Clinical Medicine > EXAM > INTRODUCTION TO CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY 10TH EDITION BY CONSTANCE VISOVSKY, CHERYL ZAMBROSKI, SHIRLEY (All)
INTRODUCTION TO CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY 10TH EDITION BY CONSTANCE VISOVSKY, CHERYL ZAMBROSKI, SHIRLEY TEST BANK
Document Content and Description Below
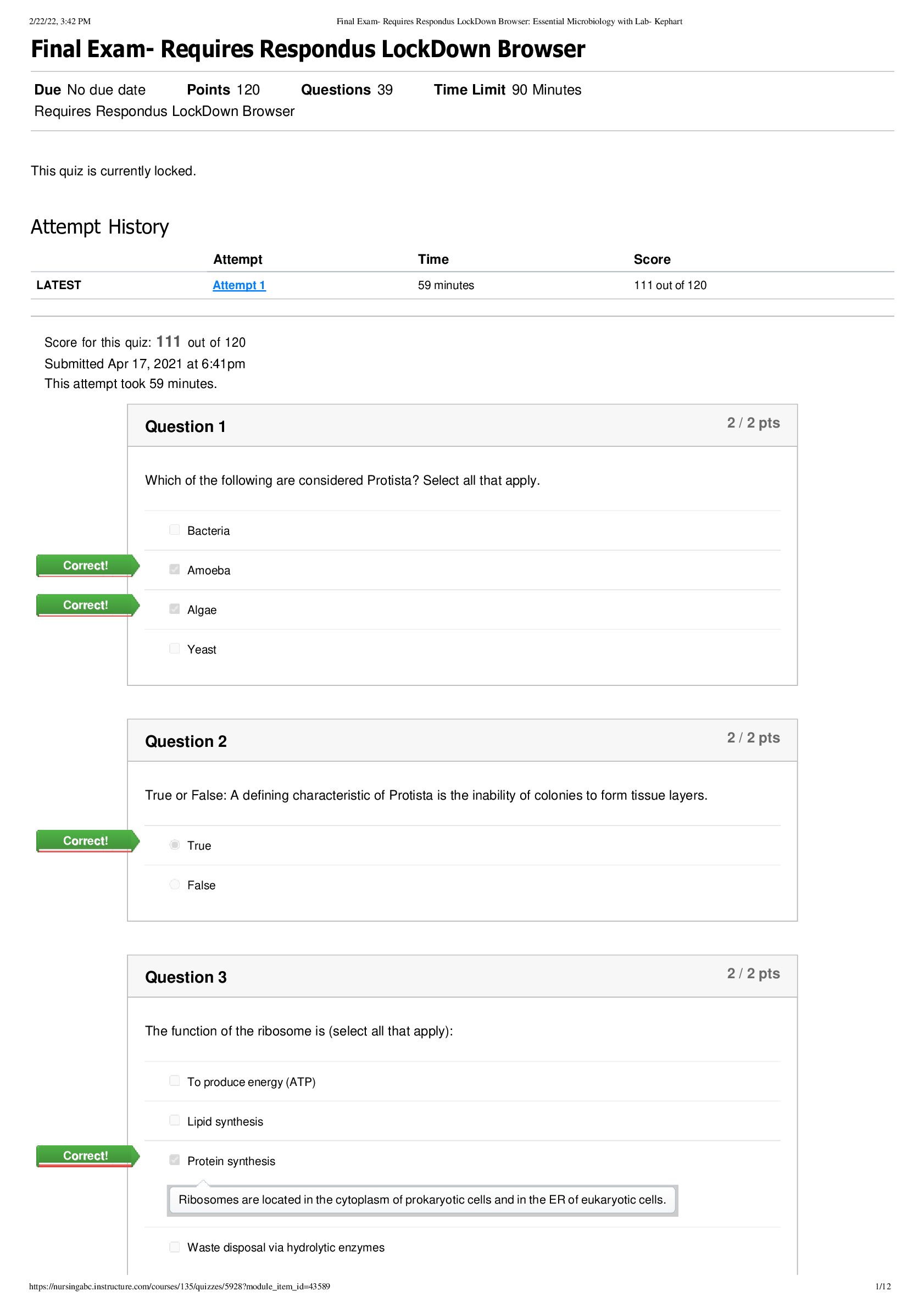
INTRODUCTION TO CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY 10TH EDITION BY CONSTANCE VISOVSKY, CHERYL ZAMBROSKI, SHIRLEY HOSLER QUESTIONS WITH CORRECT ANSWERS AND RATIONALE MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The LPN is collecting d... ata for the initial assessment of a patient upon admission to a long-term care facility before giving the patient’s prescribed drugs. Which action should the LPN consider to be the highest priority? a. Obtain any special equipment that will be needed to give the patient’s drug. b. Monitor the patient for a response to the drug given. c. Collect data about the patient and the patient’s health condition. d. Review the nursing care plan to verify that it is accurate. ANS: C Collecting and documenting data about the patient and the patient’s health condition is a critical step before any drugs are given. Information regarding the present illness, any signs and symptoms, review of medical records, drug history, and vital signs are needed before drugs are given. Deciding on special equipment that will be needed to give the patient’s drug is part of the planning phase of the nursing process. Monitoring the patient for his response to given drug is part of the evaluation stage of the nursing process. Reviewing the nursing care plan to verify that it is being followed accurately is part of the implementation stage of the nursing process. DIF: Cognitive Level: Applying REF: p. 2 2. The LPN is working with a patient in the planning stage of the nursing process related to the patient’s prescribed drugs. Which action should the LPN take during this stage? a. Develop a nursing goal to plan the procedures needed to give drug. b. Develop a teaching plan for the patient regarding the drug’s actions. c. Determine that the patient is experiencing the expected response to his drug. d. Determine how much the patient understands about his drug. ANS: D Determining how much the patient understands about his drug is part of the diagnosis phase of the nursing process. Developing a nursing goal to plan the procedures needed to give drug and developing a teaching plan for the patient regarding the drug’s actions are part of the planning phase of the nursing process. DIF: Cognitive Level: Applying REF: p. 2 3. You are teaching a patient with depression about the potential adverse effects of a prescribed drug. What part of the nursing process related to drug therapy are you engaging in at this point of the teaching plan? a. Assessment b. Implementation c. Evaluation d. Diagnosis ANS: C In the evaluation phase of the nursing process, the LPN understands and teaches to the patient the drug’s therapeutic effects, expected side effects, and potential adverse effects. DIF: Cognitive Level: Remembering REF: p. 2 4. Which of the following is an example of subjective data? a. The patient states she has pain in her left arm. b. The medical chart has a recorded blood pressure of 128/88. c. The serum potassium level is 3.8 mmol/L. d. The patient’s ECG shows normal sinus rhythm. ANS: A Reports from the patient or patient’s caregiver are considered subjective data. Symptoms such as pain, nausea, or dizziness are examples of symptoms that cannot be “seen” and are data collected from the patient, caregiver, or others. Laboratory values, ECG results, or vital sign data from a medical chart are examples of objective data. DIF: Cognitive Level: Remembering REF: p. 2 5. Which statement provides an example of objective data? a. The wife states the patient was confused last night. b. Grimacing with movement is present during the examination. c. The patient reports moderate alcohol consumption. d. The patient states pain is severe. ANS: B Measurable data obtained during a physical exam such as grimacing with movement is an example of objective data. Subjective data includes information presented by the patient or family that cannot be substantiated such as a wife’s report of a patient’s confusion, patient report of degree of