*NURSING > TEST BANK > Canadian Nursing Health Assessment, A Best Practice Approach, 2nd Canadian Edition by Stephen Test B (All)
Canadian Nursing Health Assessment, A Best Practice Approach, 2nd Canadian Edition by Stephen Test Bank
Document Content and Description Below
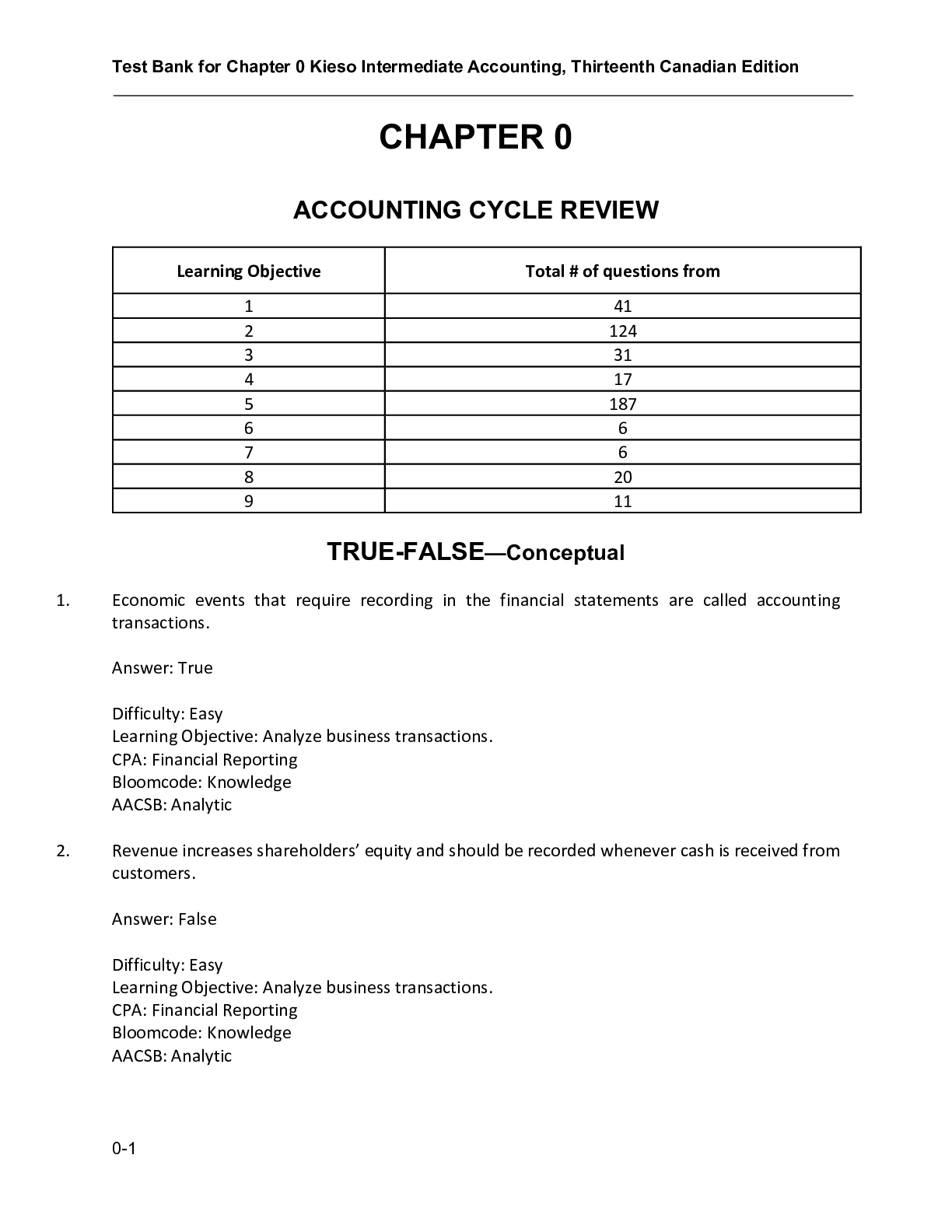
Test Bank for Canadian Nursing Health Assessment, A Best Practice Approach, 2nd Canadian Edition, 2ce by Tracey C. Stephen, Lynn Skillen TEST BANK ISBN-13: 9781975108113 FULL CHAPTERS INCLUDED ... Unit 1 Foundations of Nursing Health Assessment 1 Health Assessment in Nursing Practice Professional Nursing Practice Advocacy Scholarship and Research Registered Nurse and Advanced Practice Nurse Roles Purposes of Health Assessment Wellness and Health Promotion Health Promotion and Health Assessment Focused Health History Related to the Case Study Risk Assessment and Health Promotion The Nursing Process Phases of the Nursing Process Assessment Analysis Planning Goals and Outcomes Planning Care Intervention/Implementation Evaluation Critical Thinking Clinical Reasoning Types of Health Assessments Urgent Assessment Comprehensive Assessment Focused Assessment Priority-Setting Frequency of Health Assessment Lifespan Issues Cultural and Environmental Considerations Components of the Health Assessment Documentation and Communication Organizing Frameworks for Health Assessment Evidence-Informed Critical Thinking 2 Interviewing and Therapeutic Communication Communication Process Nonverbal Communication Skills Verbal Communication Skills Active Listening Restatement Reflection Elaboration (Facilitation) Silence Focusing Clarification Summarizing Nontherapeutic Responses Failing to Listen False Reassurance Sympathy Giving Advice Being Judgmental Changes of Subject Distractions Technical or Overwhelming Language Interrupting Professional Expectations Intercultural Communication Patients with Limited Language Understanding Working with an Interpreter Gender and Sexual Orientation Issues Phases of the Interview Process Preinteraction Phase Beginning Phase Working Phase Closing Phase Lifespan Issues Newborns and Infants Children and Adolescents Older Adults Special Situations Patients with Hearing Impairment Patients with Altered Level of Consciousness Patients with Cognitive Impairment Patients with Mental Health Illness Patients with Anxiety Patients Who Are Crying Patients Who Are Angry Patients under the Influence of Alcohol or Drugs Personal Questions Sexual Aggression 3 The Health History Subjective and Objective Data Signs and Symptoms Primary and Secondary Data Sources Reliability of the Source Components of the Health History Date and Time of Health History Demographic Data or Identifying Data Reason for Seeking Care or Chief Concern Present Illness Pain Goal Functional Goal Past Health History Current Medications and Indications Family History Functional Health Assessment Growth and Development Review of Systems Psychosocial and Lifestyle Factors Social, Cultural, and Spiritual Assessment Mental Health Alcohol and Substance Use Human Violence Sexual History and Orientation Lifespan Considerations Women Who Are Pregnant Newborns, Children, and Adolescents Aging Adults 4 Physical Examination Techniques and Equipment Overview of Anatomical Terms Anatomical Position Anatomical Quadrants Anatomical Regions Anatomical Terms of Comparison and Movement Routine Practices and Additional Precautions Hand Hygiene Routine Practices Additional Precautions Latex Allergy Skin Reactions Cultural Considerations Subjective Data Collection Objective Data Collection Promoting Patient Comfort, Dignity, and Safety Inspection