NR 507 Week 2 Quiz - Questions & Answers_Graded A+
Document Content and Description Below
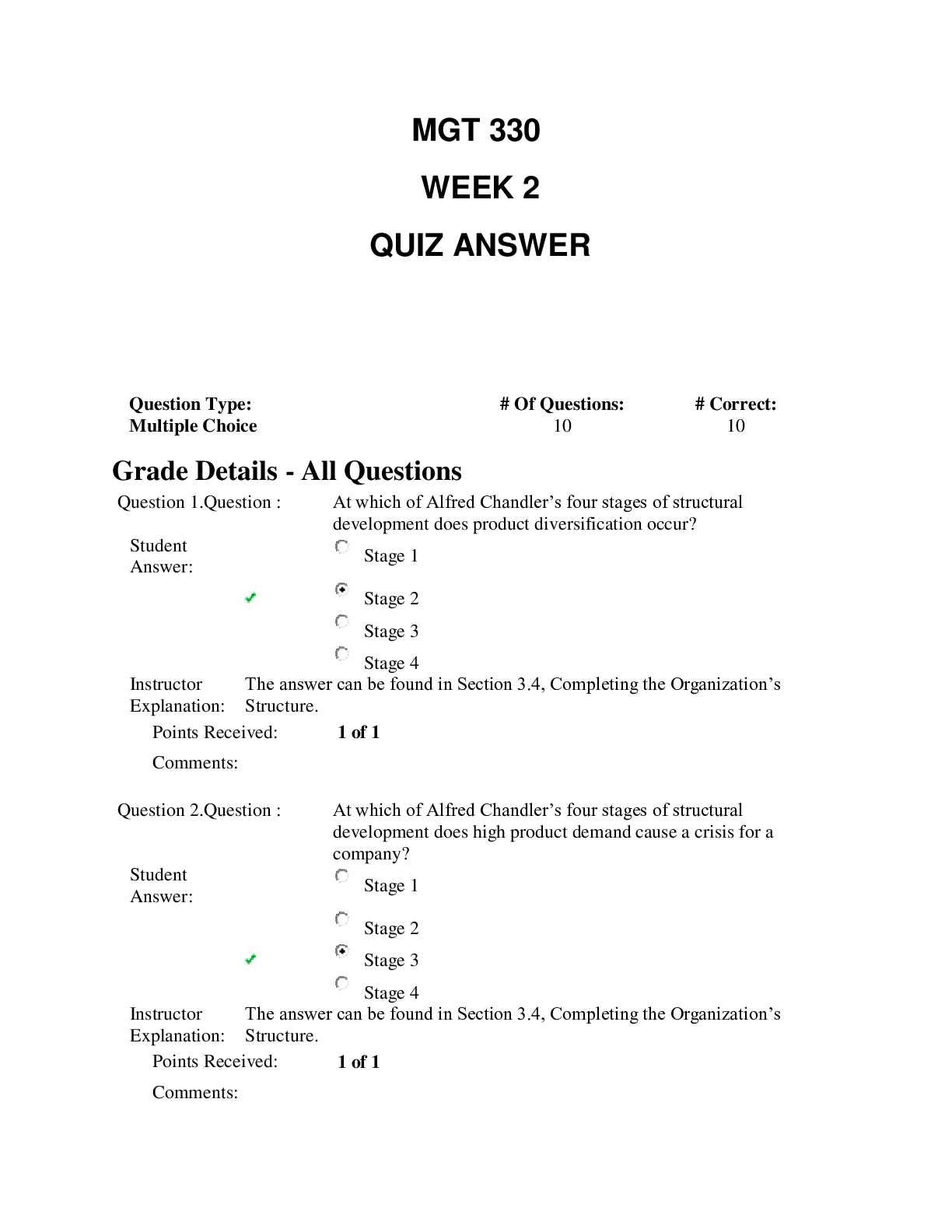
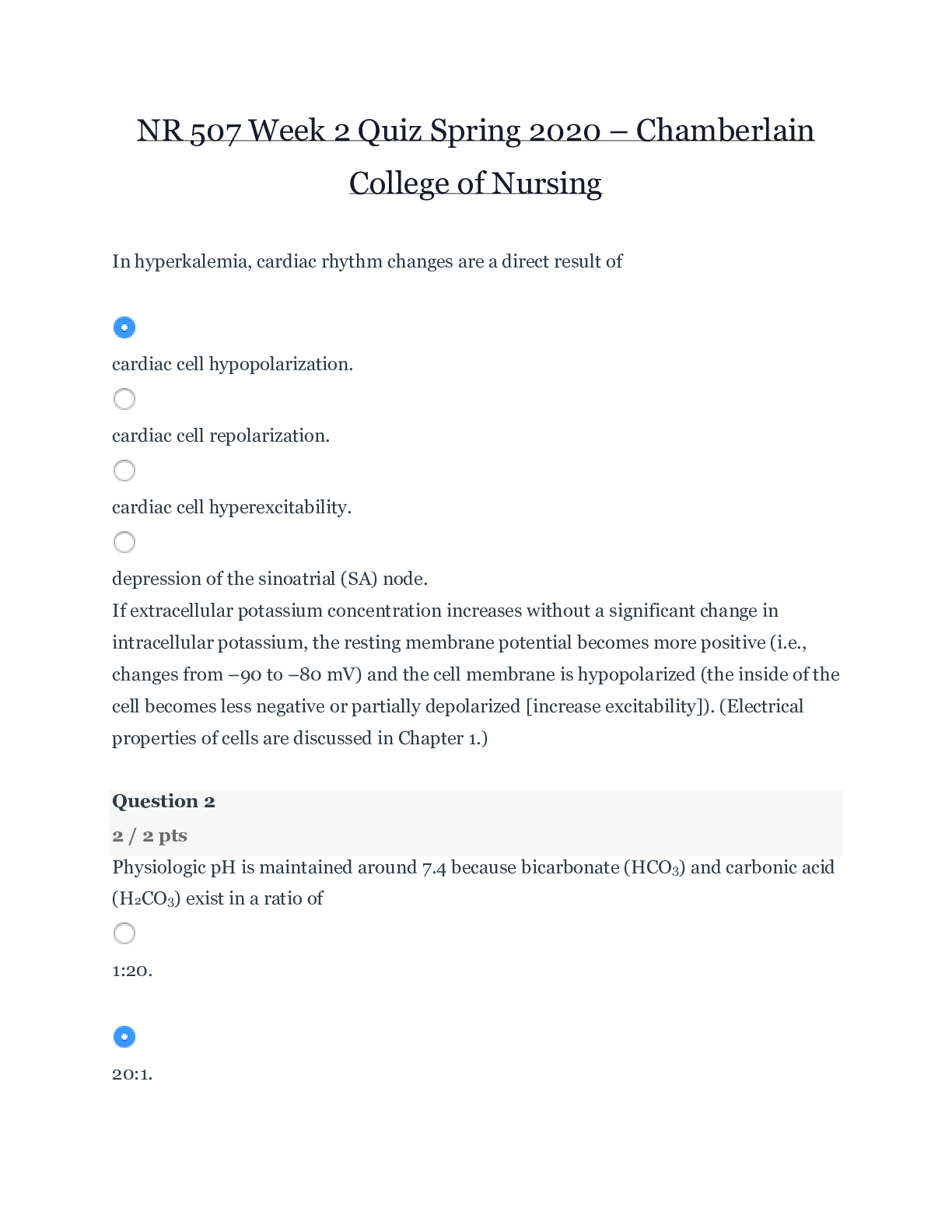
NR 507 Week 2 Quiz _ updated Questions & Answers – Chamberlain College of Nursing NR 507 Week 2 Quiz In hyperkalemia, cardiac rhythm changes are a direct result of (Pts. : 2) car... diac cell hypopolarization. When thirst is experienced, how are osmoreceptors activated? (Pts. : 2) By an increase in the antidiuretic hormone secreted into the plasma By an increase in aldosterone secreted into the plasma By an increase in the hydrostatic pressure of the plasma By an increase in the osmotic pressure of the plasma Which are indications of dehydration? (Pts. : 2) Decreased hemoglobin & hematocrit Muscle weakness & decreased deep tendon reflexes Tachycardia & weight loss Polyuria & hyperventilation At the arterial end of capillaries, fluid moves from the intravascular space into the interstitial space because the (Pts. : 2) interstitial hydrostatic pressure is higher than the capillary hydrostatic pressure. capillary hydrostatic pressure is higher than the capillary oncotic pressure. interstitial oncotic pressure is higher than the interstitial hydrostatic pressure. capillary oncotic pressure is lower than the interstitial hydrostatic pressure. Which enzyme is secreted by the juxtaglomerular cells of the kidney when circulating blood volume is reduced? (Pts. : 2) Angiotensin I Angiotensin II Aldosterone Renin Why are infants susceptible to significant losses in total body water (TBW)? (Pts. : 2) Because more than half of an infant’s body weight is water Because infants have a slow metabolic rate Because an infant’s kidneys are not mature enough to counter fluids losses Because they are unable communicate adequately when they are thirsty Physiologic pH is maintained around 7.4 because bicarbonate (HCO3) & carbonic acid (H2CO3) exist in a ratio of (Pts. : 2) 20:1. 1:20. 10:2. 