alcohol consumption, and a patient’s pain rating. DIF: Cognitive Level: Remembering REF: p. 3 6. The LPN/VN is assessing a patient before giving a drug for blood pressure management. The nurse notes the blood pressure to be 90/50 mm Hg. What is the nurse’s best action? a. Hold the drug and report the blood pressure to the RN. b. Give the patient a full glass of water before giving the drug. c. Come back in 30 minutes and recheck the blood pressure. d. Have the patient perform pursed lip breathing before giving the drug. ANS: A The best action is to hold the drug and contact the RN. The patient may need an adjustment to the dose of the blood pressure drug or switching to another drug. Giving water with the drug is not contraindicated but does not recognize the patient’s risk for hypotension. Pursed lip breathing has no role in this situation. DIF: Cognitive Level: Remembering REF: p. 4 7. The LPN is collecting objective data for inclusion in the nursing assessment. Which piece of information indicates that the LPN hasa clear understanding of objective assessment data? a. A patient’s rating of chest pain as 8 on a 1 to 10 scale. b. Family members report that patient has been experiencing pain for 1 month. c. Detailed history of the patient’s current illness upon admission. d. Compilation of past laboratory results and x-ray reports. ANS: D The patient’s past laboratory and x-ray results are examples of objective data. A pain rating of 8/10, a family member’s descriptionof the patient’s pain, and history of current illness are examples of subjective data. DIF: Cognitive Level: Remembering REF: p. 3 8. A patient recently began a taking blood pressure drug and presents for a follow-up appointment. The office nurse reviews the patient’s daily blood pressure recordings. Which stage of the nursing process corresponds to this review? a. Assessment b. Planning c. Diagnosis d. Evaluation ANS: D The evaluation phase involves examining the results that occur when the plan is implemented. Reviewing the patient’s daily blood pressure recording examines the patient’s response to the drug. The assessment phase provides initial information about the patient, the problem, and anything that may change the choice of treatment. The planning phase involves using patient assessment data and diagnoses to set goals and write care plans. The diagnosis phase involves decision-making about the patient’s problems, including medical diagnoses made by the healthcare provider and nursing diagnoses developed through the North American Nursing Diagnosis Association (NANDA). DIF: Cognitive Level: Remembering REF: p. 2 9. After receiving report, the LPN gives drugs to her assigned patients on the evening shift. With which stage of the nursing process does this activity correspond? a. Implementation b. Assessment c. Planning d. Diagnosis ANS: A The implementation phase involves actively following the plan of care and accurately giving ordered drug to the patients. The assessment phase involves obtaining initial information about the patient, the problem, and anything that may change the choice of treatment. The planning phase involves using patient assessment data and diagnoses to set goals and write care plans. The diagnosis phase involves decision-making about the patient’s problems, including medical diagnoses made by the healthcare provider and nursing diagnoses developed through the North American Nursing Diagnosis Association (NANDA). DIF: Cognitive Level: Remembering REF: p. 5 10. You are reviewing a patient’s new antihypertensive drug order. The order as written is unclear as to the number of times per day the drug is to be given. What is your best action? a. Call the healthcare provider to clarify the order. b. Refer the question to the hospital pharmacy. c. Give the drug according to the information in a drug handbook. d. Hold the drug until the healthcare provider returns the following day. ANS: A Your responsibility as a nurse giving drugs is to apply knowledge about the specific drug and drug orders. No part of the drug order should be unclear. Any questions related to the drug, dose or appropriateness for the specific patient should be answered before the drug is given. DIF: Cognitive Level: Understanding REF: p. 4 11. A patient is receiving an antibiotic for pneumonia. On the third day of the treatment regimen, a rash appears on her chest, and