Physics > QUESTION PAPER (QP) > AQA 2022// GCSE COMBINED SCIENCE: TRILOGY Foundation Tier Physics Paper 1F (All)
AQA 2022// GCSE COMBINED SCIENCE: TRILOGY Foundation Tier Physics Paper 1F
Document Content and Description Below
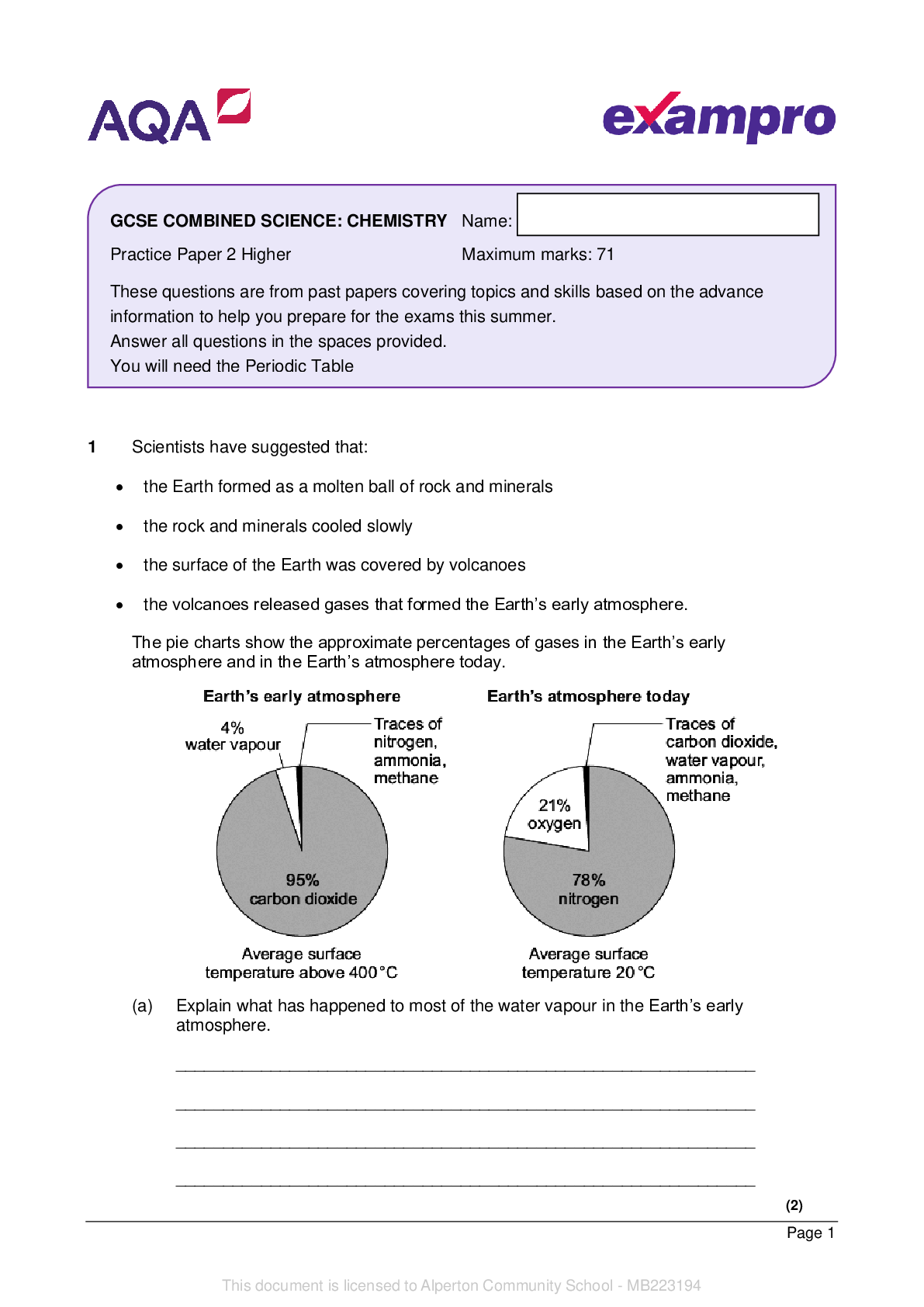
Materials For this paper you must have: • a ruler • a scientific calculator • the Physics Equations Sheet (enclosed). Instructions • Use black ink or black ball-point pen. • Pencil sh... ould only be used for drawing. • Fill in the boxes at the top of this page. • Answer all questions in the spaces provided. • If you need extra space for your answer(s), use the lined pages at the end of this book. Write the question number against your answer(s). • Do all rough work in this book. Cross through any work you do not want to be marked. • In all calculations, show clearly how you work out your answer. Information • The maximum mark for this paper is 70. • The marks for questions are shown in brackets. • You are expected to use a calculator where appropriate. • You are reminded of the need for good English and clear presentation in your answers. Please write clearly in block capitals. Centre number Candidate number Surname Forename(s) Candidate signature I declare this is my own work. GCSE COMBINED SCIENCE: TRILOGY Foundation Tier Physics Paper 1F F 2 *02* IB/M/Jun22/8464/P/1F 0 1 A student investigated how the potential difference across a filament lamp affects the current in the lamp. Figure 1 shows the circuit the student used. Figure 1 0 1 . 1 Figure 2 shows a circuit symbol. Figure 2 What component does the symbol represent? [1 mark] Tick () one box. Ammeter Battery Lamp Variable resistor Do not write outside the box 3 *03* Turn over ► IB/M/Jun22/8464/P/1F Do not write outside the 0 1 box . 2 Which component from Figure 1 did the student use to adjust the potential difference across the lamp? [1 mark] 0 1 . 3 When the voltmeter was not connected to the circuit it gave a reading of 0.4 volts. How can the student correct all the readings taken from the voltmeter? [1 mark] Tick () one box. Add 0.4 volts to each reading Divide each reading by 0.4 volts Multiply each reading by 0.4 volts Subtract 0.4 volts from each reading Question 1 continues on the next page 4 *04* IB/M/Jun22/8464/P/1F Do not write outside the box 0 1 . 4 The student recorded three values of current for each potential difference. Table 1 shows the results for 2.5 volts. Table 1 Potential difference in volts Current in amps 1 2 3 2.5 0.54 0.58 0.53 Calculate the mean current in the lamp. [2 marks] Mean current = A 0 1 . 