Anatomy and Physiology - A&P 2 > EXAM > BIO 152 A&P II Final Exam (100 OUT OF 100) Questions and Answer elaborations/ TOP SCORE (All)
BIO 152 A&P II Final Exam (100 OUT OF 100) Questions and Answer elaborations/ TOP SCORE
Document Content and Description Below
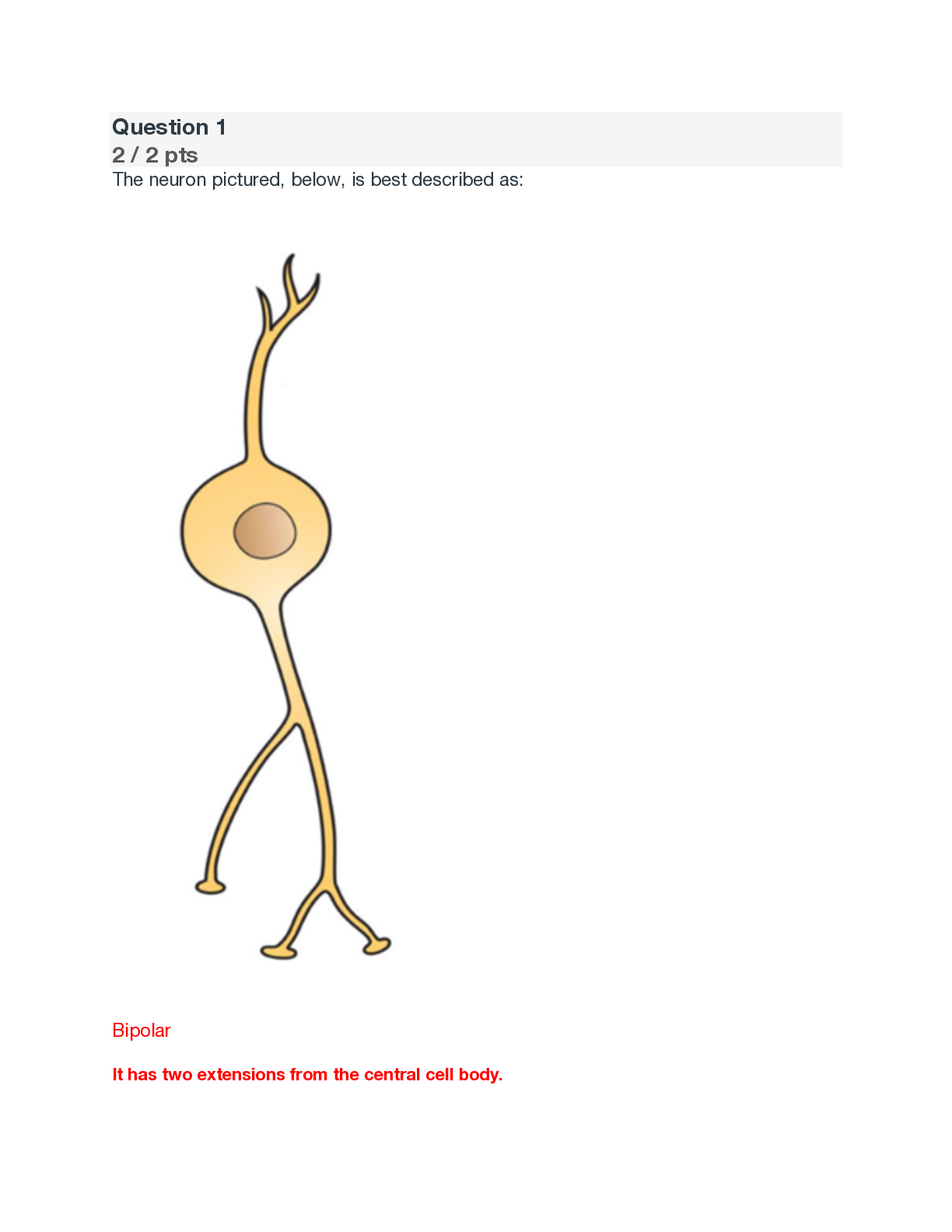
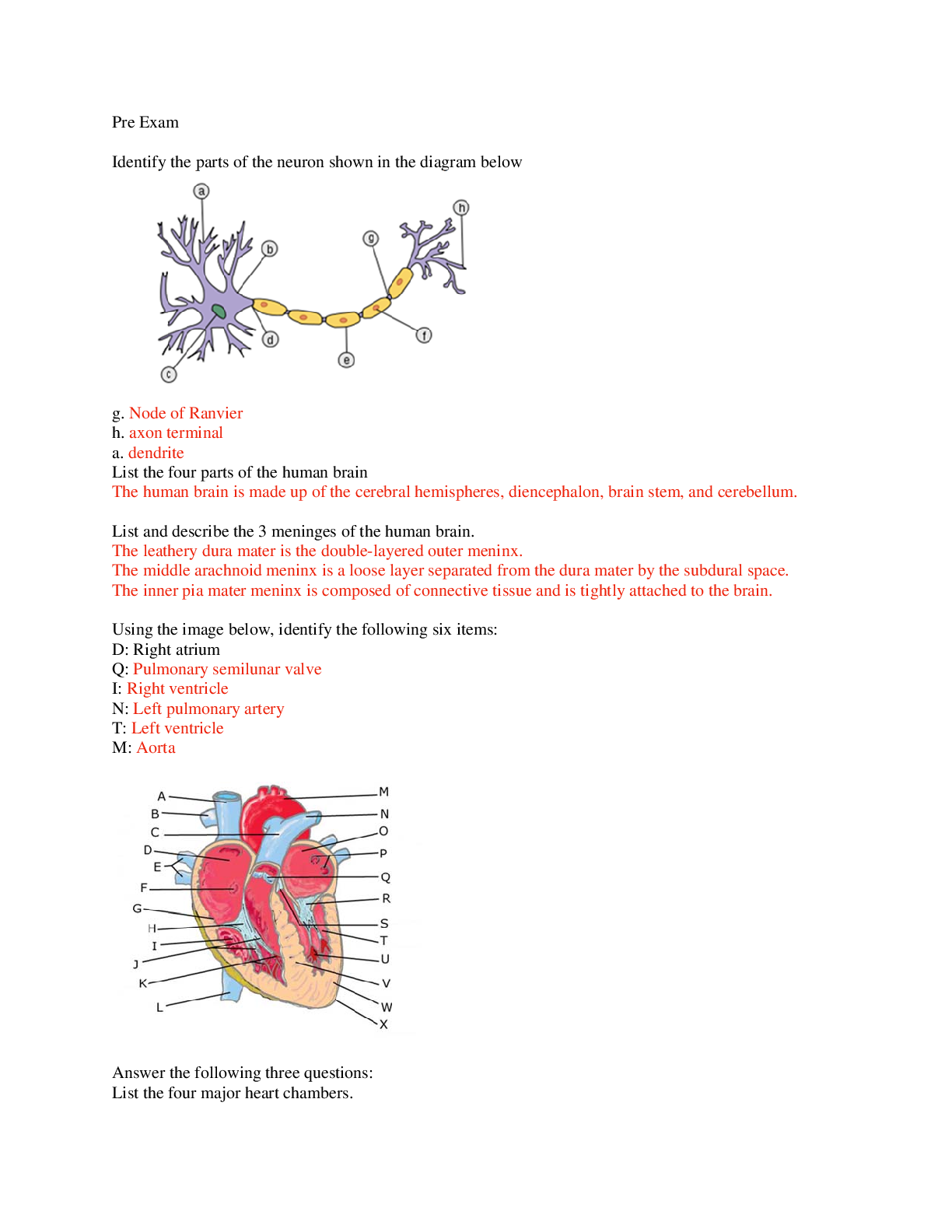
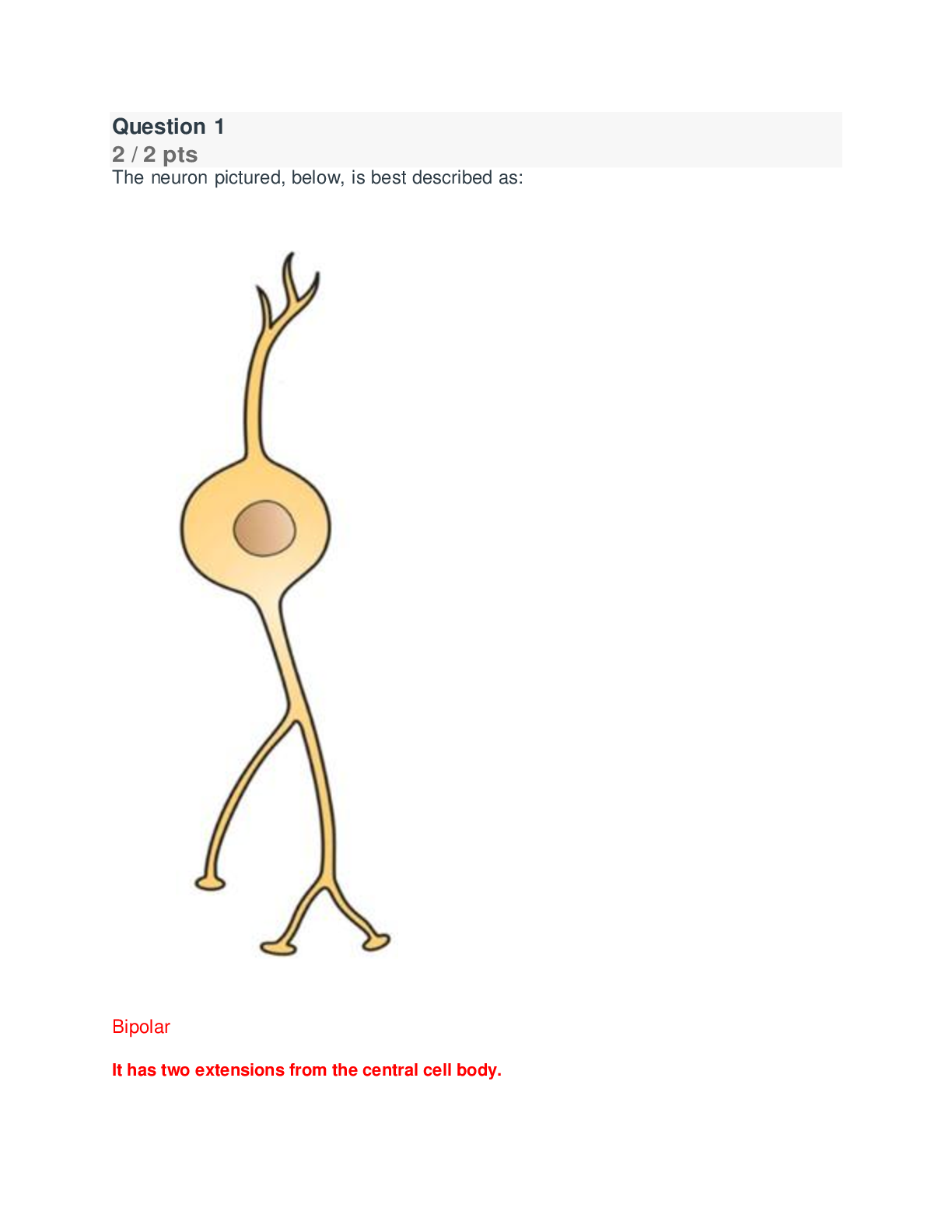
The neuron pictured, below, is best described as: Bipolar It has two extensions from the central cell body. Multipolar Unipolar Pseudounipolar Name and describe what i... s occurring in the neuron cell membrane in section 4 of the diagram. Include the charge of the membrane during this phase. Your Answer: • Afterpolarization (Hyperpolarization) Potassium gates are slow to close and there is an undershoot of the potential. • The charge drops below -70mV and then returns to -70mV once at resting state again. Where is the integration center of a reflex located? CNS (central nervous system) What is true about the flexor withdrawal reflex? A. It does not involve interneurons. B. It involves excitatory interneurons. C. It involves inhibitory interneurons. D. The effect of the reflex is to create a co-contraction of two muscles E. A&D F. B&C Label the nerves (A-C) in the figure below: A: B: C: A- Lateral femoral cutaneous B- Femoral nerve C- Saphenous Which of the following is most likely a symptom of ALS? Impaired ability to swallow Decreased sensation in the hands Shrinkage of cerebral cortex Increased size of brain ventricles All the above What is the purpose of the blood-brain barrier? Describe its maintenance from a cellular level. The blood-brain barrier is a diffusion barrier which prevents most particles from entering the central nervous system tissue, keeping the brain and spinal cord separate from general blood circulation. The blood-brain barrier is formed by the relatively impermeable brain capillaries, due to the glial cells astrocytes. Maintenance of the blood-brain-barrier is important to provide a stable chemical environment for the nervous system. A patient damaged the radial nerve. What action is most likely limited? Elbow flexion Hip extension Wrist flexion Wrist extension What is muscle tone and how is it maintained? Muscle tone is the degree at which