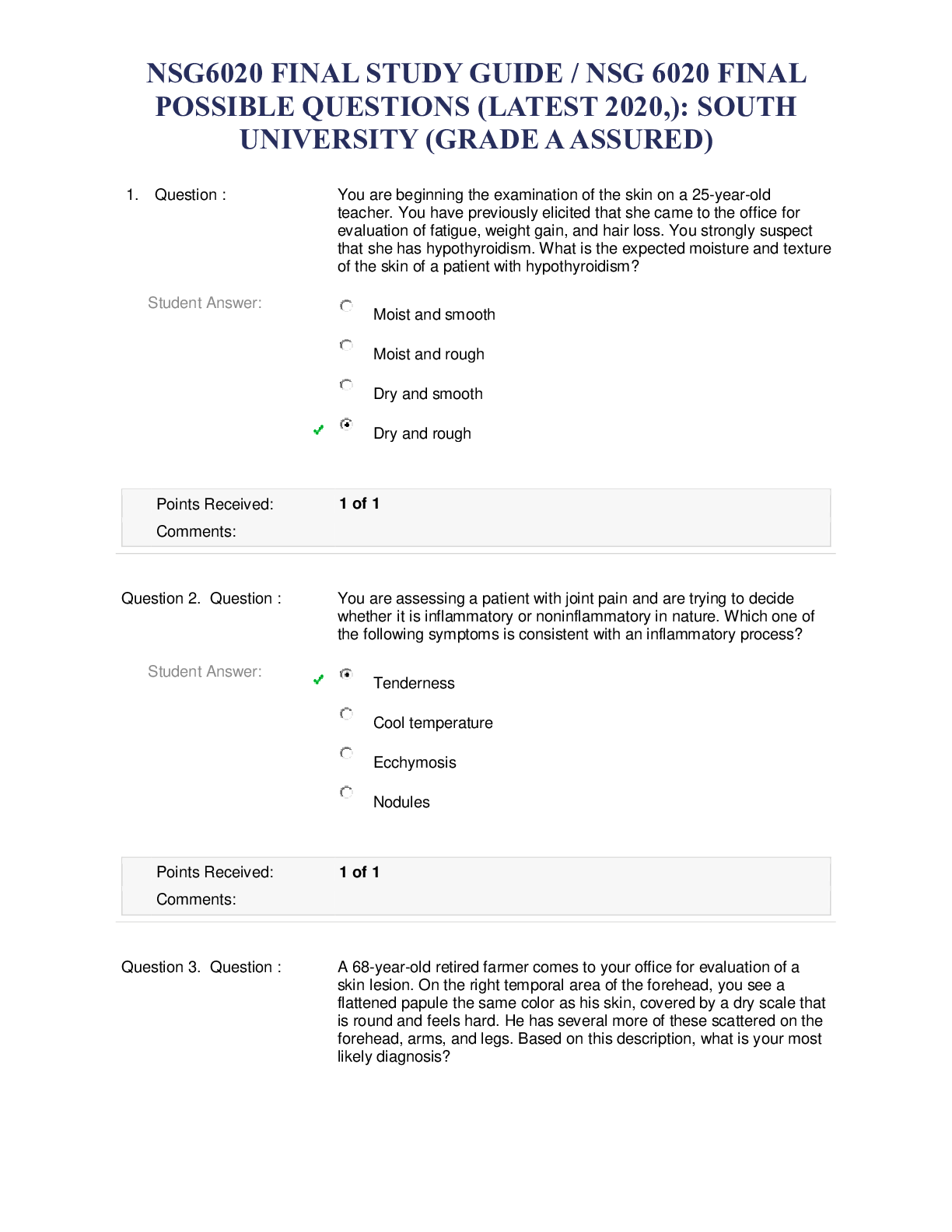
*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > ECPI UNIVERSITY (NURSING 255) Chapter 13 Assessment and Care of Patients with Fluid and Electrolyte (All)
ECPI UNIVERSITY (NURSING 255) Chapter 13 Assessment and Care of Patients with Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalances (ALREADY GRADED A)
Document Content and Description Below
NURSING 255 Chapter 13: Assessment and Care of Patients with Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalances Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The nurse observes skin tenting on the back of the older adult clien... t’s hand. Which action by the nurse is most appropriate? a. Notify the physician. b. Examine dependent body areas. c. Assess turgor on the client’s forehead. d. Document the finding and continue to monitor. 2. The client is taking a medication that inhibits aldosterone secretion and release. The nurse assesses for what potential complication? a. Fluid retention b. Hyperkalemia c. Hyponatremia d. Hypervolemia 3. Which assessment does the nurse use to determine the adequacy of circulation in a client whose blood osmolarity is 250 mOsm/L? a. Measuring urine output b. Measuring abdominal girth c. Monitoring fluid intake d. Comparing radial versus apical pulses 4. Which statement made by the older adult client alerts the nurse to assess specifically for fluid and electrolyte imbalances? a. “My skin is always so dry, especially here in the Southwest.” b. “I often use a glycerin suppository for constipation.” c. “I don’t drink liquids after 5 PM so I don’t have to get up at night.” d. “In addition to coffee, I drink at least one glass of water with each meal.” 5. A client has been taught to restrict dietary sodium. Which food selection by the client indicates to the nurse that teaching has been effective? a. Chinese take-out, including steamed rice b. A grilled cheese sandwich with tomato soup c. Slices of ham and cheese on whole grain crackers d. A chicken leg, one slice of bread with butter, and steamed carrots 6. A client is on a potassium-restricted diet. Which protein choice by the client indicates a good understanding of the dietary regimen? a. 1% or 2% milk b. Grilled salmon c. Poached eggs d. Baked chicken 7. Which assessment finding obtained while taking the history of an older adult client alerts the nurse that the client needs further assessment for fluid or electrolyte imbalance? a. “I am often cold and need to wear a sweater.” b. “I seem to urinate more when I drink coffee.” c. “In the summer, I feel thirsty more often.” d. “My rings seem to be tighter this week.” 8. Which client is at greatest risk for dehydration? a. Younger adult client on bedrest b. Older adult client receiving hypotonic IV fluid c. Younger adult client receiving hypertonic IV fluid d. Older adult client with cognitive impairment 9. Which question does the nurse ask the client who has isotonic dehydration to determine a possible cause? a. “Do you take diuretics, or ‘water pills’?” b. “What do you normally eat over a day’s time?” c. “How many bowel movements do you have daily?” d. “Have you been diagnosed with diabetes mellitus?” 10. Which intervention in a client with dehydration-induced confusion is most likely to relieve the confusion? a. Measuring intake and output every four hours b. Applying oxygen by mask or nasal cannula c. Increasing the IV flow rate to 250 mL/hr d. Placing the client in a high Fowler’s position 11. A client is being treated for dehydration. Which statement made by the client indicates understanding of this condition? a. “I must drink a quart of water or other liquid each day.” b. “I will weigh myself each morning before I eat or drink.” c. “I will use a salt substitute when making and eating my meals.” d. “I will not drink liquids after 6 PM so I won’t have to get up at night.” 