Palpation Light Palpation Deep Palpation Characteristics of Sound and Sound Transmission Percussion Direct Percussion Indirect Percussion Auscultation Advanced Techniques Lifespan Considerations Older Adults Women Who Are Pregnant Newborns and Infants Children and Adolescents 5 Documentation and Interprofessional Communication Patient Health Record Purposes of the Patient Health Record Legal Document Communication and Planning Care Quality Assurance Education Research Components of the Patient Health Record Electronic Patient Health Record Principles Governing Documentation Confidential Accurate and Complete Organized Timely Concise Critical Thinking and Clinical Judgment Nursing Admission Assessment Flow Sheets Plan of Care/Clinical Pathway Progress Notes Narrative Notes SOAP Notes PIE Notes Focus Notes Charting by Exception Discharge Note Written Handoff Summary Verbal Communication Verbal Handoff Reporting Qualities of Effective Reporting SBAR Reporting with Other Health Care Professionals Telephone Communication Patient Rounds and Conferences Critical Thinking and Clinical Judgment Unit 2 General Examinations 6 General Survey and Vital Signs Assessment Cultural Considerations Urgent Assessment Risk Assessment and Health Promotion Objective Data Collection Promoting Patient Comfort, Dignity, and Safety General Survey: General Inspection Anthropometric Measurements Vital Signs Temperature Pulse Respirations Blood Pressure Vital Signs Monitor Doppler Technique Evidence-Informed Critical Thinking Lifespan Considerations Older Adults Infants and Children 7 Pain Assessment Anatomy and Physiology and Theories of Pain Gate Control Theory Nociception: Peripheral Nervous System Nociception: Central Nervous System Pain Classification Duration: Acute Pain Duration: Chronic (Persistent) Pain Frequency: Continuous or Intermittent/Episodic Pain Form: Nociceptive Pain Form: Neuropathic Pain Location Etiology Association with Cancer Cultural Considerations Urgent Assessment Subjective Data Collection Assessment of Risk Factors Health Promotion Focused Health History Related to Common Symptoms/Signs Pain Measurement Tools One-Dimensional Pain Scales Multidimensional Pain Scales Special Situations Patients Unable to Report Pain Patients with Opioid Tolerance Objective Data Collection Equipment Promoting Patient Comfort, Dignity, and Safety Comprehensive Physical Examination: Pain Evidence-Informed Critical Thinking Clinical Reasoning Reassessing and Documenting Pain Lifespan Considerations Older Adults Anatomy and Physiology Overview Subjective and Objective Data Women Who Are Pregnant Anatomy and Physiology Overview Subjective and Objective Data Newborns, Infants, and Children Anatomy and Physiology Overview Subjective and Objective Data 8 Nutrition Assessment Nutritional Concepts Primary Nutrients Carbohydrates Proteins Lipids Vitamins and Minerals Water Food, Nutrients, Supplements, and Drug Interactions Food Safety Nutritional Guidelines Types of Reference Values Canada’s Food Guide Nutrition Care Process Collecting Nutritional Data Sexual Orientation and Gender Identity Considerations Cultural Considerations Urgent Assessment Subjective Data Collection Assessment of Risk Factors Risk Assessment and Health Promotion Focused Health History Related to Nutrition-Associated Symptoms/Signs Comprehensive Nutritional History Dietary Assessment Tools Direct Observation Objective Data Collection Promoting Patient Comfort, Dignity, and Safety Initial Survey and Focused Physical Examination Evidence-Informed Critical Thinking Organizing and Prioritizing Common Laboratory and Diagnostic Testing Serum Proteins Hemoglobin and