5 Calculate the power of the lamp when the potential difference across the lamp was 4.8 V The current in the lamp was 0.75 A Use the equation: power = potential difference × current [2 marks] Power = W 5 *05* Turn over ► IB/M/Jun22/8464/P/1F Do not write outside the 0 1 box . 6 Calculate the resistance of the lamp when the potential difference across the lamp was 4.8 V The current in the lamp was 0.75 A Use the equation: resistance = potential difference current [2 marks] Resistance = Ω 0 1 . 7 Complete the sentence. Choose answers from the box. Each answer may be used once, more than once or not at all. [2 marks] decrease increase stay the same Increasing the current in a filament lamp makes the temperature of the lamp and the resistance of the lamp . Question 1 continues on the next page 6 *06* IB/M/Jun22/8464/P/1F Do not write outside the box 12 0 1 . 8 Which graph shows the relationship between potential difference and current for a filament lamp? [1 mark] Tick () one box. 7 *07* Turn over ► IB/M/Jun22/8464/P/1F Do not write outside the Turn over for the next question box DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAGE ANSWER IN THE SPACES PROVIDED 8 *08* IB/M/Jun22/8464/P/1F Do not write outside the 0 2 Figure 3 shows a lift near the bottom of a building. box The lift is attached by a cable to a counterweight. An electric motor moves the lift. The lift is moving up. Figure 3 0 2 . 1 As the lift moves up, how far does the counterweight move down? [1 mark] Tick () one box. A shorter distance than the lift. The same distance as the lift. A longer distance than the lift. 9 *09* Turn over ► IB/M/Jun22/8464/P/1F Do not write outside the 0 2 box . 2 What happens to the gravitational potential energy of the counterweight as it moves down? [1 mark] Tick () one box. It decreases It stays the same It increases 0 2 . 3 Calculate the change in gravitational potential energy of the lift when it moves up 4.0 m The mass of the lift is 1300 kg gravitational field strength = 9.8 N/kg Use the equation: gravitational potential energy = mass [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 37 pages
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 04, 2023
Number of pages
37
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 04, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
73

















.png)