12. What intervention is most important to teach the client about identifying the onset of dehydration? a. Measuring abdominal girth b. Converting ounces to milliliters c. Obtaining and charting daily weight d. Selecting food items with high water content 13. A nurse is caring for several clients with dehydration. The nurse assesses the client with which finding as needing oxygen therapy? a. Tenting of skin on the back of the hand b. Increased urine osmolarity c. Weight loss of 10 pounds d. Pulse rate of 115 beats/min 14. Which action does the nurse teach a client to reduce the risk for dehydration? a. Restricting sodium intake to no greater than 4 g/day b. Maintaining an oral intake of at least 1500 mL/day c. Maintaining a daily oral intake approximately equal to daily fluid loss d. Avoiding the use of glycerin suppositories to manage constipation 15. Which item of assessment data obtained by the home care nurse suggests that an older adult client may be dehydrated? a. The client has dry, scaly skin on bilateral upper and lower extremities. b. The client states that he gets up three or more times during the night to urinate. c. The client states that he feels lightheaded when he gets out of bed or stands up. d. The nurse observes tenting on the back of the hand when testing skin turgor. 16. A client is being discharged with mild dehydration. Which statement by the client indicates an understanding of measures to prevent mild dehydration from becoming more severe? a. “I will weigh myself at the same time daily wearing the same clothes.” b. “When I feel lightheaded, I will drink a full glass of water.” c. “I will decrease my fluid intake if my urine output increases.” d. “If I forget to take my diuretic, I will take twice the dose next time.” 17. During assessment of hydration status, the client tells the nurse that she usually drinks 3 quarts of liquids each day. Which question by the nurse is best? a. “Do you usually drink liquids that are hot or cold?” b. “How much salt do you add to your food?” c. “What kinds of liquids do you usually drink?” d. “Do you drink fluids with meals or between meals?” 18. A nurse is caring for several clients at risk for overhydration. The nurse assesses the older client with which finding first? a. Has had diabetes mellitus for 12 years b. Uses sodium-containing antacids frequently c. Just received 3 units of packed red blood cells d. Had abdominal surgery and has a nasogastric tube 19. A client has been diagnosed with overhydration and is confused. Which intervention does the nurse include in the client’s plan of care to relieve the confusion? a. Measuring intake and output every shift b. Slowing the IV flow rate to 50 mL/hr c. Administering diuretic agents as prescribed d. Placing the client in Trendelenburg position 20. The nurse assesses distended neck veins in a client sitting in a chair to eat. What intervention is the nurse’s priority? a. Document the observation in the chart. b. Measure urine specific gravity and volume. c. Assess the pulse and blood pressure. d. Assess the client’s deep tendon reflexes. 21. A client in the emergency department has potassium of 2.9 mEq/L. For which disease process or condition does the nurse assess the client? a. Diabetes mellitus b. Addison’s disease c. Hyperaldosteronism d. Diabetes insipidus 22. A client is taking furosemide (Lasix) and becomes confused. Which potassium level does the nurse correlate with this condition? a. 2.9 mEq/L b. 3.8 mEq/L c. 5.0 mEq/L d. 6.0 mEq/L 23. A client has hypokalemia. Which question by the nurse obtains the most information on a possible cause? a. “Do you use sugar substitutes?” b. “Do you use diuretics or laxatives?” c. “Do you have any kidney disease?” d. “Have your bowel habits changed recently?” 