Pathophysiology > Quiz > NUR2603 Essentials of Pathophysiology Exam 1 Focused Review (All)
NUR2603 Essentials of Pathophysiology Exam 1 Focused Review
Document Content and Description Below
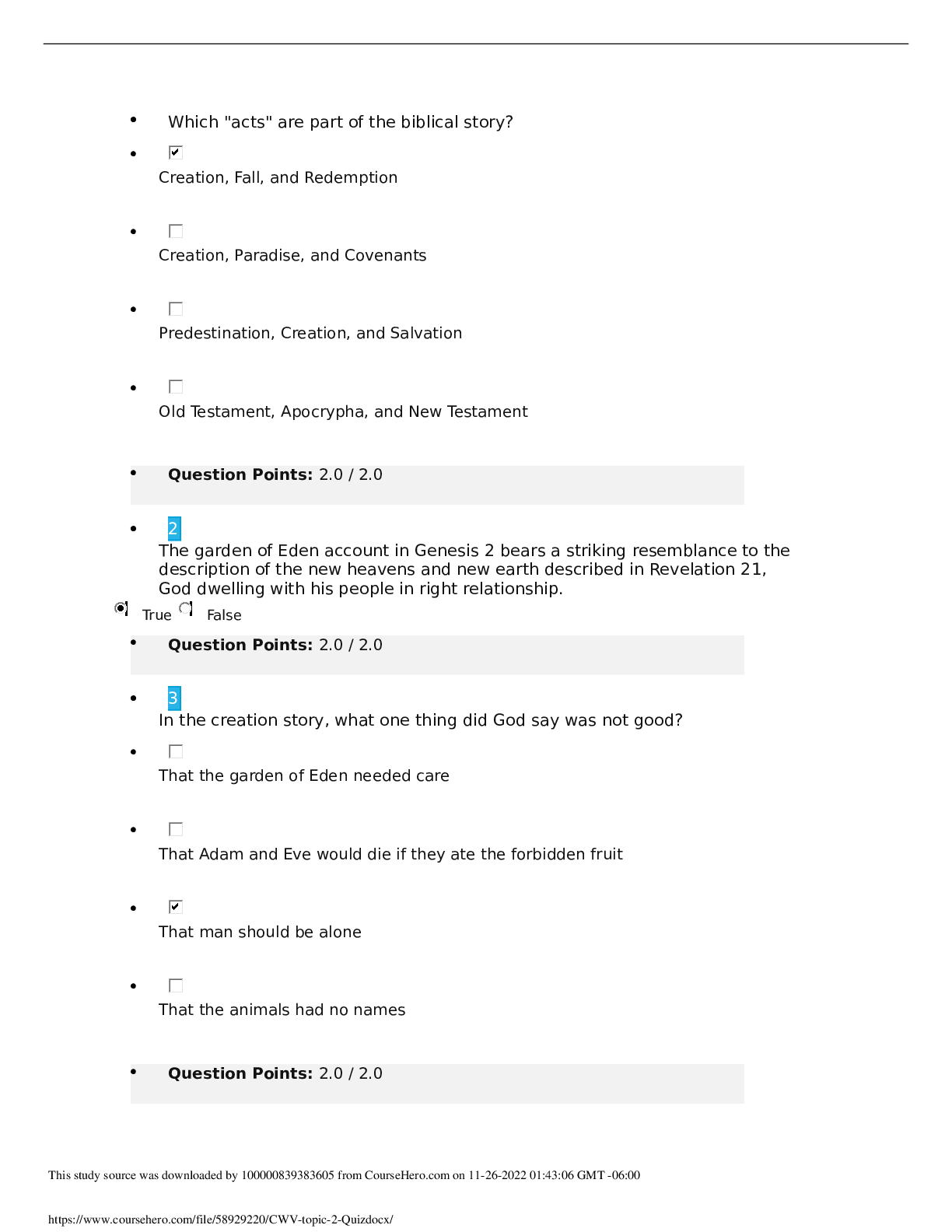
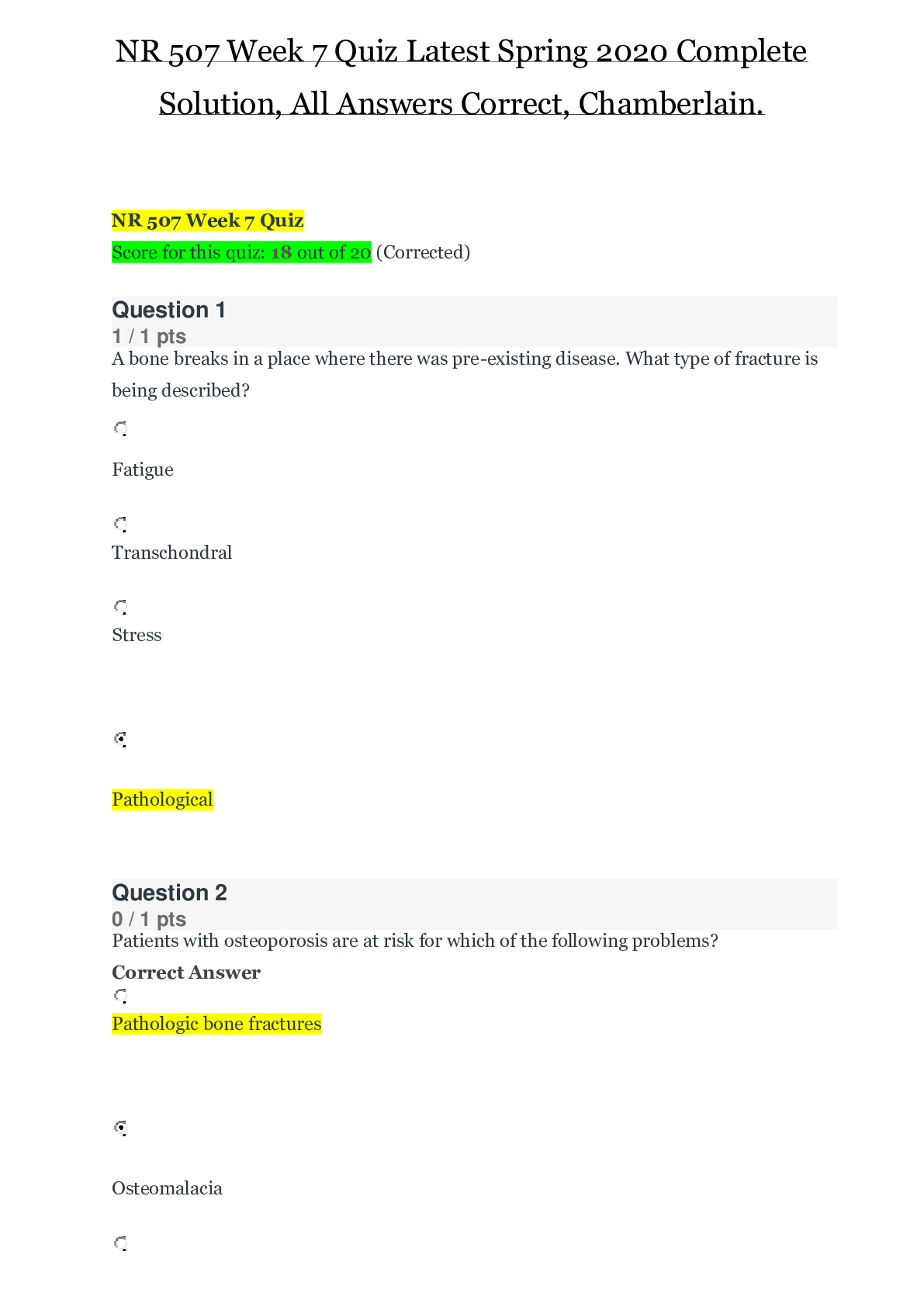
NUR2603 Essentials of Pathophysiology Exam 1 Focused Review • What is pathophysiology? o the study of abnormalities in physiologic functioning of living beings. It is studies in terms of common... , or classic, presentations of disorders. • Stress response o body’s attempt to try to restore the balance; is helpful but can become damaging when repeatedly activated or does not cease. • Flight or flight o The alarm stage; because it provides a surge of energy and physical alterations to either evade or confront danger. (when the hypothalamus senses a need to activate the GAS in response to a stimulus, a stressors placing the balance of homeostasis at risk) • Epidemiology and the treatment of disease o the study of health events and patterns of disease involving aggregates of people, their distribution, and associated causative factors in a defined population • Hans Selye’s General Adaptation Syndrome o Alarm (fight or flight), resistance (adaptation; move beyond the alarm stage), exhaustion (no longer able to effect a return to homeostasis) stages • What is homeostasis? Allostasis? o Maintaining internal conditions in a stable state by keeping things relatively the same, or balanced o ability to successfully adapt to challenges to maintain survival and well-being (i.e. BP, HR, glucose levels) o Allostatic overload- when adaptation mechanisms are inadequate or total amount of allostatic load is excessive; homeostasis cannot be obtained • Osmosis vs passive transport vs filtration o Movement of water across a semipermeable membrane to equalize the particle concentration of the fluid on both sides of the membrane. o Called facilitated diffusion; particles move through the cell membrane from an area of higher concentration to an area of low concentration w/o the use of energy o Particles move through the cell membrane from an area of low concentration to high concentration; requires the use of energy; ATP • Edema o Excess of fluid in interstitial compartment; may be