*NURSING > EXAM > Chamberlain University College of Nursing: NR 341 Complex Health Quiz 1-4 Questions and Answers,100% (All)
Chamberlain University College of Nursing: NR 341 Complex Health Quiz 1-4 Questions and Answers,100% CORRECT
Document Content and Description Below
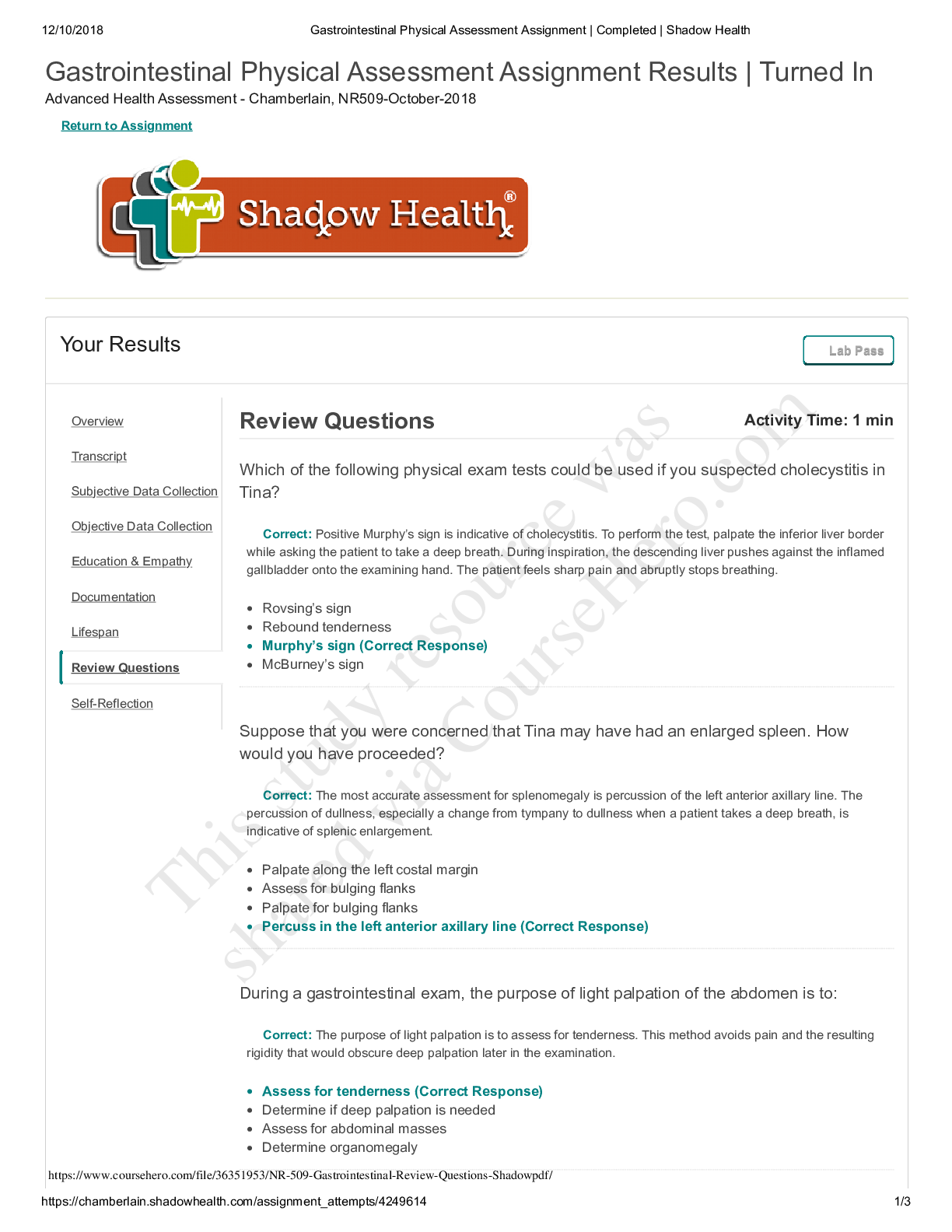
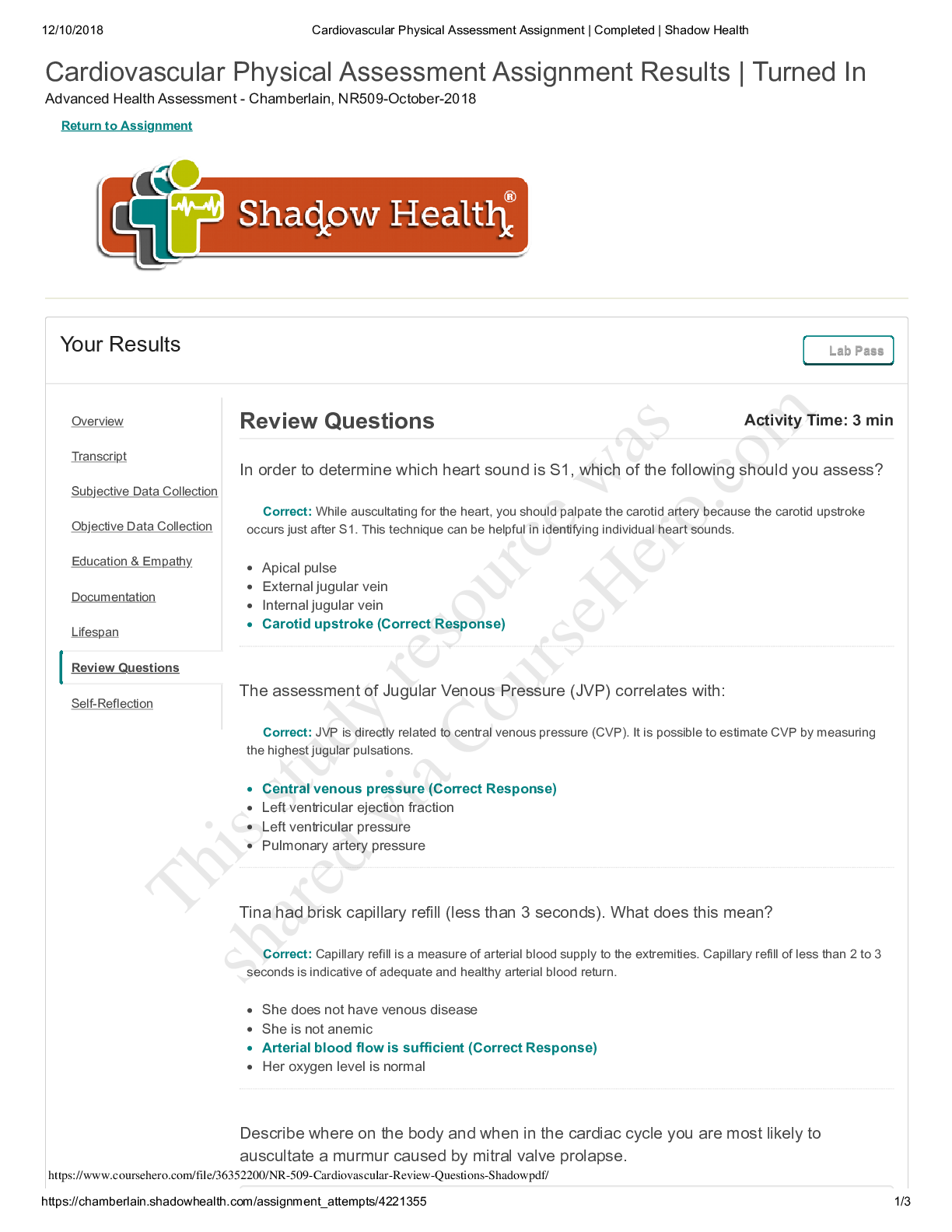
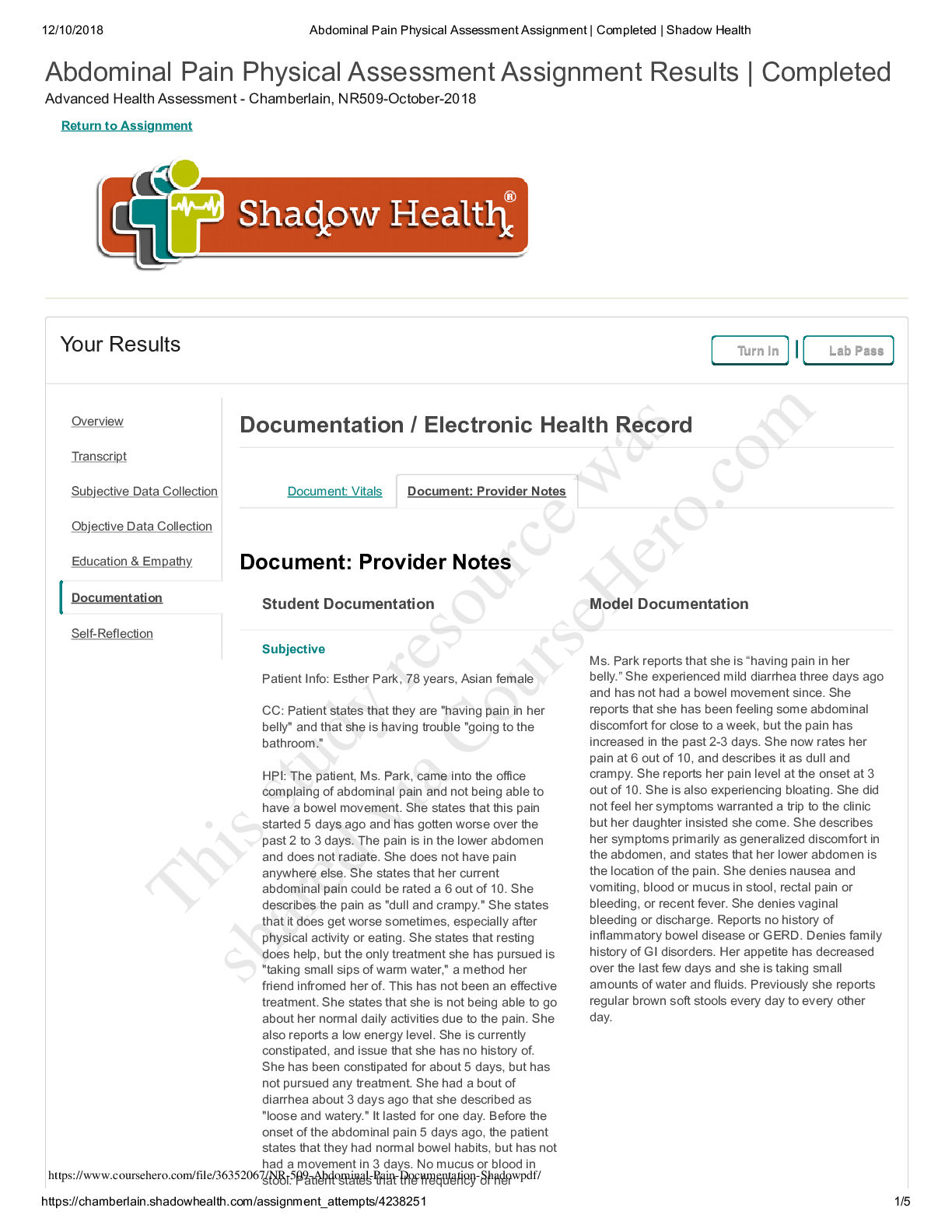
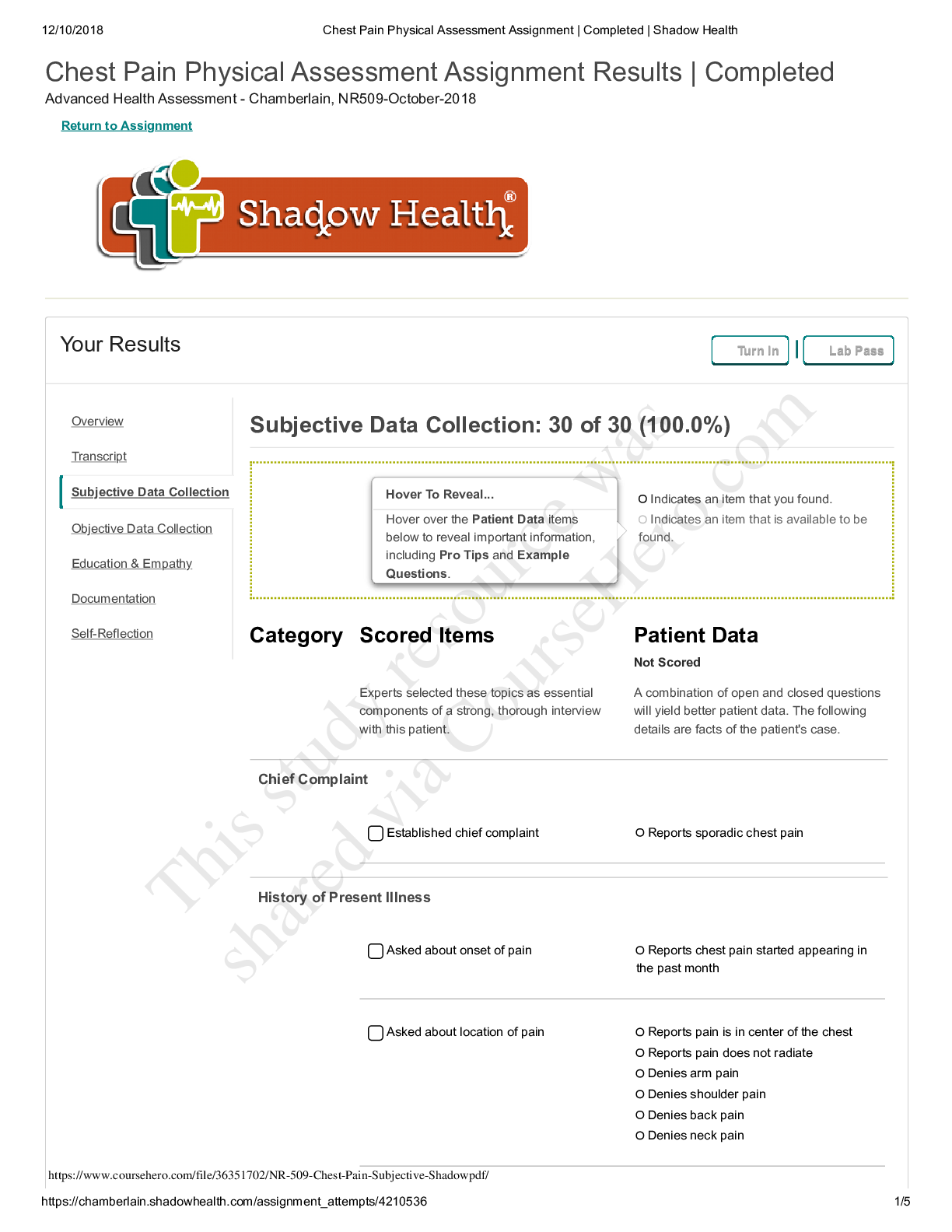
Chamberlain University College of Nursing: NR 341 Complex Health Quiz 1-4 Questions and Answers Complex health exam 1 The nurse is planning care for a patient with fluid volume overload and ... hyponatremia. Which intervention should be included in this patient's plan of care? Administer Intravenous fluids Restrict fluids Provide Kayexalate (sodium polystyrene sulfonate) Administer intravenous Normal Saline with Furosemide (Lasix) restrict fluids A patient's blood gas show a pH of 7.53 and bicarbonate level of 36 mEq/L. The nurse prepares to treat this patient for which acid-base disorder? Respiratory alkalosis Metabolic alkalosis Respiratory acidosis Metabolic acidosis Metabolic Alkalosis A patient's serum potassium is 2.2 mEq/L. Which nursing action is the highest priority for this patient? Intiate cardiac monitoring Intiate seizure precuations Administer Sodium polystrene (Kayexalate) as prescribe Start oxygen at 2L/ min initiate cardiac monitoring A 61 year old client is admitted with pneumonia. Her ABG results are pH 7.46, PaO2 94, PaCO2 30, HCO3 19, and SaO2 72%. The nurse interprets this as: Metabolic Alkalosis Respiratory Alkalosis Respiratory Acidosis Metabolic Acidosis Respiratory Alkalosis A client is brought to the emergency department with a suspected narcotic (heroin) overdose. The nurse anticipates that assessment findings and ABGs will reveal: restlessness and hypoxemia agitation and alkalosis decreased level of consciousness and acidosis tachypnea and acidosis decreased level of consciousness and acidosis A nurse is admitting a client who reports nausea, vomiting, and weakness. Upon assessment, the client has dry oral mucous membranes, temperature 38.5 C (101.3 F), pulse 92/min, respiration 24/min, skin cool with tenting present, and blood pressure 102/ 64 mm Hg. His urine is concentrated with a high specific gravity. Which of the following is not a clinical manifestation of fluid volume deficit? Decreased skin turgor Bradycardia Concentrated urine Low-grade fever Bradycardia A patient is being treated for an intestinal obstruction. The nurse inserts a nasogastric tube and attaches it to low continuous suction. Which acid base imbalance is the patient at risk for? Respiratory alkalosis Metabolic acidosis Metabolic alkalosis Respiratory acidosis Metabolic alkalosis A nurse is caring for a client who has a laboratory finding of serum potassium 5.7 mEq/L. The nurse should assess for which of the following clinical manifestations? Polyuria Constipation Hypotension EKG changes EKG changes A patient is diagnosed with severe hyponatremia. The nurse realizes this patient will mostly likely need which precautions implemented? Hypertensive precautions Infection precautions Neutropenic precautions Seizure precautions Seizure precautions What are common precipitating factors of hypoglycemia? Select all that apply. Hemodialysis Missing meals or snacks Excessive insulin Wrong type of insulin Missing meals or snacks, Excessive insulin,Wrong type of insulin The nurse is preparing patients newly diagnosed with diabetes mellitus (DM) for discharge from an acute care facility. What should the nurse include in patient teaching regarding medications to treat DM? Type 1 diabetes may progress to type 2 if blood glucose levels are not well controlled. Patients with type 1 diabetes will always need an exogenous source of insulin. Patients with type 2 diabetes generally need a combination of oral medications and insulin to achieve normal blood glucose levels. Patients with type 1 diabetes may achieve normal blood glucose levels with oral medications. Patients with type 1 diabetes will always need an exogenous source of insulin. The nurse instructs the client recently diagnosed with type 1 diabetes about proper meal planning. Which action should the nurse take first? Teach the client how to use the Exchange List for Meal Planning. Obtain a diet history that includes the client's favorite foods and usual meal patterns. Inform the client that 50-60% of calories should come from carbohydrates. Instruct the client about the importance of eating regular meals. Obtain a diet history that includes the client's favorite foods and usual meal patterns. The nurse understands that which type of insulin has the longest duration of action? Glargine (Lantus) Aspart (Novolog) Regular (Novolin R) NPH (Novolog mix 70/30) Glargine (Lantus) The client with diabetes mellitus requests a medication for headache soon after returning from an early morning x-ray procedure. The nurse observes the client is upset about the headache, angry at missing breakfast, and has moist hands. What priority action should the nurse take at this time? Acknowledge his dissatisfaction, offer to obtain a snack, and give the medication. Administer the medication for headache and arrange for a breakfast tray. Administer the headache medicine and review the day's lab test results. Check the blood glucose level and be prepared to give 4 ounces of juice immediately. Check the blood