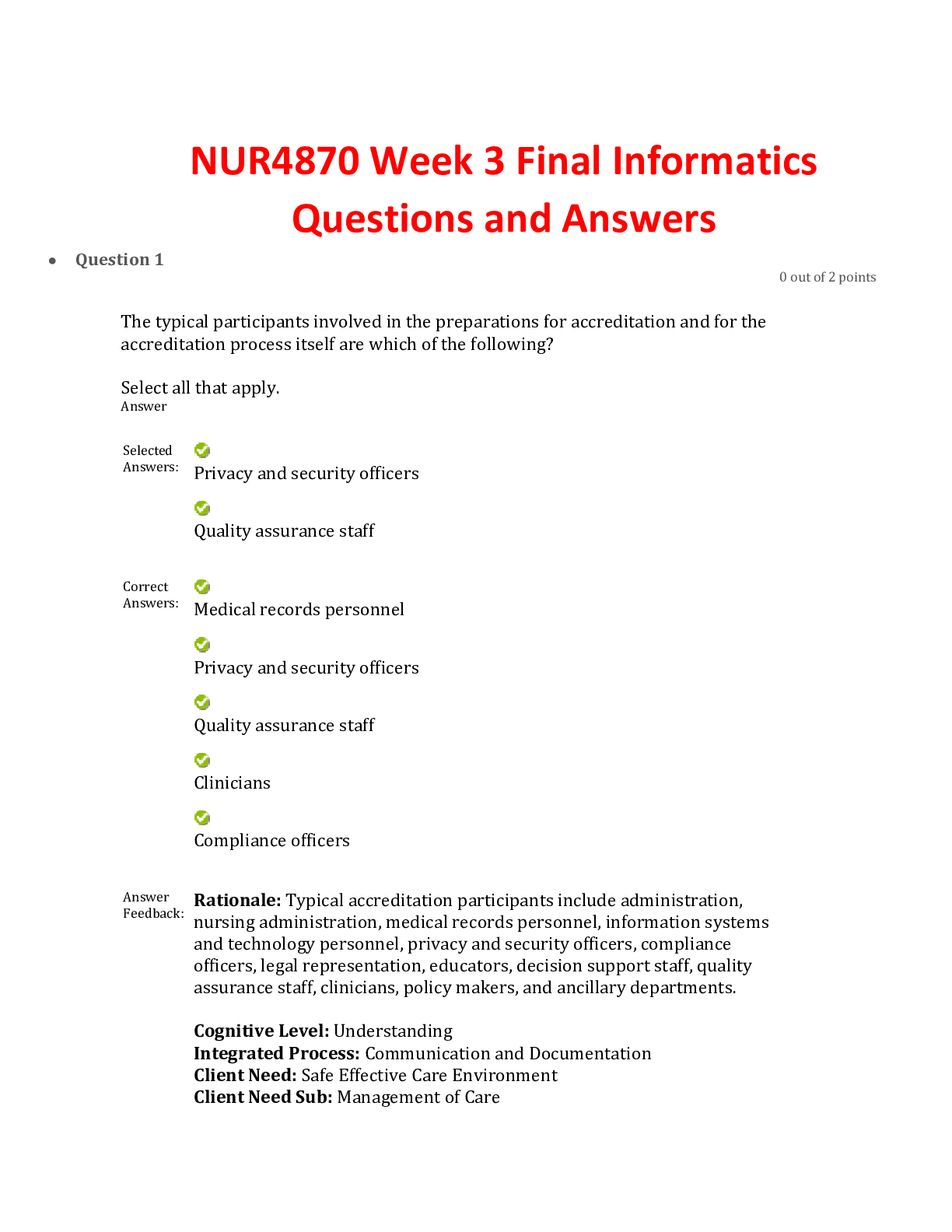
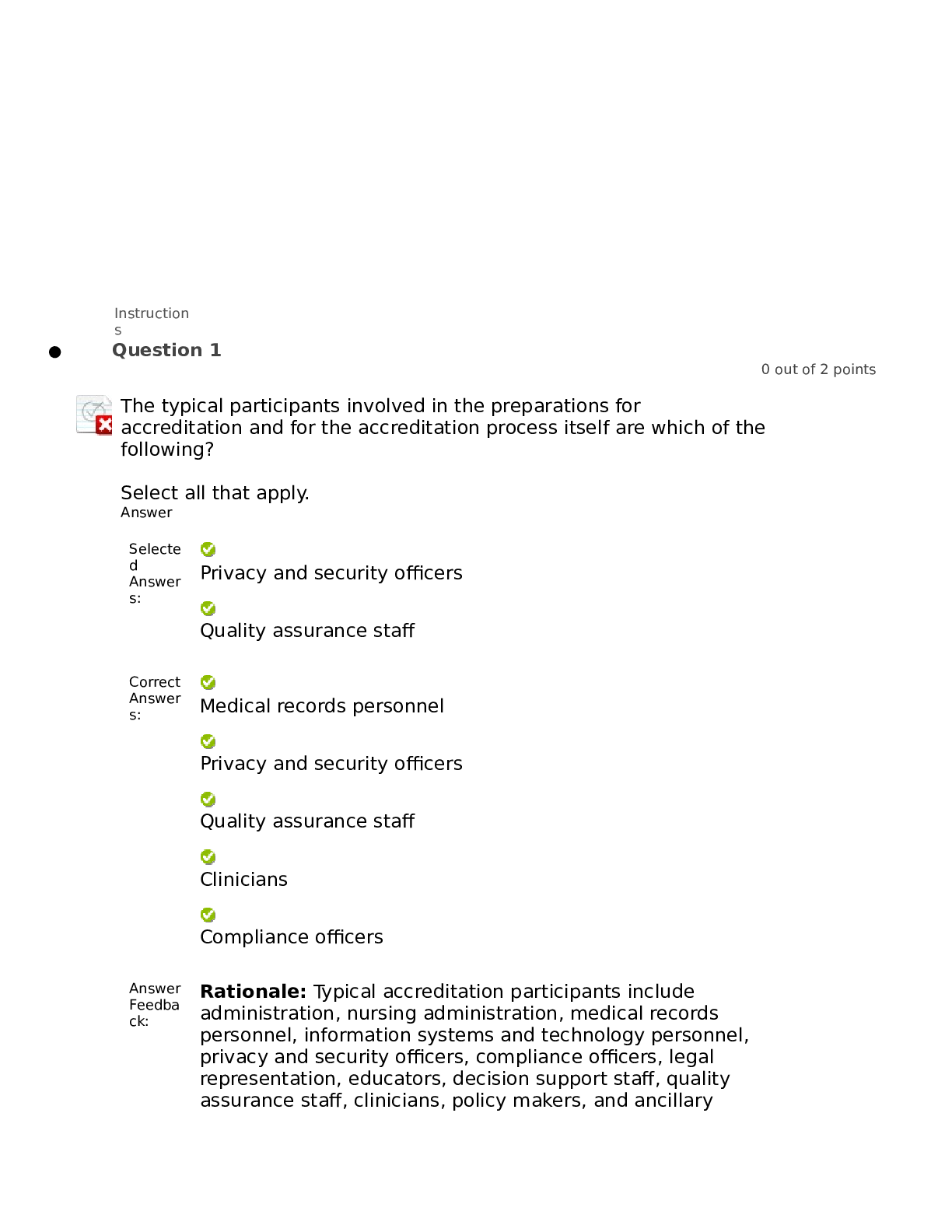
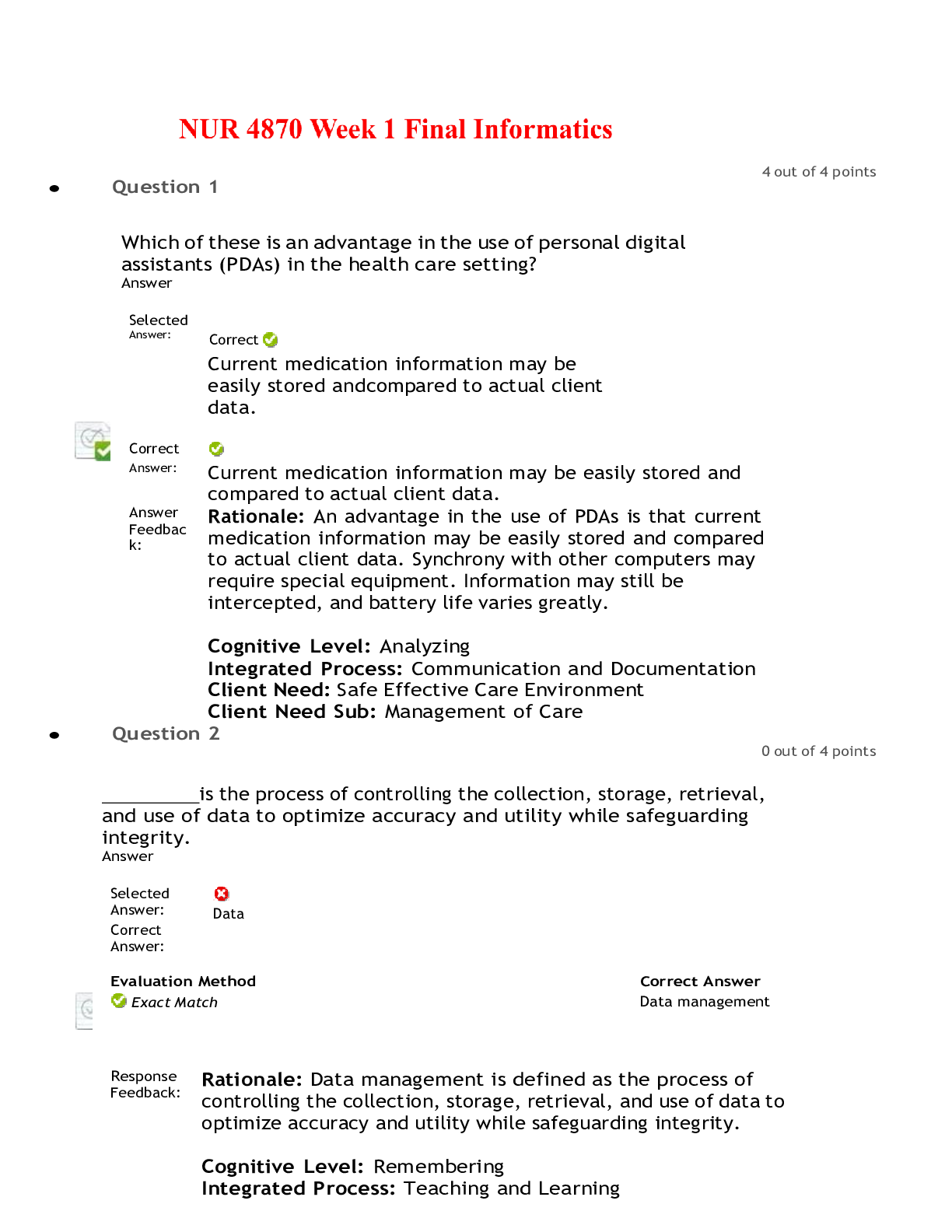
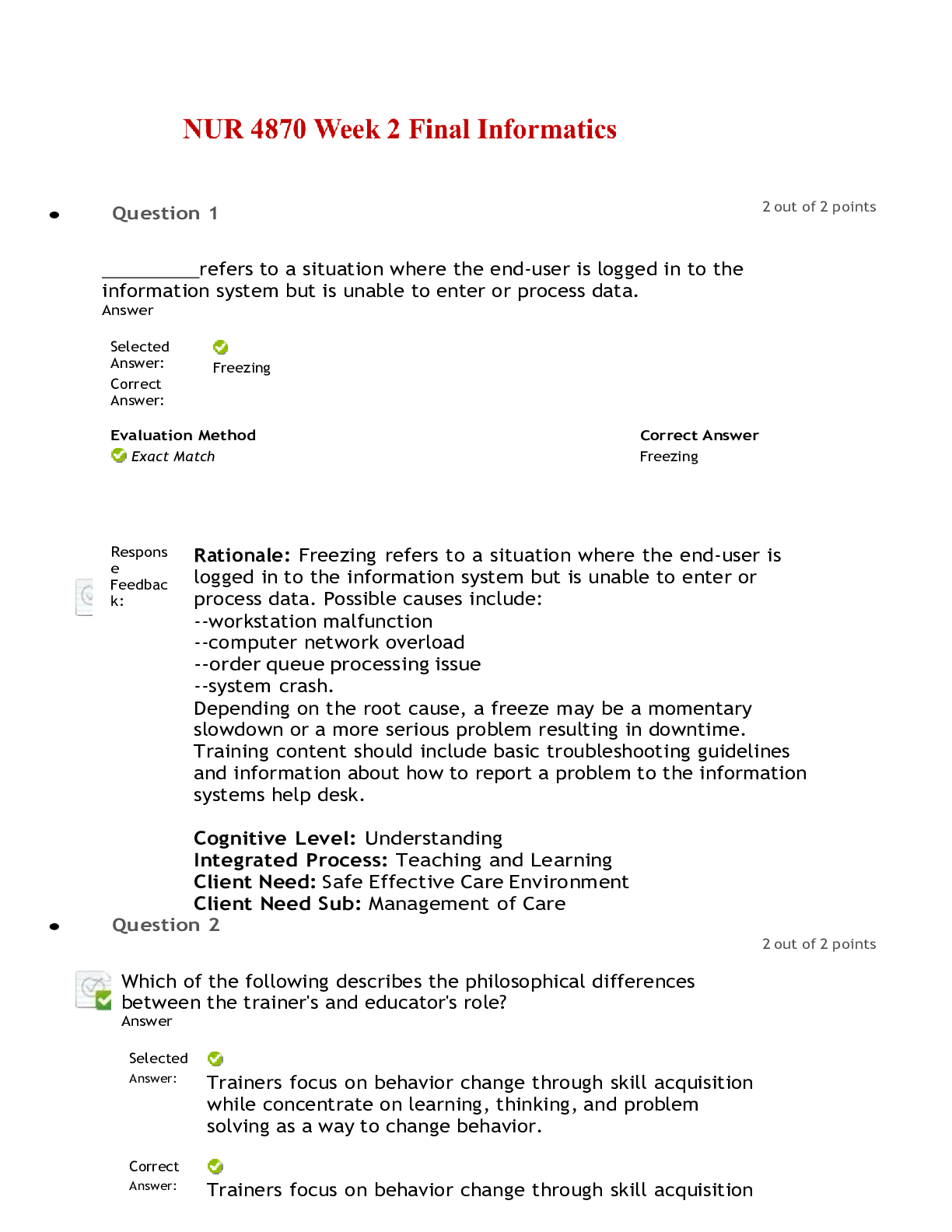
Health Computing > EXAM > WGU Nursing Informatics Questions and Answer (Verified) (All)
WGU Nursing Informatics Questions and Answer (Verified)
Document Content and Description Below
WGU D220 LATEST UPDATE (2022/2023)American Recover and Reinvestment Act (ARRA) Authorized INCENTIVE PAYMENTS to specific types of hospitals and healthcare professionals for adopting and using interope... rable Health Information Technology and EHR's. ARRA provides economic stimuli and incentives for the adoption of EHRs. Admission-Transfer-Discharge (ADT) System Classified under the hospitals' administrative info system. It's one of the foundational systems that allows operational activities such as bed placement, transportation coordination, room readiness, and the general coordination of services focused on the patient's phase of movement. Tracks a patient's activities and location from admission to discharge. Analytical Science Uses a variety of methods and instruments to answer 2 basic questions: What do I have? How much of it do I have? Environment, pharmacy, safety & security, fraud detection, and healthcare diagnostics. Asynchronous Applications Patient-centered and allows consumers to participate in their own care by using designated health technology to share health metrics and data with their healthcare provider via technology (remote patient-monitoring - the use of devices to capture patient data at one location and then transmit it electronically to healthcare professionals at a different location, allowing the review of data for clinical decision-making, i.e. MobileHealth). Audit Trails Software that is used for detecting security violations, performance problems, and flaws. Records activity by users and system. Goal is to improve data integrity. Audit trails are only one of the ways to ensure data integrity. An audit trail must contain the name of the user, the application triggering the audit, the workstation, the specific document, a description of the event being audited, and the date and time to determine the integrity of data. Authentication Action that verifies the authority of users to receive specified data. Barcode Medication Administration MANDATED BY FDA Benchmark The continual process of measuring services and practices against the toughest competitors in the healthcare industry. Comparing the performance of an organization or clinician to others. Big Data Very large data sets that are beyond human capability to analyze or manage without the aid of information technology. Big data is considered data originating from very large data sets that help identify patterns