*NURSING > EXAM > NR 351 Week 2 exam with answers - Wagner College (A grade) | NR351 Week 2 exam with answers - A grad (All)
NR 351 Week 2 exam with answers - Wagner College (A grade) | NR351 Week 2 exam with answers - A grade
Document Content and Description Below
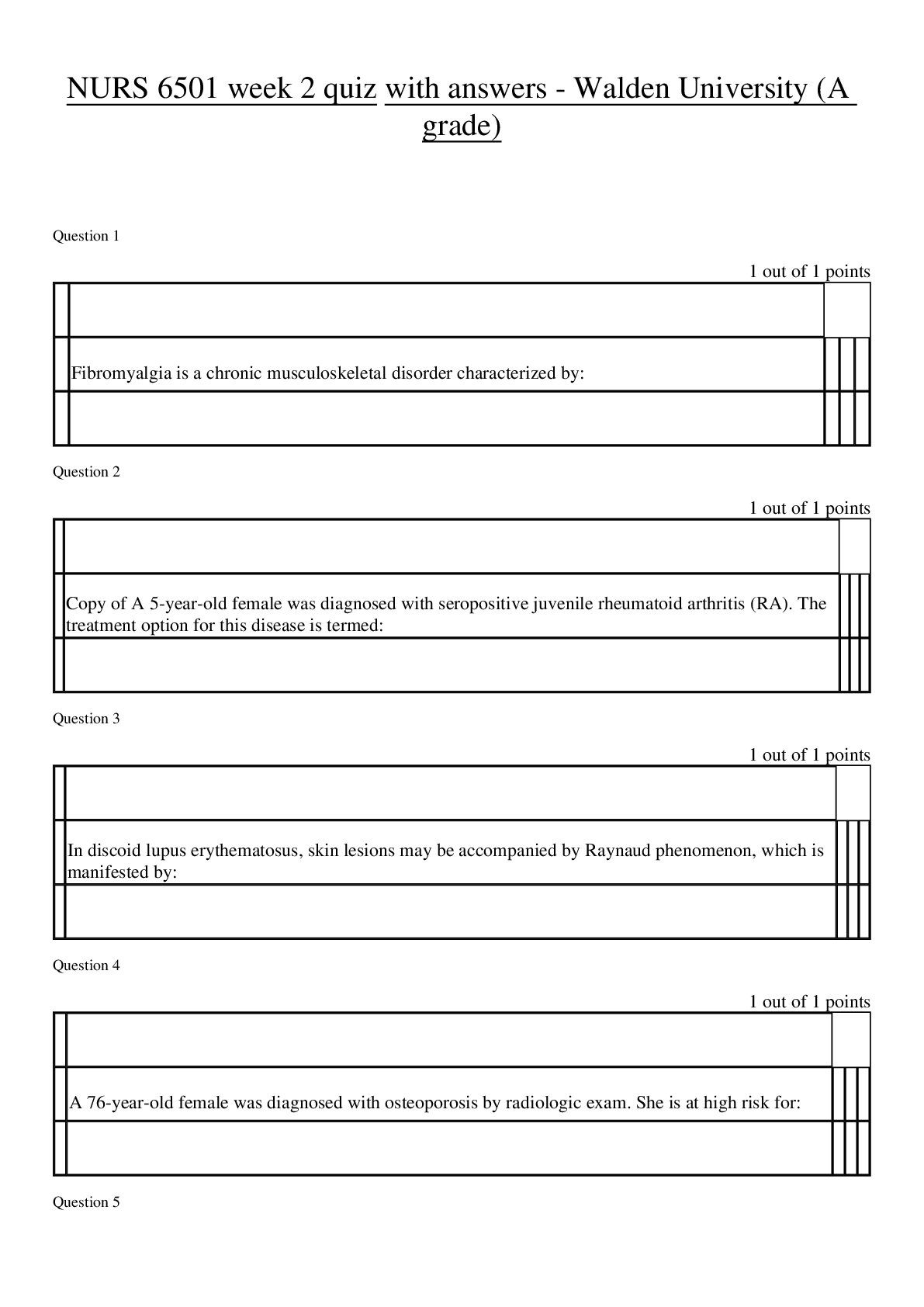
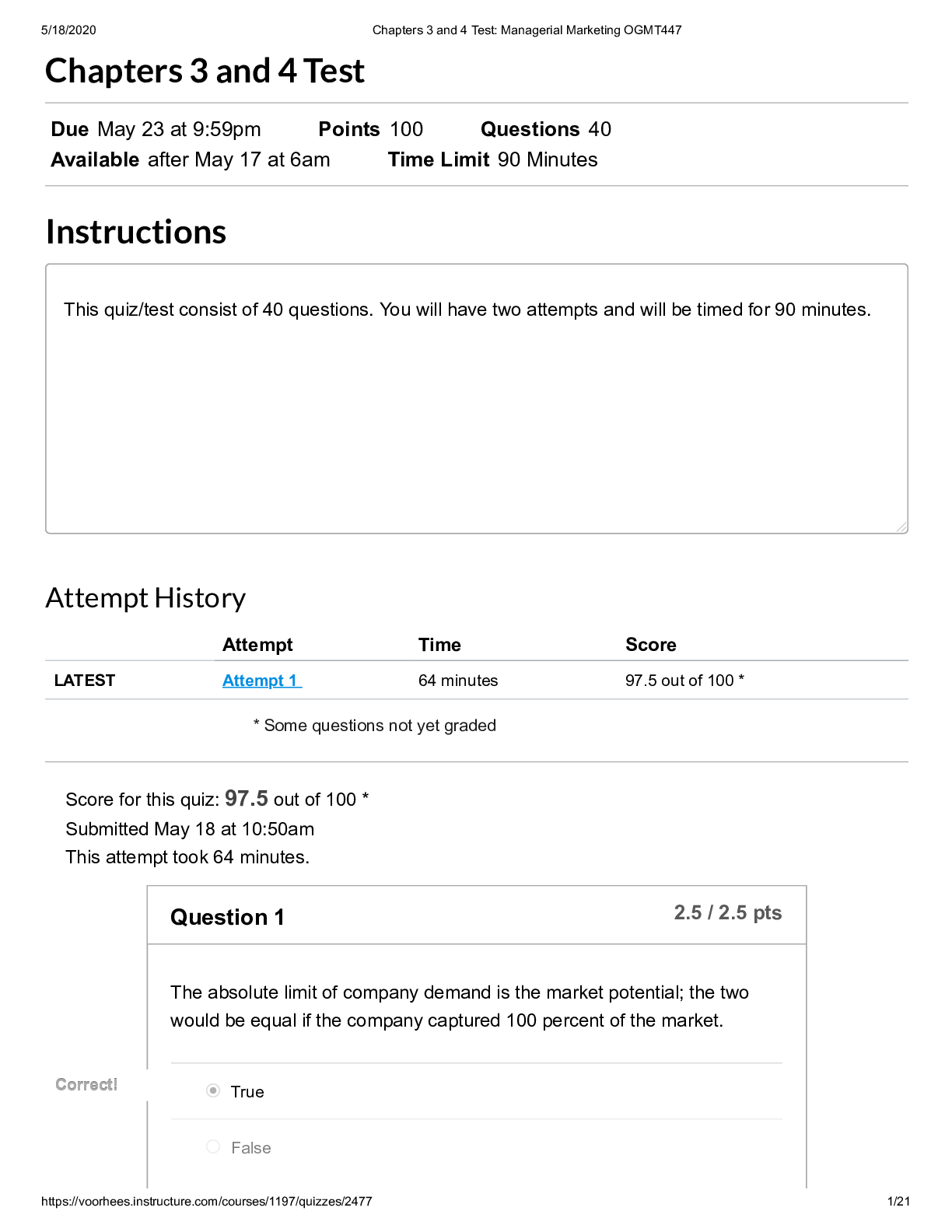
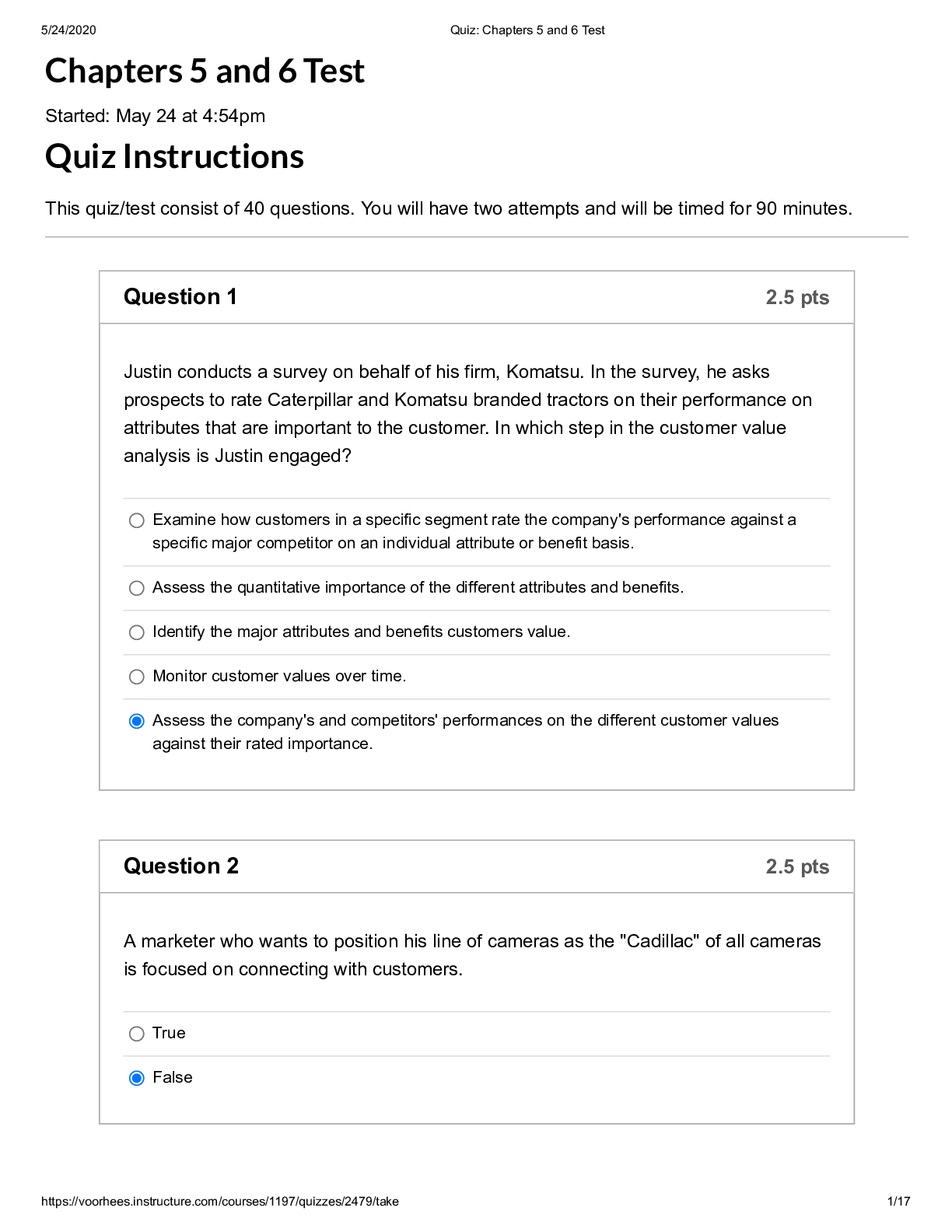
NR351 Week 2 exam with answers - Wagner College (A grade) NR 351 EXAM 2 Chapter 3 Health- a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being, not the absence of disease or infirmity ... Illness- the unique response of a person to a disease; an abnormal process involving changed level of functioning Wellness- an active state of being healthy by living a lifestyle promoting good physical, mental and emotional health Acute Illness- has a rapid onset of symptoms and lasts only a short time *Pain is most significant symptom— if needed, treatment resolves issue Ex/ appendicitis, pneumonia, diarrhea, common cold Chronic Illness- slow onset and may have periods of remission; irreversible altercation that requires long period of care Ex/ diabetes mellitus, lung disease, arthritis, lupus Stages of Illness Behavior • Experiencing symptoms- ex/pain,fever,rash • Assuming the sick role- defining yourself as sick • Assuming a dependent role- complying with treatment plan • Achieving recovery and rehabilitation – giving up dependent role Dimensions Affecting Health -Physical- genetic inheritance, age, developmental level, race and gender -Emotional- how the mind affects the body -Intellectual- cognitive abilities, educational background -Environmental- housing; sanitation; pollution; food -Sociocultural- economic level, lifestyle -Spiritual- beliefs