24. A client has been treated for hypokalemia. Which clinical manifestation or condition indicates that treatment has been effective? a. Having a bowel movement daily b. Gaining 2 lb during the past week c. Electrocardiogram (ECG) showing inverted T-waves d. Fasting blood glucose level of 106 mg/dL 25. The nurse notes that the handgrip of the client with hypokalemia has diminished since the previous assessment one hour ago. Which intervention by the nurse is the priority? a. Assess the client’s respiratory rate, rhythm, and depth. b. Measure the client’s pulse and blood pressure. c. Document findings and monitor the client. d. Call the health care provider. 26. The client is receiving an intravenous infusion of 60 mEq of potassium chloride in a 1000 mL solution of dextrose 5% in 0.45% saline. The client states that the area around the IV site burns. What intervention does the nurse perform first? a. Notify the physician. b. Assess for a blood return. c. Document the finding. d. Stop the IV infusion. 27. A client has been taught to increase potassium in the diet. What dietary meal selection indicates to the nurse that teaching has been effective? a. Toasted English muffin with butter and blueberry jam, and tea with sugar b. Two scrambled eggs, a slice of white toast, and a cup of strawberries c. Sausage, one slice of whole wheat toast, cup of raisins, and a glass of milk d. Bowl of oatmeal with brown sugar, cup of sliced peaches, and coffee 28. Which client statement indicates the need for more teaching regarding identification of the early manifestations of hypokalemia? a. “I have been weighing myself every day.” b. “When I am constipated, I drink more fluids.” c. “When my muscles feel weak, I eat a banana.” d. “I check my pulse each morning and each night.” 29. A nurse is caring for several clients. Which client does the nurse assess most carefully for hyperkalemia? a. Client with heart failure using a salt substitute b. Client taking a thiazide diuretic for hypertension c. Client taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs daily d. Client with type 2 diabetes taking an oral antidiabetic agent 30. A client at risk for continuing hyperkalemia states that she is upset because she cannot eat fruit every day. Which response by the nurse is best? a. “You are correct. Fruit is usually very high in potassium.” b. “If you cook the fruit first, that lowers the potassium.” c. “Berries, cherries, apples, and peaches are low in potassium.” d. “Fresh fruit is higher in potassium than dried fruit.” 31. A client is being discharged and needs to self-monitor for the development of hyperkalemia. Which intervention is most important for the nurse to teach the client? a. Weighing self daily at the same time of day b. Assessing radial pulse for a full minute twice a day c. Ensuring an oral intake of a least 3 L of fluids per day d. Restricting sodium as well as potassium intake 32. A client is admitted with hyponatremia. Four hours after the initial assessment, the nurse notes that the client has new hyperactive bowel sounds in all four quadrants. What analysis about the client’s condition is correct? a. The hyponatremia is worse. b. The hyponatremia is the same. c. The hyponatremia is better. d. The client now has hypernatremia. 