glucose level and be prepared to give 4 ounces of juice immediately A patient with diabetes mellitus has the flu and is not able to keep his food down. The nurse knows the patient needs more teaching when the patient states: I don't need to take my Metformin (Glucophage) because I haven't eaten and my blood sugar is going to be low I should try to drink some extra water I should try to find something to eat, so my blood sugar doesn't get too low I can take my Tamiflu (Oseltamivir) without worrying that it will affect my blood glucose I don't need to take my Metformin (Glucophage) because I haven't eaten and my blood sugar is going to be low The nurse knows that the patient is exhibiting when the patient wakes up with hyperglycemia without prior hypoglycemia because the patient has the growth hormone secreted at night. Prediabetes Somogyi effect Dawn Phenomenon Nocturnal hyperglycemia Dawn Phenomenon When administering sliding scale insulin, the nurse knows to check which of the below before administering? Select all that apply. Shake the vial to mix it good before administering How many calories the patient plans on eating Correct type of insulin Recent blood glucose level When the patient plans on eating Drug order and calculation Correct type of insulin Recent blood glucose level When the patient plans on eating Drug order and calculation Mr. Glick is a 52 year old male with Type 2 Diabetes. Mr. Glick wants to start exercising more because his HgbA1C is 7.2%. The nurse knows that it is important to tell the patient which of the following? The patient must use good fitting shoes during his workout Make sure the patient knows the symptoms of hyperglycemia, which can be induced from exercise If the patient starts sweating, he must stop immediately because he could be hypoglycemic The patient should only be checking his glucose after he exercises The patient must use good fitting shoes during his workout When caring for a male client with diabetes, the nurse assesses for which of the following chronic complications of diabetes? Hypoglycemia Erectile dysfunction Diabetic ketoacidosis Icteric sclera Erectile dysfunction A diabetic patient complains of frequent corns and asks for information about managing the condition. What is the nurse's best response? "Make sure you select shoes that fit correctly." "Apply a generous amount of emollient lotion on and between the toes twice daily." "You can use corn pads to gradually remove the growths." "Corns are best treated by shaving them off." "Make sure you select shoes that fit correctly." A newly admitted patient has a fasting serum blood glucose level of 125 mg/dL. How should the nurse interpret this value? The patient has type 1 diabetes. This is a critical value that should be reported immediately. The patient may be prediabetic. The patient has normal glucose metabolism. The patient may be prediabetic. The nurse is assessing a patient who has a family history of type 2 diabetes. Which finding would require follow-up by the nurse? The patient reports having a new prescription for prednisone for asthma exacerbation. The patient delivered a baby that weighed 8 pounds and 10 ounces. Measurements indicate the patient has decreased the waist-to-hip ratio through dietary changes. The patient's fasting blood glucose level is 95 mg/dL. The patient reports having a new prescription for prednisone for asthma exacerbation. The nurse recognizes that which factor in a patient's history increases the risk for type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM)? Body mass index of 23 Physical inactivity Low waist-to-hip ratio Blood pressure of 130/80 Physical inactivity A nurse is planning care for a client to prevent postoperative atelectasis. Which of the following interventions should the nurse include in the plan of care? Select all that apply. Encourage the use of incentive spirometry every 2 hours Instruct client to splint incision when coughing and deep breathing Reposition the client every 2 hours Administer antibiotic therapy Assist with early ambulation Assist with early ambulation,Reposition the client every 2 hours, Instruct client to splint incision when coughing and deep breathing When a patient is experiencing hypotension in the PACU, what are some of the assessments that the nurse would expect to see in addition to the hypotension? An increased heart rate and warm flushed skin A decreased heart rate and warm flushed skin A decreased heart rate and cold, clammy, pale skin An increased heart rate and cold, clammy, pale skin An increased heart rate and cold, clammy, pale skin The nurse takes an informed consent document to the patient's room in preparation for an emergency surgical procedure. The patient states, "Doc said he would tell me all about the surgery when he gets here. Do you know what they are going to do?" What is the nurse's best response? "Go ahead and sign this so we will have that part done when the physician gets here." "Let's wait on signing this until your physician has talked to you." "I am not certain; let me call the nursing supervisor to explain it to you." "Let me go get a medical surgical textbook so I can use the pictures to explain the procedure." "Let's wait on signing this until your physician has talked to you." During the course of a surgical procedure, the patient's heart rate increases and the blood pressure drops. Which care provider would address these physiological