*NURSING > EXAM REVIEW > NR 293 Exam 3 Review Diabetes, CV Endo GI. (All)
NR 293 Exam 3 Review Diabetes, CV Endo GI.
Document Content and Description Below
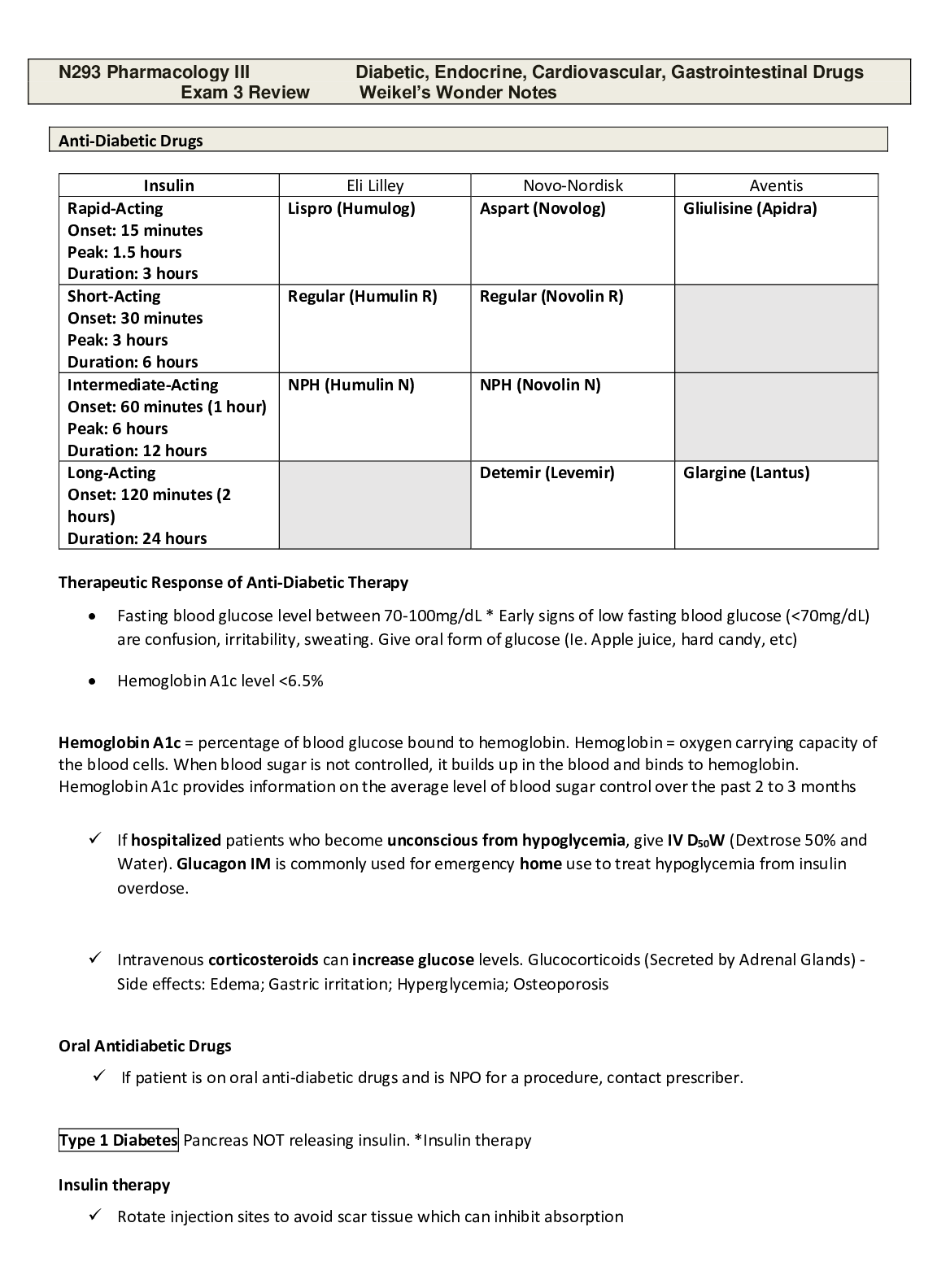
NR 293 Exam 3 Review Diabetes, CV Endo GI. N293 Pharmacology III Diabetic, Endocrine, Cardiovascular, Gastrointestinal Drugs Exam 3 Review Weikel’s Wonder Notes Anti-Diabetic ... Drugs Insulin Eli Lilley Novo-Nordisk Aventis Rapid-Acting Onset: 15 minutes Peak: 1.5 hours Duration: 3 hours Lispro (Humulog) Aspart (Novolog) Gliulisine (Apidra) Short-Acting Onset: 30 minutes Peak: 3 hours Duration: 6 hours Regular (Humulin R) Regular (Novolin R) Intermediate-Acting Onset: 60 minutes (1 hour) Peak: 6 hours Duration: 12 hours NPH (Humulin N) NPH (Novolin N) Long-Acting Onset: 120 minutes (2 hours) Duration: 24 hours Detemir (Levemir) Glargine (Lantus) Therapeutic Response of Anti-Diabetic Therapy • Fasting blood glucose level between 70-100mg/dL * Early signs of low fasting blood glucose (<70mg/dL) are confusion, irritability, sweating. Give oral form of glucose (Ie. Apple juice, hard candy, etc) • Hemoglobin A1c level <6.5% Hemoglobin A1c = percentage of blood glucose bound to hemoglobin. Hemoglobin = oxygen carrying capacity of the blood cells. When blood sugar is not controlled, it builds up in the blood and binds to hemoglobin. Hemoglobin A1c provides information on the average level of blood sugar control over the past 2 to 3 months If hospitalized patients who become unconscious from hypoglycemia, give IV D50W (Dextrose 50% and Water). Glucagon IM is commonly used for emergency home use to treat hypoglycemia from insulin overdose. Intravenous corticosteroids can increase glucose levels. Glucocorticoids (Secreted by Adrenal Glands) - Side effects: Edema; Gastric irritation; Hyperglycemia; Osteoporosis Oral Antidiabetic Drugs If patient is on oral anti-diabetic drugs and is NPO for a procedure, contact prescriber. Type 1 Diabetes Pancreas NOT releasing insulin. *Insulin therapy Insulin therapy Rotate injection sites to avoid scar tissue which can inhibit absorption When mixing insulins, draw up the ‘clear’ (Ie. Regular) into the syringe first. Long-acting insulin Ie. Detemir (Levemir) and Glargine (Lantus) CANNOT be mixed as the pH will change and affect absorption rate. If patient has both Long-acting Ie. Glargine (Lantus) or Detemir (Levemir) and Regular insulin ordered, do not mix. Use two different INSULIN syringes. 1. Put air into long-acting insulin vial and draw up correct dose with insulin syringe. 