muscles remain partially contracted while at rest. Muscle tone is continuously monitored and maintained by the cerebellum to keep bones and joints in place. A patient had a CVA in the area indicated by the red x in the figure, below. What type of blindness is the patient most likely to incur? Explain your reasoning. A. Left eye blindness B. Right eye blindness C. Bilateral left visual field blindness D. Bilateral right visual field blindness. C The right optic tract is damaged. All the sensory information from the left visual fields travels together after the optic chiasm to the right side of the brain. Match the numbers (1-5) in the figure below with the correct terms (A-H). Note: not all terms will be used. 1- A: Cochlear Nerve 2- B: Facial Nerve 3- C: Tympanic Membrane 4- D: Cochlea 5- E: Malleus F: Vestibule G: Semicircular canal H: Incus 1 A. Cochlear Nerve B. Facial Nerve Correct! 2 Correct! 3 E. Malleus Correct! 4 D. Cochlea Correct! 5 C. Tympanic Membrane H. Incus The tongue helps form food into a compact mass called a . Papillae Gustatory cell Taste Bud Bolus True of False The tongue contains nociceptors and thermoreceptors in addition to chemoreceptors. True False What is the purpose of the fossa ovalis in a fetus? The fossa ovalis marks the place of an opening between the atria which is present in all developing fetuses. It allows fetal blood to move directly from right to left atrium, bypassing he undeveloped lungs. The fossa ovalis closes during birth so that the lungs can receive oxygen once the baby is born. Name the vessel in the figure below: (highlighted in blue, also indicated by the arrow) Posterior Intraventricular artery Use the figure below to answer the following question. Portion A is filled with air. Which part of the medical equipment shown below (B-F) releases the air from A? E. The valve The sends deoxygenated blood to the lungs to be oxygenated. Left, systemic circuit Right, pulmonary circuit Left, pulmonary circuit Right, systemic circuit You are reviewing your patient’s results from an EKG. The findings indicate a problem with ventricular depolarization. Where should you look on the EKG to find this abnormal rhythm? T-wave Correct Answer QRS complex P-wave The electrical activity cannot be read on an EKG A