and values Health Promotion Primary- directed toward promoting health and preventing the development of disease processes or injury Ex/ immunization clinics, family planning services, accident-prevention education Secondary- focus on screening for early detection of disease with prompt diagnosis and treatment of any found Ex/ assessing children for normal growth and development Tertiary- begins after an illness is diagnosed and treated with the goal of reducing disability and helping rehabilitate patients to a maximum level of functioning Ex/ coaching a diabetic through treatment and preventing complications Models of Health and Illness • Agent-Host-Environment Model- creates risk factors that increase the probability of disease • The Health-Illness Continuum- measures persons level of health • Views health as constantly changing • The Health Promotion Model- how people react to their environment as they pursue health • The Health Belief Model-what someone believes to be true about their health Risk factors- increases chance of illness -age/genetic factors/health habits/lifestyle/environment/physiologic factors Chapter 4 *individualized care Maslow’s Hierarchy of Human Needs -meeting basic needs restores health -common to all people; essential for health and survival 1. Physiologic oxygen- MOST ESSENTIAL water/food elimination/rest temperature sexuality/physical activity 2. Safety and Security physical and environmental components being protected from potential or actual harm ex/ proper hand hygiene; proper use of electrical equipment HIGHER LEVEL NEEDS 3. Love and Belonging understanding and acceptance of others in both giving/receiving love feeling of “belonging” unmet needs produce loneliness ex/widowers ex/include family