and trends. Big data cannot be managed without the use of technology to analyze its output. Clinical Decision Support System (CDSS) Supports healthcare practitioners in making patient-care decisions by integrating patient data with current clinical knowledge. CDSS is technology that provides recommendations for care and must be balanced with professional judgment, not used in place of it. Clinical Information System Software used to access client data, plan, implement, and evaluate care. May be specific to certain departments: lab, radiology, pharmacy, or particular patient populations. Provides patient centric decision-making functionality to help guide a nurse with decision-making while caring for a patient. Acquires patient data so that healthcare professionals can review it and use the information to deliver care. Computer Literacy Familiarity with the use of personal computers. Computer literacy is defined as the knowledge and ability to use computers and technology efficiently. Computer literacy allows patients to interact with the internet. Computerized Provider Order Entry (CPOE) The prescriber's decisions to enter orders and immediately share the orders with appropriate health professionals who execute the orders and departments that need to dispense, schedule, or immediately deliver services to patients. Confidentiality Unspoken understanding that private information shared in a situation, in which a relationship has been established for the purpose of treatment or delivery of services will remain protected. Configurability Refers to the extent that a given software product can be adapted or changed to meet a user's preference. Connected Health Model or platform by which technology assisted healthcare is delivered between at least two points, involving either synchronous or asynchronous exchange. Consolidated-Clinical Document Architecture (C-CDA) Allows interoperability of health information exchange between hospital systems. Consumer Health Informatics (CHI) Use of electronic information and communication to improve medical outcomes and health-care decision making from the patient/consumer perspective. Three barriers include: Privacy issues, cognitive disabilities, low health literacy. Five examples: Personal Health Records, Telehealth, Mobile Health, Games for Health, and Health 2.0. Telehealth is defined as healthcare at a distance through the use of technology that connects the patient and the clinician in real time. Continuity of Care Record (CCD) Snapshot of a person's health and healthcare to a provider who does not have access to the person's EHR. Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL) Primary database used for nursing literature. Data Collection of numbers, characters, or facts that are gathered according to some perceived need for analysis. Data Analysis The processing of data that identify trends and patterns of relationships. Data Information Knowledge Wisdom (DIKW) Framework Data are the most discrete components of the DIKW framework. They are mostly presented as discrete observations with little interpretation. Information is a continuum of progressively developing and clustered data. Relations and interactions are not yet evident in information alone. Knowledge is information that is processed and organized so that relations and interactions are identified. Wisdom is an appropriate use of knowledge to manage and solve human problems. Wisdom includes ethics or knowing why certain things or procedures should or should not be implemented in specific cases. Data Integrity Ability to collect, store, and retrieve correct, complete, and current data so that the data are available to authorized users when needed. Can be compromised by incorrect entry of information, data tampering, and system failure. Prevention by implementing security measures and audit trails. Data integrity is the state wherein data are uncorrupted, accurate, and valid. Data Mining Technique that look for hidden patterns and relationships in large groups of data using software. Data Scrubbing Data scrubbing is the process by which incorrect, incomplete, duplicate, or improperly formatted items are removed using special software designated for this purpose. Data Warehouse - Provides a powerful method of managing and analyzing data Decision Support Tool / Clinician Decision Support (CDS) / Decision Support System/Software (DDS) Software/app to help in the human decision process. The software will look at the patient's data and suggest appropriate medical/nursing interventions. It can also trigger prompts/alerts to the user. Requires human user input. Decreases patient safety risk and increases positive patient outcomes (ex: alerts for abnormal vitals, lab results, medication contraindications, etc.) The right components of a CDS include a trigger, such as a medication order; input data, such as lab values; intervention information, such as other options provided; and an action step, such as the action selected by the clinician. Electronic Health Record (EHR) A database of an individual's healthcare data during healthcare encounters. It's comprised of any patient data stored in electronic form. Electronic Medical Record (EMR) Legal record created in hospitals and ambulatory settings of a single encounter or visit that is the source of data for the electronic health record. Brings together diagnostic and treatment information for an individual in a specific healthcare setting. Electronic Medical Record Adoption Model (EMRAM) Measures clinical