10:5. In ARDS, alveoli & respiratory bronchioles fill with fluid as a result of the (Pts. : 2) compression on the pores of Kohn, thus preventing collateral ventilation. increased capillary permeability, which causes alveoli & respiratory bronchioles to fill with fluid. inactivation of surfactant & the impairment of type II alveolar cells. increased capillary hydrostatic pressure that forces fluid into the alveoli & respiratory bronchioles. Dyspnea is not a result of (Pts. : 2) decreased pH, increased PaCO2, & decreased PaO2. decreased blood flow to the medulla oblongata. stimulation of stretch or J-receptors. fatigue of the intercostal muscles & diaphragm. Clinical manifestations of pulmonary hypertension include (Pts. : 2) systemic blood pressure greater than 130/90. productive cough & rhonchi bilaterally. dyspnea on exertion & paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea. peripheral edema & jugular venous distention. Pulmonary edema usually begins at a pulmonary capillary wedge pressure or left atrial pressure of _____ mm Hg. (Pts. : 2) 10 20 30 40 Clinical manifestations that include unexplained weight loss, dyspnea on exertion, use of accessory muscles, & tachypnea with prolonged expiration are indicative of (Pts. : 2) chronic bronchitis. emphysema. pneumonia. asthma. Which pleural abnormality involves a site of pleural rupture that act as a one-way valve, permitting air to enter on inspiration but preventing its escape by closing during expiration? (Pts. : 2) Spontaneous pneumothorax Tension pneumothorax Open pneumothorax Secondary pneumothorax A(n) _____ is a circumscribed area of suppuration & destruction of lung parenchyma. (Pts. : 2) consolidation cavitation empyema abscess Which of the following is a true statement? (Pts. : 2) Hypoventilation causes hypocapnia. Hyperventilation causes hypercapnia. Hyperventilation causes hypocapnia. Hyperventilation results in an increased PaCO2. High altitudes may produce hypoxemia through (Pts. : 2) shunting. hypoventilation. decreased inspired oxygen. diffusion abnormalities. The most successful treatment for chronic asthma begins with (Pts. : 2) elimination of the causative agent. broad-spectrum antibiotics. drugs that reduce bronchospasm. drugs that decrease