she reports itching and shortness of breath. Which term describes the effect that has occurred? a. Therapeutic effect b. Adverse effect c. Side effect d. Overdose effect ANS: B An itchy rash with shortness of breath that develops in response to drug is an example of an allergic reaction or adverse effect to the antibiotic. Therapeutic effects occur when an antibiotic fights infection without causing any adverse effects. Side effects of drugs are known potential effects of the antibiotic that range from mild to moderate. An overdose occurs if a patient receives too much of a drug. DIF: Cognitive Level: Understanding REF: p. 9 12. An LPN enters a patient’s room to give a scheduled drug. Before administration, the patient states, “I can’t take that drug; I’m allergic to it.” What should the nurse do first? a. Reassure the patient that the drug is needed and observations regarding possible allergic symptoms will be made. b. Review the patient record and encourage the patient to take the drug if no allergies have been documented. c. Assess the patient’s allergic history and notify the healthcare provider to determine a course of action. d. Document patient refusal and leave a note on the patient chart for the healthcareprovider. ANS: C The patient has shared information that indicates the potential for the ordered drug to cause adverse effects. Before giving the drug, the nurse should investigate further by obtaining a more detailed drug history and notifying the healthcare provider who wrote the order. Although the order may be accurately written, determining whether the drug’s benefits outweigh the risks is not an action within the legal scope of the nurse’s practice. The nurse should not offer false reassurance and as an advocate for patient safety, should investigate further before giving the drug. The patient has raised concerns regarding the drug that should promptly be brought to the provider’s attention. A note on the chart leaves potential for information to be missed. DIF: Cognitive Level: Applying REF: p. 4 13. The LPN is preparing to give the initial dose of an antibiotic to a patient diagnosed with an infection. The patient says, “I broke outin a rash the last time I took that pill.” What action should the LPN take next? a. Give the drug and check the patient in 30 minutes for a rash. b. Document that the patient refused the drug per agency policy. c. Leave the drug at the bedside while checking the chart for the patient’s allergies. d. Notify the registered nurse or healthcare provider. ANS: D This is a possible adverse reaction, and the RN or healthcare provider should be notified immediately. You would never give the drug to see if it does cause a rash. Drug should never be left at the bedside. The patient did not refuse the drug. DIF: Cognitive Level: Applying REF: p. 9 14. Which priority assessment must you make before giving any patient a drug by mouth? a. Quiz the patient about the action of each drug. b. Make sure the patient can swallow. c. Find out whether the patient prefers cold or room temperature liquids. d. Ask the patient to repeat his or her name and birthdate. ANS: B Before the patient can take any drug by mouth, they must be able to swallow. Asking the patient to repeat his name and birthdate may be part of using two identifiers but this is important with all patients. Preferences are also important, but the priority is that the patient be able to swallow the drug. DIF: Cognitive Level: Understanding REF: p. 8 MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1. You are preparing to give the morning drugs to your assigned patients. Before giving each drug, which steps are considered to be “rights” of giving a drug? (Select all that apply.) a. The right plan b. The right time c. The right dose d. The right patient e. The right to self-administer f. The right drug ANS: B, C, D, F The nine rights associated with giving drugs are as follows: right patient, right drug, right time, right dose, right route, right documentation, right reason, right response, and right to refuse. DIF: Cognitive Level: Remembering REF: p. 5 [Show More]
Last updated: 2 days ago
Preview 1 out of 134 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$18.00
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 08, 2024
Number of pages
134
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 08, 2024
Downloads
0
Views
19