outcomes, patient engagement, and clinical use of EMR technology to strengthen organizational performance and health outcomes across patient populations. Basically, it evaluates Health Information Systems. Ergonomics Scientific study of work and space, including details that impact productivity and health Evidenced Based Practice (EBP) Current, best evidence for patient care. Improves the consistency and quality of patient outcomes. Foundation of clinical practice and guides clinicians. Found in stand orders (ex. Sepsis protocol). Expert System A type of CDS/DDS but does NOT need human intervention, uses artificial intelligence (ex. Insulin pump). *Fishbone A tool for analyzing the organizational processes and its effectiveness. Helps team members visually diagram a problem or condition's root causes, allowing them to truly diagnose the problem rather than focusing on symptoms Health Information Exchange (HIE) Electronic sharing of patient information between healthcare providers according to nationally recognized standards, allows insurance companies and providers to share data, must be secure and maintain integrity. It works by improving the speed, quality, safety, and cost of patient care. Query-based exchange is often used for unplanned events. Like a visit to the emergency department. It allows providers to find and request information on a patient from other providers. Directed exchange is used to support coordinated care and allows the ability to send and receive secure information electronically between care providers. Consumer-mediated exchange allows the ability for patients to review, manage, and control the use of their health information among providers. Health Information Technology (HIT) Various systems and technology used to record, monitor, and deliver patient care, as well as perform managerial and organizational functions. HIT is used to support systems that collect data needed for patient care, population health management, and for the sharing of this information within a secure system. Health Information Technology for Economic & Clinical Health Act (HITECH Act) The HITECH Act provides funds and incentives to increase EHRs by providers, improve policy decisions, and allocate services, funded workforce training, and new technology research. HITECH strongly recommends increasing meaningful use of HIT to decrease overall healthcare cost and to improve population health. Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) - Sets the national Standard of Personal Health Information. Legal Protection for PHI. Electronic transactions need to have HIPAA compliant codes. Signing into devices should require authentication encryption and should never be left unattended. Fines prior to 2/18/09 are $100/violation with a max of $25000 yearly. If after 2009, fine can be $100-50000+/violation, with a max of $1.5 million yearly. Criminal penalty fines can be up to $50000 and 1-year in jail. Health Level 7 (HL7) A standard/framework for the exchange of data (PHI) between information systems with an extensive set of rules that applies to all data that is exchanged, shared, integrated, or retrieved. Refers to both an organization and its standards to exchange data. Specifies how the data is coded Health Literacy Health literacy is more than just the ability to read and understand basic medical terminology and instructions. It is also the capacity of an individual to express their needs and preferences and to respond to the need for information about services provided for them. Low health literacy is not language dependent since it is also highly impacted by culture, ethnicity, race, environment, and social class. Health literacy involves teaching patients enough information about their illnesses and about how the health system works so that they can be legitimate partners in the appropriate management of their health. The most common challenge in advancing health literacy is assuming that patients understand the medical terminology that healthcare professionals are comfortable with. Health literacy is not restricted to knowing how to interact with the internet for their health information. Informatics INTERDISCIPLINARY FIELD. It is the science and art of turning data into information. Combines computer/decision/information/management/cognitive sciences and organizational theory. Informatics Innovator Expected to be educationally prepared to conduct informatics research, generate informatics theory, and have advanced understanding and skills in information management and computer technology. Informatics Specialist A nurse with advanced skills specific to health information management and computer technology with expertise in systems development life cycles. Information - Data that has been interpreted. Information Literacy Ability to recognize when information is needed as well as the skills to find, evaluate, and use needed information effectively. Information literacy is the knowledge and ability to locate, organize, use, communicate, and interpret print and electronic sources of information. Information Security Information has value and requires protection. Confidentiality Relationship has been established where private information is shared but not disclosed unless the patient givens permission. Phishing Deceptive method used to steal sensitive information. In phase 1, the recipient typically receives a phish, or e-mail. Phase 2 involves the victim following through on what they are asked to do, such as completing a form. Once the recipient