airway inflammation. In tuberculosis, the body walls off the bacilli in a tubercle by stimulating (Pts. : 2) macrophages that release TNF-. phagocytosis by neutrophils & eosinophils. formation of immunoglobulin G to initiate the complement cascade. apoptotic infected macrophages that activate cytotoxic T cells. The release of fibroblast growth factors affects ARDS by causing (Pts. : 2) atelectasis & decreased lung compliance. disruption of alveolocapillary membrane. pulmonary hypertension. pulmonary fibrosis. An accurate description of childhood asthma is that it is a(n) (Pts. : 2) obstructive airway disease characterized by reversible airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperreactivity, & inflammation. pulmonary disease characterized by severe hypoxemia, decreased pulmonary compliance, & diffuse densities on chest x-ray. pulmonary disorder involving an abnormal expression of a protein producing viscous mucus that lines the airways, pancreas, sweat ducts, & vas deferens. obstructive airway disease characterized by atelectasis & increased pulmonary resistance as a result of a surfactant deficiency. What is the primary cause of RDS of the newborn? (Pts. : 2) An immature immune system Small alveoli A surfactant deficiency Anemia Cystic fibrosis (CF) is caused by a(n) (Pts. : 2) autosomal recessive inheritance. autosomal dominant inheritance. infection. malignancy. Chest wall compliance in infants is _____ in adults. (Pts. : 2) lower than higher than the same as unlike that Which of the following types of croup is most common? (Pts. : 2) Viral Which of the following statements about the advances in the treatment of RDS of the newborn is incorrect? (Pts. : 2) Administering oxygen to mothers during preterm labor increases their arterial oxygen before birth of the fetus. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 month ago
Preview 1 out of 6 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 06, 2020
Number of pages
6
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 06, 2020
Downloads
2
Views
126













 – CHAMBERLAIN COLLEGE OF NURSING.png)