*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > Med Surg 1 FINAL STUDY GUIDE. LATEST 2020/2021 (All)
Med Surg 1 FINAL STUDY GUIDE. LATEST 2020/2021
Document Content and Description Below
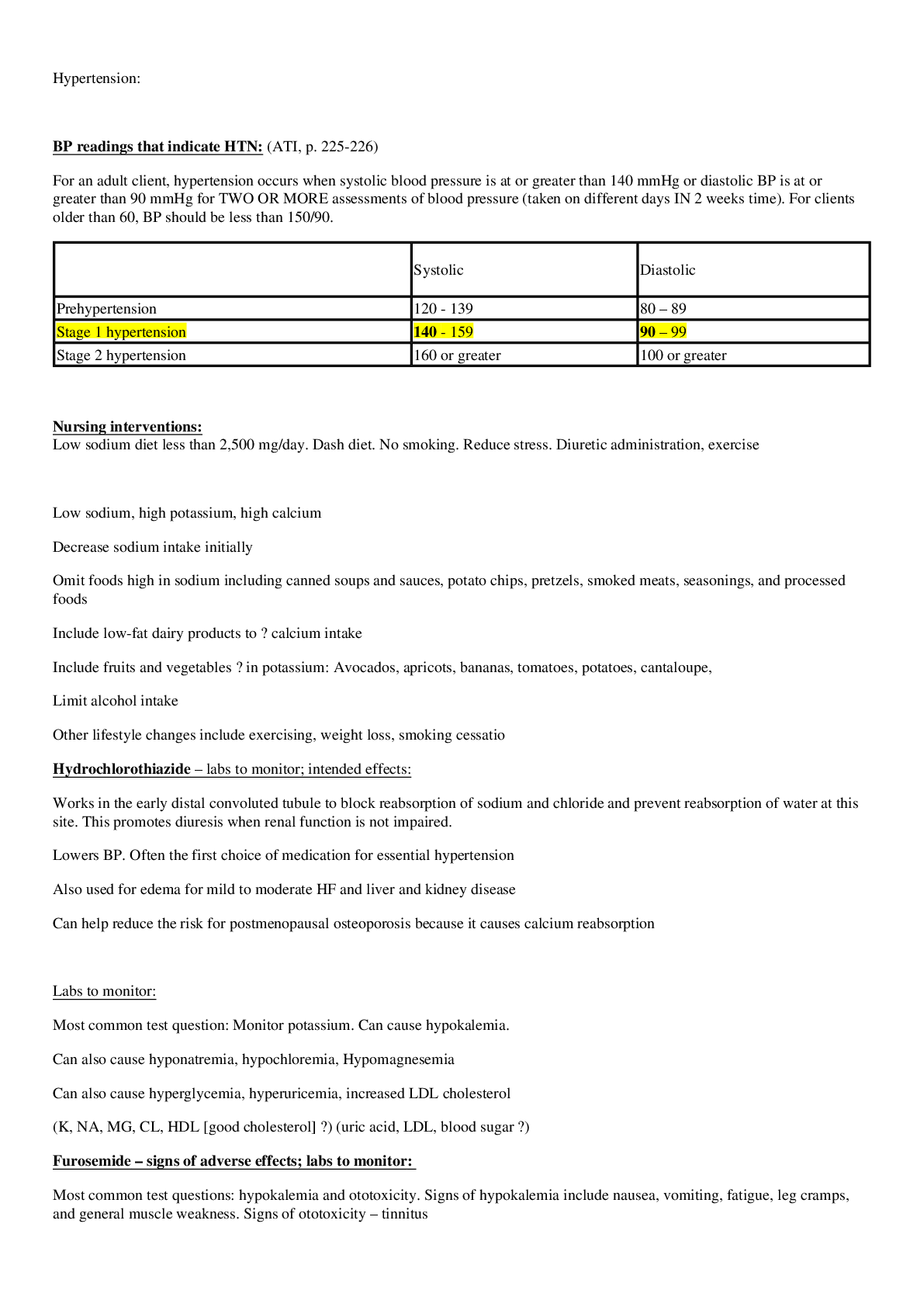
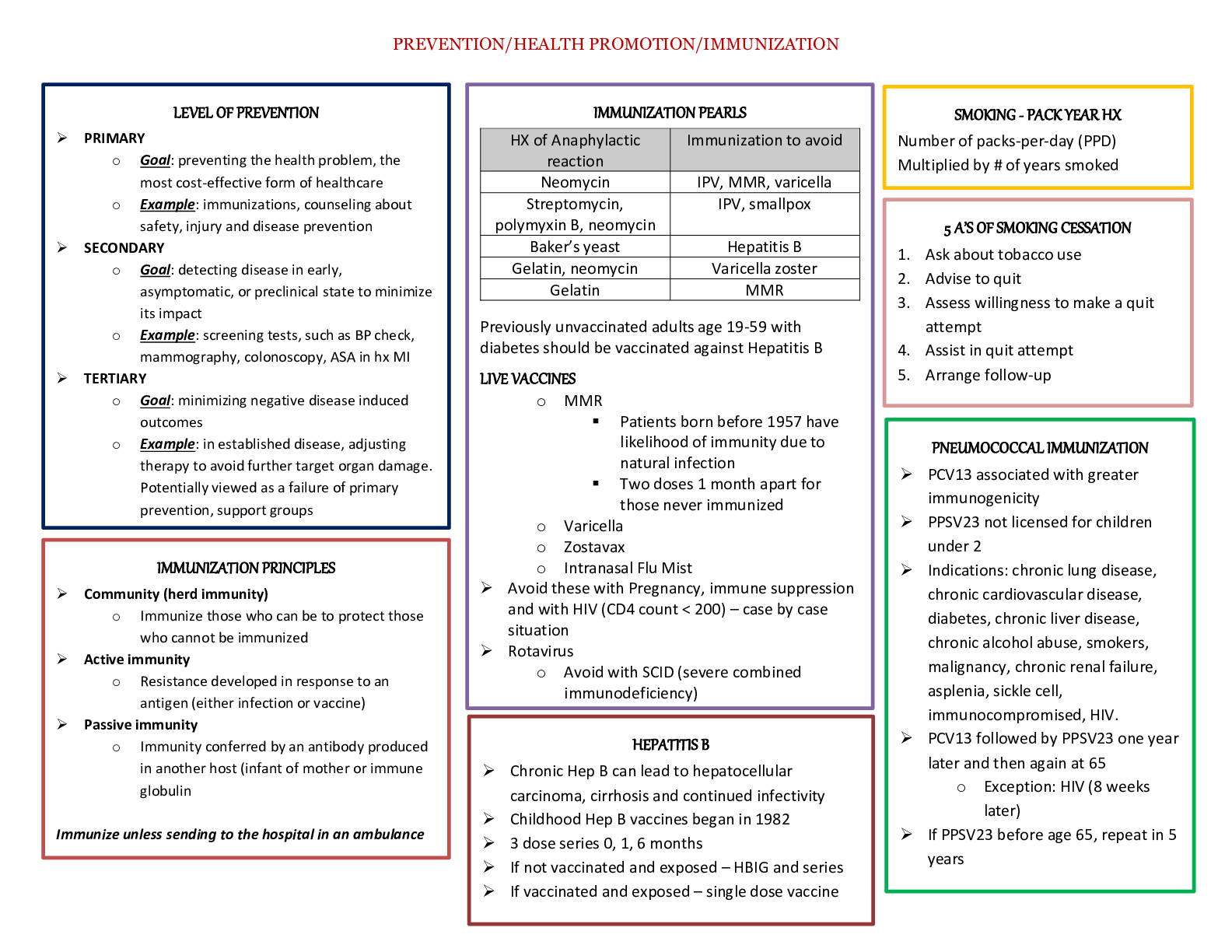
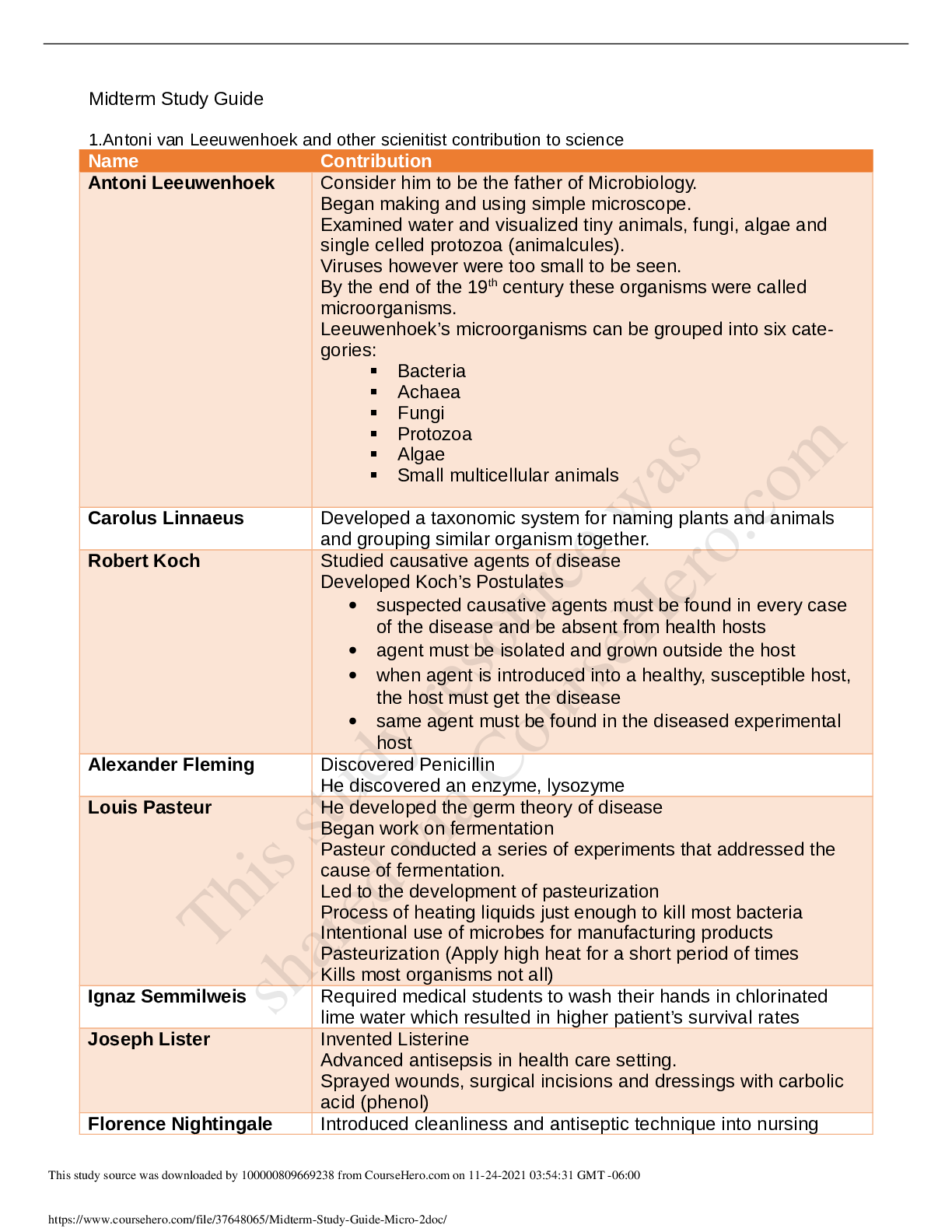
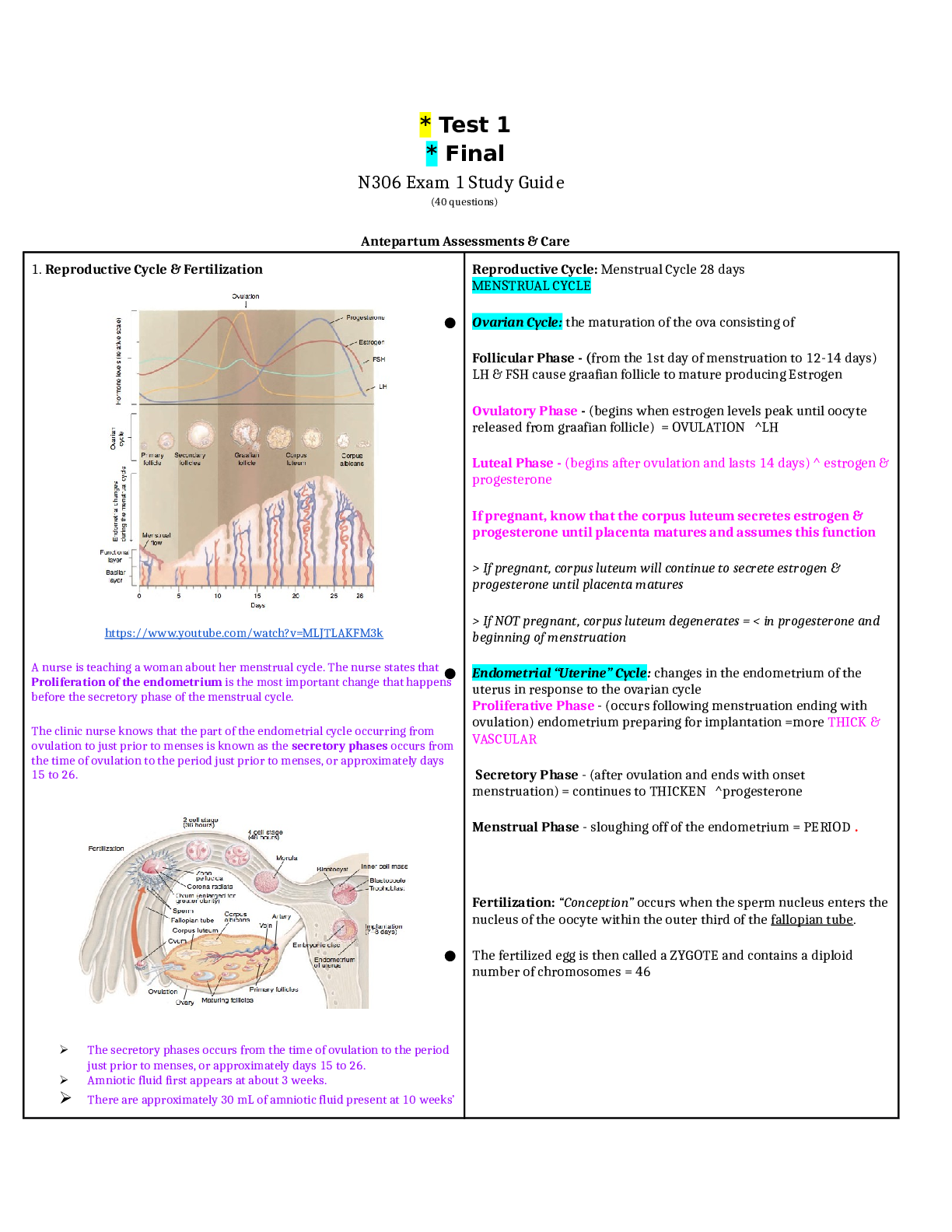
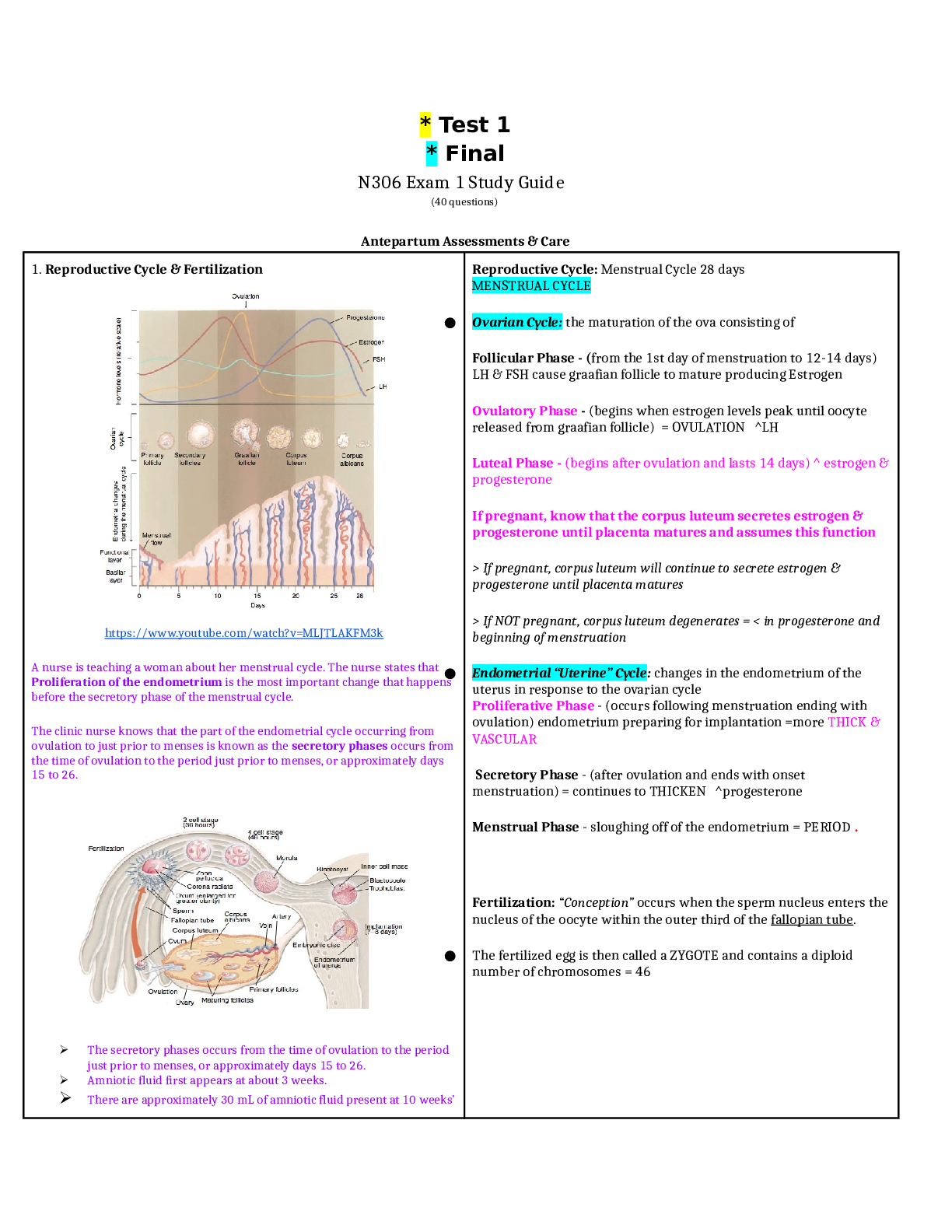
Med Surg 1 FINAL STUDY GUIDE. LATEST 2020/2021. 1. Hypertension: BP readings that indicate HTN: (ATI, p. 225-226) • For an adult client, hypertension occurs when systolic blood pressure is at or... greater than 140 mmHg or diastolic BP is at or greater than 90 mmHg for TWO OR MORE assessments of blood pressure (taken on different days IN 2 weeks time). For clients older than 60, BP should be less than 150/90. Systolic Diastolic Prehypertension 120 - 139 80 – 89 Stage 1 hypertension 140 - 159 90 – 99 Stage 2 hypertension 160 or greater 100 or greater Nursing interventions: Low sodium diet less than 2,500 mg/day. Dash diet. No smoking. Reduce stress. Diuretic administration, exercise • Low sodium, high potassium, high calcium • Decrease sodium intake initially < 2,300 mg/day, then gradually decreased to < 1,500 mg/day for maximum benefit • Omit foods high in sodium including canned soups and sauces, potato chips, pretzels, smoked meats, seasonings, and