patient is suspected to have peripheral edema due to heart failure. Which side of the heart would be in failure? Explain your answer. The right side of the heart would be in failure. If the right side of the heart cannot pump blood into the heart efficiently, blood and fluid will back up into the veins, causing swelling in body tissues. Name the lymphatic vessel below (highlighted in blue, also indicated by the arrow): Thoracic Duct/Left Lymphatic Duct Blood enters the spleen via the . Your Answer: splenic artery Splenic artery Interferons inhibits what type of infection agent: Your Answer: virus Virus A patient is admitted to the ER with hives and difficulty breathing. What is most likely happening? Your Answer: the patient is likely experiencing anaphylaxis because of an allergic reaction Anaphylaxis Match the cell with its best description. Select all that apply. Performs phagocytosis Neutrophil Correct! Eosinophil Correct Answer Basophil Correct! Macrophage Correct! Monocyte Label the regions of the reproductive system below: (A-C) A: B: C: Your Answer: A. PREPUCE B. URETHRAL ORIFICE C. VESTIBULE A: Prepuce B: Urethral orifice C: Vestibule The connects the seminal vesicle with the urethra to allow sperm to exit the body. Your Answer: EJACULATORY DUCT Correct Answer Correct Answer Ejaculatory duct Which of the following is true concerning human cells? A. Haploid cells contain the full number of chromosomes (46). B. Diploid cells contain half the number of chromosomes (23). C. Gamete cells are haploid cells. D. A zygote has 23 chromosomes. E. A&B are true Name and discuss the stage of labor that best describes the figure below: The second stage, delivery of the baby, is the time it takes for the baby to be pushed out of the birth canal after full dilation has been accomplished. During this stage a woman uses her abdominal muscles to push the baby, with the help of the uterus contracting, through the cervix and out the vagina. This stage is much shorter, lasting, on average, 50 minutes in a first delivery and 20 minutes in later ones. After the child is born the umbilical cord is tied and cut. Based strictly on anatomical structural differences, are males or females more likely to get a UTI? Explain your answer. Female; The female urethra