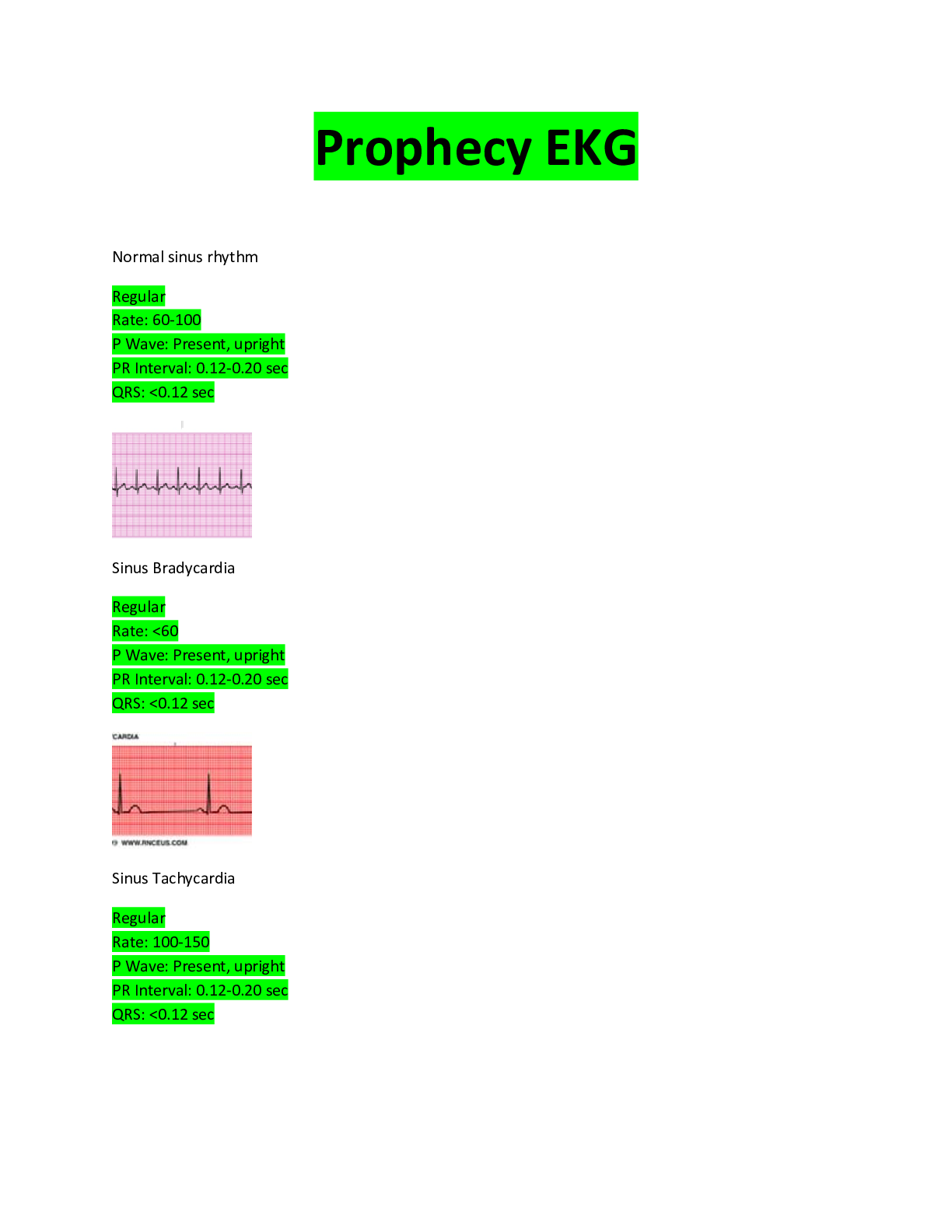
Health Care > EXAM > NR304 / NR 304 Exam 1 Study Guide (Latest 2021/2022): Health Assessment II - Chamberlain College (All)
NR304 / NR 304 Exam 1 Study Guide (Latest 2021/2022): Health Assessment II - Chamberlain College
Document Content and Description Below
NR304 / NR 304 Exam 1 Study Guide (Latest 2021/2022): Health Assessment II - Chamberlain College NR304 / NR 304 Exam 1 Study Guide (Latest 2021/2022): Health Assessment II - Chamberlain College of ... Nursing. NR-304 Physical Assessment Study Guide – Exam 1 50 Questions – Multiple Choice, Select All That Apply, HOTSPOT, Multiple Sequences Chapter 18 – Peripheral Vascular Major arteries, veins and lymphatics of body – location 2 Pediatric (BP measurements; lymph nodes) Do not take blood pressure measurements until the child is 18 months of age. There is an increased pulse rate with fever Lymphatic system o At birth it is well developed o Grows rapidly until 10 to 11 years of age o Lymph nodes are relatively large and often palpable Pregnant (BP changes throughout, varicosities) Need to monitor blood pressure throughout pregnancy o Vasodiation due to hormone change o There is hyotension during the third trimester o Preeclampsia may result in hypertension Preeclampsia is when a pregnant woman develops high blood pressure and protein in the urine after the 20th week (late 2nd or 3rd trimester) of pregnancy. Varicosities in the legs and the rectal area o This is because the uterus obstructs the iliac veins and inferior vena cava This causes an increase in the venous pressures of the lower legs. Geriatric (Systolic BP & pulse changes; enlargement of calf veins; lymph nodes) There is an increase in blood pressure, especially the systolic o Arteriosclerosis - peripheral blood vessels more rigid Decrease in pulse with some irregularities Progressive enlargement of calf veins o You have an increased risk for deep vein thrombosis (DVT) Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) occurs when a blood clot (thrombus) forms in one or more of the deep veins in your body, usually in your legs. o possible pulmonary embolism (PE) Pulmonary embolism is when one or more pulmonary arteries in your lungs become blocked. In most cases, pulmonary embolism is caused by blood clots that travel to the lungs from the legs o DVT and PE cause prolonged bed rest, immobility, and CHF o Low-dose anticoagulation (ASA 80-160mg) reduces risk