Health Care > EXAM > TNCC 10TH EDITION FINAL EXAM 2024 QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS LATEST UPDATE A GRADES (All)
TNCC 10TH EDITION FINAL EXAM 2024 QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS LATEST UPDATE A GRADES
Document Content and Description Below
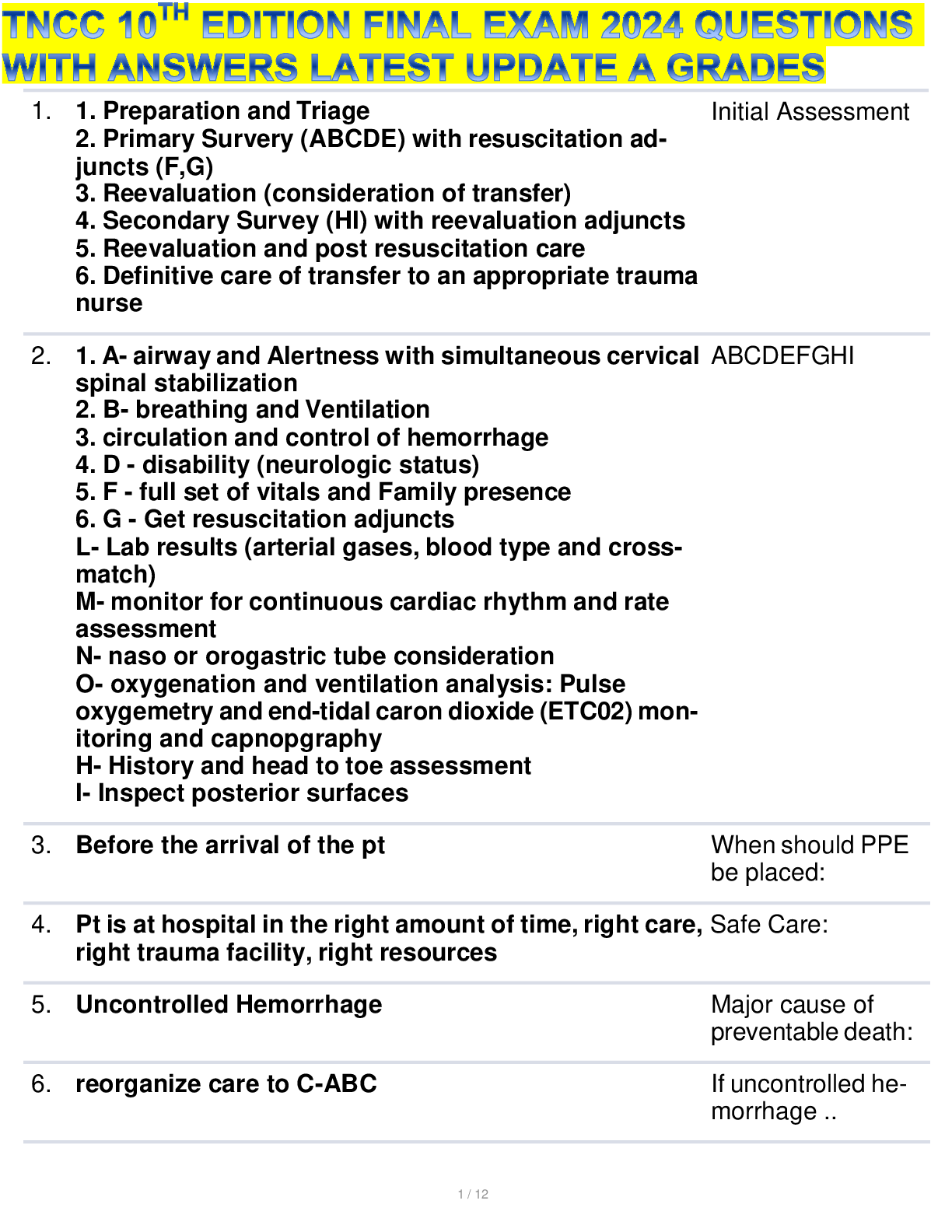
TNCC 10TH EDITION FINAL EXAM 2024 QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS LATEST UPDATE A GRADES 1. 1. Preparation and Triage 2. Primary Survery (ABCDE) with resuscitation ad- juncts (F,G) 3. Reevaluation (consider... ation of transfer) 4. Secondary Survey (HI) with reevaluation adjuncts 5. Reevaluation and post resuscitation care 6. Definitive care of transfer to an appropriate trauma nurse 2. 1. A- airway and Alertness with simultaneous cervical spinal stabilization 2. B- breathing and Ventilation 3. circulation and control of hemorrhage 4. D - disability (neurologic status) 5. F - full set of vitals and Family presence 6. G - Get resuscitation adjuncts L- Lab results (arterial gases, blood type and cross- match) M- monitor for continuous cardiac rhythm and rate assessment N- naso or orogastric tube consideration O- oxygenation and ventilation analysis: Pulse oxygemetry and end-tidal caron dioxide (ETC02) mon- itoring and capnopgraphy H- History and head to toe assessment I- Inspect posterior surfaces Initial Assessment ABCDEFGHI 3. Before the arrival of the pt When should PPE be placed: 4. Pt is at hospital in the right amount of time, right care, Safe Care: right trauma facility, right resources 5. Uncontrolled Hemorrhage Major cause of preventable death: 6. reorganize care to C-ABC If uncontrolled he- morrhage .. 7. Used at the beginning of the initial assessment 1. A Alert. If the pt is alert he or she will be able to maintain his or her airway once it is clear. 2. V responds to verbal stimuli responds to pain. If the patient needs verbal stimulation to respond, an airway adjunct may be needed to keep the tongue from obstructing the airway. 3. P responds to pain. If the pt. responds only to pain, he or she may not be able to maintain his or her airway adjunct may need to be placed while further assess- ment is made to determine the need for intubation. 4. U Unresponsive. If the pt. is unresponsive, an- nounce it loudly to the team and direct someone to chk in the pt is pulseless while assessing if the cause of the problem is the airway. Airway and AVPU: 8. ask pt to pen his or her mouth While assessing airway the patient is alert and re- sponds to ver- bal stimuli you should.. 