completes the information, the hackers now have information that they can use for nefarious purposes. Privacy The right to control access, disclosure, nondisclosure, and the timing and extent to which information is disclosed. Integration Process by which two different information systems are able to exchange data in a way that is seamless to the end-user. Interface Computer program that tells 2 different systems how to exchange data. International Classification of Diseases-10th Revision (ICD-10) Is the international standard diagnostic classification for health-management purposes, and clinical use. The ICD diagnoses are used to classify mortality and morbidity data from inpatient and outpatient records. Also used for reimbursement. Interoperability The ability of two entities, human or machine, to exchange and predictably use data or information while retaining the original meaning of the data. A nurse informaticist can increase interoperability by promoting standardized vocabulary and coding. This reduces errors, increases revenue, and increases communication. Interoperability allows timely and seamless portability of information and optimizes the health of individuals and populations globally through this seamless exchange. Joint Commission ACCREDITATION. Key standards of information management: protect and aggregate data, uniform definitions/language, teach information management (training), and address disaster and preparedness. Knowledge Synthesizing information from different sources to produce a concept of idea. Knowledge Management The generation, storage, distribution, and application of both tacit knowledge (personal experience) and explicit knowledge (evidence). Knowledge Work/Workflow The work of gathering data to create information. Knowledge Worker Individual with a high degree of expertise, education, or experience who creates, distributes, and applies knowledge. Lewin's Change Model One of several foundational theories for leading others through planned change; identifies three steps: unfreezing, changing, and refreezing. Logical Security Non-tangible protocols used for identification, authentication, authorization, and accountability (ex: automatic sign-off after a period of inactivity). *Meaningful Use (MU) Use of health information technology (HIT) legislated by ARRA of 2009 to collect specific data with the intent to improve care and populations health, engage patients, and ensure privacy and security, with financial incentive from Medicare and Medicaid to providers. (Goals - engage patients, exchange data in an accurate/complete way, improve patient care in a cost-effective way, improve healthcare overall). Meaningful Use (MU) Core Requirements Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) developed