Hematocrit Lymphocyte Count Creatinine Excretion Nitrogen Balance Skin Testing Serum Lipid Measurements Other Laboratory Tests Clinical Reasoning Nursing Analysis, Outcomes, and Interventions Lifespan Considerations Older Adults Anatomy and Physiology Overview Objective Data Collection Women Who Are Pregnant Anatomy and Physiology Overview Objective Data Collection Infants and Children Anatomy and Physiology Overview Objective Data Collection Adolescents Anatomy and Physiology Overview Objective Data Collection 9 Psychosocial and Cognitive Development Subjective Data Collection Psychosocial Development Infant: Trust versus Mistrust Toddler: Autonomy versus Shame and Doubt Preschooler: Initiative versus Guilt School-Age Child: Industry versus Inferiority Adolescent: Identity versus Role Confusion Early Adult: Intimacy versus Isolation Middle Adult: Generativity versus Self-Absorption Late Adult: Ego Integrity versus Despair Cognitive Development Infant: Sensorimotor Toddler and Preschooler: Preoperational School-Age Child: Concrete Operational Adolescent: Formal Operations Young Adult: Formal Operations Middle Adult: Cognitive Expertise Older Adult: Wisdom Language Development Cultural Considerations Urgent Assessment Objective Data Collection Physical Growth Motor Development Evidence-Informed Critical Thinking Clinical Reasoning 10 Mental Health Assessment Mental Health and Psychiatric Assessment in Nursing Practice Cultural Considerations Urgent Assessment Subjective Data Collection Risk Assessment and Health Promotion Anxiety Depression Suicide Dementia Substance Use Problems Assessment of Risk and Protective Factors Objective Data Collection Initial Survey and Mental Status Assessment Assessment of Dementia, Delirium, and Depression Evidence-Informed Critical Thinking Clinical Reasoning 11 Social, Cultural, and Spiritual Health Assessment Models of Health Social Assessment Social Assessment of the Individual Social Assessment of the Community Social Assessment at the Societal Level Cultural Assessment Characteristics of Culture Goals of Cultural Assessment Cultural Health Beliefs and Practices Cultural Food and Nutrition Practices Cultural Beliefs and Practices of Pregnancy and Childbirth Cultural Beliefs and Expressions of Illness and Pain Spiritual Assessment Evidence-Informed Critical Thinking Nursing Analysis, Outcomes, and Interventions 12 Human Violence Assessment Types of Human Violence Family Violence Child Maltreatment Sibling Violence Intimate Partner Violence Elder Abuse Violence against Adults with Disabilities Youth and School Violence “Punking” and Bullying Workplace Violence Sexual Violence Hate Crimes Human Trafficking War-Related and Military Violence Importance of Violence/Safety Assessment Trauma-Informed Care Subjective Data Collection Interviewing Patients about Human Violence Objective Data Collection Documentation Mandated Reporting Lifespan Considerations Women Who Are Pregnant Infants, Children, and Adolescents Older Adults Cultural Considerations Evidence-Informed Critical Thinking Nursing Analysis, Outcomes, and Interventions Unit 3 Regional Examinations 13 Skin, Hair, and Nails Assessment Anatomy and Physiology Overview Skin Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous Layer Hair Nails Sweat Glands Cultural Considerations Urgent Assessment Subjective Data Collection Assessment of Risk Factors Risk Assessment and Health Promotion Focused Health History Related to Common Symptoms Objective Data Collection Promoting Patient Comfort, Dignity, and Safety Common and Specialty or Advanced Techniques Comprehensive Skin Assessment Lifespan Considerations Women Who Are