2. Put air into Regular insulin vial and draw up correct dose. Basal Dosing Delivers constant dose of insulin Done with intermediate or long acting insulin Mimics body’s 24-hour release of insulin Regular insulin can be used for intravenous (IV) insulin drip Bolus Dosing Bolus Dosing based on Carbohydrate Counting: Administer 1-2 units of insulin for every 15 grams of carbohydrate to be consumed in a meal to prevent blood glucose spikes. Type 2 Diabetes Pancreas IS releasing insulin, but the body is not utilizing it properly. Oral medications and diet. Oral Antidiabetic Drugs 1. Biguanides • Metformin (Glucophage). Given to decrease production of glucose in the liver. 2. Sulfonylureas “Glee Club” • Glipizide (Glucotrol) • Glimepiride (Amaryl) CONTRAINDICATED with Repaglinide (Prandin) due to similar mechanism of action. • Glyburide (Diabeta) • Take in the morning 30’ before breakfast. • Adverse effects: Hypoglycemia 3. Meglitinides • Repaglinide (Prandin) Contraindicated with Glimepiride (Amaryl) due to similar mechanism of action. • Rapidly decreases blood sugar. Taking medication and skipping a meal can lead to severe hypoglycemia. Give 15-30 minutes before meal or right before eating. 4. Alpha Glucosidase inhibitors • Ascarbose (Precose) • Side effects: Abdominal pain and discomfort; Bloating; Diarrhea; Flatulence - *CONTRAINDICATED in irritable bowel disease 5. Thiazolidinediones – “glitazones” • Piaglitazone (Actos) • Worsen Heart Failure (including edema) and cause Upper Respiratory Infections (URI) 6. DPP-IV inhibitors – “gliptans” • Sitagliptin (Januvia) • Oral anti-diabetic medication used to control blood glucose. Used with diet and exercise, but not yet shown to be effective with insulin. Therefore, not prescribed in conjunction with insulin. • Delays breakdown of incretin hormones (incretin hormones stimulate insulin release with meals to lower blood sugar) so giving insulin can be ineffective. 7. SGLT2 inhibitors • Dapciglifozin (Farxiga) [sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor) • Causes glucosuria and increases urine volume to decrease glucose. CONTRAINDICATED in Renal Failure 8. Other – Adjunct drugs used to treat Type 2 Diabetes Coleselvelam (Welchol) ..............continued............ [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 10 pages
Instant download
Instant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Feb 15, 2021
Number of pages
10
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Feb 15, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
36















.png)