9. jaw thrust maneuver to open airway and assess for obstruction. If pt has a suspected csi, the jaw thrust procedure should be done by two providers. One provider can maintain c-spine and the other can per- form the jaw thrust maneuver. 10. 1. The tongue obstructing the airway 2. loose or missing teeth 3. foreign objects 4. blood, vomit, or secretions' 5. edema 6. burns or evidence of inhalation injury While assessing airway pt is un- able to open mouth, responds only to pain, or is unresponsive you should.. Inspect the mouth for: Auscultiate or listen for: 1. Obstructive airway sounds such as snoring or gur- gling 2. Possible occlusive maxillofacial bony deformity 3. Subcutaneous emphysema 11. 1. Check the presence of adequate rise and fall of the chest with assisted ventilation 2. Absence of gurgling on auscultation over the epi- gastrium 3. Bilateral breath sounds present on auscultation 4. Presence of carbon dioxide (CO2) verified by a CO2 device or monitor 12. 1. Suction the airway 2, Use care to avoid stimulating the gag reflex 3. If the airway is obstructed by blood or vomitus secretions, use a rigid suction device If foreign body is noted, remove it carefully with for- ceps or another appropriate method 13. 1. Apnea 2. GCS 8 or less 3. Maxillary fractures 4. Evidence of inhalation injury (facial burns) 5. Laryngeal or tracheal injury or neck hematoma 6. High risk of aspiration and patients inability to pro- tect the airway 7. Compromised or ineffective ventilation 14. Breathing: To assess breathing expose the chest: 1. Inspect for a. spontaneous breathing b. symmetrical rise and fall c. depth, pattern, and rate of respiration d. signs of difficulty breathing such as accessory muscle use e. skin color (normal, pale, flushed, cyanotic) f. contusions, abrasions, deformities (flail chest) g. open pneumothoraces (sucking chest wounds) If the pt has a definitive airway in what should you do? If Airway is not patent Following condi- tions might require a definitive airway [Show More]
Last updated: 5 months ago
Preview 1 out of 12 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$14.00
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jan 06, 2024
Number of pages
12
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jan 06, 2024
Downloads
0
Views
55


















.png)

.png)




