*NURSING > NCLEX-RN > NCLEX PRACTICE QUESTIONS » URINARY DISORDERS NCLEX PRACTICE QUIZ #2 (50 QUESTIONS UPDATED ON MARCH (All)
NCLEX PRACTICE QUESTIONS » URINARY DISORDERS NCLEX PRACTICE QUIZ #2 (50 QUESTIONS UPDATED ON MARCH 19, 2022 BSN, R.N)
Document Content and Description Below
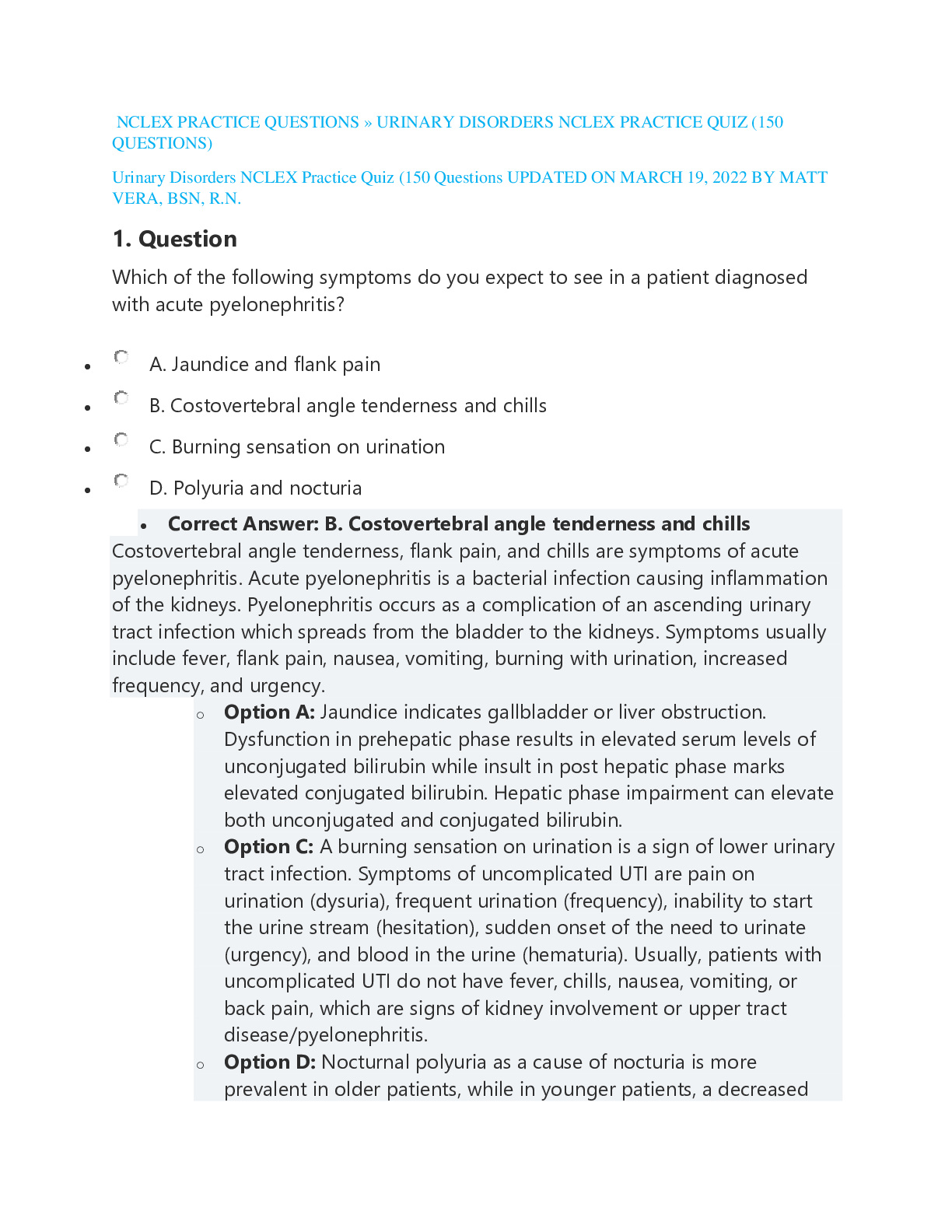
NCLEX PRACTICE QUESTIONS » URINARY DISORDERS NCLEX PRACTICE QUIZ #2 (50 QUESTIONS UPDATED ON MARCH 19, 2022 BSN, R.N) Urinary Disorders NCLEX Practice | Quiz #2: 50 Questions A clear understandin... g of the renal system’s anatomy, physiology, and diagnostic tests will help the nurse in problem-solving about renal function in the clinical setting. It will also assist the nurse in teaching the client about the purpose of tests or procedures and physically and emotionally preparing the client for assessment. Below is a 50-item examination that can help you in your NCLEX exam. Questions here include topics like renal failure, dialysis, and more. 1. 1. Question A client is complaining of severe flank and abdominal pain. A flat plate of the abdomen shows urolithiasis. Which of the following interventions is important? o A. Strain all urine. o B. Limit fluid intake. o C. Enforce strict bed rest. o D. Encourage a high calcium diet. Correct Answer: A. Strain all urine. Urine should be strained for calculi and sent to the lab for analysis. Strain all urine. Document any stones expelled and sent to the laboratory for analysis. Retrieval of calculi allows identification of type of stone and influences choice of therapy. Option B: Fluid intake of three (3) to four (4) L is encouraged to flush the urinary tract and prevent further calculi formation. Promote sufficient intake of fluids. Increased hydration flushes bacteria, blood, and debris and may facilitate stone passage. Offer fruit juices, particularly cranberry juice to help acidify urine. Option C: Ambulation is encouraged to help pass the calculi through gravity. Encourage the patient to walk if possible to facilitate spontaneous passage. Determine patient’s normal voiding pattern and note variations. Calculi may cause nerve excitability, which causes sensations of an urgent need to void. Usually, frequency and urgency increase as calculus nears ureterovesical junctions. Option D: A low-calcium diet is recommended to help prevent the formation of calcium calculi. Reduces risk of calcium stone formation. Note: Research suggests that restricting dietary calcium is not helpful in reducing calcium-stone formation, and researchers, although not advocating high-calcium diets, are urging that calcium limitation be reexamined. 2. 2. QuestionA client is receiving a radiation implant for the treatment of bladder cancer. Which of the following interventions is appropriate? A. Flush all urine down the toilet. B. Restrict the client’s fluid intake. C. Place the client in a semi-private room. D. Monitor the client for signs and symptoms of cystitis. Correct Answer: D. Monitor the client for signs and symptoms of cystitis. Cystitis is the most common adverse reaction of clients undergoing radiation therapy; symptoms include dysuria, frequency, urgency, and nocturia. Document the color of the patient’s urine. Be aware that patients who complain of dysuria may require a urinalysis to rule out infection. Option A: Urine of clients with radiation implants for bladder cancer should be sent to the radioisotopes lab for monitoring. Teaching is a primary responsibility of nursing care for radiation patients. Patients and families must know what to expect, get a chance to ask questions, and have those questions answered to their satisfaction. Option B: It is recommended that fluid intake be increased. A dehydrated patient may require I.V. fluids. Teach the patient to report dehydration signs and symptoms, such as weakness, dizziness, and decreased urine output. If the patient reports diarrhea or vomiting, assess for volume depletion and check orthostatic vital signs and weight. Option C: Clients with radiation implants require a private room. Helping patients and families manage side effects is a key nursing responsibility. Unlike the systemic side effects of chemotherapy, radiation side effects are specific to the treatment site. Make sure the patient receives an explanation of the treatment and its potential side effects. 