changes? Anesthesiologist Registered nurse first assistant (RNFA) Scrub nurse Surgeon Anesthesiologist During a surgical procedure, the patient begins to demonstrate signs of malignant hyperthermia. The nurse would expect to participate in which actions in the care of this patient? Provide 21% oxygen Hydrate by increasing oral intake Apply a cooling blanket Administer calcium-channel blockers Apply a cooling blanket Pause for the Cause, also known as STO (surgical time out) is a Joint Commission Universal Protocol aimed at preventing wrong- surgery, wrong-site, and/or wrong- person surgery is compatible with which of the following statements: This procedure is by the scrub nurse and circulating nurse just before the first incision Pause for the Cause or STO places responsibility for wrong site/procedure/patient solely with the individual surgeon This procedure is done just after the induction of anesthesia All personnel in the operating room stop what they are doing to pay attention to the identification of patient, procedure, and site All personnel in the operating room stop what they are doing to pay attention to the identification of patient, procedure, and site A 75-year-old patient is received into the postanesthesia recovery room (PACU) following a 6-hour abdominal surgery. The patient's hemodynamic status is stable. Based on knowledge of the patient's surgery and the common postoperative complications the patient might be at risk for, the recovery room nurse would perform which interventions? Keep the room temperature at 75 degrees, consider supplemental oxygen, and provide warm blankets. You Answered Assess the patient's blood pressure more frequently than for younger clients and provide oxygen. Consider increasing the IV fluids, assess for urine output, and monitor the oxygen saturation. Provide postoperative instructions to avoid straining and eat a low-fiber diet. Keep the room temperature at 75 degrees, consider supplemental oxygen, and provide warm blankets. You Answered Mr. Davis is an asthmatic who is being discharged from the urgent care unit. His wheezing has improved. The nurse know that Mr. Davis understands his discharge instructions if he says "I should rinse my mouth out after I use the long acting steroid inhaler ". "I wait 25 minutes between my inhalation puffs". "I will able able to discontinue my medication once my asthma is controlled". " Quitting smoking is not needed with asthma". "I should rinse my mouth out after I use the long acting steroid inhaler ". The nurse understands oxygen therapy for a patient with COPD requires close monitoring because of which of the following? Hypoxic respiratory drive Hypercapneic respiratory drive Alkalotic respiratory drive Acidotic respiratory drive Hypoxic respiratory drive A client presents with dyspnea, pruritis, and localized swelling of the forearm after being stung by a bee. What is the priority nursing intervention? Check the tongue for swelling and listen for stridor Place the client in the Trendelenburg position Keep the client warm with soft blankets Remove the stinger from the client's arm Check the tongue for swelling and listen for stridor The nurse has been providing TB education to the patient. The nurse knows that teaching has been effective when the patient states which of the following? "My family does not need to get get tested too" "My family will not need to wear the mask when they visit me in the hospital" " I should not drink alcohol while taking TB medications" " after I take the antibiotics for 24 hours I can go to the cafeteria" " I should not drink alcohol while taking TB medications" The nurse is discussing the long-term care of a child with cystic fibrosis (CF) with the parents. Which goals should the nurse include in this plan? Maintaining antibiotic therapy to cure the disease Improvement of nutrition Preventing common neurologic complications Assure the patient understands the importance of using braces to walk Improvement of nutrition The nurse is assessing a patient with COPD for evidence of cor Pulmonale. Which of the following findings could indicate the presence of cor Pulmonale? Jugular vein distension Left ventricular hypertrophy Bibasalar crackles Cyanosis Jugular vein distension An important component of teaching a patient with sleep apnea is To elevate the head of the bed to 90o To avoid the use of nighttime sedatives To eat a large meal before bedtime To use the BiPAP only when he snores To avoid the use of nighttime sedatives The nurse is providing discharge teaching for a patient who was hospitalized for an exacerbation of chronic bronchitis. Which of the following points should the nurse not include in the teaching? Increase fluid intake Report fever or change in sputum to healthcare provider Perform 60 minutes of cardio 5X a week Complete all prescribed antibiotics Perform 60 minutes of cardio 5X a week A patient with a tracheostomy has a continuous pulse ox monitor. The SpO2 drops from 95-89%. Identify appropriate nursing actions for this patient. (Select all that apply). Suction the tracheostomy Give the prescribed bronchodilator Assess breath sounds Initiate mechanical ventilation Check the oxygen flow rate and connections Suction the tracheostomy, Give the prescribed bronchodilator, Assess breath sounds, Check the oxygen flow rate and connections A patient tells the nurse he has a "cold" every spring that lasts for 8 to 10 weeks. The nurse