Pregnant Newborns and Infants Newborns, Infants, Children, and Adolescents Older Adults Evidence-Informed Critical Thinking Organizing and Prioritizing Common Laboratory and Diagnostic Testing Clinical Reasoning Nursing Analysis, Outcomes, and Interventions 14 Head and Neck with Lymphatics and Vascular Assessment Anatomy and Physiology Overview The Head The Neck Trachea Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands Lymphatics Cultural Considerations Urgent Assessment Subjective Data Collection Assessment of Risk Factors Health Promotion Focused Health History Related to Common Symptoms Objective Data Collection Promoting Patient Comfort, Dignity, and Safety Common and Advanced Techniques Initial Survey Evidence-Informed Critical Thinking Organizing and Prioritizing Common Laboratory and Diagnostic Testing Clinical Reasoning Nursing Analysis, Outcomes, and Interventions Lifespan Considerations Older Adults Anatomy and Physiology Overview Objective Data Collection Women Who Are Pregnant Anatomy and Physiology Overview Objective Data Collection Newborns and Infants Anatomy and Physiology Overview Objective Data Collection Children and Adolescents Anatomy and Physiology Overview Objective Data Collection 15 Eyes and Vision Assessment Anatomy and Physiology Overview Extraocular Structures Extraocular Muscle Function Intraocular Structures Vision Cultural Considerations Urgent Assessment Subjective Data Collection Assessment of Risk Factors Health Promotion Focused Health History Related to Common Symptoms Objective Data Collection Promoting Patient Comfort, Dignity, and Safety Common and Advanced Techniques Assessment of Visual Acuity Assessment of Visual Fields Assessment of Extraocular Muscle Movements Assessment of External Eyes Assessment of Internal Ocular Structures Evidence-Informed Critical Thinking Organizing and Prioritizing Common Lab and Diagnostic Tests Lifespan Considerations Older Adults Women Who Are Pregnant Anatomy and Physiology Overview Objective Data Collection Newborns, Preschoolers, Children, and Adolescents Newborns Preschoolers, Older Children, and Adolescents Objective Data Collection 16 Ears and Hearing Assessment Anatomy and Physiology Overview External Ear Middle Ear Inner Ear Hearing Air and Bone Conduction Hearing Disorders Vestibular Function Cultural Considerations Urgent Assessment Subjective Data Collection Assessment of Risk Factors Health Promotion Focused Health History Related to Common Symptoms Objective Data Collection Promoting Patient Comfort, Dignity, and Safety Evidence-Informed Critical Thinking Organizing and Prioritizing Common Laboratory and Diagnostic Testing Clinical Reasoning Lifespan Considerations Older Adults Women Who Are Pregnant Newborns, Infants, and Children Adolescents 17 Nose, Sinuses, Mouth, and Throat Assessment Anatomy and Physiology Overview Nose Sinuses Mouth Tongue Salivary Glands Teeth and Gums Throat Cultural Considerations Urgent Assessment Subjective Data Collection Assessment of Risk Factors Risk Assessment and Health Promotion Focused Health History Related to Common Symptoms/Signs Cultural Considerations Objective Data Collection Promoting Patient Comfort, Dignity, and Safety Common and Advanced Techniques Comprehensive Physical Examination: Nose, Sinuses, Mouth, and Throat Cultural Considerations Evidence-Informed Critical Thinking Organizing and Prioritizing: Common Laboratory and Diagnostic Testing Clinical Reasoning: Nursing Analysis, Outcomes, and Interventions Lifespan Considerations Older Adults Anatomy and Physiology Overview Subjective Data Collection Women Who Are Pregnant Anatomy and Physiology Overview