core criteria that defined basic functions of EHRs must demonstrate. Basic entry of clinical information, requiring standardized terminology across the board, use of several software applications, entry of clinical orders with safety measures. (Three required stages include: stage 1 - electronic capturing & sharing of data between hospitals/providers; stage 2 - requires pts to view, download, or transmit their health information online, capability for secure messaging between providers/patients, and reporting public health measures, advancing clinical processes; stage 3 - focuses on the enhanced use of EHRs to promote Health Information Exchange & Improve care, and improving patient outcomes (ex: electronic prescribing)). Medical Informatics Application of informatics to all of the healthcare disciplines as well as to the practice of medicine. Merit-Based Incentive Payment System (MIPS) QUALITY. Ensures Medicare patients get the right care at the right time. Uses PQRS (physician quality reporting systems) and Medicare EHRs that will be measured on quality, resource use, clinical-practice environment, and meaningful use of EHRs technology. For physicians to qualify for MIPS, they must bill Medicare more than $90,000/year and see more than 200 Medicare patients annually. Mission Purpose or reason for an organization's existence, representing the fundamental and unique aspirations that differentiate it from others. National Quality Forum (NQF) Nonprofit, membership-based organization that works to improve healthcare through meaningful measurement. Nurse Informatics Specialist A nurse with advanced computer technology skills with expertise in system development life cycles. The nurse needs to: play an active role in the adoption of standard technologies, be aware of legislation, educate users, assist users on troubleshooting, provide advice and recommendations, act as a liaison between nurses and technology, serve as a resource, manage data and information, develop tools and methods, and monitor data security, accuracy, and integrity by monitoring for patterns & exceptions. Nursing Informatics Uses nursing knowledge along with information and communication technology to promote the health of individuals, families, and entire populations. Nursing Role in Informatics: Assessment - analysis of what is needed Developing - develop the care/project plan Implementing - implement the plan Monitoring - monitor the outcomes Evaluating - lessons learned with knowledge transfer Patient-Generated Health Data (PGHD) Health-related data created, recorded, or gathered by the patient/caregivers to help address health concerns. Without in-person enrollment, verifying that a patient is eligible to participate in a study can be difficult. Patient