suspects that the patient is experiencing which condition? Vasomotor rhinitis Acute viral rhinitis Atrophic rhinitis Allergic rhinitis Allergic rhinitis A patient who had a Mantoux test for tuberculosis 2 days ago has a 2 mm area of erythema at the site of the test. How should the nurse evaluate this result? As indicating need for a repeat PPD As negative As positive for tuberculosis As indicating a sputum test for acid-fast bacilli is needed As negative The nurse is explaining what the ABG results mean to the client. How does the nurse explain an arterial pH of 7.47? Alkalosis Compensation Acidosis Homeostasis Alkalosis The nurse knows that the lungs act as an acid base buffer by decreasing the respiratory rate and depth when CO2 levels in the blood are low, increasing acid load. decreasing respiratory rate and depth when CO2 levels in the blood are high, reducing the acid load increasing respiratory rate and depth when CO2 levels in the blood are high, reducing acid load. increasing respiratory rate and depth when CO2 levels in the blood are low, reducing base load increasing respiratory rate and depth when CO2 levels in the blood are high, reducing acid load. The school nurse is assessing a teenage client who is anxious and presents with an increased respiratory rate. The client is complaining of headache, tingling, palpitations, and is having a difficult time focusing. The nurse would suspect which acid base disorder? Metabolic alkalosis Respiratory alkalosis Metabolic acidosis Respiratory acidosis Respiratory alkalosis The nurse is planning care for a patient who has just had a permanent tracheostomy following total laryngectomy. What should the nurse consider when planning this care? Select all that apply The patient will be unable to speak normally The patient will require enteral feedings until healed The family will be unable to communicate with the patient Writing will be an important form of communication immediately postoperatively The patient will require isolation until the site is healed Writing will be an important form of communication immediately postoperatively The patient will require enteral feedings until healed The patient will be unable to speak normally When a patient's airway becomes obstructed, which sign will the nurse see first? A sudden change in mentation A decrease in urine output The patient's hands become cold Pallor changing to cyanosis A sudden change in mentation An 81-year-old woman who lives alone is in the clinic for an annual physical. She reports that she has noticed that her sense of smell is not as acute as it used to be. Which nursing interventions are indicated? Recommend that the patient limit the amount she drives her car Ask the patient if she has a cat or dog living in her house Remind the patient of the need to change batteries in her smoke detectors twice a year Suggest that the patient use fewer spices when cooking Remind the patient of the need to change batteries in her smoke detectors twice a year A client who has been diagnosed with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis says, "I don't know what to expect. How will this disease affect my life?" Which nursing response is correct? "As long as you stay on your medication, the disease should not have a serious impact on how you live your life." "There really isn't a cure for this disease. You will have to work to manage symptoms as they arise." "There is no treatment for this disease, but it will go away on its own in the next few months. Then you will feel the same as you did before you got sick." "You will be pretty sick until you have surgery, but then you should feel well within 2 or 3 weeks." "There really isn't a cure for this disease. You will have to work to manage symptoms as they arise." Which of the following are ways for the nurse to recommend decreasing the risk for lung cancer? Low fat diet Annual chest x-ray screening NR 341 Exam 2 What kind of shock is this? ⬇ HR, CO, CI, CVP, SVR Neurogenic shock What kind of shock is this? ⬆ HR, ⬇ CO, CI, CVP, PAOP Anaphylactic shock What kind of shock is this? ⬆ HR, CVP, PAP, PAOP ⬇ CO, CI Obstructive shock What kind of shock is this? ⬆ HR, CVP, PAOP ⬇ CO, CI, Cardiogenic shock What kind of shock is this? ⬆ HR, SVR ⬇ CO, CI, CVP, PAOP, BP Hypovolemic shock What is MODS Multi organ dysfunction syndrome (SIRS can transition into MODS). What is the initial stage of shock? Slight drop of BP and slight increase in HR. most of the time HCP don't catch it. Patient feels fatigued. Give fluids and bed rest What is compensatory stage of shock? Lower BP than before but not a lot. Pale, tachycardia, and restless. Give antibiotics, fluid boils, and rest What is progressive stage of shock BP drops, hypoxia, oLiguria, rapid pulse, low PH, increased lactic acid, edema, SIRS. Give vasopressin's and fluids What is refractory stage of shock? Excessive cell/ organ damage. Hard to bring back. What is hypovolemic shock? loss of too much blood/fluid in the body What is treatment of hypovolemic shock? Stop the cause, give blood, or give NACL or LR (an isotonic fluid) What is cardiogenic shock? Occurs when the heart is damaged and unable to supply sufficient blood to the body (MI, myocarditis, myocardial contusion) will often hear crackles in the lungs What is the treatment for cardiogenic shock? What is obstructive shock? Conditions that obstruct the blood flow, decrease the perfusion to tissues. (Cardiac