the nurse implement first in response to an incorrect dose of insulin to a patient given by a colleague? a. Assess the patient. b. Notify the nurse manager. c. Instruct the nurse to complete an incident report. d. Report the medication error to the health care provider. Rationale: The first priority is to assess the patient to verify any urgent safety issues. Chapter 5 Page 72 27. Which is the most appropriate question for the nurse to ask a newly admitted patient when verifying medications taken at home? a. "Do you take any medication for high blood pressure?" b. "What medications did you take with your last hospitalization?" c. "Can you tell me which prescribed medications you are taking?" d. "Can you have someone bring in all of your medications from home?" Rationale: When comparing medications to what the patient is taking and what is on the MAR, the best way to find out what the patient is truly taking is by asking them strictly what they are taking. Since some patient are not compliant they could be prescribed something by a physician but do not actually take the medication due to whatever reason. Chapter 5 page 72 28. A patient developing a topical rash after taking a medication is an example of which type of response? a. Error b. Allergic c. Near miss d. Idiosyncratic Rationale: Various medications can cause an allergic reaction such as a rash. Chapter 5 page 70 29. The nurse asks a patient to provide a list of all medications that the patient is currently taking, including herbal and over-the-counter drugs. Which term describes the nurse's action? a. Error reporting b. Notifying the patient c. Quality improvement d. Medication reconciliation Rationale: When communicating with the patient regarding a full list of medications which includes the herbal and over the counter drugs is called medication reconciliation. Chapter 5 page 70 30. The nurse is caring for an older adult. The patient tells the nurse, "I cannot take this medication because this tablet is a different color from the tablets at home." Which action is most appropriate? a. Verify the patient’s prescription. b. Suggest that the patient take the medication. c. Inform the patient that a new medication is prescribed. d. Notify the health care provider to change the medication. Rationale: If a patient makes this statement, the nurse must verify the patient’s prescription to verify that the correct medication is given to the patient. Chapter 5 page 71 31. When planning care for an assigned patient, the nurse identifies the outcome of "Patient will be able to safely self-administer enoxaparin subcutaneously upon discharge." Which method evaluates the patient’s achievement of this outcome? a. Visually demonstrate the correct procedure to the patient. b. Have the patient verbalize the correct procedure step by step. c. Have the patient perform a return demonstration of the procedure. d. Give the patient detailed written instructions illustrating the procedure. Rationale: When evaluating the patient’s progress in the nursing process, having the patient do a return demonstration helps show the nurse that the patient has an understanding at the task at hand. Chapter 3 page 47 32. The nurse is providing medication education to a non-English-speaking patient. Which resources would assist with translation in this situation? Select all that apply. a. A certified translator b. Computer-/web-based translator system c. A family member who does speak English d. A layperson versed in the person’s language e. Another health care provider who speaks the language Rationale: When communicating with a non-English speaking patient a certified translator or another health care provider that speaks the patient’s native language to help explain medical information. Chapter 6 page 78 33. Which would the nurse include in the teaching about the safe administration of drugs? a. Reinforcement b. Self-care ability c. Emotional status d. Drug-food interaction Rationale: The patient must know about any reactions that can be caused between various foods and medications and which to avoid. Chapter 6 page 82 34. Which is the time to begin patient education and the teaching-learning process? a. At the time discharge planning is begun b. Once the medical diagnosis is established c. When there are written orders for teaching d. Upon the patient’s admission to the health care setting Rationale: Once the patient comes into the hospital, patient teaching starts to ensure that the patient has all the information by the time that they leave. Chapter 6 page 81 35. Which information about the risk of over-the-counter (OTC) medications for cough and cold would the nurse include in patient teaching? a. Expensive b. Rarely work c. Interact with many prescription drugs d. Work just as well as prescription drugs Rationale: A patient should be educated about the reaction between over the counter drugs and other prescription drugs in order to avoid any side effects or adverse effects. Chapter 7 page 86 36. Which herb or dietary supplement would the nurse teach a patient in acute renal failure to avoid? a. Kava b. Garlic c. Cranberry d. Saw palmetto Rationale: Patient teachings regarding acute renal failure should include to avoid cranberries because it decreases the reaction of medications related to the kidneys. Chapter 7 page 89 37. Which criteria must be present for a medication to be allowed as over-the-counter? Select all that apply. a. Low therapeutic index b. Drug must be easy to use c. Low potential for drug abuse d. Minimal interactions with other drugs e. Consumer must have a medical diagnosis Rationale: Characteristics of over counter drugs must be easy to use, low potential for drug abuse, and minimal interactions with other drugs. Chapter 7 page 85 38. A patient is prescribed an antiplatelet medication. Which herbal supplement would the nurse warn the patient to avoid? a. Ginkgo b. Valerian c. Hawthorn d. Evening primrose Rationale: Patient should not take Ginkgo with any antiplatelet medication in order to avoid any reactions and increase bleeding. Chapter 7 Page 89 39. Which herbal supplement should patients avoid when taking a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) for depression? a. Kava b. Valerian c. Echinacea d. St. John’s wort Rationale: St John’s wort could lead to serotonin syndrome if used with other serotonigentic drug. Chapter 7 page 89 40. Which medications are the most commonly used over-the-counter (OTC) products? Select all that apply. a. Analgesics b. Antidepressants c. Antihypertensives Rationale: The most common over the counter medications include analgesics, histamine blockers, and topical medications. Chapter 7 page 86 [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 12 pages
Instant download

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 17, 2022
Number of pages
12
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 17, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
143






.png)











 – South University Savannah.png)
 - Prescription (102 Questions) – South University Savannah.png)
 _ Dermatology Prescription (100 Questions and Answers) – South University Savannah.png)
 Assessment question of Endocrinology (48 Questions) – South University Savannah.png)
 Dermatology (64 questions and answers) – South University Savannah.png)
 Prescription Gastroenterology (85 Questions) – South University Savannah.png)