Subjective Data Collection Newborns and Infants Anatomy and Physiology Overview Objective Data Collection Children and Adolescents Anatomy and Physiology Overview Subjective Data Collection Objective Data Collection 18 Thorax, Lungs, and Respiratory Assessment Anatomy and Physiology Overview The Thorax Anterior Thoracic Landmarks Posterior Thoracic Landmarks Reference Lines Lobes of the Lungs Lower Respiratory Tract Upper Respiratory Tract Mechanics of Respiration Cultural Considerations Urgent Assessment Subjective Data Collection Assessment of Risk Factors Health Promotion Smoking Cessation Radon Detection in the Home Prevention of Occupational Exposure Prevention of Asthma Immunizations Focused Health History Related to Common Symptoms Objective Data Collection Promoting Patient Comfort, Dignity, and Safety Common and Advanced Techniques Evidence-Informed Critical Thinking Organizing and Prioritizing Common Laboratory and Diagnostic Testing Clinical Reasoning Nursing Analysis, Outcomes, and Interventions Lifespan Considerations Older Adults Anatomy and Physiology Overview Objective Data Collection Women Who Are Pregnant Anatomy and Physiology Objective Data Collection Newborns and Infants Anatomy and Physiology Objective Data Collection Children and Adolescents Anatomy and Physiology Subjective Data Collection Objective Data Collection 19 Cardiovascular Assessment Anatomy and Physiology Overview Anatomy Neck Vessels Heart Chambers Valves Heart Wall Coronary Arteries and Veins Conduction System Physiology Pulmonary and Systemic Circulation Cardiac Cycle Jugular Pulsations Cultural Considerations Urgent Assessment Subjective Data Collection Assessment of Risk Factors and Health Promotion Smoking Cessation Control of Blood Pressure and Cholesterol Level Control of Weight and Stress Focused Health History Related to Common Symptoms and Signs Objective Data Collection Promoting Patient Comfort, Dignity, and Safety Initial Survey Auscultation of the Precordium Extra Sounds Murmurs Evidence-Informed Critical Thinking Organizing and Prioritizing Common Laboratory and Diagnostic Testing Clinical Reasoning Lifespan Considerations Older Adults Anatomy and Physiology Overview Objective Data Collection Women Who Are Pregnant Anatomy and Physiology Overview Objective Data Collection Newborns and Infants Anatomy and Physiology Overview Objective Data Collection Children and Adolescents Anatomy and Physiology Overview Objective Data Collection 20 Peripheral Vascular and Lymphatic Assessment Anatomy and Physiology Overview Arterial System Venous System Capillaries Lymphatic System Fascia Compartments of the Limbs Cultural Considerations Urgent Assessment Subjective Data Collection Assessment of Risk Factors Risk Assessment and Health Promotion Patients with Peripheral Arterial Disease Patients with Venous Disease Patients with Lymphatic Disorders Focused Health History Related to Common Symptoms and Signs Objective Data Collection Promoting Patient Comfort, Dignity, and Safety Initial Survey Evidence-Informed Critical Thinking Organizing and Prioritizing Common Laboratory and Diagnostic Testing Clinical Reasoning Nursing Analysis, Outcomes, and Interventions Lifespan Considerations Older Adults Anatomy and Physiology Overview Objective Data Collection Women Who Are Pregnant Anatomy and Physiology Overview Objective Data Collection Newborns, Children, and Adolescents Anatomy and Physiology Overview Objective Data Collection 21 Breasts and Axillae Assessment Anatomy and Physiology Overview Landmarks Breast Structures Axillae and Lymph Nodes Cultural Considerations Urgent Assessment Subjective Data Collection Assessment of