3. 3. Question A client has just received a renal transplant and has started cyclosporine therapy to prevent graft rejection. Which of the following conditions is a major complication of this drug therapy? A. Depression B. Hemorrhage C. Infection D. Peptic ulcer disease Correct Answer: C. Infection Infection is the major complication to watch for in clients on cyclosporine therapy because it’s an immunosuppressive drug. Urinary tract infections are common within the first 6 months. Opportunistic infections are more likely to occur 1–6 months after transplantation, reflectingthe greater impact of immunosuppression during this time. Reactivation of latent pathogens such as polyomavirus BK, hepatitis C virus (HCV), and mycobacterium tuberculosis may also occur. Option A: Depression may occur posttransplantation but not because of cyclosporine. While kidney transplantation offers several advantages in terms of improved clinical outcomes and quality of life compared to dialysis modalities, depressive symptoms are still present in approximately 25% of patients, rates comparable to that of the hemodialysis population. Option B: Hemorrhage is a complication associated with anticoagulant therapy. Bleeding is the most important complication of VKAs and a major concern for both physicians and patients. The occurrence of bleeding during treatment is not only important for the treated subjects, but also for correct and complete use of this therapy in all the subjects who have a clear clinical indication for anticoagulation. Option D: Peptic ulcer disease is a complication of steroid therapy. It is suggested that the mechanisms responsible for peptic ulcer formation induced by corticosteroids include enhanced gastrin and parietal cell hyperplasia with increased acid secretion, diminished gastric mucus synthesis, and suppressed arachidonic acid metabolism and prostaglandin (PG) synthesis. 4. 4. Question A client received a kidney transplant 2 months ago. He’s admitted to the hospital with the diagnosis of acute rejection. Which of the following assessment findings would be expected? A. Hypotension B. Normal body temperature C. Decreased WBC count D. Elevated BUN and creatinine levels Correct Answer: D. Elevated BUN and creatinine levels In a client with acute renal graft rejection, evidence of deteriorating renal function is expected. In renal transplantation matching of MHC class II antigens are more critical than MHC class I antigen compatibility in determining graft survival. Matching of the ABO blood group system is also essential since A and B antigens can express endothelium. When there is a genetic disparity between donor and receptor, MHC class I and II can be seen as foreign by the immune system. Option A: The client would most likely have acute hypertension. After a few days or weeks of successful transplantation surgery, the patient complains about tenderness at the site of the graft, pyrexia, and abnormal function of the organ or tissue graft, for example, in renal transplantation appears anuria, an increasing serum creatinine levels, and metabolic problems including hyperkalemia. Option B: Acute rejection can associate with a high incidence of infections and other complications as the lethal graft-versus-host disease. It can recognize a single episode ofacute rejection and promptly treat it, often preventing organ or tissue failure, but the recurrence can lead to chronic rejection. Option C: The nurse would see elevated WBC counts and fever because the body is recognizing the graft as foreign and is attempting to fight it. Acute rejection relates well with class I and class II HLA gene disparity between donor and receptor. ABO matching protects against hyperacute transplantation rejection, which cannot be prevented with the use of immunosuppressive drug [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 38 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 29, 2022
Number of pages
38
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 29, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
54










.png)

.png)
 UPDATED ON MARCH 19, 2022, BSN, R.png)