and friends in care of patient 4. Self Esteem need for a person to feel good about oneself; sense of accomplishment; confidence; independence factors affecting: role changes; body image changes 5. Self Actualization acceptance of self and others as they are respect and happiness for all people ability to discriminate between good and evil Family Structures Family- any group of people who live together and depend on one another for physical, emotional, and financial support Nuclear Family- traditional family; two parents and their children Extended Family- includes aunts, uncles and grandparents Blended Family: two parents and their unrelated children from previous relationships Single-parent Family: may be separated, divorced, widowed or never married - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Promoting Regular Bowel Habits -timing -positioning -privacy -nutrition -exercise -Constipation Patients: -patients taking constipating medicines -depressed patients -reduced fluids or bulk diet -central nervous system diseases (MS, Paralysis) -Diarrhea Patients (frequent, loose, watery stool) -answer call bells immediately -“acute” = sudden onset ex/meal they ate -“chronic”= may last 4-6 weeks ex/ parasite -prevent food poisoning, which can cause diarrhea Methods of Emptying Colon of Feces • Enema- solution into large intestine to remove feces • Types of enemas: • Cleansing • Retention • Oil-retention: lubricate the stool and intestinal mucosa, easing defecation • Carminative: help expel flatus from the rectum • Medicated: provide medications absorbed through the rectal mucosa • Anthelmintic: destroy intestinal parasites • Large volume • Small volume • Rectal suppositories- inserted into rectum • Oral intestinal lavage- oral