is shorter and only carries urine while the male urethra is about 5 times longer. Since the female urethra is short and the external opening is close to the anus, improper wiping or poor hygiene after defecation can easily carry fecal bacteria into the urethra. Bacteria enter the urethra and travel up to the bladder, causing a urinary tract infection (UTI). Describe the difference between the two types of nephrons. - Cortical nephrons are in the cortex region of the kidney, except for a portion of their loop of Henle which extends into the medulla. - The remaining nephrons, called juxtamedullary nephrons, pass deeply into the medulla because of their location and their longer loops of Henle. Which of the following is true concerning cardiovascular baroreceptors? They are mechanoreceptors found in the aortic arch and carotid sinus. They are in the lungs and the kidneys. These are chemoreceptors found in the hypothalamus. They are regulated by the hypoglossal and spinal accessory cranial nerves. A person is hyperventilating. This falls under what control mechanism? Explain what hyperventilation accomplishes. • Respiratory control- Hyperventilation is an increase in the respiratory rate, helping to remove additional CO2. Within minutes increasing amounts of CO2is removed. Removing CO2 uses up H+ causes the pH to rise (becomes more alkaline) and restores correct blood pH. • (Optional) this reaction shifts to the left: CO2+ H2O HCO - H2CO3 H+ + Describe in detail what happens during an emergency to control the rate of blood to the kidney. During these times the renal autoregulatory system is superseded by higher level nervous system controls. When the nervous system takes over regulation, the afferent arterioles diameter is narrowed by sympathetic nerve fibers. The release of the hormone epinephrine by the adrenal medulla causes a decrease in renal blood flow and decreases the GFR. Constriction of the renal arteries is only to be used for a short time. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 19 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jun 09, 2022
Number of pages
19
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jun 09, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
25



.png)


















 (1).png)