Risk Factors and Health Promotion Teaching the “Know Your Breasts” Approach Focused Health History Related to Common Symptoms and Signs Objective Data Collection Promoting Patient Comfort, Dignity, and Safety Initial Survey Evidence-Informed Critical Thinking Organizing and Prioritizing Laboratory and Diagnostic Testing Clinical Reasoning Nursing Analysis, Outcomes, and Interventions Lifespan Considerations Older Adults Women Who Are Pregnant/Lactating Newborns and Infants Children and Adolescents 22 Abdominal Assessment Anatomy and Physiology Overview Anatomical Landmarks Reference Lines Abdominal Organs Gastrointestinal Organs Genitourinary Organs Blood Vessels, Peritoneum, and Muscles Ingestion and Digestion Absorption of Nutrients Elimination Cultural Considerations Urgent Assessment Subjective Data Collection Assessment of Risk Factors Health Promotion Focused Health History Related to Common Symptoms/Signs Objective Data Collection Promoting Patient Comfort, Dignity, and Safety Initial Survey Evidence-Informed Critical Thinking Organizing and Prioritizing Common Laboratory and Diagnostic Testing Esophagogastroduodenoscopy Barium Enema Colonoscopy Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography Computerized Tomography Scan Magnetic Resonance Imaging Clinical Reasoning Lifespan Considerations Older Adults Anatomy and Physiology Overview Objective Data Collection Women Who Are Pregnant Anatomy and Physiology Overview Objective Data Collection Newborns, Infants, and Children Anatomy and Physiology Overview Objective Data Collection 23 Musculoskeletal Assessment Anatomy and Physiology Overview Bones Muscles Joints Temporomandibular Joint Shoulder Elbow Wrist and Hand Hip Knee Ankle and Foot Spine Cultural Considerations Urgent Assessment Subjective Data Collection Assessment of Risk Factors Health Promotion Back Injury Prevention and Occupational Hazards Lifestyle Considerations Fall Risk Bone Density Psychosocial History Focused Health History Related to Common Symptoms/Signs Objective Data Collection Promoting Patient Comfort, Dignity, and Safety Advanced Techniques Comprehensive Physical Examination: The Musculoskeletal System Evidence-Informed Critical Thinking Organizing and Prioritizing Laboratory and Diagnostic Testing Clinical Reasoning Nursing Analysis, Outcomes, and Interventions Lifespan Considerations Older Adults Anatomy and Physiology Overview Subjective Data Collection Objective Data Collection Women Who Are Pregnant Subjective Data Collection Objective Data Collection Newborn and Infants Subjective Data Collection Objective Data Collection Children and Adolescents Subjective Data Collection Objective Data Collection 24 Neurological Assessment Anatomy and Physiology Overview Central Nervous System Brain Protective Structures of the CNS Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System Cranial Nerves Spinal Nerves Autonomic Nervous System Cultural Considerations Urgent Assessment Subjective Data Collection Assessment of Risk Factors Health Promotion Stroke Prevention Injury Prevention Reduction of Risk for Seizure Activity Focused Health History Related to Common Symptoms Objective Data Collection Promoting Patient Comfort, Dignity, and Safety Neurological Assessment in Selected Situations Screening Examination of a Healthy Patient Serial Neurological Assessment and Documentation Assessment of Meningeal Signs Assessing the Unconscious Patient Brain Herniation Syndromes Initial Survey Focused Physical Examination: Neurological System Evidence-Informed Critical Thinking Organizing and Prioritizing Common Laboratory and Diagnostic Testing Clinical Reasoning Lifespan