processed foods • Include low-fat dairy products to ↑ calcium intake • Include fruits and vegetables ↑ in potassium: Avocados, apricots, bananas, tomatoes, potatoes, cantaloupe, • Limit alcohol intake • Other lifestyle changes include exercising, weight loss, smoking cessatio Hydrochlorothiazide – labs to monitor; intended effects: o Works in the early distal convoluted tubule to block reabsorption of sodium and chloride and prevent reabsorption of water at this site. This promotes diuresis when renal function is not impaired. o Lowers BP. Often the first choice of medication for essential hypertension o Also used for edema for mild to moderate HF and liver and kidney disease o Can help reduce the risk for postmenopausal osteoporosis because it causes calcium reabsorption Labs to monitor: o Most common test question: Monitor potassium. Can cause hypokalemia. o Can also cause hyponatremia, hypochloremia, Hypomagnesemia o Can also cause hyperglycemia, hyperuricemia, increased LDL cholesterol o (K, NA, MG, CL, HDL [good cholesterol] ↓) (uric acid, LDL, blood sugar ↑) Furosemide – signs of adverse effects; labs to monitor: o Most common test questions: hypokalemia and ototoxicity. Signs of hypokalemia include nausea, vomiting, fatigue, leg cramps, and general muscle weakness. Signs of ototoxicity – tinnitus o Dehydration, hyponatremia, hypochloremia: assess for decreased urine output (report < 30mL/Hr), dry mouth, increased thirst, weight loss. If headache, chest, calf, or pelvic pain occur, notify provider as may indicate thrombosis or embolism. o Hypotension: Monitor BP. Advise clients to sit or lie down if feeling dizzy. Move slowly o Other adverse effects: Hyperglycemia, hyperuricemia, hypocalcemia, hypomagnesemia, ↓ HDL, ↑ LDL Labs to monitor: o Electrolytes, especially K. BP, daily weights, Blood sugar, uric acid, HDL, LDL o (K, NA, CL, MG, CA, HDL, ↓) (Blood sugar, uric acid, LDL ↑) 2. Angina and MI: Cardiac enzymes: purpose of test: (Pearson, p. 1194) o To establish diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction o Ordered on admission and for 3 succeeding time frames. Serial blood levels help establish the diagnosis and determine the extent of myocardial damage Aspirin: Classification: o There are a few. Aspirin is considered an antiplatelet/salicylic. It is also considered an NSAID, and a cyclooxygenase 1 and 2 inhibitor (COX 1/COX 2 inhibitor). 3. MI MONA • Morphine: Decreases myocardial consumption and demand. Also reduces pain which reduces catecholamine release (epi and norepi). • Oxygen: Oxygen is given to reduce myocardial work load. The more oxygen is available, the less tachycardia the heart needs to do. The less the workload of the heart • Nitroglycerin: Prevents coronary artery vasospasm and reduces preload and afterload, decreasing myocardial oxygen demand. Dilates blood vessels. • Aspirin: Prevents vasoconstriction. Antiplatelet effects, so slows clotting and reduces the size of the clot that is already forming. Sequence of steps: • In the field, Nitro and aspirin would be given first • In the ER, it would be O2, ECG, then nitro and aspirin. 4. Fluticasone: Intended effect: o Inhaled glucocorticoid agent used for long-term prophylaxis of asthma. Promotes decreased frequency and severity of exacerbations. NOT used for an acute attack. o Prevents inflammation o Suppresses airway mucous production o Reduction of airway mucosa edema o Promotes responsiveness of beta 2 receptors in the bronchial tree. (It does this by reducing the mucous and inflammation that blocks the receptors, NOT by activating the receptors) Side effects: o Most commonly asked: Oral candidiasis. Have client rinse mouth after inhalation o Others: all the same as prednisone. Bone loss, hyperglycemia and glycosuria, hypokalemia (muscle weakness), fluid retention, ↑ risk for infection, myopathy (muscle weakness), adrenal gland suppression, peptic ulcer disease 5. Heparin: Antidote: o Protamine sulfate - heParin = Protamine Labs to monitor: o aPTT. Normal aPTT is 30 – 40 seconds. o When on heparin, aPTT