tamponade, tension pneumothorax, pericarditis, pulmonary embolism, severe HTN). treatment of obstructive shock Treat the blockage, rest, and fluid What is anaphylactic shock? an extreme, often life-threatening allergic reaction to an antigen to which the body has become hypersensitive. Treatment of anaphylactic shock Re-establishment of airway and oxygen therapy, administration of epinephrine to raise blood pressure and dilate bronchi, administration of diphenhydramine to block additional release of histamine, corticosteroids to help with inflammation, and fluids S/S of anaphylactic shock Priorities, flush, urticaria, throat fullness, anxiety, chest tight, SOB, lightheaded, altered mental status, respiratory distress. What is neurogenic shock? Injury to the spinal cord from T6 & up. blood vessels don't get signals from sympathetic nervous system treatment of neurogenic shock secure airway, spinal stabilization, fluid resuscitation, maintain MAP 85-90, treat bradycardia (atropine or pacemaker), crystalloid or vasopressor what is CVP and what does it monitor? central venous pressure measuring right ventriculr preload What should CVP be? 2-6 mmhg What do you do if CVP is too low? Give fluid bolus What do you do if CVP is too high? If body can't compensate give diuretics What is MAP and where should it be? Greater than 65. It measures adequate tissue perfusion. What should cardiac output be? 4-6 L/min ejection fraction measurement of the volume percentage of lef t ventricular contents ejected with each contraction. Should be 60-70% What is cardiac index? Takes into effect the body surface area and if they are getting enough blood flow according to size. Should be 2.5-4 L/min hemodynamic monitoring the use of pressure monitoring devices to directly measure cardiovascular function. BP cuff or arterial line to measure pressure at 300 mg What is an overdamped arterial line? Kink in line or decreased flow in circuit What is an underdamped arterial line? Too much extension tubing and can't get accurate reading. What are arterial line complications? Thrombosis (flush line), embolism, hemorrhage, infection What does a central line measure for hemodynamics Measures the CVP What are CVP complications: Pneumothorax, hemothorax, dysthymia's, heart puncture, infection What is a pulmonary artery catheter? Flow directed catheter with a balloon at the tip that allows the catheter to be "floated" into the pulmonary artery to measure SVR. What is the VAP bundle? HOB 30-45 degrees Awaken daily and assess readiness to wean Stress ulcer prophylaxis (give PPI or H2 blockers) DVT prophylaxis Oral care (chlorohexidine twice per shift) What happens when PEEP is used too long? Barotrauma (pneumothorax) What is a high pressure alarm on ventilator? Kink in line, secretions, biting, coughing, or fighting vent What is low pressure alarm on ventilator Disconnected from patient or machine, not giving O2 What is respiratory acidosis? Inability to excrete CO2. Hypoventilation. Patient with be jittery, disoriented, drowsy, confused, and headaches from increased ICP What is respiratory alkalosis? Hyperventilation and excretes too much CO2. ⬇ potassium, tachycardia, numbness, seizures, increased anxiety, irritable, hyper reflexes What is metabolic acidosis An accumulation of acids as a byproduct of metabolism. DKA, kussmauls respirations, renal failure, change in LOC, shock, warm flushed skin, headache. What is metabolic alkalosis? elevation of HCO3- usually caused by an excessive loss of metabolic acids. Severe vomiting, diarrhea, ng tube suctioning, restless, lethargic, dysthymias, hypoventilation, confusion, tremors, muscle cramps. What is normal PaO2 range? 80-100 mmHg What is bumatadine? Diuretic What could suctioning without hypoventilation cause? PVCs with irregular pulse What is a normal blood sugar for a patient in the ICU 60-150 How can you tell if a patient is in pain while sedated? Grimacing, tachycardia, tachypnea, wiggling What lab test is measure for heart failure? BNP- over 100 is bad What diagnostic test reveals fluid in the lung fields? Chest xray What diagnostic test tells us an ejection fraction and what should it be? Echocardiogram 60-70% Management of heart failure? Diuretics How much oxygen do you give with a nonrebreatjer mask? 10-15 L What is a hypertensive crisis? > or = 180 or a diastolic > or = 120 mm Hg or higher or MAP greater than 150. damages blood vessels. They become inflamed and may leak fluid or blood. As a result, the heart may not be able to pump blood effectively. How do you treat hypertensive crisis? Labetalol or hydralazine IV push. That doesn't work do a drip. Nitroprusside, nicardapine, or nitroglycerine. Complications of hypertensive crisis Nephrosclerosis, aortic dissection, HF, stroke!, peripheral vascular disease (eyes and kidneys) What diagnostic procedure do you to for pericarditis? Pericardiocentesis or pericardial window S/S of pericarditis Complaints of chest pain, worsens with cough, swallow, inhalation. Relieve sitting forward, pericardial friction rub, st segment in all leads. Tx for pericarditis NSAIDs, colchicine, steroids, indomethacin, toradol. Antibiotics. Percardiocentesis or window Diagnostic test for endocarditis TEE looking for vegetation Treatment for endocarditis Antipyretics and antibiotics. S&S with right sided HF Edema, increased CVP, JVD, hepatomegaly, and ascites Left sided HF Crackles, rales, exertional dyspnea, cough NPPV