Considerations Older Adults Anatomy and Physiology Overview Objective Data Collection Women Who Are Pregnant Anatomy and Physiology Overview Objective Data Collection Newborns and Infants Anatomy and Physiology Overview Objective Data Collection Children and Adolescents Anatomy and Physiology Overview Objective Data Collection 25 Male Genitalia and Rectal Assessment Anatomy and Physiology Overview External Genitalia Internal Genitalia Testes Ducts Secretory Structures Rectum and Anus Rectum Anal Canal and Anus Cultural Considerations Urgent Assessment Subjective Data Collection Risk Assessment and Health Promotion Testicular Self-Examination (TSE) Screening for Prostate Cancer Safer Sexual Practices Protection during Contact Sports Focused Health History Related to Common Symptoms and Signs Cultural Considerations Objective Data Collection Promoting Patient Comfort, Dignity, and Safety Focused Physical Assessment: Male Genitalia and Rectal Assessment Evidence-Informed Critical Thinking Organizing and Prioritizing Common Laboratory and Diagnostic Testing Clinical Reasoning Nursing Analysis, Outcomes, and Interventions Lifespan Considerations Older Adult Anatomy and Physiology Overview Objective Data Collection Infants and Children Anatomy and Physiology Overview Objective Data Collection Adolescents Anatomy and Physiology Overview Objective Data Collection 26 Female Genitalia and Rectal Assessment Anatomy and Physiology Overview External Genitalia Internal Genitalia Vagina Uterus Cervix Fallopian Tubes Ovaries Rectum, Anal Canal, and Anus Hormone Regulation Cultural Considerations Urgent Assessment Excessive Vaginal Bleeding Abdominal Pain Bartholin Gland Infection Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Ruptured Tubal Pregnancy Subjective Data Collection Human Papillomavirus Risk Assessment and Health Promotion Human Papillomavirus Female Genital Mutilation Focused Health History Related to Common Symptoms/Signs Objective Data Collection Promoting Patient Comfort, Dignity, and Safety Advanced Techniques Evidence-Informed Critical Thinking Common Laboratory and Diagnostic Testing Nursing Analysis, Outcomes, and Interventions Lifespan Considerations Older Adults Women Who Are Pregnant Newborns and Infants Children and Adolescents Unit 4 Special Populations 27 Women Who Are Pregnant Anatomy and Physiology Overview Preconception First Trimester Second Trimester Third Trimester Determining Weeks of Gestation Role of the Nurse in the Outpatient Setting Cultural Considerations Urgent Assessment Subjective Data Collection Assessment of Risk Factors Risk Assessment and Health Promotion Focused Health History Related to Common Symptoms/Signs in Pregnancy Objective Data Collection Promoting the Woman’s Comfort, Dignity, and Safety Assessment during the Initial Visit Assessment during Routine Pregnancy Visits Evidence-Informed Critical Thinking Common Laboratory and Diagnostic Testing Nonstress Test Leopold Manoeuvres Clinical Reasoning Plan of Care, Interventions, and Outcomes 28 Newborns and Infants Anatomy and Physiology Overview Physical Growth Motor Development Language, Psychosocial, and Cognitive Development Urgent Assessment Emergent Concerns Subjective Data Collection Assessment of Risk Factors Risk Assessment and Health Promotion Safe Sleep Habits Choking Immunization Schedules Child Safety Car Seat Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Training for Parents Poison Control Breast-feeding and Iron-rich Foods Baby Bottle Tooth Decay Focused Health History Related to Common Symptoms/Signs Objective Data Collection Promoting Patient Comfort, Dignity, and Safety Comprehensive Physical