33. A nurse is assessing clients for fluid and electrolyte imbalances. Which client is at greatest risk for developing hyponatremia? a. Client who is NPO receiving intravenous D5W b. Client taking a sulfonamide antibiotic c. Client taking ibuprofen (Motrin) d. Client taking digoxin (Lanoxin) 34. The nurse is providing discharge teaching for a client who is at risk for mild hypernatremia. What action is most important for the nurse to teach the client? a. “Weigh yourself every morning and every night.” b. “Check your radial pulse twice a day.” c. “Read food labels to determine sodium content.” d. “Bake or grill the meat rather than frying it.” 35. A client has a history of hypothyroidism. Which laboratory value is the nurse most concerned about? a. Na+ 146 mEq/L b. K+ 3.6 mEq/L c. Ca2+ 8.2 mg/dL d. Mg2+ 1.1 mEq/L 36. When taking the blood pressure of a very ill client, the nurse observes that the client’s hand undergoes flexion contractions. Which intervention is most appropriate? a. Administer isotonic intravenous fluids. b. Remove the blood pressure cuff and give oxygen. c. Ensure the client has a patent intravenous line. d. Document the finding in the client’s chart. ) 37. A client has the following laboratory values: Ca2+ 8.7 mg/dL; K+ 4.2 mEq/L; Na+ 142 mEq/L. Which intervention by the nurse is most appropriate? a. Prepare to administer IV potassium chloride. b. Ask the lab to redraw and rerun the tests. c. Document findings and continue to assess. d. Prepare to administer aluminum hydroxide. 38. A client has a history of hypocalcemia. What intervention is most important for the nurse to add to this client’s care plan? a. Push fluids to 2 L/day. b. Strain all urine output. c. Use nonslip footwear to get out of bed. d. Position the client supine twice a day. 39. Which client is at greatest risk for developing hypercalcemia? a. Client taking furosemide (Lasix) for heart failure b. Client with long-standing osteoarthritis c. Woman who is pregnant with twins d. Client with hyperparathyroidism 40. A client has a calcium level of 14 mg/dL. Which intervention is the priority? a. Forcing fluids to 2 L/day b. Placing the client on a cardiac monitor c. Assessing for Chvostek’s sign every 2 hours d. Administering IV calcium chloride 41. A client is admitted with multiple fractures from a motor vehicle crash (MVC). Which of the client’s previous or concurrent health problems is most likely to increase the client’s risk for hypophosphatemia? a. Chronic alcoholic pancreatitis b. 50–pack-year smoking history c. Prostate cancer history d. Heart surgery 8 years ago 42. A client with hypophosphatemia is being discharged. Which activity demonstrated by the client indicates that discharge teaching has been effective? a. Assessing radial pulse rate and rhythm b. Interspersing daily activities with periods of rest c. Selecting foods high in phosphorus and low in calcium d. Weighing himself or herself correctly at the same time each day 43. The nurse observes that the handgrip of the client with hypophosphatemia has diminished in strength since the last assessment 2 hours ago. What is the nurse’s primary intervention? a. Document the finding and continue to assess. b. Assess respiratory status immediately. c. Request an order for a serum calcium level. d. Administer a rapid bolus of intravenous phosphorus. MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1. Which ethnic groups should the nurse screen specifically for hypocalcemia? (Select all that apply.) a. Whites b. Blacks c. Asians d. Hispanics e. American Indians [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 16 pages
Instant download

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 12, 2020
Number of pages
16
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 12, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
52















.png)






 and Autoimmunity, Questions and Answers with Explanations, 100% Correct, Download to Score A.png)