noninvasive positive pressure ventilation- treating patients with inadequate breathing distress in the form of CPAP. NR 341 Exam 3 Review Immediate nursing interventions for a patient with a swollen PICC line. -Stop the infusion immediately and do not infuse anything else. -Notify HCP -Measure the circumference of the affected extremity and compare to baseline. Dietary considerations for a patient with end-stage renal disease. Decrease potassium intake What is the nurse's priority assessment upon a patient's return from dialysis? Obtain the patient's BP (fluid removal can cause hypotension) A patient in the ER complains of the "worst headache of their life," what do you suspect? Hemorrhagic stroke How do you test cranial nerve III? PERRLA Your patient has SIADH and their sodium level is 123. What is your priority intervention? Restrict fluid intake Where is McBurney's point? 1/3 the distance from superior iliac spine to umbilicus in the RLQ What are the steps of taking a patients blood glucose level? -Make sure that the test strips aren't expired -Identify the pt -Apply gloves -Clean the site with alcohol -Poke on the side of the finger pad -Wipe away the first drop of blood then collect the sample How do you draw up cloudy and clear insulin into the same syringe? *Clear before cloudy* 1. Wipe the top of both viles 2. Put air into cloudy 3. Put air into clear 4. Withdraw clear 5. Withdraw cloudy Important nursing actions prior to initiating tube feeding via NG tube -Check placement via x-ray -Check residual -Hook up feeding and re-feed amount removed to check residual What are the signs and symptoms of organ rejection? -Fever -Organ might stop working (I.e., dec. urine output for a pt with kidney transplant) -Flu-like symptoms (N/V, chills) A patient suffered a femur fracture, what are they most at-risk for? Fat embolism What are the signs and symptoms of autonomic dysreflexia? -High BP -Irritation -Sweating above level of injury -Nasal congestion -Cool below level of injury What kind of insulin drip will the nurse start for a patient in DKA? Regular insulin drip only Nursing considerations for a patient with Bell's palsy -Educate that this occurs suddenly, causes facial drooping, and must run its course and goes away on its own. -Offer emotional support and reassurance. What are the signs and symptoms of liver cirrhosis? -Abd distention (ascites) -Rigid abd -Jaundice -Easily bruised -Confusion -Esophageal varices What are the diabetes sick day rules? -Stay hydrated (240-360 mL of water every hour) -Check urine for ketones A patient is septic and bleeding from their IV sites and in their stools, what do you suspect is going on? DIC Signs and symptoms of peritonitis in a patient receiving peritoneal dialysis How do you assess the neurovascular status of a patient with a cast on? -Check the cap refill, temp, and pulses of the affected extremity. -Ask if the pt is experiencing tingling and numbness. -Ask if they can wiggle their fingers/toes. What is included in a primary survey for the care of an emergency patient? • Aims to identify life threatening conditions so appropriate interventions can be started • Airway, breathing, circulation, disability, exposure and environmental control, facilitation of adjuncts and family, resuscitation adjuncts What is included in the secondary survey for the care of an emergency patient? • Begins after addressing each step of the primary survey and starting any life saving interventions • Brief, systematic process that aims to identify all injuries • History, head to toe assessment • Inspect posterior surfaces Describe the onset or initiation phase of AKI Initial insult, onset of event Describe the oliguria phase of AKI Urine output <400ml/24 hrs, accompanied by increase in serum concentration of substances usually excreted by kidneys Describe the diuresis phase of AKI Gradual increase in urine output, daily urine output 1-3L per day (due to osmotic diuresis) signals that filtration has started to recover, kidneys has recovered ability to excrete wastes but not to concentrate the urine, observe closely for hyponatremia, hypokalemia, dehydration Describe the recovery phase of AKI Signals the improvement of renal function(increasing GFR), may take 3-12 months What lab values are associated with AKI? -Hyperkalemia -Hyponatremia -Metabolic acidosis -Increased BUN and Cr -Hypovolemia -Reduction in urine output What is CN I and how do you assess it? Olfactory (sensory): smell. Have pt identify familiar scent with eyes closed. What is CN II and how do you assess it? Optic (sensory): vision and pupil reactivity to light and accommodation. Snellen chart, identify number of fingers with one eye closed. What is CN III and how do you assess it? Oculomotor (motor): eyelid elevation, most EOMs, pupil size and reactivity. PERRLA; have patient look up, down, side to side with eyes only. What is CN IV and how do you assess it? What is CN V and how do you assess it? Trigeminal (mixed): chewing, facial and mouth sensation, corneal reflex. have pt hold mouth open while you try to close it. What is CN VI and how do you assess it? Abducens (motor): EOMs Have pt move eyes from side to side What is CN VII and how do you assess it? What is CN VIII and how do you assess it? Vestibulocochlear (sensory): hearing, equilibrium. Use a tuning fork, whisper in eear, etc. What is CN IX and how do you assess it? Glossopharyngeal (mixed): gagging/swallowing, taste. Have