Examination: Newborn and Infant Documentation of Examination Findings Cultural Considerations Evidence-Informed Critical Thinking Organizing and Prioritizing Common Laboratory and Diagnostic Testing Clinical Reasoning Nursing Analysis, Outcomes, and Interventions 29 Children and Adolescents Anatomy and Physiology Overview Physical Growth Motor Development Language Psychosocial and Cognitive Development Cultural Considerations Urgent Assessment Subjective Data Collection Important Topics for Health Promotion Focused Health History Related to Common Symptoms Cultural Considerations Objective Data Collection Equipment Promoting Patient Comfort, Dignity, and Safety Developmental Assessment Evidence-Informed Critical Thinking Common Laboratory and Diagnostic Testing Clinical Reasoning 30 Older Adults Anatomy and Physiology Overview Skin, Hair, and Nails Head and Neck Eyes and Vision Ears and Hearing Nose, Mouth, and Throat Thorax and Lungs Heart and Neck Vessels Peripheral Vascular and Lymphatics Breasts and Lymphatics Abdomen, Metabolism, and Elimination Musculoskeletal Neurological Male and Female Genitourinary Endocrine Immune System Frailty and Geriatric Syndromes Cultural Considerations Urgent Assessment Subjective Data Collection Interviewing the Older Adult Assessment of Risk Factors Health Promotion Cultural Considerations Objective Data Collection Promoting Patient Comfort, Dignity, and Safety Comprehensive Physical Examination: The Older Adult Instruments Evidence-Informed Critical Thinking Organizing and Prioritizing Common Laboratory and Diagnostic Testing Clinical Reasoning Nursing Analysis, Outcomes, and Interventions 31 Individuals with Obesity Demographics of Obesity Measuring Obesity Edmonton Obesity Staging System Contributors to Obesity Day-to-Day Struggles Psychology of Obesity Social Injustice Related to Obesity Weight Bias RESPECT: A Model for the Sensitive Treatment of the Bariatric Patient Anatomy and Physiology Overview Vital Signs Pain Blood Pressure Pulse Temperature Oxygen Saturation Respirations Skin Head and Neck Torso Extremities Genitalia Endocrine and Metabolic Functioning Dyslipidemia/Hyperlipidemia Cultural Considerations Urgent Assessment Subjective Data Collection Assessment of Risk Factors Health Promotion Building Self-Esteem and Confidence Physical Activity Weight Reduction Nutrition Assessment Bariatric Consultation Medications Surgical Health-Promoting Options Gastric Bypass Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy Duodenal Switch Focused Health History Related to Selected Common Symptoms and Signs Objective Data Collection Promoting Patient Comfort, Dignity, and Safety Comprehensive Physical Examination: The Individual with Obesity Initial Survey Physical Examination Evidence-Informed Critical Thinking Organizing and Prioritizing Common Laboratory and Diagnostic Testing Diagnostic Imaging Clinical Reasoning Lifespan Considerations Older Adults Women Who Are Pregnant Children and Adolescents Unit 5 Pulling It All Together 32 A Complete Health Assessment Acute Assessment Subjective Data Collection Areas for Health Promotion Assessment of Risk Factors Demographic Data History of Present Concern or Illness Past Health History Growth and Development Review of Systems Psychosocial History Functional Health Status Activities of Daily Living [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 312 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$39.00
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Oct 19, 2022
Number of pages
312
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Oct 19, 2022
Downloads
1
Views
146















.png)