There is a loss of lymph tissue o There are less lymph nodes and a decrease in size of the nodes 3 Subjective Leg pain or cramps – differences between acute and chronic arterial and venous pain (see handout) Claudication distance; 6 Ps; Leriche syndrome; risk factors/conditions Claudication distance – number of blocks or stairs climbed to produce pain; relieved by rest To relieve arterial pain you dangle your legs over a ledge To relieve venous pain raise your legs up Night leg pain is common with aging Restless leg syndrome, muscle cramping or rest pain associated with vascular disease. In addition, some patients suffer from restless leg syndrome pain at night, worsening with rest and relief with motion of the legs. One diagnoses restless leg syndrome by history and physical examination Nocturnal cramping is much more common in older patients. As noted earlier, nocturnal cramping is typically associated with dehydration, low calcium, low sodium, low potassium or low magnesium, which one may assess by standard laboratory studies and treat by appropriate supplement therapy. Leriche's syndrome is the term used for a group of symptoms that are caused by a certain type of peripheral arterial disease of the legs. In Leriche's syndrome, blood flow in the aorta is blocked in the stomach area. This blocks blood flow to the legs. In men, blood flow to the penis is also blocked. When your iliac arteries narrow or become blocked, your legs may not receive the blood and oxygen they need. This lack of oxygen is called ischemia and it can cause pain. Skin changes – color (redness, pallor, blueness, brown); varicose veins; ulcers (arterial versus venous) Color- redness, pallor, blueness, brown Varicose veins- leg veins bulging or cooked Temperature- excessive warm or cool Swelling – bilaterally versus unilateral; aggravating and relieving factors; associated symptoms Bilaterally is CHF Unilateral is obstruction and inflammation Lymphedema Lymphedema refers to swelling that generally occurs in one of your arms or legs. Although lymphedema tends to affect just one arm or leg, sometimes both arms or both legs may be swollen. Lymphedema is caused by a blockage in yo [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 24 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Aug 04, 2022
Number of pages
24
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Aug 04, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
37





.png)