pt swallow, touch back of throat with tongue depressor What is CN X and how do you assess it? What is CN XI and how do you assess it? What is CN XII and how do you assess it? Hypoglossal (motor): tongue movement, articulation of speech. Have pt stick out tongue and move it side to side; assess articulation. What are the symptoms of SIADH? • Low urine output, increased body weight, headache, weakness • Urine chemistry (Think CONCENTRATED; Increased urine sodium; Increased urine osmolality0 • Blood chemistry (Think DILUTED; Decreased serum sodium; Decreased serum osmolality) What is the treatment for SIADH? • Fluid restriction • Loop diuretic (if sodium at least 125 mEq/L) • Monitor intake and output • Monitor vital signs • Assess lung sounds for pulmonary edema, signs of heart failure • Daily weight When are vasopressor receptor antagonists contraindicated in the treatment of SIADH? Contraindicated in patients with liver disease What is diabetes insipidus? -Deficiency of ADH from decreased secretion of ADH from posterior pituitary or decreased renal response to ADH What is syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone? -Abnormally high production of ADH (secreted by the posterior pituitary) -Increased permeability of the renal distal tubule and collecting duct which leads to the reabsorption of water What are the clinical manifestations of DI? • Polydipsia, polyuria (4-30L/day of dilute urine) • Extreme thirst, hypotension, tachycardia What is the water deprivation test for the treatment of DI? »Measures kidneys ability to concentrate urine, determines causes of diabetes insipidus (DI) »Fluid withheld for a specific number of hours »Controlled setting to monitor for dehydration »Baseline sodium and urine osmolality »Hourly urine samples, blood samples every 2 hours »Dose of vasopressin or desmopressin (analog of ADH) given with urine osmolality tested after 30-60 minutes (Central DI: increase in osmolality and decrease in urine output) What is the treatment goal for the treatment of DI? Maintenance of fluid and electrolyte balance What is the treatment for Central DI? »Desmopressin (analog of ADH) can be given orally, subcutaneously, IV or nasal spray »Assess pulse, BP, level of consciousness, intake/output What is the treatment for nephrogenic DI? »Hormone therapy has little effect »Dietary measures (low sodium diet- decreases urine output) »Thiazide diuretics (reduces flow to ADH sensitive distal nephrons) »Indomethacin (increases renal responsiveness to ADH) What is Addisonian crisis? -Triggered by stress, sudden withdrawal from corticosteroid hormone therapy, adrenal surgery or sudden pituitary gland destruction -Hypotension (can lead to shock), fever, weakness, hypoglycemia, hyperkalemia What are examples of rapid-acting insulins? What is the onset, peak, and duration? Lispro, aspart, glulisine. Onset: 10-30 min Peak: 30 min-3 hr Duration: 3-5 hr What are examples of short-acting insulins? What is the onset, peak, and duration? Regular insulin. Onset: 30 min-1 hr Peak: 2-5 hr Duration: 5-8 hr What are examples of intermediate acting insulins? What is the onset, peak, and duration? NPH. Onset: 1.5-4 hr Peak: 4-12 hr Duration: 12-18 hr What are examples of long acting insulins? What is the onset, peak, and duration? Glargine, detemir, degludec. Onset: 0.8-4 hr Peak: less defined or no pronnounced peak. Duration: 16-24 hr What are examples of inhaled insulins? What is the onset, peak, and duration? Afrezza. Onset: 12-15 mins Peak: 60 min Duration: 2.5-3 hr Complex Health Quiz 4 What is the most common fracture location -Ulna/Radius What is the most common type of fracture in children Greenstick Greenstick fracture Bending and incomplete break of a bone What is present in stage 1 of bone healing Inflammatory process What is the biggest risk with an open fracture Infection What are the S/S that a fat embolism is present -Sudden change in vital signs -Sudden change in LOC -SOB -Petechiae Where is the most common location of a fat embolism Femur Rhabomyolysis -Characterized by muscle necrosis -Muscles release myoglobin Why can rhabo cause kidney failure Increased myoglobin in the body which is toxic on the renal system What is the treatment of rhabo -Fluid replacement -Temporary dialysis (sometimes) What color will the urine be if a patient had rhado Dark brown/red Acute compartment syndrome -Imbalance of muscle, bloof and nerves within the fascia compartment What is the cause of compartment syndrome Result of inflammatory process What are the 5 P's on compartment syndrome -Pain -Paraylysis -Parethesia -Poikelothermia -Diminished pulse quality What is the best non-invasive interventions for compartment syndrome -Elevation -Ice -Ensuring the cast is not too tight What is the surgical intervention for compartment syndrome -Cut open the affected area and keep open for at least 72 to allow the pressure to be relieved What is the most important intervention for all muscularskeletal injuries -Neurovascular assesement What is the one s/s that is different between a PE and fat embolism Petechiae will be present with fat embolism What is the first interventions for an actively bleeding wound -Pressure -Elevate ORIF Open Reduction and Internal Fixation What is the typical pain intervention for musculoskeletal injury -IV tylenol -Toradol (IV PB) -Tramadol (oral) 6 most important interventions to prevent muscularskeletal injury complications -Promote mobility -VTE preventioon -Infection prevention -Early dections of neurovascular changes -Pain management -Maintain issue integrity What patient population is SCI most common Elderly What is the most common cause of SCI MVC What can cause a SCI -Bone displacement -Ischemia to cord -Compression of cord Apootopsis Programmed cell death Why are definitive diagnosis of SCI not made until at least 72 hours Inflammatory process ends at 72 hours and sometimes it can be inflammation that is causing the SCI systoms What does the healing progression of SCI look like Stready improvement for about 6 months and then caps out What is spinal shock characterized by -Decreased reflexes -Loss of sensation -Paralysis below injury How long can spinal shock last Days to months S/S of neurogenic shock What causes the hypotension and bradycardia in neurogenic shock Sympathetic tissue injury How many vertebrae are there 33 -7 cervical -12 thoracic -5 lumbar -5 sacral -4 coccyx What is the skeletal level of injury How far down a patient still has skeletal involvement What is the neurologic level of injury How far up a patient still has feelings What are the two degress of SCI -Complete (full cord involement) -Incomplete (loss of sensatioon and movement below area of injury) Where is a lumbar puncture performed and why Below L2 to avoid injury to the spinal cord and nerves What is the biggest risk for SCI at C4 or higher -Inability to control resp center -Perminant vent w/ trach What is the biggest risk for SCI at T6 Autonomic hypereflexia What is the most common complication for cervival and thoracic SCI Pneumonia What organ systems will been involved with a thoracic SCI -GI -Decreased intercostal function -Decreased cough reflex Why are injuried at T6 at highest risk for neurogenic shock Dysfunction of SNS Neurogenic bladder -Do not have good bladder tone What can a decrease in bladder tone cause -Frequent and uncontrolled urination -Inability to urinate What are the interventions for neurogenic bladder -Indwelling catheter -Straight cath every 4-6 hours What is the biggest risk with indwelling catheter UTI What are issues with GI systems when SCI is present -Delayed gatric emptying which can cause N/V What is the med of choice when there is delayed gastric emptying and why is it given -PPI -Decreases risk of ulcer that could cause GI bleed Dysphagia difficulty swallowing Poikilothermism -Taking on the temperature of the environment below the level of injury What causes Poikilothermism Inability to shiver or sweat What is the most common cause of metabolic alkalosis NG sunctioning What is the treatment for metabolic alkalosis Treat cause of metabolic alkalosis What are the dietary needs for a patient with SCI High protein high calorie Nociceptive pain Dull and achey pain that feels internal Neuropathic pain Sharp, tingling and buring pain at and below site of injury Fantom pain Sensation of pain in limb that has been ampuated What is the #1 diagnostic study for SCI CT scan Why is CT scan important in possible SCI R/O head bleed Immediate nursing goals for SCI -Patent airway -Adeqauate ventilation/breathing -Adequate circulating blood Think ABC's Why is it so difficult to maintain systolic BP above 90 in a patient with a SCI Constant vasodialtion is occuring What can abominal grith show Abdominal bleeding What #1 sign of concussion Amnesia and repeating How often should vital signs be taken in a patient with SCI 5-10 minutes Would does a tender and firm abdomen indicate Bleeding in abdomen What types of meds are used in patients with SCI -Levenox -Vasopressors What is the most important thing to understand about GI dysfuntion and pharmacolical interventions in SCI GI dysfunction caused from SCI can decrease drug metabolism Where are contractures most common Hands What is the biggest risk for cardiac system in SCI Cardiac arrest due to dysthemias What would indicate a paralytic illius is present -Absent/hypoactive bowel sounds -Abdonominal pain -Abdominal distention What is the intervention for paralytic illius NG tube Is blanching of skin good or bad Good What is no blanching upon skin assesement indicative of Skin breakdown Automonic hypereflexia Significant vasoconstriction due to disfunction in ANS inabilty to stop SNS stimulation s/s of autonomic dysreflexia -Hypertension -Bardycardia -Pounding headache -Flushing -Sweating What is the biggest risk with autonomic dysreflexia Stroke What is the #1 interventions for autonomic dysreflexia Sit up to semi-fowlers position What level of injury is autonomic dysreflexia associated with T6 or higher What causes bradycardia in autonomic dysreflexia Vagus nerve (PNS) Why does bradycardia occue in autonmoic dysreflexia Bodies attempt to decrease BP S/S of Rhabo -Muscle spain -Dark brown/red urine -Tachycardia -Hypotension -Metabolic acidosis What causes the S/S of autonomic dysreflexia What is the lab value for rhabo CPK How is the amount of fluid replacement in Rhabo determined CPK levels Why is fluid replacement so important in rhabo -Washes out the myoglobin from kidneys -Myoglobin plugs up glomerlous that can cause AKI [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 41 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$15.00
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 30, 2023
Number of pages
41
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 30, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
76