solution such as GOLYTELY to cleanse intestines of stool • Digital removal of stool- breaking up stool • Can be done manually- need MD order- very uncomfortable Nasogastric Tubes (into nose and down stomach) -inserted through nasopharynx -pliable single or double lumen -drains the stomach of fluid or unwanted stomach contents -used to allow GI tract to rest before surgery or promote healing; monitors bleeding Types of Ostomies -Sigmoid colostomy (L) -Ascending colostomy (R) -Transverse colostomy (M) -Descending colostomy (L) ALL bring piece of colon onto the outside of abdomen -location depends on where you are removing from -farther along on the colon = more formed feces -ileostomy – part of ileum removed -attachment is called a STOMA – pink/moist on skin Colostomy Care (whether temporary or permanent) -keep the patient free of odors by emptying appliance frequently -inspect the stoma regularly- note size; keep skin around the stoma clean and dry ex/ pale stoma- anemia blue stoma- ischemia -measure patients fluid intake and output -explain and teach each aspect; support -Patient Teaching: -explain the reason for bowel diversion -demonstrate positive body image -verbalize related fears and concerns -describe follow-up care and support resources -encourage recommended diet and exercise -use medications only as needed -apply ointments or astringent (witch hazel) -do not want to negatively affect stool [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 15 pages
Instant download
.png)
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jan 18, 2021
Number of pages
15
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jan 18, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
51
.png)


















.png)
.png)
.png)