localized or generalized; stages +1, +2, +3, +4 • Osteoporosis o Most common metabolic bone disease in which reduction in bone mass results from bone resorption proceeding at a rate faster than that of new bone formation. (s/s: shortened stature, muscle wasting, back muscle spasms, difficulty bending over) • Transmission of infections o An unbroken chain of events must occur to allow one human to infect another. o Direct transmission: body fluids-droplet, animal bites/soil, placenta transfer o Indirect transmission: vehicle-borne (infectious agent is transported to the host), vector-borne (mechanical or biological transfer), airborne (with aerosols) o Most effective ways to break the chain of transmission: handwashing • Myasthenia Gravis o Chronic autoimmune disease; affects neuromuscular function of voluntary muscles o Acetylcholine receptor antibodies destroy or block acetylcholine receptors of muscle end- plate of the neuromuscular junction. o Manifestations: profound muscle weakness and fatigability o Can lead to respiratory depression from weakness o Mind to head • Osteoarthritis o A common, local degenerative joint disease, associated with aging, characterized by progressive loss of articular cartilage, cartilage calcifies, wear of underlying bone, and by formation of new bone from subchondral bone at joint margins. • Pressure ulcers o Localized areas of cellular necrosis resulting from prolonged pressure between any bony prominence and an external object such as a bed or wheelchair o Prevention: turn Q2HR, keep areas clean and dry o Stages I, II, III, & IV • Histamine o An early mediator of the inflammatory response; causes bronchial constriction and mucus production. o Receptor-blocking agents are widely used in allergic reactions, such as skin reactions and hay fever to suppress the inflammatory actions. • Herpes simplex o Two types: HSV-1: occurs above the waist; lips, mouth, face; HSV-2: infections in the genital area o Vesicles and erythema; crusts before healing; no cure [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 7 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Oct 15, 2022
Number of pages
7
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Oct 15, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
66