Protection & Affordable Care Act Guarantees access to healthcare for ALL Americans and incentives to change clinical practice to encourage better coordination and quality care. Personal Health Record (PHR) Lifelong tool for managing health information, such as conditions, allergies, medications, past surgeries, and other relevant information. (Potential barriers include poor or no internet, poorly designed applications, limited clinical integration) Physical Security The protection of physical items, objects, or areas from unauthorized access and misuse. Measures include the placement of computers, file servers, routers, switches, and computers in restricted areas. Other examples include physical locks on devices. Privacy The right to control access and disclosure or nondisclosure of information pertaining to oneself and to control the circumstances, timing, and extent to which information may be disclosed. Process Interoperability Coordinates systems enabling business processes at organizations and allowing systems to work together. Project Implementation Team / Committee FIRST TASK IS TO DEVELOP A TIMELINE - Comprised of representatives from the ser departments. Project team needs to be actively involved as an end-user. Implementation committee determines the project implementation strategy. Interdisciplinary will plan, test, train, etc. after the EHR is purchased. Project Management Lifestyle Cycle (PLMC 1) Design/Plan - Scope document: Official document that details how the project will be managed and what the project requirements are. Scope Creep - Unapproved change, which can cause serious delays or project failure. As the scope and charter are developed, a GAP analysis is completed and used to identify needed changes in workflow. GAP Analysis - A list of features & functions desired, but not immediately available in the new system as identified. 2) Implementation - Training the staff/end-users in this phase. With change, different behaviors can develop (ex: resignation, resistance, feelings of loss, etc.) Lewin's Change Theory - One of several foundational theories for leading others through planned change. Identifies 3 steps: Unfreezing, changing, refreezing. INVOLVES EMPLOYEES IN THE DECISION-MAKING PROCESS Big Bang Conversion - [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 13 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)

WGU D220 Exams (NEW UPDATE) With Complete Verified Answers.
WGU D220 Exams (NEW UPDATE) With Complete Verified Answers.
By Goodluck Academia 1 year ago
$14.5
3
Reviews( 0 )
$12.00
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 25, 2023
Number of pages
13
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 25, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
43






.png)