should be 60 – 80 seconds, or 1.5 – 2x baseline. o If the question gives you an aPTT number above 80, bleeding is too fast! Give protamine sulfate. o Also monitor CBC, platelets, hematocrit (HCT) 6. Warfarin: Patient health teaching: o Monitor PT levels (should be 18 – 24 seconds on warfarin) and INR levels (2 – 3). o Plan for frequent PT and INR monitoring. Clients can self-monitor at home when appropriate o Instruct clients that anticoagulant effects can take 8-12 hours, and full effects are not achieved for 3-5 days. For clients in a hospital setting, explain the need to continue heparin infusion when starting warfarin until warfarin therapeutic levels are achieved o Anticoagulant effects can last 5 days after discontinuing warfarin o Avoid alcohol and OTC medications to prevent interactions and risk of bleeding o Avoid sitting for long periods. Don’t wear constrictive clothing. Elevate and move legs when sitting. o Wear a medical alert bracelet and notify all other providers/dentists of warfarin use o Record dose, route, and time of administration daily o Use a soft-bristle toothbrush and electric razor for shaving o Avoid fluctuations of vitamin K intake (green leafy vegetables). Keep intake consistent. Name at least 7 herbal meds that can interact with warfarin All of these increase bleeding: o Bromelains (a pineapple extract) o Danshen, Dong quai , Devil’s claw o Garlic, Ginkgo biloba, Ginseng, Ginger o Kava Others found online: Glucosamine/chondroitin, grapefruit juice, cranberry juice, Vitamin E (above 400 IU/day), melatonin, Vitamin A (above 10,000 IU/day), Green tea, soy, St. John’s Wart, evening primrose, feverfew, fish oil, flaxseed oil, horse chestnut, papain, red clover, saw palmetto, sweet clover, sweet woodruff 7. Clopidogrel, Heparin, Warfarin, Aspirin – How many days should they be stopped before surgery? Clopidogrel – 5 days Heparin – 6 – 12 hours Warfarin – 5 days Aspirin – 7 days 8. Simvastatin Indications: • Hyperlipidemia/hypercholesterolemia • Prevention of coronary events (primary and secondary) • Also given to diabetic patients to reduce mortality – reduces risk for CAD, MI, stroke Foods to avoid: • Grapefruit juice – increases statin level • Foods ↑ in cholesterol – cancels out the whole point in taking the medication 9. Atherosclerosis: Modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors: [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 26 pages
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Feb 19, 2021
Number of pages
26
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Feb 19, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
40














.png)





 Correct Study Guide, Download to Score A.png)





.png)

